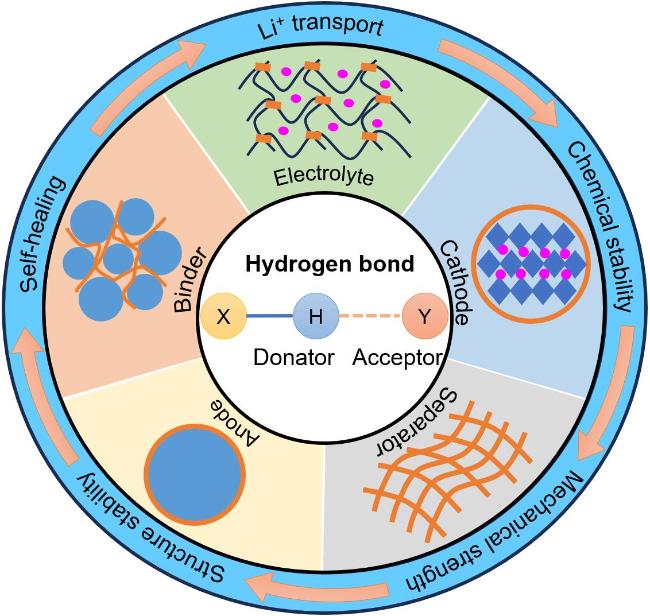
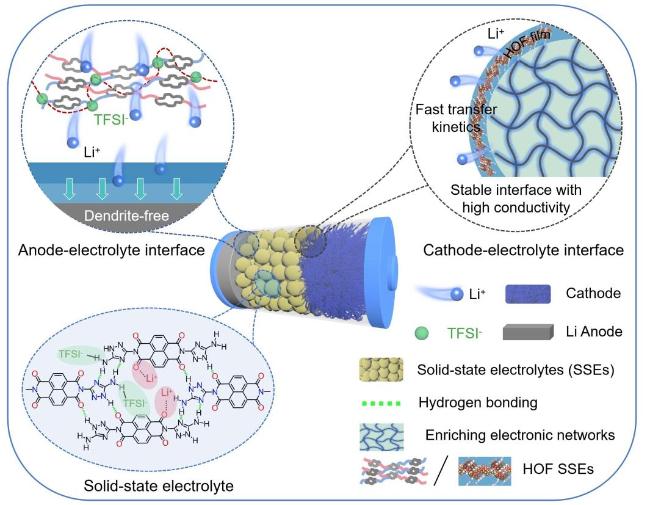
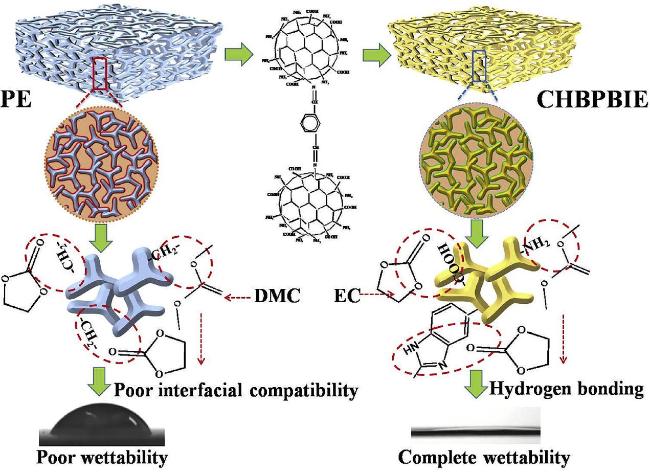
1 引言
2 氢键化学稳定正极材料
2.1 氢键稳定正极材料界面
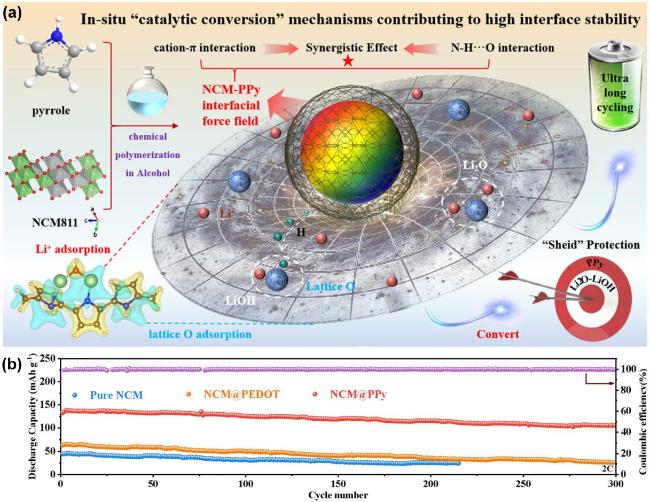
图2 (a) PPy包覆NCM正极材料的结构设计及原理示意图, (b)纯NCM、NCM@PEDOT、NCM@PPy在全固态金属锂电池中的循环性能对比 图[16]Figure 2 (a) The structural design and schematic diagram of PPy coated NCM cathode material, (b) The cycling performance of ASSLMBs paired with pure NCM, NCM@PEDOT, and NCM@PPy. Reprinted with permission from Ref.[16]. Copyright 2024, The Royal Society of Chemistry |
2.2 氢键抑制有机物正极材料的溶解
2.3 氢键功能粘结剂稳定硫正极
3 氢键化学用于电解质优化
3.1 氢键调控液态电解质的溶剂化结构
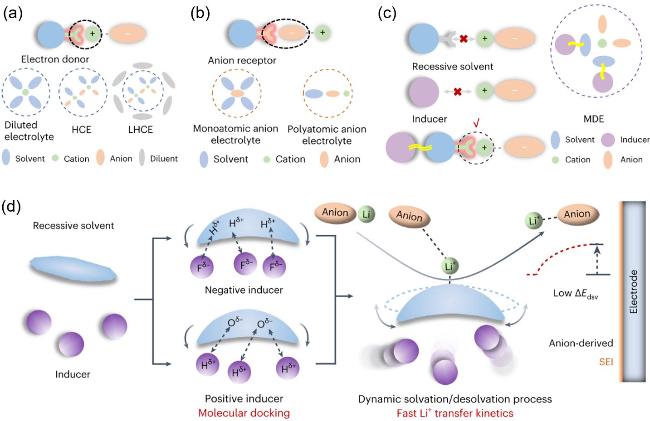
图3 显性和隐性溶剂化示意图. 基于电子给体的典型溶剂化壳结构(a)和阴离子受体(b), 两者溶剂化过程都会自发解离锂盐并参与溶剂化鞘的形成; 隐性溶剂和诱导剂的相互作用导致了隐形溶剂化(c); 通过分子对接激活隐性溶剂的机制(d)[35]Figure 3 Schematic of dominant and recessive solvation. Typical solvation shell structures based on the electron donor (a) and anion receptor (b), both of which spontaneously dissociate the salt and participate in the formation of the solvation sheath; recessive solvation enabled by the interacted recessive solvent and inducer (c); activation of the recessive solvent via molecular docking mechanism (d). Reprinted with permission from Ref.[35]. Copyright 2024, Springer Nature |
3.2 氢键改性优化凝胶聚合物电解质
3.2.1 氢键抑制凝胶聚合物电解质的锂枝晶生长
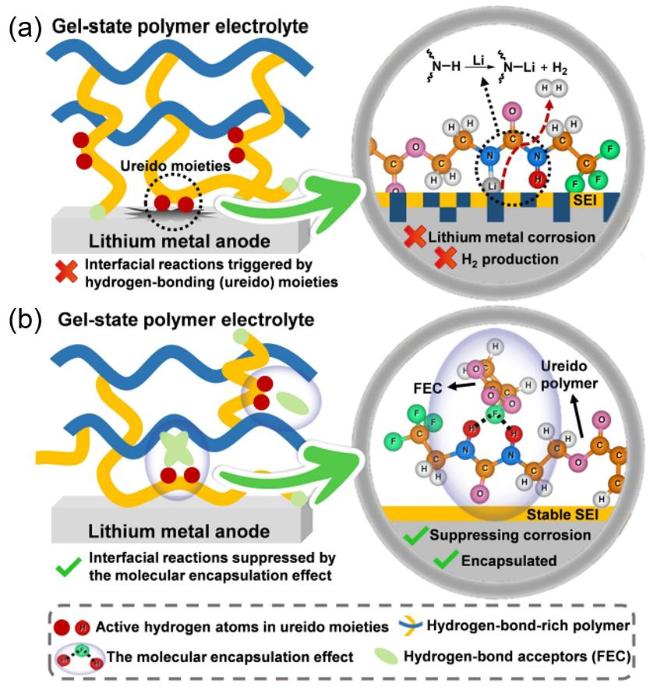
图4 富含氢键的凝胶聚合物电解质与锂金属负极(LMAs)发生界面反应的示意图. (a)富含氢键的凝胶聚合物电解质与LMAs存在着严重的界面副反应; (b)通过分子封装效应可以抑制富含氢键的凝胶聚合物电解质与LMAs的界面副反应[43]Figure 4 Schematics of interfacial reactions between hydrogen-bond-rich gel-state polymer electrolytes and LMAs. (a) The severe interfacial reactions between hydrogen-bond-rich electrolytes and LMAs. (b) The interfacial reactions between hydrogen-bond-rich electrolytes and LMAs are suppressed via the molecular encapsulation effect. Reprinted with permission from Ref.[43] Copyright 2024, Wiley-VCH |
3.2.2 氢键增强凝胶电解质的锂离子传输能力
3.2.3 氢键提高凝胶聚合物电解质的界面稳定性
3.2.4 氢键赋予凝胶聚合物电解质自修复功能
3.3 氢键优化固态聚合物电解质
3.3.1 氢键增强聚合物电解质的锂离子传输性能
3.3.2 氢键提升聚合物电解质的机械性能
3.3.3 氢键拓宽固态聚合物电解质的电化学窗口
3.4 氢键改性优化有机无机复合固态电解质
4 氢键化学用于隔膜修饰
5 氢键化学用于负极材料
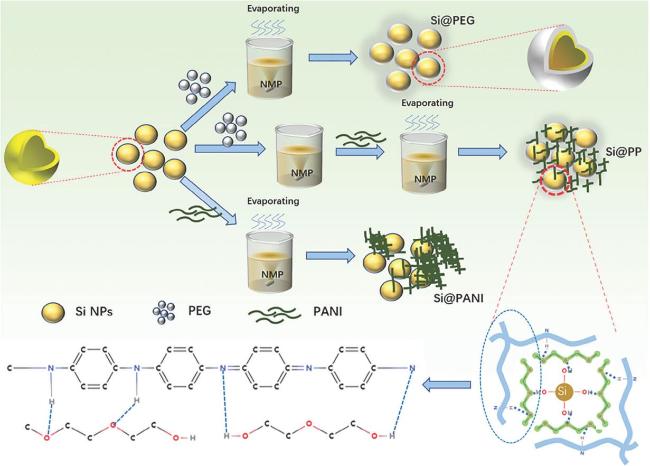
5.1 聚合物包覆层的氢键网络稳定硅负极
5.2 基于氢键交联的自修复高弹性粘结剂用于硅负极
5.3 氢键稳定锂负极界面
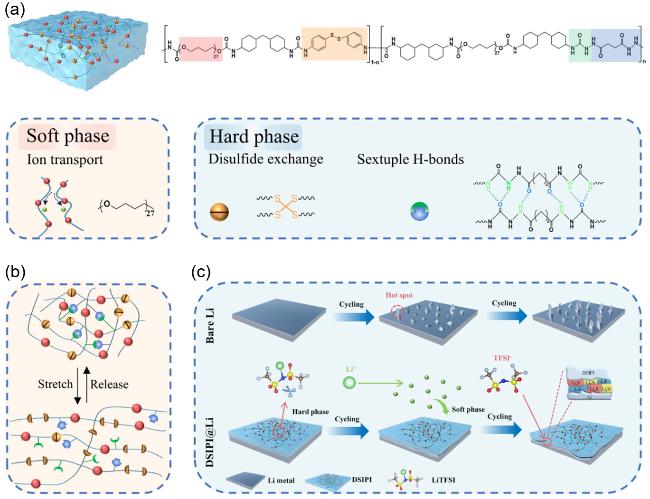
图8 (a)具有高韧性、自修复功能和弹性的动态超分子聚氨酯-脲(DSP-n)的结构设计和机理示意图; (b)分子链段在拉伸过程的运动示意图; (c) Li在裸Li和动态超分子聚氨酯-脲界面(DSIPI)@Li上的沉积示意图, 说明了DSIPI用于无枝晶和高效LMA的机制[21]Figure 8 (a) Structural design and mechanism diagram of DSP-n featuring high toughness, self-healing capabilities, and stretchability. (b) Schematic diagram illustrating the movement of polymer chain segments during the stretching process. (c) Schematic of Li plating/stripping on bare Li and DSIPI@Li anodes, revealing the mechanism of action of DSIPI for a dendrite-free and efficient Li metal anode. Reprinted with permission from Ref.[21] Copyright 2024, Wiley-VCH |