Acta Chimica Sinica ›› 2023, Vol. 81 ›› Issue (2): 131-145.DOI: 10.6023/A22110462 Previous Articles Next Articles
Review
查汉a,b, 房进b, 闫翎鹏a,c,*( ), 杨永珍c,d,*(
), 杨永珍c,d,*( ), 马昌期b,*(
), 马昌期b,*( )
)
投稿日期:2022-11-14
发布日期:2022-12-23
通讯作者:
闫翎鹏, 杨永珍, 马昌期
作者简介: |
查汉, 太原理工大学材料科学与工程学院2020级硕士研究生, 现于中科院苏州纳米技术与仿生研究所联合培养, 研究方向为有机太阳能电池的衰减机理和稳定性提升. |
 |
闫翎鹏, 太原理工大学副研究员, 工学博士, 硕士研究生导师, 研究方向包括: 有机太阳能电池的衰减机理及其稳定性提升研究, 碳纳米材料制备、功能化及其光电应用. |
 |
杨永珍, 太原理工大学教授, 工学博士, 博士研究生导师, 主要从事纳米碳功能材料、碳基光电材料和生物医药材料的研究. 马昌期, 中国科学院苏州纳米技术与纳米仿生研究所研究员, 中国科学院百人计划研究员, 博士生导师, 主要研究方向包括: 有机光电功能半导体材料与器件, 特别是可印刷光电半导体材料以及印刷制备纳米薄膜光电器件工艺与性能研究. |
 |
马昌期, 中国科学院苏州纳米技术与纳米仿生研究所研究员, 中国科学院百人计划研究员, 博士生导师, 主要研究方向包括: 有机光电功能半导体材料与器件, 特别是可印刷光电半导体材料以及印刷制备纳米薄膜光电器件工艺与性能研究. |
基金资助:
Han Zhaa,b, Jin Fangb, Lingpeng Yana,c( ), Yongzhen Yangc,d(
), Yongzhen Yangc,d( ), Changqi Mab(
), Changqi Mab( )
)
Received:2022-11-14
Published:2022-12-23
Contact:
Lingpeng Yan, Yongzhen Yang, Changqi Ma
Supported by:Share
Han Zha, Jin Fang, Lingpeng Yan, Yongzhen Yang, Changqi Ma. Research Progress of Thermal Failure Mechanism and Ternary Blending to Improve Thermal Stability of Organic Solar Cells[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(2): 131-145.
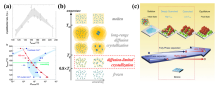

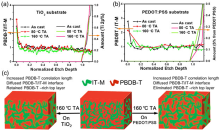

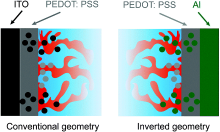

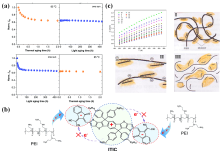

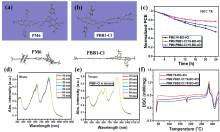





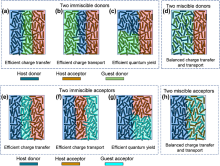

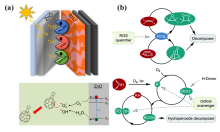

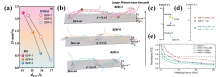
| [1] |
Li, S. X.; Li, C. Z.; Shi, M. M.; Chen, H. Z. ACS Energy Lett. 2020, 5, 1554.
doi: 10.1021/acsenergylett.0c00537 |
| [2] |
Xu, Y.; Cui, Y.; Yao, H. F.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, J. Q.; Ma, L. J.; Wang, J. W.; Wei, Z. X.; Hou, J. H. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2101090.
doi: 10.1002/adma.202101090 |
| [3] |
Wang, J. Y.; Zhan, X. W. Chin. J. Chem. 2022, 40, 1592.
doi: 10.1002/cjoc.202200027 |
| [4] |
Zhu, L.; Zhang, M.; Xu, J.; Li, C.; Yan, J.; Zhou, G.; Zhong, W.; Hao, T.; Song, J.; Xue, X.; Zhou, Z.; Zeng, R.; Zhu, H.; Chen, C. C.; MacKenzie, R. C. I.; Zou, Y.; Nelson, J.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, F. Nat. Mater. 2022, 21, 656.
doi: 10.1038/s41563-022-01244-y |
| [5] |
Wang, W. X.; Wang, J. Q.; Zheng, Z.; Hou, J. H. Acta Chim. Sinica. 2020, 78, 382. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A20020032 |
|
(王文璇, 王建邱, 郑众, 侯剑辉, 化学学报, 2020, 78, 382.)
doi: 10.6023/A20020032 |
|
| [6] |
Burlingame, Q.; Ball, M.; Loo, Y. L. Nat. Energy. 2020, 5, 947.
doi: 10.1038/s41560-020-00732-2 |
| [7] |
Liu, Y. F.; Li, S. L.; Jing, Y. N.; Xiao, L. G.; Zhou, H. Q. Acta Chim. Sinica. 2022, 80, 993. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A22020081 |
|
(刘彦甫, 李世麟, 荆亚楠, 肖林格, 周惠琼, 化学学报, 2022, 80, 993.)
doi: 10.6023/A22020081 |
|
| [8] |
Soon, Y. W.; Cho, H.; Low, J.; Bronstein, H.; McCulloch, I.; Durrant, J. R. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 1291.
doi: 10.1039/c2cc38243a |
| [9] |
Wang, C.; Ni, S. F.; Braun, S.; Fahlman, M.; Liu, X. J. J. Mater. Chem. C. 2019, 7, 879.
doi: 10.1039/C8TC05475D |
| [10] |
Balar, N.; Xiong, Y.; Ye, L.; Li, S.; Nevola, D.; Dougherty, D. B.; Hou, J.; Ade, H.; O'Connor, B. T. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2017, 9, 43886.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.7b13719 |
| [11] |
Mateker, W. R.; McGehee, M. D. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1603940.
doi: 10.1002/adma.201603940 |
| [12] |
Lim, F. J.; Krishnamoorthy, A.; Ho, G. W. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2015, 7, 12119.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.5b02383 |
| [13] |
Cho, H. W.; An, N. G.; Park, S. Y.; Shin, Y. S.; Lee, W.; Kim, J. Y.; Song, S. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 1903585.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.201903585 |
| [14] |
Reddy, P. G.; Pal, S. P.; Kumar, P.; Pradeep, C. P.; Ghosh, S.; Sharma, S. K.; Gonsalves, K. E. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2017, 9, 17.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.6b10384 |
| [15] |
Planes, E.; Juillard, S.; Matheron, M.; Charvin, N.; Cros, S.; Qian, D. P.; Zhang, F. L.; Berson, S.; Flandin, L. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 7, 2000293.
|
| [16] |
Ye, L.; Gao, M. Y.; Hou, J. H. Sci. China Chem. 2021, 64, 1875.
doi: 10.1007/s11426-021-1087-8 |
| [17] |
Zhang, Z. J.; Miao, J. H.; Ding, Z. C.; Kan, B.; Lin, B. J.; Wan, X. J.; Ma, W.; Chen, Y. S.; Long, X. J.; Dou, C. D.; Zhang, J. D.; Liu, J.; Wang, L. X. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3271.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-10984-6 |
| [18] |
Wang, Y. L.; Zhu, Q. L.; Naveed, H. B.; Zhao, H.; Zhou, K.; Ma, W. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 1903609.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.201903609 |
| [19] |
Zerio, A. D. d.; Müller, C. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1702741.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.201702741 |
| [20] |
Huang, W. C.; Cheng, P.; Yang, Y.; Li, G.; Yang, Y. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1705706.
doi: 10.1002/adma.201705706 |
| [21] |
Ni, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Feng, Z.; Tu, D.; Guo, X.; Li, C. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2022, 14, 12461.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.1c23513 |
| [22] |
Luo, D.; Jiang, Z. Y.; Yang, W. L.; Guo, X. G.; Li, X. H.; Zhou, E. J.; Li, G. Q.; Li, L. Q.; Duan, C. H.; Shan, C. W.; Wang, Z. J.; Li, Y. H.; Xu, B. M.; Kyaw, A.K.K. Nano Energy. 2022, 98, 107186.
doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2022.107186 |
| [23] |
Duan, X. P.; Song, W.; Qiao, J. W.; Li, X. M.; Cai, Y. H.; Wu, H. B.; Zhang, J.; Hao, X. T.; Tang, Z.; Ge, Z. Y.; Huang, F.; Sun, Y. M. Energy Environ. Sci. 2022, 15, 1563.
doi: 10.1039/D1EE03989J |
| [24] |
Ma, R. J.; Yan, C. Q.; Fong, P. W. K.; Yu, J. S.; Liu, H.; Yin, J. L.; Huang, J. H.; Lu, X. H.; Yan, H.; Li, G. Energy Environ. Sci. 2022, 15, 2479.
doi: 10.1039/D2EE00740A |
| [25] |
Xu, X.; Li, Y.; Peng, Q. Adv. Mater. 2021, 2107476.
|
| [26] |
An, Q. S.; Zhang, F. J.; Zhang, J.; Tang, W. H.; Deng, Z. B.; Hu, B. Energy Environ. Sci. 2016, 9, 281.
doi: 10.1039/C5EE02641E |
| [27] |
Yang, L. Q.; Yan, L.; You, W. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2013, 4, 1802.
doi: 10.1021/jz400723u |
| [28] |
Xu, W. D.; Gao, F. Mater. Horiz. 2018, 5, 206.
doi: 10.1039/C7MH00958E |
| [29] |
Yan, T. T.; Song, W.; Huang, J. M.; Peng, R. X.; Huang, L. K.; Ge, Z. Y. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1902210.
doi: 10.1002/adma.201902210 |
| [30] |
An, Q. S.; Zhang, F. J.; Gao, W.; Sun, Q. Q.; Zhang, M.; Yang, C. L.; Zhang, J. Nano Energy. 2018, 45, 177.
doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2017.12.050 |
| [31] |
Zhang, M.; Zhang, F. J.; An, Q. S.; Sun, Q. Q.; Wang, W. B.; Zhang, J.; Tang, W. H. Nano Energy. 2016, 22, 241.
doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2016.02.032 |
| [32] |
Song, J. L.; Li, C.; Zhu, L.; Guo, J.; Xu, J. Q.; Zhang, X. N.; Weng, K. K.; Zhang, K. N.; Min, J.; Hao, X. T.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, F.; Sun, Y. M. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1905645.
doi: 10.1002/adma.201905645 |
| [33] |
Yang, W.; Luo, Z.; Sun, R.; Guo, J.; Wang, T.; Wu, Y.; Wang, W.; Guo, J.; Wu, Q.; Shi, M.; Li, H.; Yang, C.; Min, J. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1218.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-14926-5 |
| [34] |
Zhu, Q.; Xue, J.; Zhang, L.; Wen, J.; Lin, B.; Naveed, H. B.; Bi, Z.; Xin, J.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, C.; Zhou, K.; Frank Liu, S.; Ma, W. Small. 2021, 17, 2007011.
doi: 10.1002/smll.202007011 |
| [35] |
Günther, M.; Blätte, D.; Oechsle, A. L.; Rivas, S. S.; Yousefi Amin, A. A.; Müller-Buschbaum, P.; Bein, T.; Ameri, T. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2021, 13, 19072.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.1c00700 |
| [36] |
Zhang, C. J.; Yuan, J.; Ho, J. K. W.; Song, J. G.; Zhong, H.; Xiao, Y. Q.; Liu, W.; Lu, X. H.; Zou, Y. P.; So, S.K. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2101627.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.202101627 |
| [37] |
Reddy, P. G.; Pal, S. P.; Kumar, P.; Pradeep, C. P.; Ghosh, S.; Sharma, S. K.; Gonsalves, K. E. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2017, 9, 17.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.6b10384 |
| [38] |
Dou, L. T.; Chen, C. C.; Yoshimura, K.; Ohya, K.; Chang, W. H.; Gao, J.; Liu, Y. S.; Richard, E.; Yang, Y. Macromolecules. 2013, 46, 3384.
doi: 10.1021/ma400452j |
| [39] |
Zhan, X.; Tan, Z.; Domercq, B.; An, Z.; Zhang, X.; Barlow, S.; Li, Y.; Zhu, D.; Kippelen, B.; Marder, S. R. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 7246.
doi: 10.1021/ja071760d |
| [40] |
Hu, L.; Liu, Y.; Mao, L.; Xiong, S. X.; Sun, L. L.; Zhao, N.; Qin, F.; Jiang, Y. Y.; Zhou, Y. H. J. Mater. Chem. A. 2018, 6, 2273.
doi: 10.1039/C7TA10306A |
| [41] |
Rosch, R.; Tanenbaum, D. M.; Jorgensen, M.; Seeland, M.; Barenklau, M.; Hermenau, M.; Voroshazi, E.; Lloyd, M. T.; Galagan, Y.; Zimmermann, B.; Wurfel, U.; Hosel, M.; Dam, H. F.; Gevorgyan, S. A.; Kudret, S.; Maes, W.; Lutsen, L.; Vanderzande, D.; Andriessen, R.; Teran-Escobar, G.; Lira-Cantu, M.; Rivaton, A.; Uzunoglu, G. Y.; Germack, D.; Andreasen, B.; Madsen, M. V.; Norrman, K.; Hoppe, H.; Krebs, F. C. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 6521.
doi: 10.1039/c2ee03508a |
| [42] |
Esselink, F. J.; Hadziioannou, G. Synthetic Met. 1995, 75, 209.
doi: 10.1016/0379-6779(96)80010-5 |
| [43] |
Zhao, W.; Qian, D.; Zhang, S.; Li, S.; Inganas, O.; Gao, F.; Hou, J. H. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 4734.
doi: 10.1002/adma.201600281 |
| [44] |
Zhu, L.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, G. Q.; Hao, T. Y.; Xu, J. Q.; Wang, J.; Qiu, C. Q.; Prine, N.; Ali, J.; Feng, W.; Gu, X. D.; Ma, Z. F.; Tang, Z.; Zhu, H. M.; Ying, L.; Zhang, Y. M.; Liu, F. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 1904234.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.201904234 |
| [45] |
Ghasemi, M.; Hu, H. W.; Peng, Z. X.; Rech, J. J.; Angunawela, I.; Carpenter, J. H.; Stuard, S. J.; Wadsworth, A.; McCulloch, I.; You, W.; Ade, H. Joule. 2019, 3, 1328.
doi: 10.1016/j.joule.2019.03.020 |
| [46] |
Gao, M.; Liang, Z.; Geng, Y.; Ye, L. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 12463.
doi: 10.1039/D0CC04869K |
| [47] |
Liang, Z. Q.; Li, M. M.; Wang, Q.; Qin, Y. P.; Stuard, S. J.; Peng, Z. X.; Deng, Y. F.; Ade, H.; Ye, L.; Geng, Y. H. Joule. 2020, 4, 1278.
doi: 10.1016/j.joule.2020.04.014 |
| [48] |
Nguyen, T. L.; Lee, T. H.; Gautam, B.; Park, S. Y.; Gundogdu, K.; Kim, J. Y.; Woo, H. Y. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1702474.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.201702474 |
| [49] |
Lindqvist, C.; Sanz-Velasco, A.; Wang, E. G.; Backe, O.; Gustafsson, S.; Olsson, E.; Andersson, M. R.; Müller, C. J. Mater. Chem. A. 2013, 1, 7174.
doi: 10.1039/c3ta11018d |
| [50] |
Yu, L.; Qian, D.; Marina, S.; Nugroho, F. A. A.; Sharma, A.; Hultmark, S.; Hofmann, A. I.; Kroon, R.; Benduhn, J.; Smilgies, D. M.; Vandewal, K.; Andersson, M. R.; Langhammer, C.; Martin, J.; Gao, F.; Müller, C. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2019, 11, 21766.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.9b04554 |
| [51] |
Xin, J. M.; Meng, X. Y.; Xu, X. B.; Zhu, Q. L.; Naveed, H. B.; Ma, W. Matter. 2019, 1, 1316.
doi: 10.1016/j.matt.2019.06.011 |
| [52] |
Han, D.; Lim, C.; Phan, T. N. L.; Kim, Y.; Kim, B. J. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2022, 43, e2200530.
|
| [53] |
Leman, D.; Kelly, M. A.; Ness, S.; Engmann, S.; Herzing, A.; Snyder, C.; Ro, H. W.; Kline, R. J.; DeLongchamp, D. M.; Richter, L. J. Macromolecules. 2015, 48, 383.
doi: 10.1021/ma5021227 |
| [54] |
Stoltzfus, D. M.; Clulow, A. J.; Jin, H.; Burn, P. L.; Gentle, I. R. Macromolecules. 2016, 49, 4404.
doi: 10.1021/acs.macromol.6b00984 |
| [55] |
Cao, Z. X.; Chen, J. L.; Liu, S. J.; Qin, M. C.; Jia, T.; Zhao, J. J.; Li, Q. D.; Ying, L.; Cai, Y. P.; Lu, X. H.; Huang, F.; Gao, Y. Chem. Mater. 2019, 31, 8533.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.9b03570 |
| [56] |
Cheng, P.; Yan, C. Q.; Wu, Y.; Wang, J. Y.; Qin, M.; An, Q. S.; Cao, J. M.; Huo, L. J.; Zhang, F. J.; Ding, L. M.; Sun, Y. M.; Ma, W.; Zhan, X. W. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 8021.
doi: 10.1002/adma.201602067 |
| [57] |
Heiber, M. C.; Baumbach, C.; Dyakonov, V.; Deibel, C. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 114, 136602.
doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.114.136602 |
| [58] |
Tessarolo, M.; Guerrero, A.; Gedefaw, D.; Bolognesi, M.; Prosa, M.; Xu, X. F.; Mansour, M.; Wang, E. G.; Seri, M.; Andersson, M. R.; Muccini, M.; Garcia-Belmonte, G. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells. 2015, 141, 240.
doi: 10.1016/j.solmat.2015.05.041 |
| [59] |
Li, N.; Perea, J. D.; Kassar, T.; Richter, M.; Heumueller, T.; Matt, G. J.; Hou, Y.; Guldal, N. S.; Chen, H.; Chen, S.; Langner, S.; Berlinghof, M.; Unruh, T.; Brabec, C. J. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14541.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms14541 |
| [60] |
Ghasemi, M.; Balar, N.; Peng, Z.; Hu, H.; Qin, Y.; Kim, T.; Rech, J. J.; Bidwell, M.; Mask, W.; McCulloch, I.; You, W.; Amassian, A.; Risko, C.; O'Connor, B. T.; Ade, H. Nat. Mater. 2021, 20, 525.
doi: 10.1038/s41563-020-00872-6 pmid: 33432145 |
| [61] |
Qin, Y. P.; Balar, N.; Peng, Z.; Gadisa, A.; Angunawela, I.; Bagui, A.; Kashani, S.; Hou, J. H.; Ade, H. Joule. 2021, 5, 2129.
doi: 10.1016/j.joule.2021.06.006 |
| [62] |
Germack, D. S.; Chan, C. K.; Kline, R. J.; Fischer, D. A.; Gundlach, D. J.; Toney, M. F.; Richter, L. J.; DeLongchamp, D. M. Macromolecules. 2010, 43, 3828.
doi: 10.1021/ma100027b |
| [63] |
Yan, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, T. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1601674.
doi: 10.1002/adma.201601674 |
| [64] |
Huang, L. Q.; Wang, G.; Zhou, W. H.; Fu, B. Y.; Cheng, X. F.; Zhang, L. F.; Yuan, Z. B.; Xiong, S. X.; Zhang, L.; Xie, Y. P.; Zhang, A. D.; Zhang, Y. D.; Ma, W.; Li, W. W.; Zhou, Y. H.; Reichmanis, E.; Chen, Y. W. ACS Nano. 2018, 12, 4440.
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.8b00439 |
| [65] |
Li, W.; Cai, J. L.; Yan, Y.; Cai, F. L.; Li, S. S.; Gurney, R. S.; Liu, D.; McGettrick, J. D.; Watson, T. M.; Li, Z.; Pearson, A. J.; Lidzey, D. G.; Hou, J. H.; Wang, T. Sol. RRL. 2018, 2, 1800114.
doi: 10.1002/solr.201800114 |
| [66] |
Sun, R.; Guo, J.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, Z. H.; Yang, W. Y.; Guo, J.; Shi, M. M.; Zhang, Y. H.; Kahmann, S.; Ye, L.; Jiao, X. C.; Loi, M. A.; Shen, Q.; Ade, H.; Tang, W. H.; Brabec, C. J.; Min, J. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 3118.
doi: 10.1039/C9EE02295C |
| [67] |
Voroshazi, E.; Uytterhoeven, G.; Cnops, K.; Conard, T.; Favia, P.; Bender, H.; Müller, R.; Cheyns, D. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2015, 7, 618.
doi: 10.1021/am506771e |
| [68] |
Suh, Y. J.; Park, S. Y.; Lee, T. H.; Chung, W. S.; Kim, K. K.; Kim, M. J. Microsc. Microanal. 2010, 16, 1378.
doi: 10.1017/S1431927610062057 |
| [69] |
Cheng, P.; Zhan, X. W. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 2544.
doi: 10.1039/c5cs00593k pmid: 26890341 |
| [70] |
Franke, R.; Maennig, B.; Petrich, A.; Pfeiffer, M. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells. 2008, 92, 732.
doi: 10.1016/j.solmat.2007.12.001 |
| [71] |
Wimmer, E.; Wolf, W.; Sticht, J.; Saxe, P.; Geller, C. B.; Najafabadi, R.; Young, G. A. Phys. Rev. B. 2008, 77, 134305.
doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.77.134305 |
| [72] |
Zhang, K.; Xia, R.; Fan, B.; Liu, X.; Wang, Z.; Dong, S.; Yip, H. L.; Ying, L.; Huang, F.; Cao, Y. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1803166.
doi: 10.1002/adma.201803166 |
| [73] |
Greenbank, W.; Hirsch, L.; Wantz, G.; Chambon, S. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 107, 263301.
doi: 10.1063/1.4938554 |
| [74] |
Greenbank, W.; Rolston, N.; Destouesse, E.; Wantz, G.; Hirsch, L.; Dauskardt, R.; Chambon, S. J. Mater. Chem. A. 2017, 5, 2911.
doi: 10.1039/C6TA09665D |
| [75] |
Yin, Y. T.; Pan, X.; Andersson, M. R.; Lewis, D. A.; Andersson, G. G. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2020, 3, 366.
doi: 10.1021/acsaem.9b01635 |
| [76] |
Zufle, S.; Neukom, M. T.; Altazin, S.; Zinggeler, M.; Chrapa, M.; Offermans, T.; Ruhstaller, B. Adv. Energy Mater. 2015, 5, 1500835.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.201500835 |
| [77] |
Bregnhoj, M.; Prete, M.; Turkovic, V.; Petersen, A. U.; Nielsen, M. B.; Madsen, M.; Ogilby, P. R. Methods Appl. Fluores. 2019, 8, 014001.
doi: 10.1088/2050-6120/ab4edc |
| [78] |
Lee, H. K. H.; Telford, A. M.; Rohr, J. A.; Wyatt, M. F.; Rice, B.; Wu, J. Y.; Maciel, A. D.; Tuladhar, S. M.; Speller, E.; McGettrick, J.; Searle, J. R.; Pont, S.; Watson, T.; Kirchartz, T.; Durrant, J. R.; Tsoi, W. C.; Nelson, J.; Li, Z. Energy Environ. Sci. 2018, 11, 417.
doi: 10.1039/C7EE02983G |
| [79] |
Hoke, E. T.; Sachs-Quintana, I. T.; Lloyd, M. T.; Kauvar, I.; Mateker, W. R.; Nardes, A. M.; Peters, C. H.; Kopidakis, N.; McGehee, M. D. Adv. Energy Mater. 2012, 2, 1351.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.201200169 |
| [80] |
Park, S.; Son, H. J. J. Mater. Chem. A. 2019, 7, 25830.
doi: 10.1039/C9TA07417A |
| [81] |
Jiang, Y. Y.; Sun, L. L.; Jiang, F. Y.; Xie, C.; Hu, L.; Dong, X. Y.; Qin, F.; Liu, T. F.; Hu, L.; Jiang, X. S.; Zhou, Y. H. Mater. Horiz. 2019, 6, 1438.
doi: 10.1039/C9MH00379G |
| [82] |
Zhang, C. H.; Heumueller, T.; Leon, S.; Gruber, W.; Burlafinger, K.; Tang, X. F.; Perea, J. D.; Wabra, I.; Hirsch, A.; Unruh, T.; Li, N.; Brabec, C.J. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 1078.
doi: 10.1039/C8EE03780A |
| [83] |
Dupont, S. R.; Novoa, F.; Voroshazi, E.; Dauskardt, R. H. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 1325.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.201302174 |
| [84] |
Balcaen, V.; Rolston, N.; Dupont, S. R.; Voroshazi, E.; Dauskardt, R. H. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells. 2015, 143, 418.
doi: 10.1016/j.solmat.2015.07.019 |
| [85] |
Vitoratos, E.; Sakkopoulos, S.; Dalas, E.; Paliatsas, N.; Karageorgopoulos, D.; Petraki, F.; Kennou, S.; Choulis, S.A. Org. Electron. 2009, 10, 61.
doi: 10.1016/j.orgel.2008.10.008 |
| [86] |
Hu, H. X.; Mu, X. Y.; Qin, W.; Gao, K.; Hao, X. T.; Yin, H. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2022, 120, 023302.
doi: 10.1063/5.0077882 |
| [87] |
Doumon, N. Y.; Yang, L. L.; Rosei, F. Nano Energy. 2022, 94, 106915.
doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2021.106915 |
| [88] |
Zhang, H.; Wang, H. E.; Zhu, T.; Liu, Z. Y.; Chen, L. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2022, 5, 5026.
doi: 10.1021/acsaem.2c00393 |
| [89] |
Wang, J. X.; Han, C. Y.; Bi, F. Z.; Huang, D.; Wu, Y. W.; Li, Y. H.; Wen, S. G.; Han, L. L.; Yang, C. M.; Bao, X. C.; Chu, J. H. Energy Environ. Sci. 2021, 14, 5968.
doi: 10.1039/D1EE02320A |
| [90] |
Gao, X.; Wang, H.; Li, Z.; Tao, X.; Qin, X.; Yang, T.; Song, X.; Bu, L.; Lu, G.; Tao, Y. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 450, 138018.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.138018 |
| [91] |
Cheng, P.; Yan, C.; Lau, T. K.; Mai, J.; Lu, X.; Zhan, X. W. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 5822.
doi: 10.1002/adma.201600426 |
| [92] |
Zhu, Y. Q.; Gadisa, A.; Peng, Z. X.; Ghasemi, M.; Ye, L.; Xu, Z.; Zhao, S. L.; Ade, H. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1900376.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.201900376 |
| [93] |
Gao, Y. X.; Zhang, C. J.; So, S. K. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2022, 120, 143301.
doi: 10.1063/5.0080456 |
| [94] |
Speller, E. M.; Clarke, A. J.; Luke, J.; Lee, H. K. H.; Durrant, J. R.; Li, N.; Wang, T.; Wong, H. C.; Kim, J. S.; Tsoi, W. C.; Li, Z. J. Mater. Chem. A. 2019, 7, 23361.
doi: 10.1039/c9ta05235f |
| [95] |
Min, J.; Cui, C. H.; Heumueller, T.; Fladischer, S.; Cheng, X.; Spiecker, E.; Li, Y. F.; Brabec, C. J. Adv. Energy Mater. 2016, 6, 1600515.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.201600515 |
| [96] |
Gasperini, A.; Jeanbourquin, X. A.; Rahmanudin, A.; Yu, X.; Sivula, K. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 5541.
doi: 10.1002/adma.201501826 |
| [97] |
Yue, Y.; Zheng, B.; Yang, W.; Huo, L.; Wang, J.; Jiang, L. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2108508.
doi: 10.1002/adma.202108508 |
| [98] |
Zhang, W.; Sun, C.; Angunawela, I.; Meng, L.; Qin, S.; Zhou, L.; Li, S.; Zhuo, H.; Yang, G.; Zhang, Z. G.; Ade, H.; Li, Y. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2108749.
doi: 10.1002/adma.202108749 |
| [99] |
Feng, W. H.; Lin, Z. K.; Cui, J. Y.; Lv, W.; Wang, W.; Ling, Q. D. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells. 2019, 200, 109982.
doi: 10.1016/j.solmat.2019.109982 |
| [100] |
Kim, T.; Choi, J.; Kim, H. J.; Lee, W.; Kim, B. J. Macromolecules. 2017, 50, 6861.
doi: 10.1021/acs.macromol.7b00834 |
| [101] |
Yang, T.; Ma, R. J.; Cheng, H.; Xiao, Y. Q.; Luo, Z. H.; Chen, Y. Z.; Luo, S. W.; Liu, T.; Lu, X. H.; Yan, H. J. Mater. Chem. A. 2020, 8, 17706.
doi: 10.1039/D0TA06146H |
| [102] |
Zheng, N. N.; Mahmood, K.; Zhong, W. K.; Liu, F.; Zhu, P.; Wang, Z. F.; Xie, B. M.; Chen, Z. M.; Zhang, K.; Ying, L.; Huang, F.; Cao, Y. Nano Energy. 2019, 58, 724.
doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2019.01.082 |
| [103] |
Chen, C. P.; Tsai, Y. Y.; Chen, Y. C.; Li, Y. H. Sol. Energy. 2018, 176, 170.
doi: 10.1016/j.solener.2018.10.038 |
| [104] |
Hultmark, S.; Paleti, S. H. K.; Harillo, A.; Marina, S.; Nugroho, F. A. A.; Liu, Y. F.; Ericsson, L. K. E.; Li, R. P.; Martn, J.; Bergqvist, J.; Langhammer, C.; Zhang, F. L.; Yu, L. Y.; Campoy-Quiles, M.; Moons, E.; Baran, D.; Müller, C. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2005462.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.202005462 |
| [105] |
Elsayed, M. H.; Jiang, B. H.; Wang, Y. P.; Chang, P. Y.; Chiu, Y. C.; Jeng, R. J.; Chou, H. H.; Chen, C. P. J. Mater. Chem. A. 2021, 9, 9780.
doi: 10.1039/D1TA00796C |
| [106] |
Kong, X.; Lin, H.; Du, X. Y.; Li, L. J.; Li, X. R.; Chen, X. W.; Zheng, C. J.; Wang, D. S.; Tao, S. L. J. Mater. Chem. C. 2018, 6, 9691.
doi: 10.1039/C8TC03004A |
| [107] |
Li, X. R.; Zhou, L.; Lu, X.; Cao, L. Y.; Du, X. Y.; Lin, H.; Zheng, C. J.; Tao, S. L. Mater. Chem. Front. 2021, 5, 3850.
doi: 10.1039/D1QM00197C |
| [108] |
Lu, X.; Cao, L. Y.; Du, X. Y.; Lin, H.; Zheng, C. J.; Chen, Z. H.; Sun, B.; Tao, S. L. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2021, 9, 2100064.
doi: 10.1002/adom.202100064 |
| [109] |
Lee, J.; Kim, J. W.; Park, S. A.; Son, S. Y.; Choi, K.; Lee, W.; Kim, M.; Kim, J. Y.; Park, T. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1901829.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.201901829 |
| [110] |
Hong, L.; Yao, H. F.; Cui, Y.; Yu, R. N.; Lin, Y. W.; Chen, T. W.; Xu, Y.; Qin, J. Z.; Hsu, C. S.; Ge, Z. Y.; Hou, J. H. Small. 2021, 17, 2101133.
doi: 10.1002/smll.202101133 |
| [111] |
Zhao, F. W.; Zhang, H. T.; Zhang, R.; Yuan, J.; He, D.; Zou, Y. P.; Gao, F. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 2002746.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.202002746 |
| [112] |
Tan, C. A. W.; Wong, B. T. Sol. RRL. 2021, 5, 2100503.
doi: 10.1002/solr.202100503 |
| [113] |
Gu, H.; Yan, L.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Luo, Q.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Wei, Z.; Ma, C. Sol. RRL. 2020, 4, 2000374.
doi: 10.1002/solr.202000374 |
| [114] |
Naveed, H. B.; Ma, W. Joule. 2018, 2, 621.
doi: 10.1016/j.joule.2018.02.010 |
| [115] |
Xu, X.; Li, Y.; Peng, Q. Nano Select. 2020, 1, 30.
doi: 10.1002/nano.202000012 |
| [116] |
Hu, H.; Ghasemi, M.; Peng, Z.; Zhang, J.; Rech, J. J.; You, W.; Yan, H.; Ade, H. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2005348.
doi: 10.1002/adma.202005348 |
| [117] |
Jung, S.; Cho, Y.; Kang, S. H.; Yoon, S. J.; Yang, C. Sol. RRL. 2022, 6, 2100819.
doi: 10.1002/solr.202100819 |
| [118] |
Gasparini, N.; Salleo, A.; McCulloch, I.; Baran, D. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2019, 4, 229.
doi: 10.1038/s41578-019-0093-4 |
| [119] |
Dominguez, I. F.; Distler, A.; Luer, L. Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1601320.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.201601320 |
| [120] |
Guo, J.; Wu, Y.; Sun, R.; Wang, W.; Guo, J.; Wu, Q.; Tang, X. F.; Sun, C. K.; Luo, Z. H.; Chang, K.; Zhang, Z. H.; Yuan, J.; Li, T. F.; Tang, W. H.; Zhou, E. J.; Xiao, Z.; Ding, L. M.; Zou, Y. P.; Zhan, X. W.; Yang, C. L.; Li, Z.; Brabec, C. J.; Li, Y. F.; Min, J. J. Mater. Chem. A. 2019, 7, 25088.
doi: 10.1039/C9TA09961A |
| [121] |
Van Erp, R.; Soleimanzadeh, R.; Nela, L.; Kampitsis, G.; Matioli, E. Nature. 2020, 585, 211.
doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2666-1 |
| [122] |
Liu, H. Q.; Wei, Z. B.; He, W. D.; Zhao, J. Y. Energy Convers Manage. 2017, 150, 304.
doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2017.08.016 |
| [123] |
Geng, C.; Chen, X.; Li, S.; Ding, Z.; Ma, W.; Qiu, J.; Wang, Q.; Yan, C.; Fan, H. J. Energy Mater. Adv. 2021, 2021, 262.
|
| [124] |
Yang, N.; Pei, F. T.; Dou, J.; Zhao, Y. Z.; Huang, Z. J.; Ma, Y.; Ma, S.; Wang, C. Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Zhu, C.; Bai, Y.; Zhou, H. P.; Song, T. L.; Chen, Y. H.; Chen, Q. Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 12, 2200869.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.202200869 |
| [125] |
Roesch, R.; Faber, T.; von Hauff, E.; Brown, T. M.; Lira-Cantu, M.; Hoppe, H. Adv. Energy Mater. 2015, 5, 1501407.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.201501407 |
| [126] |
Gevorgyan, S. A.; Heckler, I. M.; Bundgaard, E.; Corazza, M.; Hosel, M.; Sondergaard, R. R.; Benatto, G. A. D.; Jorgensen, M.; Krebs, F. C. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 2017, 50, 103001.
doi: 10.1088/1361-6463/50/10/103001 |
| [127] |
Wang, G. H.; Zhao, Y.; Yuan, Y. L. Aip Adv. 2021, 11, 085011.
doi: 10.1063/5.0060730 |
| [128] |
Datt, R.; Lee, H. K. H.; Zhang, G.; Yip, H. L.; Tsoi, W. C. Chin. J. Chem. 2022, 40, 2927.
doi: 10.1002/cjoc.202200481 |
| [1] | Yige Wang, Hangyue Li, Zewei Lyu, Minfang Han, Kaihua Sun. Study of Operating Conditions for High Efficiency and Anode Safety of Industrial-Size Solid Oxide Fuel Cell [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(8): 1091-1099. |
| [2] | Yuanhao Geng, Xiaoqiu Lin, Yaxin Sun, Huiyu Li, Yue Qin, Congju Li. Preparation of Bimetallic Conductive Metal-organic Framework Material Ni/Co-CAT for Electrocatalytic Oxygen Reduction [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(6): 748-755. |
| [3] | Wenyuan Lin, Qingzhe Zhu, Yunlong Ma, Peng Wang, Shuo Wan, Qingdong Zheng. Rationally Tuning Blend Miscibility of Polymer Donor and Nonfullerene Acceptor for Constructing Efficient Organic Solar Cells※ [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(6): 724-733. |
| [4] | Hongtao Cao, Pengfei Hou, Qing Cao, Yanang Li, Shasha Wang, Linghai Xie. Exciplex Emission and Property Investigation Based on Cyano-substituted 9-Phenylfluorene Derivative [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(11): 1476-1484. |
| [5] | Junhui Miao, Zicheng Ding, Jun Liu, Lixiang Wang. Research Progress in Organic Solar Cells Based on Small Molecule Donors and Polymer Acceptors [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(5): 545-556. |
| [6] | Tengfei Li, Xiaowei Zhan. Advances in Organic Photovoltaics [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(3): 257-283. |
| [7] | Min Lv, Ruimin Zhou, Kun Lu, Zhixiang Wei. Research Progress of Small Molecule Donors with High Crystallinity in All Small Molecule Organic Solar Cells [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(3): 284-302. |
| [8] | Wang Wenxuan, Wang Jianqiu, Zheng Zhong, Hou Jianhui. Research Progress of Tandem Organic Solar Cells [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2020, 78(5): 382-396. |
| [9] | Hu Yuhui, Wu Wenlin, Yu Liyang, Luo Kaijun, Xu Xiaopeng, Li Ying, Peng Qiang. Synthesis and Photovoltaic Properties of Perylene Diimide Based Small Molecular Acceptors with a Diketopyrrolopyrrole Core [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2020, 78(11): 1246-1254. |
| [10] | Chen Xinyu, Xie Junjie, Wang Wei, Yuan Huihui, Xu Di, Zhang Tao, He Yunlong, Shen Hujiang. Research Progress of Compositional Controlling Strategy to Perovskite for High Performance Solar Cells [J]. Acta Chim. Sinica, 2019, 77(1): 9-23. |
| [11] | Pan Bina, Zhu Yi-Zhou, Qiu Changjuana, Wang Binga, Zheng Jian-Yu. Synthesis of Phenothiazine Dyes Featuring Benzothiadiazole Unit for Efficient Dye-sensitized Solar Cells [J]. Acta Chim. Sinica, 2018, 76(3): 215-223. |
| [12] | Ma Mingshuo, Zou Luyi, Li Yan, Ren Aimin, Ding Xiaoli. Theoretical Studies on Photophysical Properties of Isomeric Iridium(Ⅲ) Complexes Ir(ppy)2(acac) Containing Dimesitylboron Moiety [J]. Acta Chim. Sinica, 2016, 74(9): 764-772. |
| [13] | Shao Rong, Yang Xinbo, Yin Shiwei, Wang Wenliang. Molecular Design of Benzothiadiazole Derivatives Electron Acceptors and Matching of Donor-Acceptor Materials [J]. Acta Chim. Sinica, 2016, 74(8): 676-682. |
| [14] | Yan Zhuojun, Yuan Ye, Liu Jia, Li Qin, Nguyen Nam-Trung, Zhang Daming, Tian Yuyang, Zhu Guangshan. Targeted Syntheses of Charged Porous Aromatic Frameworks for Iodine Enrichment and Release [J]. Acta Chim. Sinica, 2016, 74(1): 67-73. |
| [15] | Ma Chunyan, Fu Weifei, Huang Guowei, Chen Hongzheng, Xu Mingsheng. Two-Dimensional WS2 Sheets as Interfacial Layer for High-Performance Organic Solar Cells [J]. Acta Chim. Sinica, 2015, 73(9): 949-953. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||