

酪氨酸衍生物调控酶催化路径可控合成功能黑色素★
收稿日期: 2023-05-19
网络出版日期: 2023-07-28
基金资助
国家自然科学基金(22025207); 国家自然科学基金(22232006); 国家自然科学基金(22077122); 国家自然科学基金(22072004)
Tyrosine Derivative Regulated Enzyme Catalytic Pathway for Controllable Synthesis of Functional Melanin★
Received date: 2023-05-19
Online published: 2023-07-28
Supported by
National Natural Science Foundation of China(22025207); National Natural Science Foundation of China(22232006); National Natural Science Foundation of China(22077122); National Natural Science Foundation of China(22072004)
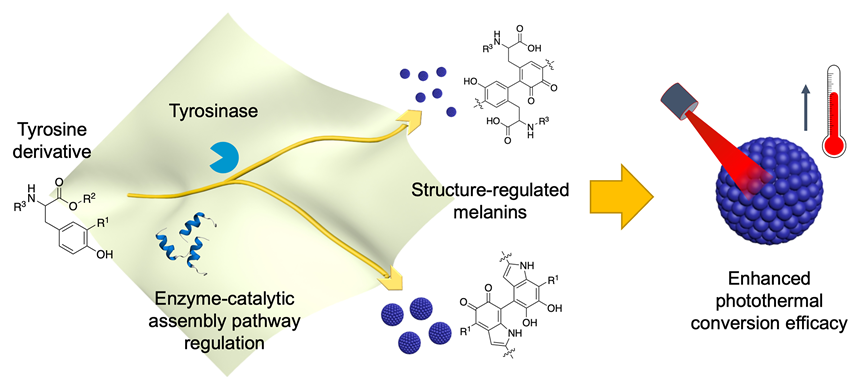
利用酶催化自组装将生物小分子构筑成具有独特功能的生物大分子聚合物是制备功能生物材料极具前景的新策略, 然而其挑战在于如何在底物层面调控生物大分子的结构和功能. 以从酪氨酸构筑黑色素为例, 通过底物结构的简单衍生化, 实现了对酶催化自组装过程中关键聚合位点的控制, 得到一系列尺寸、形貌各异的黑色素产物. 进一步表征了各黑色素产物的光热转换性能, 在细胞层次验证了结构修饰的黑色素用于光热材料的潜力. 揭示了通过改变底物核心基团周边化学结构调控酶催化路径, 进一步调控黑色素产物性质及功能的可行性, 为构筑新型功能黑色素材料提供了新思路, 同时对揭示生物大分子结构与生物功能的关系提供了有益启示.
苏东芮 , 任小康 , 于沄淏 , 赵鲁阳 , 王天宇 , 闫学海 . 酪氨酸衍生物调控酶催化路径可控合成功能黑色素★[J]. 化学学报, 2023 , 81(11) : 1486 -1492 . DOI: 10.6023/A23050240
Construction of biomacromolecules via enzyme-mediated catalytic assembly from small biomolecules is fascinating for preparing functional biological materials. The challenge remains on how to control the structure and functions of biomacromolecules through substrate regulation. A sequence of crucial biomacromolecules, melanin, were prepared via simple substrate derivation, which controls the key polymerization sites in enzyme catalyzed self-assembly process. In detail, we designed three tyrosine derivatives, namely, 3-fluorotyrosine [Tyr(F)], N-acetyltyrosine [Tyr(N-Ac)], and tyrosine ethyl ester [Tyr(OEt)]. The three substrates corresponded to the blockage of different tyrosinase-mediated polymerization active site, and tyrosine was used as the reference. The above small molecules as substrates (1.0 mmol/L) and tyrosinase (2 U) were mixed in phosphate buffer (pH=8.5, 0.10 mol/L, 2.0 mL), which was stirred in an air environment of 25 ℃. After 24 h, the reaction was quenched and the mixture was centrifuged to obtain different melanin nanoparticle products (MNPs). Characterizations from transmission electron microscopy (TEM), infrared spectroscopy (IR), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) showed that all the melanin products had eumelanin-like skeleton, but were different in the degree of polymerization and microscopic chemical structures. These structure-modified MNPs showed overall absorption in the ultraviolet-visible-near infrared (UV-vis-NIR) region, thus enabling photothermal conversion in the NIR-I region. The photothermal conversion efficiency of MNP, MNP(F), and MNP(OEt) (3 mg•mL-1) was measured to be 46.6%, 37.0%, and 25.8% [laser 808 nm, 1.5 W, where MNP(N-Ac) was not available due to rather low temperature increase]. Interestingly, in vitro experiment showed that MNP(OEt) exhibited better photothermal cytotoxicity than MNP, and this was probably because MNP(OEt) had a smaller particle size and less negative ζ-potential, which could ease cell endocytosis. This work demonstrated the feasibility to regu-late enzyme-mediated catalytic pathway via simple substrate derivation. It provides insights for the construction of new functional melanin materials and for revealing the relationship between biological macromolecular structure and function.

| [1] | Sorrenti A.; Leira-Iglesias J.; Markvoort A. J.; de Greef T. F. A.; Hermans T. M. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 5476. |
| [2] | Li Y.; Sun P.; Zhao L.; Yan X.; Ng D. K. P.; Lo P. C. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 23228. |
| [3] | Chen K.; Xing R.; Yan X. Aggregate 2021, 2, 84. |
| [4] | Han J.; Liu K.; Chang R.; Zhao L.; Yan X. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 2000. |
| [5] | Lampel A.; Mcphee S. A.; Park H.; Scott G. G.; Humagain S.; Hekstra D. R.; Yoo B.; Frederix P. W. J. M.; Li T.; Abzalimov R. R.; Greenbaum S. G.; Tuttle T.; Hu C.; Bettinger C. J.; Ulijn R. V. Science 2017, 1068, 1064. |
| [6] | Wang Y.; Dong W. Mater. China 2019, 38, 470. (in Chinese) |
| [6] | 汪洋, 东为富, 中国材料进展, 2019, 38, 470). |
| [7] | Ren Y.; Yang L.; Gao L.; Wang F.; Shi N.; Zhao Y.; Guo L.; Wang H. Mater. Rep. 2020, 34, 11145. (in Chinese) |
| [7] | 任燕玲, 杨柳, 高莉, 王芳, 史楠, 赵英虎, 郭丽晓, 王海宾, 材料导报, 2020, 34, 11145). |
| [8] | Zhou J.; Wang H.; Tong L. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2023, 68, 1406 (in Chinses). |
| [8] | 周建良, 王怀雨, 童丽萍, 科学通报, 2023, 68, 1406). |
| [9] | Yang P.; Zhang S.; Zhang N.; Wang Y.; Zhong J.; Sun X.; Qi Y.; Chen X.; Li Z.; Li Y. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 42671. |
| [10] | D’Ischia M.; Napolitano A.; Ball V.; Chen C. T.; Buehler M. J. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 3541. |
| [11] | Cao W.; Zhou X.; McCallum N. C.; Hu Z.; Ni Q. Z.; Kapoor U.; Heil C. M.; Cay K. S.; Zand T.; Mantanona A. J.; Jayaraman A.; Dhinojwala A.; Deheyn D. D.; Shawkey M. D.; Burkart M. D.; Rinehart J. D.; Gianneschi N. C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 2622. |
| [12] | Partlow B. P.; Applegate M. B.; Omenetto F. G.; Kaplan D. L. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2, 2108. |
| [13] | McCallum N. C.; Son F. A.; Clemons T. D.; Weigand S. J.; Gnanasekaran K.; Battistella C.; Barnes B. E.; Abeyratne-Perera H.; Siwicka Z. E.; Forman C. J.; Zhou X.; Moore M. H.; Savin D. A.; Stupp S. I.; Wang Z.; Vora G. J.; Johnson B. J.; Farha O. K.; Gianneschi N. C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 4005. |
| [14] | Cao W.; McCallum N. C.; Ni Q. Z.; Li W.; Boyce H.; Mao H.; Zhou X.; Sun H.; Thompson M. P.; Battistella C.; Wasielewski M. R.; Dhinojwala A.; Shawkey M. D.; Burkart M. D.; Wang Z.; Gianneschi N. C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 12802. |
| [15] | Della Vecchia N. F.; Luchini A.; Napolitano A.; D’Errico G.; Vitiello G.; Szekely N.; d’Ischia M.; Paduano L. Langmuir 2014, 30, 9811. |
| [16] | Ren X.; Zhao L.; Yuan C.; Shi M.; Xing R. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 450, 138293. |
| [17] | Ren X.; Zou Q.; Yuan C.; Chang R.; Xing R.; Yan X. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 5872. |
| [18] | Ito S. Pigment Cell Res. 2003, 16, 230. |
| [19] | Ito S.; Wakamatsu K. Photochem. Photobiol. 2008, 84, 582. |
| [20] | Lampel A.; McPhee S. A.; Kassem S.; Sementa D.; Massarano T.; Aramini J. M.; He Y.; Ulijn R. V. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 7564. |
| [21] | Zhao L.; Ren X.; Yan X. CCS Chem. 2021, 3, 678. |
| [22] | Yasunobu K. T.; Peterson E. W.; Mason H. S. J. Biol. Chem. 1959, 234, 3291. |
| [23] | Ramsden C. A.; Riley P. A. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2014, 22, 2388. |
| [24] | Yang P.; Gu Z.; Zhu F; Li Y. CCS Chem. 2020, 2, 128. |
| [25] | Zong S.; Wang L.; Yang Z.; Wang H.; Wang Z.; Cui Y. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 5896. |
| [26] | Xi Z. Y.; Xu Y. Y.; Zhu L. P.; Wang Y.; Zhu B. K. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 327, 244. |
| [27] | Panzella L.; Gentile G.; D’Errico G.; Della Vecchia N. F.; Errico M. E.; Napolitano A.; Carfagna C.; D’Ischia M. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 12684. |
| [28] | Stypczyńska A.; Nixon T.; Mason N. Eur. Phys. J. D 2014, 68, 333. |
| [29] | Ding Y.; Weng L.-T.; Yang M.; Yang Z.; Lu X.; Huang N.; Leng Y. Langmuir 2014, 30, 12258. |
| [30] | Guo C.; Wang B.; Ma X. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 967. (in Chinese) |
| [30] | 郭彩霞, 王博, 马小杰, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 967). |
| [31] | Zou Q.; Abbas M.; Zhao L.; Li S.; Shen G.; Yan X. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 1921. |
| [32] | Zhao L.; Zou Q.; Yan X. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2019, 92, 70. |
| [33] | Chang R.; Zhao L.; Xing R.; Li J.; Yan X. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2023, 52, 2688. |
| [34] | Chang R.; Zou Q.; Zhao L.; Liu Y.; Xing R.; Yan X. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2200139. |
| [35] | Li S.; Zhang W.; Xing R.; Yuan C.; Xue H.; Yan X. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2100595. |
| [36] | Zhao L.; Liu Y.; Chang R.; Xing R.; Yan X. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1806877. |
| [37] | Zhao L.; Liu Y.; Xing R.; Yan X. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 3793. |
| [38] | Qiu B.; Xue L.; Yang Y.; Bin H.; Zhang Y.; Zhang C.; Xiao M.; Park K.; Morrison W.; Zhang Z. G.; Li Y. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 7543. |
| [39] | Yang Y.; Zhang Z. G.; Bin H.; Chen S.; Gao L.; Xue L.; Yang C.; Li Y. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 15011. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |