

固定化与溶剂设计协同提高脂肪酶合成维生素E琥珀酸酯效率机制研究
收稿日期: 2024-10-29
网络出版日期: 2025-02-05
基金资助
国家重点研发计划(2021YFC2103800); 国家自然科学基金(22178174); 江苏省先进生物制造创新中心(XTC2206)
Study on the Mechanism of Synergistic Enhancement of Lipase Efficiency in Vitamin E Succinate Synthesis through Immobilization and Solvent Design Strategies
Received date: 2024-10-29
Online published: 2025-02-05
Supported by
National key R&D program of China(2021YFC2103800); National Natural Science Foundation of China(22178174); Jiangsu Synergetic Innovation Center for Advanced Bio-Manufacture(XTC2206)
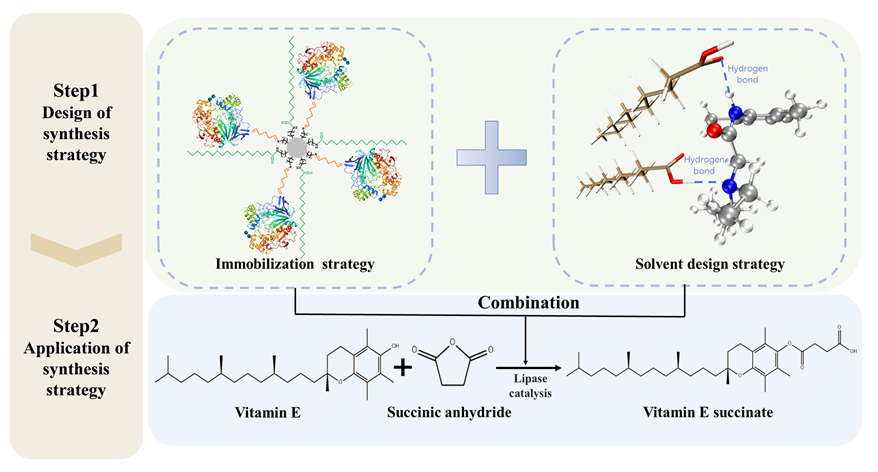
酶的固定化策略以及反应体系对酶促反应至关重要. 为此, 本研究以维生素E琥珀酸酯(VES)的合成为模型反应, 协同酶固定化以及溶剂设计策略, 采用双官能团大孔树脂固定化脂肪酶结合新型低共熔溶剂设计, 显著提升了脂肪酶的活性、重复利用性等酶学性能. 在最优条件下, VES的最终收率可达99.3%, 且循环使用5次后, 酯化产率仍能保持在80.0%以上, 显著优于传统有机溶剂体系. 分子动力学模拟结果表明, 低共熔溶剂有助于稳定酶的结构, 同时提升酶对底物的亲和力, 从而提升其催化效率. 本研究开发的合成策略具有绿色、高效、催化剂可重复利用性强的特点, 在生物合成领域具有广阔的应用前景.
张子晗 , 马光政 , 年彬彬 , 胡燚 . 固定化与溶剂设计协同提高脂肪酶合成维生素E琥珀酸酯效率机制研究[J]. 化学学报, 2025 , 83(2) : 119 -125 . DOI: 10.6023/A24100326
Vitamin E is one of the most widely used antioxidants, extensively applied in the medical and food industries. However, its susceptibility to oxidation poses significant challenges during production, storage, and transportation. In recent years, a derivative of Vitamin E—Vitamin E succinate (VES) has garnered increasing attention. VES not only retains the biological functions of Vitamin E but also exhibits excellent stability and unique anti-tumor properties. The main methods for preparing VES include chemical synthesis and enzymatic synthesis. Enzymatic synthesis has become a popular research topic due to its environmental friendliness and high efficiency. Nevertheless, the high cost and poor reusability of free enzymes severely limit the industrial application of this method. Designing enzyme-friendly solvents and immobilized enzyme technologies has proven to be effective strategies to overcome these limitations. In this study, the synthesis of VES was employed as a model reaction to integrate immobilization and solvent design strategies. The lipase was immobilized in a dual-functional macroporous resin, combined with a novel deep eutectic solvent, significantly enhancing the performance of lipase. Under the optimal conditions, the experimental results revealed a VES yield of 99.3%. When scaled up tenfold, the system achieved a 99.1% esterification yield, with the catalytic activity remaining above 80.0% even after five reuse cycles. Notably, molecular dynamics simulation results indicated that the deep eutectic solvent has excellent biocompatibility, which enhances the stability and reusability of lipase. Furthermore, this solvent improves the affinity of lipase for the substrate, thereby increasing the yield of VES. The synthetic strategy developed in this study is environmentally friendly, catalytically efficient, and offers broad applications in the field of biosynthesis.

Key words: lipase; immobilization; vitamin E succinate; deep eutectic solvent; biocatalysis
| [1] | Zaaboul, F.; Liu, Y. F. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 964. |
| [2] | Galli, F.; Azzi, A.; Birringer, M.; Cook-Mills, J. M.; Eggersdorfer, M.; Frank, J.; Cruciani, G.; Lorkowski, S.; ?zer, N. K. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 102, 16. |
| [3] | Ma, G. Z.; Chong, W. Y.; Qi, Y.; Lu, Z. P.; Zhang, Z. H.; Nian, B. B.; Hu, Y. Bioprocess. Biosyst. Eng. 2023, 46, 1695. |
| [4] | Zheng, L. L.; Wang, Y. Q.; Li, X. G.; Zhang, W. B. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2022, 42, 3714. |
| [5] | Zhang, C.; Zhang, L. J.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, H.; Hu, Y. Acta Chim. Sinica 2016, 74, 74 (in Chinese). |
| [5] | (张川, 张鲁嘉, 张洋, 黄和, 胡燚, 化学学报, 2016, 74, 74.) |
| [6] | Nian, B. B.; Li, X. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 217, 255. |
| [7] | Gao, F. Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y. L.; Jiang, Y. C. Acta Chim. Sinica 2023, 81, 338 (in Chinese). |
| [7] | (高丰琴, 刘洋, 张引莉, 蒋育澄, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 338.) |
| [8] | Durand, E.; Lecomte, J.; Villeneuve, P. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2013, 115, 279. |
| [9] | Ma, G. Z.; Zhang, Z. H.; Lu, Z. P.; Qi, Y.; Nian, B. B.; Hu, Y. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 394, 10. |
| [10] | Qi, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liang, C.; Chong, W.; Nian, B.; Hu, Y. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 23401. |
| [11] | Ma, G. Z.; Zhang, Z. H.; Chen, M.; Zhang, Y. F.; Nian, B. B.; Hu, Y. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2024, 104, 2669. |
| [12] | Datta, S.; Christena, L. R.; Rajaram, Y. R. S. 3 Biotech. 2013, 3, 1. |
| [13] | Ismail, A. R.; Baek, K. H. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 163, 1624. |
| [14] | Rodrigues, R. C.; Berenguer-Murcia, A.; Carballares, D.; Morellon-Sterling, R.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Biotechnol. Adv. 2021, 52, 37. |
| [15] | Zhang, Y. F.; Ma, G. Z.; Wang, S. S.; Nian, B. B.; Hu, Y. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2023, 103, 7849. |
| [16] | Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liang, C.; Nian, B.; Hu, Y. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 23345. |
| [17] | Goncalves, D.; Silva, A. G.; Guidini, C. Z. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 7399. |
| [18] | Khan, Z.; Javed, F.; Shamair, Z.; Hafeez, A.; Fazal, T.; Aslam, A. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 103, 80. |
| [19] | Maffucci, I.; Laage, D.; Sterpone, F.; Stirnemann, G. Chem.-Eur. J. 2020, 26, 10045. |
| [20] | Xia, J. J.; Bin, Z.; Zhou, R. Y. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 3186. |
| [21] | Jiang, X. J.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, L.; Gong, J. H.; Huang, H. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2013, 29, 223. |
| [22] | Hou, X. Y.; Shi, Q. H. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2023, 62, 182. |
| [23] | He, W. S.; Zhu, H. Y.; Chen, Z. Y. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 3047. |
| [24] | Berendsen, H. J. C.; Vanderspoel, D.; Vandrunen, R. Comput. Phys. Commun. 1995, 91, 43. |
| [25] | Maier, J. A.; Martinez, C.; Kasavajhala, K.; Wickstrom, L.; Hauser, K. E.; Simmerling, C. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2015, 11, 3696. |
| [26] | Trott, O.; Olson, A. J. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455. |
| [27] | Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |