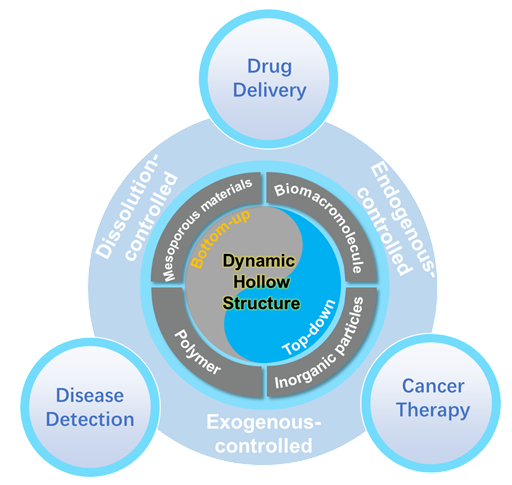
The dynamic evolution of living organisms has inspired extensive research on multi-level dynamic assembly materials, a cutting-edge direction in materials chemistry that bridges fundamental science and practical applications. Driven by dynamic chemistry, these materials rely on covalent and non-covalent interactions to gain intelligent properties like stimulus responsiveness, structural reversibility and self-healing, strongly supporting their great potential in biomedicine, especially in precise diagnosis and targeted therapy. Hollow structures, featuring unique spatial configurations, high volume ratio cavities and modifiable surfaces properties, are inspired by natural systems like cells and blood vessels. It naturally fulfills indispensable functions of protection, loading and transportation. Through elaborate internal space design, researchers have further constructed multi-core, multi-shell, and multi-compartment structures, significantly expanding the hollow structure's functional boundaries and application scenarios, and endowing it with irreplaceable advantages in drug delivery, energy conversion and storage. Combining these advantages, dynamic intelligent hollow materials have emerged as a prominent research hotspot in biomedicine, while facing critical challenges. Their design demands establishing clear structure-activity relationships to achieve controllable fabrication of multi-level structures and precise regulation of size and morphology. Additionally, these materials must integrate core functions including targeting, theranostics and self-healing, while balancing in vivo stability, biocompatibility and metabolic safety, and effectively resolving the controllability and long-term efficacy of dynamic evolution under complex and dynamic physiological environments. This review presents systematic strategies for constructing multifunctional systems with dynamic hollow structures, focusing on the systematic summary of dynamic building blocks (e.g., polymers, inorganic nanoparticles, biological macromolecules) and driving forces (including pH, light and solvent environment), classified into top-down and bottom-up approaches. Furthermore, applications of dynamic hollow structures in drug delivery, disease detection, and cancer treatment are discussed in detail. Finally, the review provides a forward-looking perspective on the rational design and synthesis of hollow multishelled structure, as well as their application prospects in hierarchical targeted therapy, pulsed drug release, and theragnostic integration, aiming to guide the development of next-generation advanced biomaterials.
[1] Lee S.; Sim K.; Moon S. Y.; Choi J.; Jeon Y.; Nam J.-M.; Park S.-J. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33 2007668.
[2] Zheng N.; Xu Y.; Zhao Q.; Xie T. Chem.Rev. 2021, 121, 1716.
[3] Wang S.; Urban M. W. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2020, 5, 562.
[4] Zhao D.; Wei Y.; Xiong J.; Gao C.; Wang D. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2300681.
[5] Webber M. J.; Tibbitt M. W. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2022, 7, 541.
[6] Zhang Q.; Qu D.-H.; Feringa B. L.; Tian H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 2022.
[7] Song N.; Chu Y.; Li S.; Dong Y.; Fan X.; Tang J.; Guo Y.; Teng G.; Yao C.; Yang D. Sci. Adv.2023, 9, eadi3602
[8] Boahen E. K.; Pan B.; Kweon H.; Kim J. S.; Choi H.; Kong Z.; Kim D. J.; Zhu J.; Ying W. B.; Lee K. J.; Kim D. H. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7699.
[9] Zhang L.; Zou Y.; Xu Z.; Liu, Y. Chem. J.Chinese U. 2023, 44, 20230134.
[10] Li Z.; Xu K.; Qin L.; Zhao D.; Yang N.; Wang D.; Yang Y. Adv.Mater. 2023, 35, 2203890.
[11] Wang J.; Wan J.; Yang N.; Li Q.; Wang D. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2020, 4, 159.
[12] Xiong J.; Shang L.; Zhao D.; Wang D. Sci.China Mater. 2024, 67, 2540.
[13] Du. S.; Wang. Y.; Wang, F.; Wang, T.; Zhan, L.; Liu, M. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2024, 25, 109256.
[14] Wei Y.; Cui S.; Yu L.; Ding J. Macromolecules 2023, 56, 2619.
[15] Jamshid K.; Zhong F.; Zhang W.; Hong C. Acta Chim Sinica 2022, 80, 913.
[16] Xia Y.;Trung Dac, N.; Yang, M.; Lee, B.; Santos, A.; Podsiadlo, P.; Tang, Z.; Glotzer, S. C.; Kotov, N. A. Nat Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 580.
[17] Belluati A.; Jimaja S.; Chadwick R. J.; Glynn C.; Chami M.; Happel D.; Guo C.; Kolmar H.; Bruns N. Nat.Chem. 2023, 16, 564.
[18] Li H.; Cheng C.; Yang Z.; Wei J. Nat.Commun. 2022, 13, 6466.
[19] Xie X.; Sun T.; Xue J.; Miao Z.; Yan Xu.; Fang W.; Li Q.; Tang R.; Lu Y.; Tang L.; Zha Z.; He T. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2000511.
[20] Chen X.; Liu X.; Khan M.; Yan Z.; Cao D.; Duan S.; Fu L.; Wang W. Research 2024, 7, 0490.
[21] Li F.; Liu Y.; Dong Y.; Chu Y.; Song N.; Yang D. J. Am. Chem. Soc.2022, 144, 4667.
[22] Li H.; Qian X.; Mohanram H.; Han X.; Qi H.; Zou G.; Yuan F.; Miserez A.; Liu T.; Yang Q.; Gao H.; Yu J. Nat.Nanotechnol. 2024, 19, 1114.
[23] Li R.; Khiman M.; Sheng L.; Sun J. Acta Chim Sinica 2020, 78, 1235.
[24] Yang Z.; Peng Y.; Qiu L.Chinese Chem. Lett. 2018, 29, 1839.
[25] Wang X.; Gao P.; Wang J.; Yang Y.; You Y.; Wu D. CCS Chem. 2021, 3, 127.
[26] Yang M.; Chan H.; Zhao G.; Bahng J. H.; Zhang P.; Kral P.; Kotov N. A. Nat. Chem. 2017, 9, 287.
[27] Wu C.; Li Z.; Bai Y.; To D.; Myung N. V.; Yin Y. Aggregate 2021, 3, e146.
[28] Yu B.; Liu J.; Cui Z.; Wang C.; Chen P.; Wang C.; Zhang Y.; Zhu X.; Zhang Z.; Li S.; Pan J.; Xie M.; Shen H.; Cao L. Nat.Chem. 2025, DOI: s41557-025-01929-2.
[29] Kundu P. K.; Samanta D.; Leizrowice R.; Margulis B.; Zhao H.; Boerner M.; Udayabhaskararao T.; Manna D.; Klajn R. Nat.Chem. 2015, 7, 646.
[30] Zou J.; He J.; Wang X.; Wang Y.; Wu C.; Shi M.; Jiang H.; Wu Z.; Liu J.; Zhang W. J. Control Release 2022, 351, 341.
[31] Zhang S.; Chu Z.; Yin C.; Zhang C.; Lin G.; Li Q. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 5709.
[32] Yan B.-B.; Zhao Y.; Li M.; Li K.; Dong L.; Yang S.-Y.; Luo Z.; Yu S.-H.Nano Lett. 2022, 22, 9181.
[33] Wang H.; Zhao D.; Yang N.; Wang D. Chem.J. Chinese U. 2023, 44, 20220237.
[34] Wang S.; Guo X.; Xiu W.; Liu Y.; Ren L.; Xiao H.; Yang F.; Gao Y.; Xu C.; Wang L. Sci. Adv.2020, 6, eaaz8204.
[35] Xie L.; Yan M.; Liu T.; Gong K.; Luo X.; Qiu B.; Zeng J.; Liang Q.; Zhou S.; He Y.; Zhang W.; Jiang Y.; Yu Y.; Tang J.; Liang K.; Zhao D.; Kong B. J. Am. Chem. Soc.2022, 144, 1634.
[36] Lian M.; Xue Z.; Qiao X.; Liu C.; Zhang S.; Li X.; Huang C.; Song Q.; Yang W.; Chen X.; Wang T. Chem 2019, 5, 2378.
[37] Wang Z.; Zeng Y.; Wang Y.; Chen C. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2024, 40, 564.
[38] Li J.; Koo K. M.; Wang Y.; Trau M. Small 2019, 15, 1904689.
[39] Kim J.; Lee S.; Kim Y.; Choi M.; Lee I.; Kim E.; Yoon. C.; Pu, K.; Kang, H.; Kim, J. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2023, 8, 710.
[40] Xie Y.; Qin Z.; Qian, M; Ren T.; Yuan L. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2024, 40, 190.
[41] Ren H.; Zeng X.; Zhao X.; Hou D.; Yao H.; Yaseen M.; Zhao L.; Xu W.; Wang H.; Li L. Nat.Commun. 2022, 13, 418.
[42] Yang S.; Cao Y.; Wang S.; Li Y.; Shi J. Chem. Res. Chinese U. 2022, 38, 99.
[43] Cao M.; Xing X.; Shen X.; Ouyang J.; Na. N. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2024, 40, 202.
[44] Yang G.; Phua S. Z.F.; Lim, W. Q.; Zhang, R.; Feng, L.; Liu, G.; Wu, H.; Bindra, A. K.; Jana, D.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, Y. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1901513.
[45] Liu X.; Chen Y.; Li H.; Huang N.; Jin Q.; Ren K.; Ji J. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 6244.
[46] Yu W.; Liu R.; Zhou Y.; Gao H. ACS Central Sci. 2020, 6, 100.
[47] Wang S.; Huang P.; Chen X. Adv.Mater. 2016, 28, 7340.
[48] Mao Q.; Fang J.; Wang A.; Zhang Y.; Cui C.; Ye S.; Zhao Y.; Feng Y.; Li J.; Shi, H., Angew. Chem. Int.Edit. 2021, 60, 23805.
[49] Gao J.; Qin H.; Wang F.; Liu L.; Tian H.; Wang H.; Wang S.; Ou J.; Ye Y.; Peng F.; Tu Y. Nat.Commun. 2023, 14, 4867.
[50] Mao D.; Wang C.; Li W.; Zhou L.; Liu J.; Zheng Z.; Zhao Y.; Cao A.; Wang, S.; Huang, J.; Huo, F.; Chen, H.; Mai, L.; Yu, R.; Wang, L.; Lu, Y.; Yu, C.; Yang, Q.; Yang, Z.; Zeng, H.; Zhao, H.; Tang, Z.; Zhao, D.; Wang, D. Chem Res Chin Univ, 2024, 40, 346.
[51] Mao D.; Wan J.; Wang J.; Wang D. Adv.Mater. 2019, 31, 1802874
[52] Wei Y.; Cheng Y.; Zhao D.; Feng Y.; Wei P.; Wang J.; Ge W.; Wang D. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2023, 62, e202302621.
[53] Zhao D.; Wei Y.; Jin Q.; Yang N.; Yang Y.; Wang D. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2022, 61, 2206807.
[54] Zhao D.; Yang N.; Wei Y.; Jin Q.; Wang Y.; He H.; Yang Y.; Han B.; Zhang S.; Wang D. Nat.Commun. 2020, 11, 4450.
[55] Sarmadi M.; Ta C.; VanLonkhuyzen A. M.; De Fiesta D. C.; Kanelli M.; Sadeghi I.; Behrens A. M.; Ingalls B.; Menon N.; Daristotle J. L.; Yu J.; Langer R.; Jaklenec, A. Sci. Adv.2022, 8, eabn5315.


