

基于氮杂螺环配体的Cu(I)配合物延迟荧光材料的设计合成及性能研究
收稿日期: 2024-04-30
网络出版日期: 2024-06-13
基金资助
国家自然科学基金(52073286); 国家自然科学基金(2021ZZ115); 国家自然科学基金(2021ZR132); 福建省自然科学基金(2021J011073); 福建省区域发展项目(2021H4008); 中国科学院科技服务网络计划(STS2023T3039)
Design, Synthesis and Properties of Cu(I) Complexes with a Nitrogen-containing Spirocycle Ligand for Delayed Fluorescence Materials
Received date: 2024-04-30
Online published: 2024-06-13
Supported by
National Natural Science Foundation of China(52073286); National Natural Science Foundation of China(2021ZZ115); National Natural Science Foundation of China(2021ZR132); Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province(2021J011073); regional development projects in Fujian Province(2021H4008); Science and Technology Service Network Initiative from the Chinese Academy of Sciences(STS2023T3039)
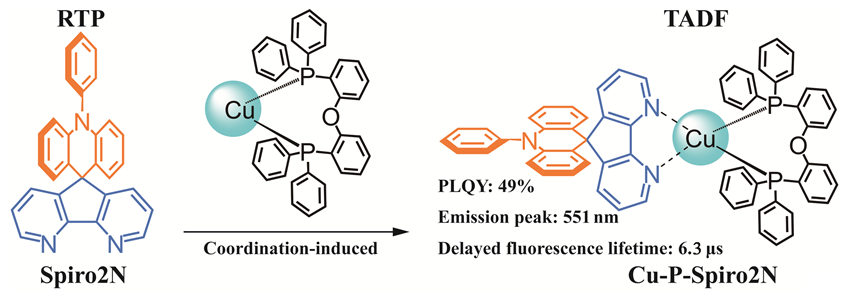
本研究通过采用具有室温磷光发射性质的给体-受体(D-A)型配体10-苯基-10H-螺[吖啶-9,9'-(4,5-二氮芴)](Spiro2N), 与辅助膦配体双(2-二苯基磷苯基)醚(POP)结合, 成功设计了具有热活化延迟荧光(TADF)性质的Cu(I)配合物发光材料Cu-P-Spiro2N. 通过核磁共振谱图确认了Cu(I)配合物的分子结构. 进一步利用X射线单晶衍射表征了配合物Cu-P-Spiro2N的晶体结构. 结果表明, 配合物Cu-P-Spiro2N属于三斜晶系, 晶胞参数分别为α=90.14(2)°, β=115.43(3)°, γ=115.55(3)°, a=15.10(6) nm, b=15.15(4) nm, c=16.62(6) nm. 由于配体分子Spiro2N具有两个相互正交的π共轭平面结构, 使得其最高占据分子轨道(HOMO)和最低未占分子轨道(LUMO)具有很小的重叠, 但具有相对较大的单重态-三重态能隙差(∆EST). 金属Cu(I)片段与配体Spiro2N配位后, 降低了HOMO-LUMO之间的能隙差, 电荷转移(CT)态能级下降. 这使得配合物Cu-P-Spiro2N具有极小的∆EST (0.05 eV). 小的∆EST有利于加速反系间窜越过程, 进而实现TADF发射. 该类配合物的发射主要来自于D-A型配体Spiro2N, 表现为金属微扰的配体内电荷转移(ILCT)性质. 室温下, 在掺杂的聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯(PMMA)薄膜(10% (w))中, 配合物Cu-P-Spiro2N表现出强烈的黄光发射, 发射峰值位于551 nm, 光致发光量子效率为49%, 激发态寿命为6.3 μs. 本研究结果表明, 通过Cu(I)离子配位, 可调控配体分子激发态能级, 降低∆EST, 从而实现TADF发射.
张登朝 , 贾吉慧 , 梁栋 , 蔡显宝 , 赵雨晴 , 胡祥龙 , 江钰冰 , 卢灿忠 . 基于氮杂螺环配体的Cu(I)配合物延迟荧光材料的设计合成及性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2024 , 82(8) : 887 -893 . DOI: 10.6023/A24040148
In this study, a Cu(I) complex luminescent material Cu-P-Spiro2N with thermally activated delayed fluorescence (TADF) properties was successfully designed by combining the donor-acceptor (D-A) type ligand 10-phenyl-10H-spiro[acridine-9,9'-(4,5-diazafluorene)] (Spiro2N) with long afterglow emission properties and the auxiliary phosphine ligand bis(2-diphenylphosphinophenyl) ether (POP). The molecular structures of the Cu(I) complex were confirmed by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, and the crystal structure of the Cu-P-Spiro2N complex was further characterized by X-ray single crystal diffraction. Cu-P-Spiro2N belongs to the triclinic crystal system with cell parameters α=90.14(2)°, β=115.43(3)°, γ=115.55(3)°, a=15.10(6) nm, b=15.15(4) nm, c=16.62(6) nm. Due to the two mutually orthogonal π-conjugated planar structures of the ligand molecule Spiro2N, its highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) and lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO) are well separated, but with a relatively large singlet-triplet energy gap (∆EST). After coordination of the metal Cu(I) fragment with the ligand Spiro2N, the energy gap between HOMO and LUMO is further reduced, and the charge transfer (CT) state energy level is further lowered, which makes the complex Cu-P-Spiro2N have a very small ∆EST of 0.05 eV. The small ∆EST facilitates the reverse intersystem crossing process, thereby achieving TADF emission. The emission of this complex mainly comes from the D-A ligand Spiro2N, which exhibits metal perturbation intramolecular ligand charge transfer (ILCT) properties. At room temperature, in the doped polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) film (10% (w)), the Cu-P-Spiro2N complex exhibits strong yellow light emission with an emission peak at 551 nm, a photoluminescence quantum efficiency of 49%, and an excited state lifetime of 6.3 μs. The results of this study indicate that by coordinating with Cu(I) ions, the excited state energy level of the ligand molecule can be modulated, reducing ∆EST and thus achieving TADF emission.

| [1] | Arias-Rotondo, D. M.; McCusker, J. K. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 5803. |
| [2] | Ma, D.; Tsuboi, T.; Qiu, Y.; Duan, L. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1603253. |
| [3] | Hong, G.; Gan, X.; Leonhardt, C.; Zhang, Z.; Seibert, J.; Busch, J. M.; Br?se, S. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2005630. |
| [4] | Li, X.; Xie, Y.; Li, Z. Chem. Asian J. 2021, 16, 2817. |
| [5] | Ge, F.; Zhang, K.; Cao, Q.; Xu, H.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, W.; Ban, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, N.; Zhu, P. Acta Chim. Sinica 2023, 81, 1157 (in Chinese). |
| [5] | (葛凤洁, 张开志, 曹清鹏, 徐慧, 周涛, 张文浩, 班鑫鑫, 张晓波, 李娜, 朱鹏, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 1157.) |
| [6] | Tao, P.; Zheng, X.; Wang, G.; Sheng, X.; Jiang, H.; Li, W.; Jin, J.; Wong, S.-H.; Miao, Y.; Wang, H.; Wong, W.-Y. Acta Chim. Sinica 2023, 81, 891 (in Chinese). |
| [6] | (陶鹏, 郑小康, 王国良, 盛星浩, 姜贺, 李文桃, 靳继彪, 王瑞鸿, 苗艳勤, 王华, 黄维扬, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 891.) |
| [7] | Kalinowski, J.; Fattori, V.; Cocchi, M.; Williams, J. A. G. Coordin. Chem. Rev. 2011, 255, 2401. |
| [8] | Yersin, H.; Rausch, A. F.; Czerwieniec, R.; Hofbeck, T.; Fischer, T. Coordin. Chem. Rev. 2011, 255, 2622. |
| [9] | Lee, J.; Chen, H. F.; Batagoda, T.; Coburn, C.; Djurovich, P. I.; Thompson, M. E.; Forrest, S. R. Nat. Mater. 2016, 15, 92. |
| [10] | Ren, B.-Y.; Yi, J.-C.; Zhong, D.-K.; Zhao, Y.-Z.; Guo, R.-D.; Sheng, Y.-G.; Sun, Y.-G.; Xie, L.-H.; Huang, W. Acta Chim. Sinica 2020, 78, 56 (in Chinese). |
| [10] | (任保轶, 依建成, 钟道昆, 赵玉志, 郭闰达, 盛永刚, 孙亚光, 解令海, 黄维, 化学学报, 2020, 78, 56.) |
| [11] | Zhu, S.; Huang, X.; Han, X.; Liu, S. Acta Chim. Sinica 2022, 80, 1066 (in Chinese). |
| [11] | (朱诗敏, 黄鑫, 韩勰, 刘思敏, 化学学报, 2022, 80, 1066.) |
| [12] | Cao, L.; Yang, X.; Li, M.; Liu, L.; Yu, J.; Tan, H. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2022, 42, 1831 (in Chinese). |
| [12] | (曹丽琴, 杨小琴, 李茂秋, 刘琳, 于俊婷, 谭华, 有机化学, 2022, 42, 1831.) |
| [13] | Czerwieniec, R.; Leitl, M. J.; Homeier, H. H. H.; Yersin, H. Coordin. Chem. Rev. 2016, 325, 2. |
| [14] | Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Yu, X.; Li, P.; Yao, Y.; Liu, Z.; Jin, Q. H.; Bian, Z.; Lu, Z. H.; Huang, C. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2019, 11, 3262. |
| [15] | Mohankumar, M.; Holler, M.; Meichsner, E.; Nierengarten, J. F.; Niess, F.; Sauvage, J. P.; Delavaux-Nicot, B.; Leoni, E.; Monti, F.; Malicka, J. M.; Cocchi, M.; Bandini, E.; Armaroli, N. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 2336. |
| [16] | Hamze, R.; Peltier, J. L.; Sylvinson, D.; Jung, M.; Cardenas, J.; Haiges, R.; Soleilhavoup, M.; Jazzar, R.; Djurovich, P. I.; Bertrand, G.; Thompson, M. E. Science 2019, 363, 601. |
| [17] | Jia, J. H.; Zhang, D. C.; Liang, D.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Z. Q.; Zhang, L.; Lu, C. Z. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2024, 12, 2303053. |
| [18] | Armaroli, N.; Accorsi, G.; Cardinali, F.; Listorti, A. Photochemistry and Photophysics of Coordination Compounds: Copper, Eds.: Balzani, V.; Campagna, S., Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, 2007, pp. 69-115. |
| [19] | Osawa, M.; Kawata, I.; Ishii, R.; Igawa, S.; Hashimoto, M.; Hoshino, M. J. Mater. Chem. C 2013, 1, 4375. |
| [20] | Klein, M.; Rau, N.; Wende, M.; Sundermeyer, J.; Cheng, G.; Che, C.-M.; Schinabeck, A.; Yersin, H. Chem. Mater. 2020, 32, 10365. |
| [21] | Shafikov, M. Z.; Suleymanova, A. F.; Czerwieniec, R.; Yersin, H. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 13274. |
| [22] | Volz, D.; Chen, Y.; Wallesch, M.; Liu, R.; Flechon, C.; Zink, D. M.; Friedrichs, J.; Flugge, H.; Steininger, R.; Gottlicher, J.; Heske, C.; Weinhardt, L.; Brase, S.; So, F.; Baumann, T. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 2538. |
| [23] | Jia, J.-H.; Liang, D.; Yu, R.; Chen, X.-L.; Meng, L.; Chang, J.-F.; Liao, J.-Z.; Yang, M.; Li, X.-N.; Lu, C.-Z. Chem. Mater. 2019, 32, 620. |
| [24] | Cai, X. B.; Liang, D.; Yang, M.; Wu, X. Y.; Lu, C. Z.; Yu, R. Chem. Commun. (Camb). 2022, 58, 8970. |
| [25] | Liang, D.; Jia, J.-H.; Cai, X.-B.; Zhao, Y.-Q.; Wang, Z.-Q.; Lu, C.-Z. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2022, 9, 6561. |
| [26] | Liang, D.; Jia, J. H.; Yang, M.; Cai, X. B.; Yu, R.; Lu, C. Z. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2022, 10, 2201130. |
| [27] | Adamo, C.; Barone, V. J. Chem. Phys. 1999, 110, 6158. |
| [28] | Perdew, J. P.; Ernzerhof, M.; Burke, K. J. Chem. Phys. 1996, 105, 9982. |
| [29] | Cances, E.; Mennucci, B.; Tomasi, J. J. Chem. Phys. 1997, 107, 3032. |
| [30] | Mennucci, B.; Cances, E.; Tomasi, J. J. Phys. Chem. 1997, 101, 10506. |
| [31] | Miertu?, S.; Scrocco, E.; Tomasi, J. Chem. Phys. 1981, 55, 117. |
| [32] | Roy, L. E.; Hay, P. J.; Martin, R. L. J. Chem. Theory. Comput. 2008, 4, 1029. |
| [33] | Hariharan, P. C.; Pople, J. A. Mol. Phys. 1974, 27, 209. |
| [34] | Czerwieniec, R.; Kowalski, K.; Yersin, H. Dalton. T. 2013, 42, 9826. |
| [35] | Volz, D.; Wallesch, M.; Grage, S. L.; Gottlicher, J.; Steininger, R.; Batchelor, D.; Vitova, T.; Ulrich, A. S.; Heske, C.; Weinhardt, L.; Baumann, T.; Brase, S. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 7837. |
| [36] | Endo, A.; Sato, K.; Yoshimura, K.; Kai, T.; Kawada, A.; Miyazaki, H.; Adachi, C. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 98, 083302. |
| [37] | Zhang, Q.; Li, J.; Shizu, K.; Huang, S.; Hirata, S.; Miyazaki, H.; Adachi, C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 14706. |
| [38] | Yersin, H.; Czerwieniec, R.; Hupfer, A. Organic Photonics V. 2012, 8435, 843508. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |