1 引言
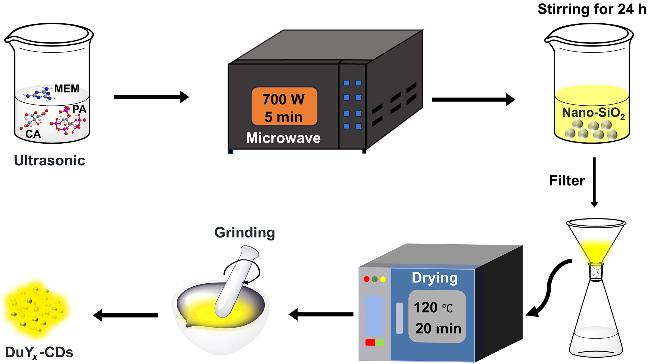
2 结果与讨论
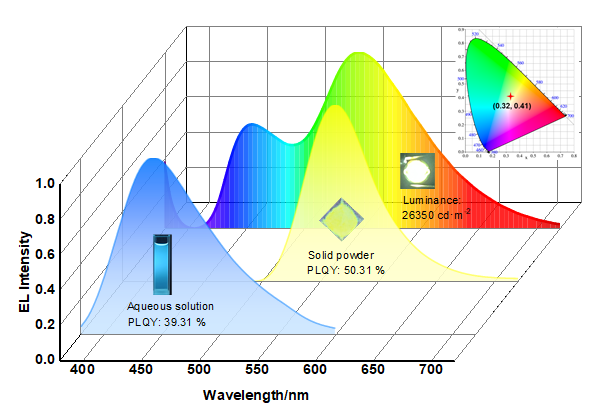
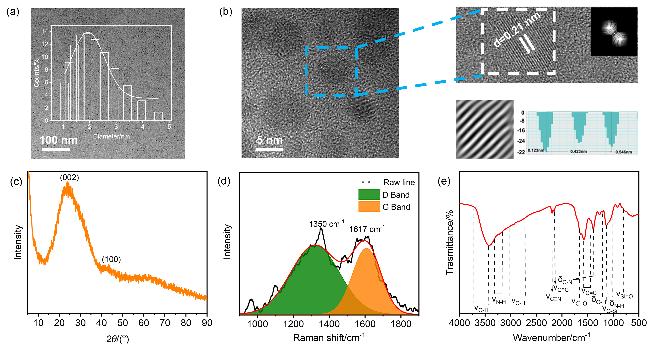
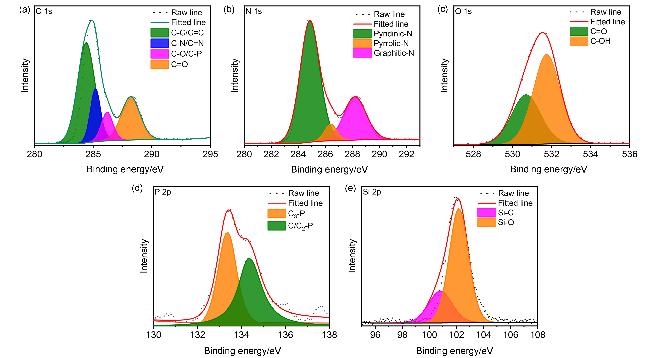
2.1 DuY8-CDs的光学性质
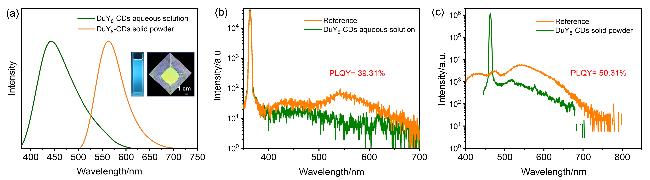
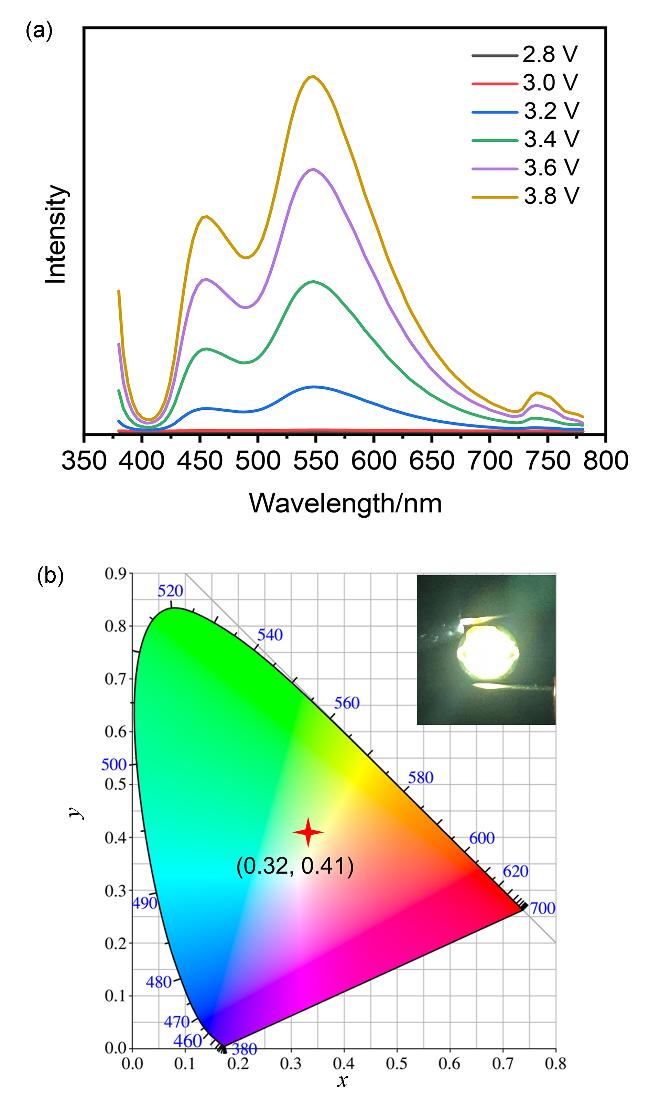
图2 (a) DuY8-CDs水溶液(6×10-6 g/mL)和粉末的归一化PL光谱(激发波长为365 nm, 插图: DuY8-CDs水溶液和粉末在365 nm紫外灯下的发光照片)、(b) DuY8-CDs水溶液(6×10-6 g/mL)的PLQY测试及(c) DuY8-CDs粉末的PLQY测试Figure 2 (a) Normalized PL spectra of DuY8-CDs aqueous solution (6×10-6 g/mL) and powder (the excitation wavelength is 365 nm, respectively. Insets: photographs of DuY8-CDs aqueous solution and powder under ultraviolet lamps with excitation wavelength of 365 nm), (b) PLQY of DuY8-CDs aqueous solution (6×10-6 g/mL), and (c) PLQY of DuY8-CDs powder |
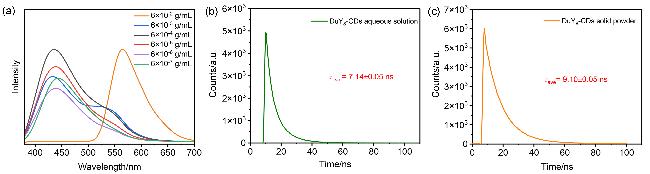
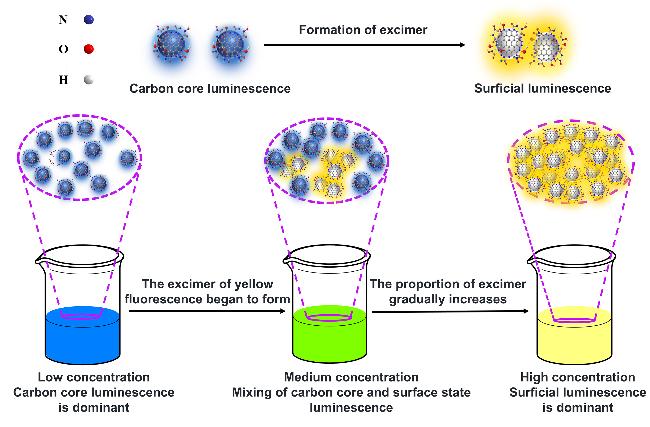
图3 (a)不同质量浓度DuY8-CDs水溶液的PL光谱、(b) DuY8-CDs水溶液(6×10-6 g/mL)的荧光衰减曲线及(c) DuY8-CDs粉末的荧光衰减曲线Figure 3 (a) PL spectra of DuY8-CDs aqueous solution at different mass concentrations, (b) fluorescence decay curve of DuY8-CDs aqueous solution (6×10-6 g/mL), and (c) fluorescence decay curve of DuY8-CDs powder |