

Mn掺杂Co3O4双功能电催化剂在碱性介质下氧还原和析氧反应中的应用
收稿日期: 2024-05-06
网络出版日期: 2024-07-10
基金资助
延安大学; 陕西煤业地质集团有限责任公司和陕西省国有资本经营预算科技创新专项资金的支持, 以及陕西省自然科学基础研究计划(2023-JC-YB-046); 陕西省教育厅自然科学基金(23JK0723)
Bifunctional Electrocatalysts of Mn-doped Co3O4 for Oxygen Reduction and Oxygen Evolution Reactions in Alkaline Medium
Received date: 2024-05-06
Online published: 2024-07-10
Supported by
Natural Science Basic Research Program of Shaanxi(2023-JC-YB-046); Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi Provincial Department of Education(23JK0723)
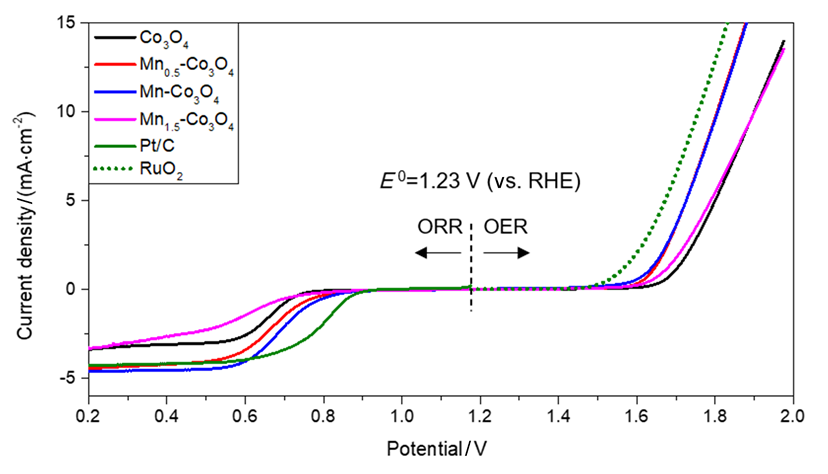
可充电锌空气电池(ZABs)由于其高能量和功率密度、高安全性和成本效益, 被认为是未来储能领域中最有前途的清洁电源之一. 然而, 其实际应用受到放电和充电过程中氧还原反应(ORR)和析氧反应(OER)动力学缓慢的阻碍. Pt和IrO2是目前公认的高效ORR和OER催化剂, 但贵金属催化剂的高成本阻碍了它们商业化的步伐. 本工作通过共沉淀法制备了一系列尖晶石催化剂(Mnx-Co3O4, x=0, 0.5, 1, 1.5), 以实现在碱性介质中高效催化ORR和OER的目的, 并进一步探索这些过渡金属氧化物催化材料作为双功能复合催化剂在取代贵金属方面的潜力. 实验结果显示: Mn-Co3O4具有优异的ORR性能(起始电位为0.85 V, 半波电位为0.69 V)和OER性能(过电位为0.57 V, 电子转移电阻为26.14 Ω). 此外, 密度泛函理论(DFT)计算表明, Mn和Co位点可以分别作为ORR和OER的潜在活性位点, 在电催化过程中具有显著的协同作用. 表征结果进一步证实锰的掺杂增加了催化剂的比表面积和氧空位, 调整了催化剂表面化学和电子状态, 从而提高了催化剂的ORR和OER性能. 另外, 该催化剂在液态可充电锌空气电池中显示出长达40 h的循环寿命. 总而言之, 本工作证明了锰钴双金属协同催化是提高ORR和OER选择性的一种有效策略.
税子怡 , 于思乐 , 陆伟 , 许留云 , 刘庆叶 , 赵炜 , 刘益伦 . Mn掺杂Co3O4双功能电催化剂在碱性介质下氧还原和析氧反应中的应用[J]. 化学学报, 2024 , 82(10) : 1039 -1049 . DOI: 10.6023/A24050152
Rechargeable zinc-air batteries (ZABs) have been extensively studied due to their high energy and power density, high safety and cost-effectiveness, which are considered to be one of the most promising clean power sources in the field of energy storage. Nevertheless, its practical application has been hampered by the sluggish kinetics of the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) and oxygen evolution reaction (OER) during the discharge and charge processes, respectively. It is well known that Pt and IrO2 are currently considered to be the most efficient ORR and OER catalysts. However, the high cost of precious metal catalysts has hindered their large-scale application. Herein, a series of spinel catalysts (Mnx-Co3O4, x=0, 0.5, 1, 1.5) are prepared by co-precipitation method to achieve bifunctional oxygen electrocatalysis in alkaline media. Meanwhile, the potential of these transition metal oxide catalytic materials as bifunctional catalysts in replacing precious metals has been further explored. The results show that Mn-Co3O4 has excellent ORR performance (onset potential of 0.85 V, half-wave potential of 0.69 V), and significantly enhanced OER performance (overpotential of 0.57 V, the electron transfer resistance of 26.14 Ω), thereby leading to excellent bifunctional property. Furthermore, density functional theory (DFT) calculations demonstrate that Mn and Co sites can serve as potential active sites for ORR and OER respectively, exhibiting significant synergistic effects in electrocatalytic processes. The characterization results further confirm that the doping of manganese in the catalyst preparation process increases the specific surface area and oxygen vacancies of the catalyst, adjusts the surface chemistry and electronic state of the catalyst, and thus improves the ORR and OER performance of the catalyst. In addition, the Mn-Co3O4 catalyst delivers high cycle life of up to 40 h in liquid rechargeable zinc air batteries. In summary, this work demonstrates that manganese-cobalt bimetallic synergistic catalysis is a promising strategy to enhance the electrocatalytic activity of ORR and OER.

| [1] | Ishihara, T.; Yokoe, K.; Miyano, T.; Kusaba, H. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 300 455. |
| [2] | Miao, H.; Wu, X.; Chen, B.; Wang, Q.; Wang, F.; Wang, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, Q. Electrochim. Acta 2020, 333 135566. |
| [3] | Dai, Y.; Yu, J.; Cheng, C.; Tan, P.; Ni, M. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 397 125516. |
| [4] | Lankauf, K.; Cysewska, K.; Karczewski, J.; Mielewczyk-Gryń, A.; Górnicka, K.; Cempura, G.; Chen, M.; Jasiński, P.; Molin, S. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45 14867. |
| [5] | Wu, X.; Miao, H.; Hu, R.; Chen, B.; Yin, M.; Zhang, H.; Xia, L.; Zhang, C.; Yuan, J. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 536 147806. |
| [6] | Béjar, J.; álvarez-Contreras, L.; Ledesma-García, J.; Arjona, N.; Arriaga, L. G. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2019, 847 113190. |
| [7] | Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Hu, T. Acta Chim. Sinica 2015, 73 316 (in Chinese). |
| [7] | (王瀛, 张丽敏, 胡天军, 化学学报, 2015, 73 316.) |
| [8] | Liu, H.; Zhu, X.; Li, M.; Tang, Q.; Sun, G.; Yang, W. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 144 31. |
| [9] | Liu, J.; Yang, N.; Li, L.; Wei, Z. Acta Chim. Sinica 2023, 81 1478 (in Chinese). |
| [9] | (刘金晶, 杨娜, 李莉, 魏子栋, 化学学报, 2023, 81 1478.) |
| [10] | Shi, C.; Ullah, S.; Li, K.; Wang, W.; Zhang, R.; Pan, L.; Zhang, X.; Zou, J.-J. Chinese J. Catal. 2020, 41 1818. |
| [11] | Chang, J.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Su, C.; Pan, J.; Wang, H.; Song, H. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2021, 129 144. |
| [12] | Fujiwara, N.; Nagai, T.; Ioroi, T.; Arai, H.; Ogumi, Z. J. Power Sources 2020, 451 227736. |
| [13] | Hu, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Lim, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, S. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2021, 282 119593. |
| [14] | Sun, Y.-R.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.-G.; Liu, Z.-K.; Kang, N.; Zhou, N.; You, W.-L.; Li, J.; Yu, X.-F. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 421 129698. |
| [15] | Liang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhou, J.; Wang, J.; Regier, T.; Dai, H. Nat. Mater. 2011, 10 780. |
| [16] | Song, K.; Yuan, L.; Li, Z.; Lv, Y.; Yang, B.; Yu, Y.; Shen, X.; Hu, X. Electrochim. Acta 2020, 353 136572. |
| [17] | Retuerto, M.; Calle-Vallejo, F.; Pascual, L.; Lumbeeck, G.; Fernandez-Diaz, M. T.; Croft, M.; Gopalakrishnan, J.; Pena, M. A.; Hadermann, J.; Greenblatt, M.; Rojas, S. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11 21454. |
| [18] | Jung, J.-I.; Risch, M.; Park, S.; Kim, M. G.; Nam, G.; Jeong, H.-Y.; Shao-Horn, Y.; Cho, J. Energy & Environ. Sci. 2016, 9 176. |
| [19] | Kim, J.; Ko, W.; Yoo, J. M.; Paidi, V. K.; Jang, H. Y.; Shepit, M.; Lee, J.; Chang, H.; Lee, H. S.; Jo, J.; Kim, B. H.; Cho, S. P.; Lierop, J.; Kim, D.; Lee, K. S.; Back, S.; Sung, Y. E.; Hyeon, T. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, e2107868. |
| [20] | Maile, N. C.; Moztahida, M.; Ghani, A. A.; Hussain, M.; Tahir, K.; Kim, B.; Shinde, S. K.; Fulari, V. J.; Lee, D. S. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 421 129767. |
| [21] | Shui, Z.; He, N.; Chen, L.; Zhao, W.; Chen, X. Acta Chim. Sinica 2020, 78 557 (in Chinese). |
| [21] | (税子怡, 何娜娜, 陈黎, 赵炜, 陈曦, 化学学报, 2020, 78 557.) |
| [22] | Li, K.; Zhang, R.; Gao, R.; Shen, G.-Q.; Pan, L.; Yao, Y.; Yu, K.; Zhang, X.; Zou, J.-J. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2019, 244 536. |
| [23] | Li, Z.; Lv, Y.; Yu, Y.; Yin, J.; Song, K.; Yang, B.; Yuan, L.; Hu, X. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 817 152736. |
| [24] | Ge, C.; Li, Q.; Hu, M.; Wang, G.; Xiao, L.; Lu, J.; Zhuang, L. J. Power Sources 2022, 520 230868. |
| [25] | Liang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhou, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Regier, T.; Dai, H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134 3517. |
| [26] | Bae, J.; Shin, D.; Jeong, H.; Choe, C.; Choi, Y.; Han, J. W.; Lee, H. ACS Catal. 2021, 11 11066. |
| [27] | Zhu, F.; Zhang, J.; Yang, B.; Shi, X.; Lu, C.; Yin, J.; Yu, Y.; Hu, X. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 749 433. |
| [28] | Li, C.; Han, X.; Cheng, F.; Hu, Y.; Chen, C.; Chen, J. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6 7345. |
| [29] | Zhang, W.; Li, M.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Niu, X.; Zhu, Y. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 590 153140. |
| [30] | Qin, C.; Wang, B.; Wang, Y. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 2022, 351 130943. |
| [31] | Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Li, W.; Li, Y.; Chen, Q.; Zhan, F. J. Power Sources 2015, 299 492. |
| [32] | Cheng, H.; Chen, J. M.; Li, Q. J.; Su, C. Y.; Chen, A. N.; Zhang, J. X.; Liu, Z. Q.; Tong, Y. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53 11596. |
| [33] | Bae, J.; Shin, D.; Jeong, H.; Kim, B.-S.; Han, J. W.; Lee, H. ACS Catal. 2019, 9 10093. |
| [34] | Wu, J.; Wang, X.; Zheng, W.; Sun, Y.; Xie, Y.; Ma, K.; Zhang, Z.; Liao, Q.; Tian, Z.; Kang, Z.; Zhang, Y. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144 19163. |
| [35] | Sun, Y.; Wu, J.; Xie, Y.; Wang, X.; Ma, K.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Liao, Q.; Zheng, W.; Kang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32 2207116. |
| [36] | Tyagi, A.; Penke, Y. K.; Sinha, P.; Malik, I.; Kar, K. K.; Ramkumar, J.; Yokoi, H. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46 22434. |
| [37] | Xu, W.; Apodaca, N.; Wang, H.; Yan, L.; Chen, G.; Zhou, M.; Ding, D.; Choudhury, P.; Luo, H. ACS Catal. 2019, 9 5074. |
| [38] | Shi, Y.; Liu, T.; Zhao, Y.; Su, J.; Zeb, S.; Nie, Y.; Qin, C.; Wang, B.; Jiang, X. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 2022, 350 130860. |
| [39] | Ho, J.; Li, Y.; Dai, Y.; Kim, T.; Wang, J.; Ren, J.; Yun, H.; Liu, X. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46 20503. |
| [40] | Hu, Z.; Zhou, X.; Lu, Y.; Jv, R.; Liu, Y.; Li, N.; Chen, S. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 296 214. |
| [41] | Zou, J.; Chen, B.; Li, B.; Yin, M.; Miao, H.; Wang, F.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, J. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47 27470. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |