

氟烷基亚磺酸钠盐电化学合成α-氟烷基酮
收稿日期: 2023-08-20
网络出版日期: 2023-10-24
基金资助
国家自然科学基金(22078161); 国家自然科学基金(22108124); 中央高校基本科研业务费专项资金(30918011314); 中央高校基本科研业务费专项资金(30922010403); 江苏省青蓝工程(苏教师函(2022)29号); 六大高峰人才
Electrochemical Synthesis of α-Fluoroalkylated Ketones using Sodium Fluoroalkylsulfinate
Received date: 2023-08-20
Online published: 2023-10-24
Supported by
National Natural Science Foundation of China(22078161); National Natural Science Foundation of China(22108124); Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities(30918011314); Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities(30922010403); Qing Lan Project (No. (2022)29); Six Talent Peaks Project in Jiangsu Province
李珊 , 路俊欣 , 刘杰 , 蒋绿齐 , 易文斌 . 氟烷基亚磺酸钠盐电化学合成α-氟烷基酮[J]. 化学学报, 2024 , 82(2) : 110 -114 . DOI: 10.6023/A23080386
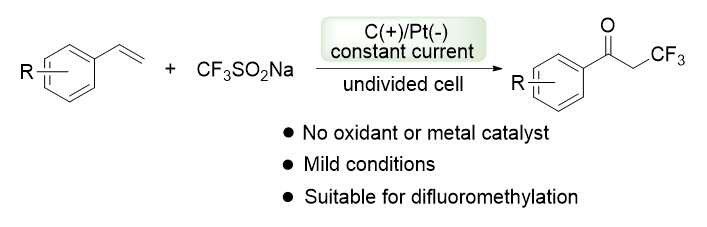
The fluorine-containing group has a significant effect on properties such as lipophilicity, permeability, and metabolic stability of compounds. Therefore, the efficient introduction of fluorine-containing groups into pharmaceutical and agrochemical compounds, as well as functional organic materials, has become an important research field of chemistry. Undoubtedly, new methodologies for the efficient and highly selective incorporation of fluorinated substituents into diverse molecular structures continue to be in strong demand. During the past few years, electrosynthesis has been considered to be a practical and environmentally friendly synthetic tool. The application of electrochemical anodic oxidation in synthetic organic chemistry has drawn increasing attention. Electrochemistry utilizes direct interaction of electrons from the anode and cathode with the nucleus, avoids using strong oxidants, and minimizes byproduct formation. Herein we describe an electrochemical synthesis of α-trifluoromethylated ketones from alkenes based on sodium trifluoromethanesulfinate. Sodium trifluoromethanesulfinate generates trifluoromethyl radicals through anodic oxidation to attack the carbon-carbon double bonds of alkenes, and then oxidized in air atmosphere to obtain the target compounds. The optimized reaction conditions of electrochemical synthesis of α-trifluoromethylated ketones are as follows: 1 equiv. of alkenes, 2 equiv. of sodium trifluoromethanesulfinate, a mixture of CH3CN/H2O (V∶V=2∶1) as the solvent, 2 equiv. of lithium perchlorate as electrolyte, CF3COOH as the sacrificial oxidant, graphite as the anode and platinum as the cathode, react at room temperature for 6 h under a constant current of 20 mA and air atmosphere, giving the corresponding α-trifluoromethyl-substituted ketones in 66%~84% yields. The reaction substrate has good applicability, and the reaction conditions are mild. Compared with the traditional methods, the electrocatalytic process avoids the use of peroxidants or expensive photocatalysts. In addition, this reaction can be applied to the synthesis of α-difluoromethylated ketones when using sodium difluoromethanesulfinate instead of sodium trifluoromethanesulfinate.
| [1] | Wadas, T. J.; Wong, E. H.; Weisman, G. R.; Anderson, C. J. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 2858. |
| [2] | Sophie, P.; Peter, R. M.; Steve, S.; Veronique, G. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 320. |
| [3] | Langlois, B. R.; Laurent, E.; Roidot, N. Tetrahedron Lett. 1992, 33, 1291. |
| [4] | Zhang, C. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2014, 356, 2895. |
| [5] | Yan, M.; Kawamata, Y.; Baran, P. S. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 13230. |
| [6] | Ye, K. Y.; Pombar, G.; Fu, N.; Sauer, G. S.; Keresztes, I.; Lin, S. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 2438. |
| [7] | Zhang, L.; Zhang, G.; Wang, P.; Li, Y.; Lei, A. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 7396. |
| [8] | Zou, Z.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Kong, L.; Karotsis, G.; Wang, Y.; Pan, Y. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 1857. |
| [9] | Ruan, Z.; Huang, Z.; Xu, Z.; Mo, G.; Tian, X.; Yu, X.-Y.; Ackermann, L. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 1237. |
| [10] | Deb, A.; Manna, S.; Modak, A.; Patra, T.; Maity, S.; Maiti, D. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 9747. |
| [11] | Zhao, L.; Li, P.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L. Org. Chem. Front. 2019, 6, 87. |
| [12] | Zhang, C. P.; Wang, Z. L.; Chen, Q. Y.; Zhang, C. T.; Gu, Y.-C.; Xiao, J.-C. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 6632. |
| [13] | Luo, H. Q.; Zhang, Z. P.; Dong, W.; Luo, X. Z. Synlett 2014, 25, 1307. |
| [14] | Tomita, R.; Yasu, Y.; Koike, T.; Akita, M. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 7144. |
| [15] | Wu, Y. B.; Lu, G. P.; Yuan, T.; Xu, Z. B.; Wan, L.; Cai, C. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 13668. |
| [16] | Yamaguchi, E.; Kamito, Y.; Matsuo, K.; Ishihara, J.; Itoh, A. Synthesis 2018, 50, 3161. |
| [17] | Xing, L.; Blakemore, D. C.; Narayanan, A.; Unwalla, R.; Lovering, F.; Denny, R. A.; Zhou, H.; Bunnage, M. E. ChemMedChem 2015, 10, 715. |
| [18] | Zafrani, Y.; Yeffet, D.; Sod-Moriah, G. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 2797. |
| [19] | Kadoh, Y.; Tashiro, M.; Oisaki, K.; Kanai, M. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2015, 357, 2193. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |