Acta Chimica Sinica ›› 2022, Vol. 80 ›› Issue (5): 652-658.DOI: 10.6023/A21120612 Previous Articles Next Articles
Special Issue: 中国科学院青年创新促进会合辑
Perspective
杨学志a, 陆达伟b, 王伟超b,c, 杨航b,c, 刘倩b,c,*( ), 江桂斌a,b,c
), 江桂斌a,b,c
投稿日期:2021-12-31
发布日期:2022-05-31
通讯作者:
刘倩
作者简介: |
杨学志, 2021年于中国科学院生态环境研究中心获得理学博士学位, 现任国科大杭州高等研究院助理研究员. 主要从事颗粒态污染物的来源、环境过程及健康效应研究. 近年来, 以第一作者在Nat. Commun.、Environ. Sci. Technol.、Environ. Pollut.等期刊发表论文. 曾获中国科学院院长优秀奖、唐孝炎环境科学创新奖一等奖及中国化学会菁青化学星火奖等奖励, 入选2020年德国林岛诺贝尔奖获得者大会中国代表团. |
 |
刘倩, 2009年于湖南大学获得理学博士学位, 现任中国科学院生态环境研究中心研究员、环境化学与生态毒理学国家重点实验室副主任. 主要研究方向为环境分析化学、环境污染与健康. 目前已在Nat. Nanotechnol.、Nat. Commun.、Environ. Sci. Technol.等期刊发表SCI收录论文120余篇. 主持国家杰出青年基金、重大研究计划集成项目及基金委原创探索计划项目等, 基金委基础科学中心骨干成员. 获第二届科学探索奖、中科院青年科学家奖、国家自然科学二等奖(排名第3)、CAIA奖特等奖(排名第1)、MIT TR35 China和中国化学会青年化学奖等奖励. 2015~2017年任中国科学院青促会理事长. |
基金资助:
Xuezhi Yanga, Dawei Lub, Weichao Wangb,c, Hang Yangb,c, Qian Liub,c( ), Guibin Jianga,b,c
), Guibin Jianga,b,c
Received:2021-12-31
Published:2022-05-31
Contact:
Qian Liu
About author:Supported by:Share
Xuezhi Yang, Dawei Lu, Weichao Wang, Hang Yang, Qian Liu, Guibin Jiang. Nano-Tracing: Recent Progress in Sourcing Tracing Technology of Nanoparticles※[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(5): 652-658.
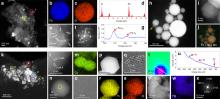

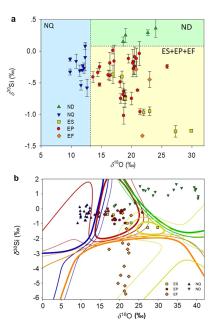



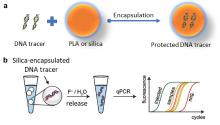

| [1] |
Hochella, M. F., Jr.; Mogk, D. W.; Ranville, J.; Allen, I. C.; Luther, G. W.; Marr, L. C.; McGrail, B. P.; Murayama, M.; Qafoku, N. P.; Rosso, K. M.; Sahai, N.; Schroeder, P. A.; Vikesland, P.; Westerhoff, P.; Yang, Y. Science 2019, 363, 1414.
doi: 10.1126/science.aau8299 |
| [2] |
Huang, X.; Liu, H. H.; Lu, D. W.; Lin, Y.; Liu, J. F.; Liu, Q.; Nie, Z. X.; Jiang, G. B. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 5243.
doi: 10.1039/d0cs00714e pmid: 33656017 |
| [3] |
Gilbertson, L. M.; Pourzahedi, L.; Laughton, S.; Gao, X. Y.; Zimmerman, J. B.; Theis, T. L.; Westerhoff, P.; Lowry, G. V. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2020, 15, 801.
doi: 10.1038/s41565-020-0706-5 pmid: 32572231 |
| [4] |
Mitrano, D. M.; Wick, P.; Nowack, B. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2021, 16, 491.
doi: 10.1038/s41565-021-00888-2 |
| [5] |
Winiger, P.; Barrett, T. E.; Sheesley, R. J.; Huang, L.; Sharma, S.; Barrie, L. A.; Yttri, K. E.; Evangeliou, N.; Eckhardt, S.; Stohl, A.; Klimont, Z.; Heyes, C.; Semiletov, I. P.; Dudarev, O. V.; Charkin, A.; Shakhova, N.; Holmstrand, H.; Andersson, A.; Gustafsson, O. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaau8052.
|
| [6] |
Kah, M.; Johnston, L. J.; Kookana, R. S.; Bruce, W.; Haase, A.; Ritz, V.; Dinglasan, J.; Doak, S.; Garelick, H.; Gubala, V. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2021, 16, 955.
doi: 10.1038/s41565-021-00964-7 |
| [7] |
Svendsen, C.; Walker, L. A.; Matzke, M.; Lahive, E.; Harrison, S.; Crossley, A.; Park, B.; Lofts, S.; Lynch, I.; Vazquez-Campos, S.; Kaegi, R.; Gogos, A.; Asbach, C.; Cornelis, G.; von der Kammer, F.; van den Brink, N. W.; Mays, C.; Spurgeon, D. J. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2020, 15, 731.
doi: 10.1038/s41565-020-0742-1 pmid: 32807878 |
| [8] |
Tsang, M. P.; Kikuchi-Uehara, E.; Sonnemann, G. W.; Aymonier, C.; Hirao, M. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2017, 12, 734.
doi: 10.1038/nnano.2017.132 |
| [9] |
Colvin, V. L. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 1166.
pmid: 14520401 |
| [10] |
Laborda, F.; Bolea, E.; Cepria, G.; Gomez, M. T.; Jimenez, M. S.; Perez-Arantegui, J.; Castillo, J. R. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 904, 10.
doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2015.11.008 |
| [11] |
Montano, M. D.; Lowry, G. V.; von der Kammer, F.; Blue, J.; Ranville, J. F. Environ. Chem. 2014, 11, 351.
doi: 10.1071/EN14037 |
| [12] |
Lu, D. W.; Luo, Q.; Chen, R.; Zhuan Sun, Y. X.; Jiang, J.; Wang, W. C.; Yang, X. Z.; Zhang, L. Y.; Liu, X. L.; Li, F.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, G. B. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2567.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16427-x |
| [13] |
Zhang, Q. H.; Lu, D. W.; Wang, D. Y.; Yang, X. Z.; Zuo, P. J.; Yang, H.; Fu, Q.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, G. B. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 9274.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.0c01841 |
| [14] |
Yang, Y.; Chen, B.; Hower, J.; Schindler, M.; Winkler, C.; Brandt, J.; Di Giulio, R.; Ge, J. P.; Liu, M.; Fu, Y. H.; Zhang, L. J.; Chen, Y. R.; Priya, S.; Hochella, M. F., J. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 194.
|
| [15] |
Yang, Y.; Colman, B. P.; Bernhardt, E. S.; Hochella, M. F. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 3375.
doi: 10.1021/es505662q pmid: 25688977 |
| [16] |
Lee, S. Y.; Bi, X. Y.; Reed, R. B.; Ranville, J. F.; Herckes, P.; Westerhoff, P. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 10291.
doi: 10.1021/es502422v |
| [17] |
Gundlach-Graham, A.; Hendriks, L.; Mehrabi, K.; Guenther, D. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 11847.
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.8b01551 pmid: 30240561 |
| [18] |
Abdolahpur Monikh, F.; Chupani, L.; Vijver, M. G.; Vancová, M.; Peijnenburg, W. J. G. M. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 1283.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.01.105 |
| [19] |
Praetorius, A.; Gundlach-Graham, A.; Goldberg, E.; Fabienke, W.; Navratilova, J.; Gondikas, A.; Kaegi, R.; Gunther, D.; Hofmann, T.; von der Kammer, F. Environ. Sci. Nano 2017, 4, 307.
doi: 10.1039/C6EN00455E |
| [20] |
Gondikas, A.; von der Kammer, F.; Kaegi, R.; Borovinskaya, O.; Neubauer, E.; Navratilova, J.; Praetorius, A.; Cornelis, G.; Hofmann, T. Environ. Sci. Nano 2018, 5, 313.
doi: 10.1039/C7EN00952F |
| [21] |
Lin, Y.; Huang, X.; Liu, Y. C.; Cao, D.; Lu, D. W.; Feng, Z. M.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Z. Y.; Jiang, G. B. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 6665.
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.0c05180 |
| [22] |
Deng, L. L.; Zhang, K. S.; Yin, Z. Y.; Li, X. Y.; Wu, W. Q.; Xiang, X. P. Environ. Sci. 2020, 41, 5276. (in Chinese)
|
|
(邓林俐, 张凯山, 殷子渊, 李欣悦, 武文琪, 向锌鹏, 环境科学, 2020, 41, 5276.)
|
|
| [23] |
Wang, Z. Y.; Li, Y. B.; Guo, L.; Song, Z. Q.; Xu, Y. L.; Wang, F.; Liang, W. Q.; Shi, G. L.; Feng, Y. C. Environ. Sci. 2022, 43, 608. (in Chinese)
|
|
(王振宇, 李永斌, 郭凌, 宋志强, 许艳玲, 王丰, 梁维青, 史国良, 冯银厂, 环境科学, 2022, 43, 608.)
|
|
| [24] |
Qi, W. H.; Dao, X.; Lv, Y. B.; Wang, C. Environ. Chem. 2016, 35, 2521. (in Chinese)
|
|
(齐炜红, 刀谞, 吕怡兵, 王超, 环境化学, 2016, 35, 2521.)
|
|
| [25] |
He, L. Y.; Hu, M.; Huang, X. F.; Zhang, Y. H. Acta Sci. Circum. 2005, 25, 23. (in Chinese)
|
|
(何凌燕, 胡敏, 黄晓峰, 张远航, 环境科学学报, 2005, 25, 23.)
|
|
| [26] |
Walder, A. J.; Platzner, I.; Freedman, P. A. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 1993, 8, 19.
doi: 10.1039/JA9930800019 |
| [27] |
Wiederhold, J. G. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 2606.
doi: 10.1021/es504683e pmid: 25640608 |
| [28] |
Lu, D. W.; Zhang, T. Y.; Yang, X. Z.; Su, P.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, G. B. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2017, 32, 1848.
doi: 10.1039/C7JA00260B |
| [29] |
Basile Doelsch, I.; Meunier, J. D.; Parron, C. Nature 2005, 433, 399.
doi: 10.1038/nature03217 |
| [30] |
Zuo, P. J.; Zong, Z.; Zheng, B.; Bi, J. Z.; Zhang, Q. H.; Li, W.; Zhang, J.; Yang, X. Z.; Chen, Z. G.; Yang, H.; Lu, D. W.; Zhang, Q. H.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, G. B. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 155.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.1c05383 |
| [31] |
Yang, X. Z.; Lu, D. W.; Tan, J. H.; Sun, X.; Zhang, Q. H.; Zhang, L. Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, W. C.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, G. B. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 7126.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.0c00984 |
| [32] |
Su, P.; Lu, D. W.; Yang, X. Z.; Wang, W. C.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, G. B. Sci. China: Chem. 2018, 48, 1163. (in Chinese)
|
|
(苏鹏, 陆达伟, 杨学志, 王伟超, 刘倩, 江桂斌, 中国科学: 化学, 2018, 48, 1163.)
|
|
| [33] |
Lu, D. W.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, T. Y.; Cai, Y.; Yin, Y. G.; Jiang, G. B. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2016, 11, 682.
doi: 10.1038/nnano.2016.93 |
| [34] |
Zhang, T. Y.; Lu, D. W.; Zeng, L. X.; Yin, Y. G.; He, Y. J.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, G. B. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 14164.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.7b04115 |
| [35] |
Yang, X. Z.; Liu, X.; Zhang, A. Q.; Lu, D. W.; Li, G.; Zhang, Q. H.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, G. B. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1620.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09629-5 |
| [36] |
Gibson, N.; Holzwarth, U.; Abbas, K.; Simonelli, F.; Kozempel, J.; Cydzik, I.; Cotogno, G.; Bulgheroni, A.; Gilliland, D.; Ponti, J.; Franchini, F.; Marmorato, P.; Stamm, H.; Kreyling, W.; Wenk, A.; Semmler-Behnke, M.; Buono, S.; Maciocco, L.; Burgio, N. Arch. Toxicol. 2011, 85, 751.
doi: 10.1007/s00204-011-0701-6 pmid: 21479952 |
| [37] |
Deline, A. R.; Nason, J. A. Environ. Sci. Nano 2019, 6, 1043.
doi: 10.1039/C8EN01187G |
| [38] |
Zhang, P.; Misra, S.; Guo, Z. L.; Rehkamper, M.; Valsami-Jones, E. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 2878.
doi: 10.1038/s41596-019-0205-z pmid: 31515516 |
| [39] |
Yin, Y. G.; Tan, Z. Q.; Hu, L. G.; Yu, S. J.; Liu, J. F.; Jiang, G. B. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 4462.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00693 |
| [40] |
Yu, S. J.; Lai, Y. J.; Dong, L. J.; Liu, J. F. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 10218.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.9b03251 |
| [41] |
Shao, Z. S.; Guagliardo, P.; Jiang, H. B.; Wang, W. X. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 433.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.0c04621 |
| [42] |
Yang, Q. Q.; Shan, W. Y.; Hu, L. G.; Zhao, Y.; Hou, Y. Z.; Yin, Y. G.; Liang, Y.; Wang, F. Y.; Cai, Y.; Liu, J. F.; Pang, G. B. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 625.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.8b02471 |
| [43] |
Nath, J.; Dror, I.; Landa, P.; Vanek, T.; Kaplan Ashiri, I.; Berkowitz, B. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 1827.
doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.07.084 |
| [44] |
Lammel, T.; Thit, A.; Cui, X. J.; Mouneyrac, C.; Baun, A.; Valsami Jones, E.; Sturve, J.; Selck, H. Environ. Sci. Nano 2020, 7, 2360.
doi: 10.1039/D0EN00227E |
| [45] |
Mahler, B. J.; Winkler, M.; Bennett, P.; Hillis, D. M. Geology 1998, 26, 831.
doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1998)026【-逻*辑*与-】#x00026;lt;0831:DLCASN【-逻*辑*与-】#x00026;gt;2.3.CO;2 |
| [46] |
Liao, R. K.; Zhao, F.; Hamada, S.; Yang, P. L.; Xu, H.; Luo, D.; Yang, D. Y. Nano Today 2020, 35, 100958.
doi: 10.1016/j.nantod.2020.100958 |
| [47] |
Liao, R. K.; Yang, P. L.; Wu, W. Y.; Luo, D.; Yang, D. Y. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 1695.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.7b02928 |
| [48] |
Mikutis, G.; Deuber, C. A.; Schmid, L.; Kittila, A.; Lobsiger, N.; Puddu, M.; Asgeirsson, D. O.; Grass, R. N.; Saar, M. O.; Stark, W. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 12142.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.8b03285 |
| [49] |
Grass, R. N.; Schälchli, J.; Paunescu, D.; Soellner, J. O. B.; Kaegi, R.; Stark, W. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2014, 1, 484.
doi: 10.1021/ez5003506 |
| [50] |
Mitrano, D. M.; Beltzung, A.; Frehland, S.; Schmiedgruber, M.; Cingolani, A.; Schmidt, F. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2019, 14, 362.
doi: 10.1038/s41565-018-0360-3 pmid: 30718833 |
| [1] | Cheng Yiyu;Chen Minjun;Wu Yongjiang. Measures for Determining the Similarity of Chemical Fingerprint and a Method of Evaluating the Measures [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2002, 60(11): 2017-2021. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||