

Li3Cs2Sr2B3P6O24:Eu2+窄带蓝色荧光粉的发光性质及其在广色域背光显示上的应用
收稿日期: 2024-06-08
网络出版日期: 2024-12-02
基金资助
国家自然科学基金(12404461); 陕西省自然科学基础研究计划项目(2024JC-YBMS-384); 陕西基础科学(化学、生物学)研究院基础科学研究计划项目(23JHQ077); 国家级大学生创新训练计划项目(202410703079)
Photoluminescence Properties of Li3Cs2Sr2B3P6O24:Eu2+ Narrow-band Blue Phosphor for Wide Color Gamut Backlight Display Applications
Received date: 2024-06-08
Online published: 2024-12-02
Supported by
National Natural Science Foundation of China(12404461); Natural Science Basic Research Program of Shaanxi Province(2024JC-YBMS-384); Shaanxi Fundamental Science Research Project for Chemistry and Biology(23JHQ077); National innovative training program for college students(202410703079)
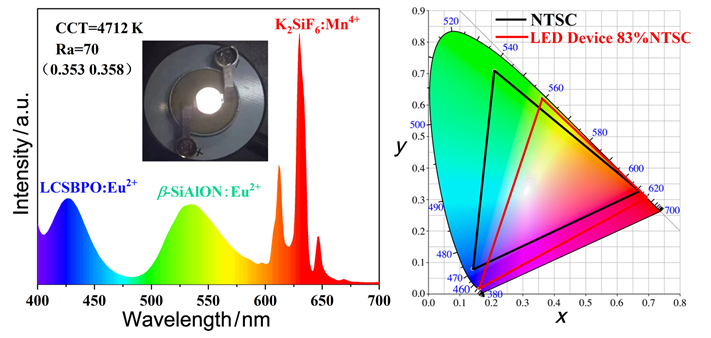
开发高量子效率、高热稳定性和高化学稳定性的窄带蓝色荧光粉是广色域背光显示技术领域急需解决的难题. 然而, 最近报道的Eu2+激活的窄带蓝色荧光粉主要集中在UCr4C4构型的基质材料中, 而且化学稳定性往往较差. 本工作采用高温固相法合成了一种硼磷酸盐Li3Cs2Sr2-xB3P6O24:xEu2+ (0.005≤x≤0.03, 下文简写成LCSBPO:xEu2+)窄带蓝色(半峰宽FWHM=34 nm, λem=432 nm)荧光粉. Eu2+离子的最佳掺杂量为0.02. LCSBPO:xEu2+荧光粉中存在两个Eu2+离子荧光中心, 分别对应占据在Sr(1)和Sr(2)两个格位的Eu2+离子. 此外, LCSBPO:0.02Eu2+荧光粉还具有较高的内/外量子效率(62.9%/16.8%)、出众的热稳定性(86.6%@150 ℃)、超高的色纯度(99%)和优异的化学稳定性(在去离子水中浸泡1个月后其发射强度能维持在93%). 在25~250 ℃温度范围内, LCSBPO:0.02Eu2+荧光粉还表现出优异的色度稳定性(Δx=0.0014, Δy=0.0024; 4×10-4≤ΔC≤9.7×10-3). 由LCSBPO:0.02Eu2+蓝光荧光粉、商用β-SiAlON:Eu2+绿色荧光粉、商用K2SiF6:Mn4+红色荧光粉和365 nm的LED芯片封装的白光发光二极管(WLED)能发射出明亮的白光, 且该WLED在CIE 1931色坐标中的色域面积可以达到NTSC (National Television System Committee)标准色域面积的83%. 上述发现证明本工作报道的LCSBPO:0.02Eu2+窄带蓝色荧光粉在WLED技术中有良好的潜在应用前景.
关键词: Li3Cs2Sr2B3P6O24:Eu2+; 窄带蓝色荧光粉; 广色域; 白光发光二极管
李明昭 , 李想 , 何洪波 , 宋芳 , 冷稚华 . Li3Cs2Sr2B3P6O24:Eu2+窄带蓝色荧光粉的发光性质及其在广色域背光显示上的应用[J]. 化学学报, 2024 , 82(12) : 1241 -1249 . DOI: 10.6023/A24060188
Developing narrow-band blue phosphor with high quantum efficiency, high thermal stability and high chemical stability is an urgent problem in the field of wide color gamut backlight display technology. However, the latest progress in the field of Eu2+ activated narrow-band blue phosphors is mainly limited to the UCr4C4-type prototype structure. And these phosphors generally exhibit poor chemical stability. Herein, a borophosphate Li3Cs2Sr2-xB3P6O24:xEu2+ (0.005≤x≤0.03, hereinafter abbreviated as LCSBPO:xEu2+) blue phosphor with narrow-band emission (λem=432 nm; full width at half maximum, FWHM=34 nm) was synthesized by high temperature solid phase method. The optimal doping concentration of Eu2+ ions is 0.02. There are two Eu2+ luminescence centers in the LCSBPO:xEu2+ phosphors, i.e. the Eu2+ ions occupied in the Sr(1) and Sr(2) sites, respectively. In addition, the LCSBPO:0.02Eu2+ phosphor also exhibits a high internal/external quantum efficiency (62.9%/16.8%), outstanding thermal stability (86.6%@150 ℃), ultra-high color purity (99%) and excellent chemical stability, whose emission intensity can still remain 93% of that of the pristine sample after being soaking in deionized water for 1 month. In the temperature range of 25~250 ℃, the LCSBPO:0.02Eu2+ phosphor also displays excellent chroma stability (Δx=0.0014, Δy=0.0024; 4×10-4≤ΔC≤9.7×10-3). White light emitting diodes (WLED), which is fabricated by LCSBPO:0.02Eu2+ blue phosphor, commercial β-SiAlON:Eu2+ green phosphor, commercial K2SiF6:Mn4+ red phosphor and 365 nm LED chip, can emit bright white light. And the color gamut area of this WLED in CIE 1931 color coordinates can reach 83% of the color gamut area of the National Television System Committee (NTSC) standard area. These aforesaid findings prove that LCSBPO:0.02Eu2+ narrow-band blue phosphor reported here has a good potential application in WLED technology.

| [1] | Chen, H. M.; Wang, L.; Zhang, P.; Bai, X. L.; Zhou, G. J. Acta Chim. Sinica 2023, 81, 771. (in Chinese) |
| [1] | (陈慧敏, 王龙, 张盼, 白西林, 周国君, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 771). |
| [2] | Zhang, J. R.; Huang, D. C.; Huang, C. C.; Liang, S. S.; Zhu, H. M. Acta Chim. Sinica 2022, 80, 453. (in Chinese) |
| [2] | (张景荣, 黄得财, 黄聪聪, 梁思思, 朱浩淼, 化学学报, 2022, 80, 453.) |
| [3] | Liang, P.; Zhang, H. S.; Huang, H. S.; Li, S. Y.; Zhang, X. T.; Wang, Y.; Li, L. Q.; Liu, Z. H. Acta Chim. Sinica 2023, 81, 371. (in Chinese) |
| [3] | (梁攀, 张宏淑, 黄宏升, 李飒英, 张笑恬, 王英, 李连庆, 刘志宏, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 371.) |
| [4] | Zhao, M.; Zhang, Q. Y.; Xia, Z. G. Mater. Today 2020, 40, 246. |
| [5] | Wang, S. W.; Wu, H. Y.; Fan, Y. F.; Wang, Q.; Tan, T.; Zhang, S.; Li, D.; Jiang, L. H.; Li, C. Y.; Zhang, H. J. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 432, 134265. |
| [6] | Qiao, J. W.; Zhou, Y. Y.; Molokeev, M. S.; Zhang, Q. Y.; Xia, Z. G. Laser Photonics Rev. 2021, 15, 2100392. |
| [7] | Pust, P.; Weiler, V.; Hecht, C.; Tücks, A.; Wochnik, A. S.; Hen?, A.; Wiechert, D.; Scheu, C.; Schmidt, P. J.; Schnick, W. Nature Mater. 2014, 13, 891. |
| [8] | Dutzler, D.; Seibald, M.; Baumann, D.; Huppertz, H. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 13676. |
| [9] | Leng, Z. H.; Zhang, D.; Bai, H.; He, H. B.; Qing, Q.; Zhao, J.; Tang, Z. B. J. Mater. Chem. C 2021, 9, 13722. |
| [10] | Tang, Z. B.; Du, F.; Leng, Z. H.; Xie, H. D.; Li, Y. Y.; Zhao, L. J. Rare Earth. 2023, 41, 1876. |
| [11] | Zhao, M.; Liao, H. X.; Ning, L. X.; Zhang, Q. Y.; Liu, Q. L.; Xia, Z. G. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1802489. |
| [12] | Liao, M.; Wang, Q.; Lin, Q. M.; Xiong, M. X.; Zhang, X.; Dong, H. F.; Lin, Z. P.; Wen, M. R.; Zhu, D. Y.; Mu, Z. F.; Wu, F. G. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2021, 9, 2100465. |
| [13] | Liao, H. X.; Ming, Z.; Zhou, Y. Y.; Molokeev, M. S.; Liu, Q. L.; Zhang, Q. Y.; Xia, Z. G. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1901988. |
| [14] | Piao, S. Q.; Wang, Y. C.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, J. S.; Zhang, X. Z.; Wu, D. Y.; Cao, Y. Z.; Li, X. P.; Chen, B. J. J. Mater. Chem. 2021, 9, 14777. |
| [15] | Wu, Q. S.; Li, Y. Y.; Wang, Y. J.; Liu, H.; Ye, S. S.; Zhao, L.; Ding, J. Y.; Zhou, J. C. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 401, 126130. |
| [16] | Zhuang, J. Q.; Xia, Z. G.; Liu, H. K.; Zhang, Z. P.; Liao, L. B. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 4350. |
| [17] | Leng, Z. H.; Bai, H.; Qing, Q.; He, H. B.; Hou, J. Y.; Li, B. Y.; Tang, Z. B.; Song, F.; Wu, H. Y. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 10966. |
| [18] | Zhang, L. J.; Li, Y. Y.; Liu, P. F.; Chen, L. Dalton T. 2016, 45, 7124. |
| [19] | Song, Z.; Lü, W.; Kang, X. J.; Zhu, Z. N.; Zeng, Q. J. Lumin. 2024, 265, 120255. |
| [20] | Suo, H. X.; Song, Z.; Kang, X. J.; Li, X. M.; Zhou, F.; Lyu, W. Chin. J. Lumin. 2023, 44, 837. (in Chinese) |
| [20] | (索慧娴, 宋志, 康晓娇, 李昕明, 周飞, 吕伟, 发光学报, 2023, 44, 837.) |
| [21] | Zhou, Y. P.; Hu, Y. S.; Liu, R. H.; Liu, Y. H.; Zhuang, W. D.; Cao, M.; Gao, T. Y.; Tian, J. H.; Li, Y. F.; Chen, G. T. J. Rare Earth. 2021, 39, 627. |
| [22] | Zhu, Y. L.; Liang, Y. J.; Liu, S. Q.; Li, H. R.; Chen, J. H. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2019, 7, 1801419. |
| [23] | Bai, H.; Wu, G. D.; Qing, Q.; Hou, J. Y.; Liu, J. H.; Song, F.; Tang, Z. B.; Leng, Z. H. J. Lumin. 2022, 252, 119346. |
| [24] | Leng, Z. H.; Li, R. F.; Li, L. P.; Xue, D. K.; Zhang, D.; Li, G. S.; Chen, X. Y.; Zhang, Y. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 33322. |
| [25] | Zhang, H. Z.; Li, H.; Liu, C. L.; Jiang, H. M.; Li, Y. X.; He, J. Y.; Wang, R.; Hu, W. B.; Zhu, J. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 490, 151727. |
| [26] | Wu, G. D.; Xue, J. Q.; Li, X. Y.; Bi, Q.; Sheng, M. J.; Leng, Z. H. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 10615. |
| [27] | Zhao, M.; Cao, K.; Liu, M. J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, R.; Zhang, Q. Y.; Xia, Z. G. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 12938. |
| [28] | Qiang, J. W.; Wang, L.; Wang, T. M.; Yu, Y.; Deng, D. S.; Wu, C. X.; Liao, S.; Li, S. X. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 17253. |
| [29] | Huang, D. C.; Zhu, H. M.; Deng, Z. H.; Zou, Q. L.; Lu, H. Y.; Yi, X. D.; Guo, W.; Lu, C. Z.; Chen, X. Y. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 3843. |
| [30] | Zhang, Z. J.; Devakumar, B.; Wang, S. Y.; Sun, L. L.; Ma, N.; Li, W.; Huang, X. Y. Mater. Today Chem. 2021, 20, 100471. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |