Acta Chimica Sinica ›› 2023, Vol. 81 ›› Issue (6): 681-690.DOI: 10.6023/A23040121 Previous Articles
Special Issue: 庆祝《化学学报》创刊90周年合辑
Review
李兰英a, 陶晴a, 闻艳丽a, 王乐乐a, 郭瑞妍a, 刘刚a,*( ), 左小磊b,*(
), 左小磊b,*( )
)
投稿日期:2023-04-08
发布日期:2023-05-31
作者简介: |
李兰英, 上海市计量测试技术研究院高级工程师, 主要从事基于polyA探针的生物传感器研究, 主持完成科研项目3项, 主持和参与省部级以上科研课题6项, 在国内外期刊上发表论文20余篇, 包含ACS Appl. Mater. Inter., Biosens. Bioelectron., Anal. Chem.等, 获得发明专利授权10余项. |
 |
刘刚, 上海市计量测试技术研究院教授级高工, 研究方向生物标准物质、生物传感方法. 美国国家标准化技术研究院(National Institute of Standard and Technology)访问学者, 获得上海市青年拔尖人才计划资助, 曾获上海市科技进步二等奖, 研发国家有证标准物质30余项, 发表论文50余篇, 其中包含ACS Appl. Mater. Inter., Biosens. Bioelectron., Anal. Chem.等, 获得发明专利授权20余项. |
 |
左小磊, 上海交通大学医学院分子医学研究院研究员, 博士生导师, 国家杰出青年科学基金获得者、国家科技部重点专项项目负责人、教育部长江学者奖励计划青年项目获得者、基金委优秀青年科学基金获得者. 曾获得中国分析测试协会一等奖(CAIA奖)、中科院百人计划等. 长期从事框架核酸、生物传感、DNA存储等领域的研究. 在Nature Nanotechnology、Nature Biomedical Engineering、Nature Protocols、Chem. Rev.、JACS, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.等学术期刊上发表论文150余篇, 论文SCI他引10000余次. |
基金资助:
Lanying Lia, Qing Taoa, Yanli Wena, Lele Wanga, Ruiyan Guoa, Gang Liua( ), Xiaolei Zuob(
), Xiaolei Zuob( )
)
Received:2023-04-08
Published:2023-05-31
Contact:
*E-mail: liug@simt.com.cn; zuoxiaolei@sjtu.edu.cn
About author:Supported by:Share
Lanying Li, Qing Tao, Yanli Wen, Lele Wang, Ruiyan Guo, Gang Liu, Xiaolei Zuo. Poly-adenine-based DNA Probes and Their Applications in Biosensors★[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(6): 681-690.


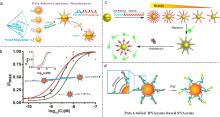



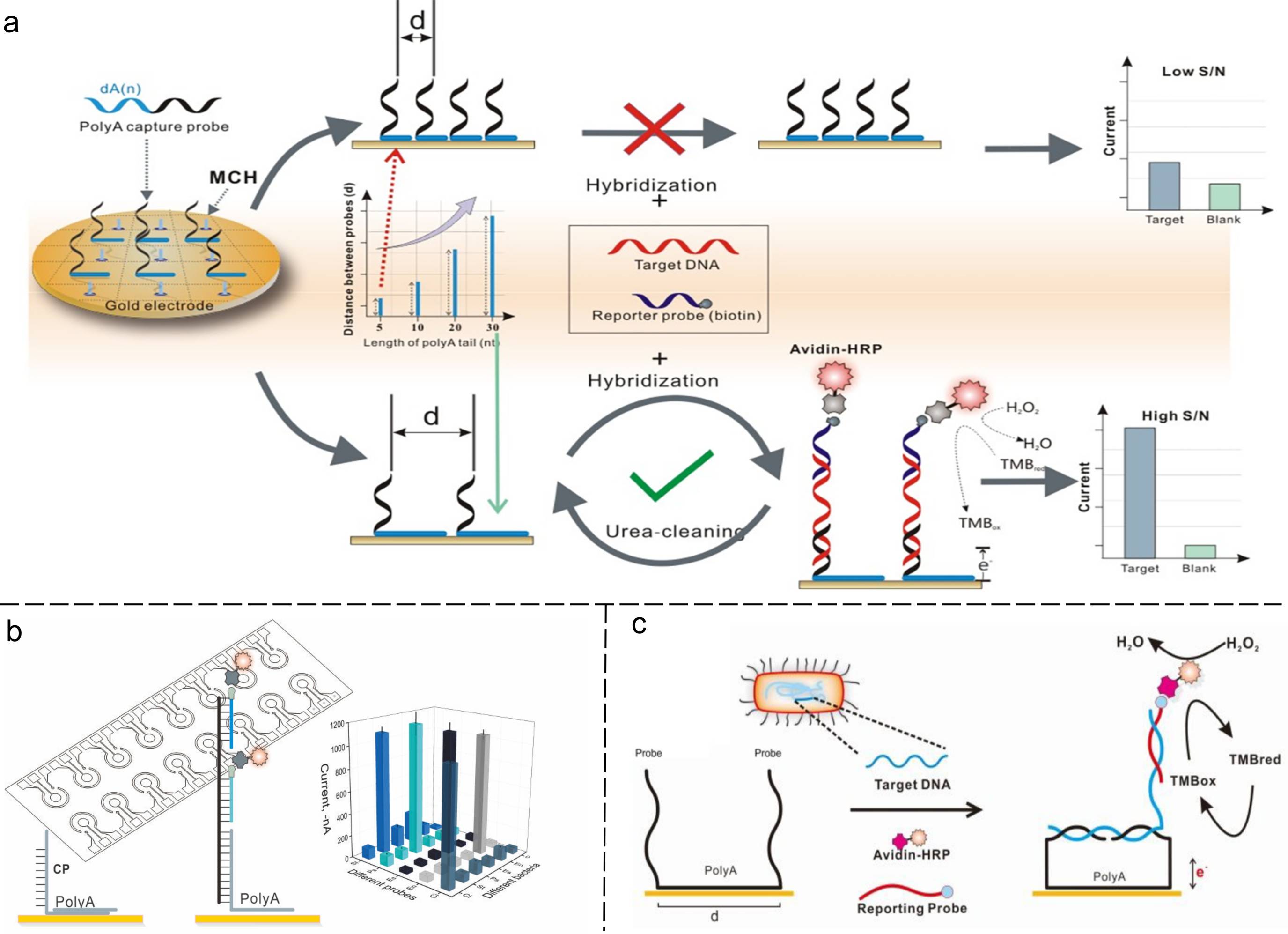
| 类型 | 优势 | 不足 |
|---|---|---|
| 比色生物传感器 | 无需巯基己醇等小分子封闭、响应快速、结果直观、适合环境水样监测现场分析 | 灵敏度不高、易受食品中蛋白和脂肪等干扰物质影响 |
| 荧光生物传感器 | 灵敏度高、特异性好、适合生物医学中细胞成像、细胞内传感 | 用于信号输出的荧光染料易被光漂白, 影响检测结果的可靠性 |
| 表面增强拉曼散射生物传感器 | 不受光漂白和光谱重叠等外界因素影响、适合生物医学中原位无损分析和成像 | 成本高、拉曼检测信号重复性和稳定性差, 准确定量分析困难 |
| 电化学生物传感器 | 成本低、易于微型化和集成化、适合食品安全和环境监控现场分析 | 响应较慢、无法在活体生物中使用 |
| 类型 | 优势 | 不足 |
|---|---|---|
| 比色生物传感器 | 无需巯基己醇等小分子封闭、响应快速、结果直观、适合环境水样监测现场分析 | 灵敏度不高、易受食品中蛋白和脂肪等干扰物质影响 |
| 荧光生物传感器 | 灵敏度高、特异性好、适合生物医学中细胞成像、细胞内传感 | 用于信号输出的荧光染料易被光漂白, 影响检测结果的可靠性 |
| 表面增强拉曼散射生物传感器 | 不受光漂白和光谱重叠等外界因素影响、适合生物医学中原位无损分析和成像 | 成本高、拉曼检测信号重复性和稳定性差, 准确定量分析困难 |
| 电化学生物传感器 | 成本低、易于微型化和集成化、适合食品安全和环境监控现场分析 | 响应较慢、无法在活体生物中使用 |
| [1] |
Chi, J.; Li, J.; Ren, S.; Su, S.; Wang, L. Acta Chim. Sinica 2019, 77, 1230. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A19070262 |
|
(迟景元, 李晶, 任少康, 苏邵, 汪联辉, 化学学报, 2019, 77, 1230.)
doi: 10.6023/A19070262 |
|
| [2] |
Yin, F.; Zhao, H.; Lu, S.; Shen, J.; Li, M.; Mao, X.; Li, F.; Shi, J.; Li, J.; Dong, B.; Xue, W.; Zuo, X.; Yang, X.; Fan, C. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2023, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-023-01348-9.
|
| [3] |
Li, F.; Li, J.; Dong, B.; Wang, F.; Fan, C.; Zuo, X. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 5650.
doi: 10.1039/d0cs01281e pmid: 33729228 |
| [4] |
Zhang, Y.; Mao, X.; Li, F.; Li, M.; Jing, X.; Ge, Z.; Wang, L.; Liu, K.; Zhang, H.; Fan, C.; Zuo, X. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 4892.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v59.12 |
| [5] |
Li, F.; Mao, X.; Li, F.; Li, M.; Shen, J.; Ge, Z.; Fan, C.; Zuo, X. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 9975.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b13737 |
| [6] |
Li, L.; Wang, L.; Xu, Q.; Xu, L.; Liang, W.; Li, Y.; Ding, M.; Aldalbahi, A.; Ge, Z.; Wang, L.; Yan, J.; Lu, N.; Li, J.; Wen, Y.; Liu, G. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 6895.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.7b17327 |
| [7] |
Lao, R.; Song, S.; Wu, H.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; He, L.; Fan, C. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 6475.
doi: 10.1021/ac050911x |
| [8] |
Lu, N.; Pei, H.; Ge, Z.; Simmons, C. R.; Yan, H.; Fan, C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 13148.
doi: 10.1021/ja302447r |
| [9] |
Chen, P.; Pan, D.; Fan, C.; Chen, J.; Huang, K.; Wang, D.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Feng, G.; Liang, P.; He, L.; Shi, Y. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 639.
doi: 10.1038/nnano.2011.141 |
| [10] |
Liu, G.; Lao, R.; Xu, L.; Xu, Q.; Li, L.; Zhang, M.; Shen, H.; Mathur, S.; Fan, C.; Song, S. Sensors-basel 2011, 11, 8018.
doi: 10.3390/s110808018 |
| [11] |
Fan, C.; Plaxco, K. W.; Heeger, A. J. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2003, 100, 9134.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1633515100 |
| [12] |
Song, P.; Shen, J.; Ye, D.; Dong, B.; Wang, F.; Pei, H.; Wang, J.; Shi, J.; Wang, L.; Xue, W.; Huang, Y.; Huang, G.; Zuo, X.; Fan, C. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 838.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-14664-8 |
| [13] |
Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Pan, D.; Song, S.; Fan, C. Chem. Commun. (Camb.) 2007, 1154.
|
| [14] |
Ye, D.; Zuo, X.; Fan, C. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2018, 11, 171.
doi: 10.1146/anchem.2018.11.issue-1 |
| [15] |
Liu, G.; Wan, Y.; Gau, V.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Song, S.; Fan, C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 6820.
doi: 10.1021/ja800554t |
| [16] |
Wen, Y.; Pei, H.; Shen, Y.; Xi, J.; Lin, M.; Lu, N.; Shen, X.; Li, J.; Fan, C. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 867.
doi: 10.1038/srep00867 |
| [17] |
Wen, Y.; Wang, L.; Xu, L.; Li, L.; Ren, S.; Cao, C.; Jia, N.; Aldalbahi, A.; Song, S.; Shi, J.; Xia, J.; Liu, G.; Zuo, X. Analyst 2016, 141, 5304.
doi: 10.1039/C6AN01435F |
| [18] |
Lin, M.; Wen, Y.; Li, L.; Pei, H.; Liu, G.; Song, H.; Zuo, X.; Fan, C.; Huang, Q. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 2285.
doi: 10.1021/ac500251t |
| [19] |
Wen, Y.; Liu, G.; Pei, H.; Li, L.; Xu, Q.; Liang, W.; Li, Y.; Xu, L.; Ren, S.; Fan, C. Methods 2013, 64, 276.
doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2013.07.035 |
| [20] |
Wen, Y.; Pei, H.; Wan, Y.; Su, Y.; Huang, Q.; Song, S.; Fan, C. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 7418.
doi: 10.1021/ac201491p |
| [21] |
Pei, H.; Li, F.; Wan, Y.; Wei, M.; Liu, H.; Su, Y.; Chen, N.; Huang, Q.; Fan, C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 11876.
doi: 10.1021/ja304118z |
| [22] |
Schreiner, S. M.; Hatch, A. L.; Shudy, D. F.; Howard, D. R.; Howell, C.; Zhao, J.; Koelsch, P.; Zharnikov, M.; Petrovykh, D. Y.; Opdahl, A. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 4288.
doi: 10.1021/ac200814y pmid: 21561066 |
| [23] |
Schreiner, S. M.; Shudy, D. F.; Hatch, A. L.; Opdahl, A.; Whitman, L. J.; Petrovykh, D. Y. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 2803.
doi: 10.1021/ac902765g pmid: 20196546 |
| [24] |
Opdahl, A.; Petrovykh, D. Y.; Kimura-Suda, H.; Tarlov, M. J.; Whitman, L. J. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2007, 104, 9.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0608568103 |
| [25] |
Jang, N. H. B. Korean Chem. Soc. 2002, 23, 1790.
doi: 10.5012/bkcs.2002.23.12.1790 |
| [26] |
Koo, K. M.; Sina, A. A. I.; Carrascosa, L. G.; Shiddiky, M. J. A.; Trau, M. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 7042.
doi: 10.1039/C5AY01479D |
| [27] |
Kimura-Suda, H.; Petrovykh, D. Y.; Tarlov, M. J.; Whitman, L. J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 9014.
pmid: 15369348 |
| [28] |
Opdahl, A.; Petrovykh, D. Y.; Kimura-Suda, H.; Tarlov, M. J.; Whitman, L. J. PNAS 2007, 104, 9.
pmid: 17190807 |
| [29] |
Liu, P.; Wang, D.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, H.; Yin, H.; Ai, S. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 80, 74.
doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2015.12.100 |
| [30] |
Wang, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Xu, Y.; Su, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Feng, D.; Wang, L.; Zuo, X.; Shi, J.; Ge, Z.; Fan, C.; Mi, X. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 127, 85.
doi: S0956-5663(18)30950-3 pmid: 30594078 |
| [31] |
Zhu, Y.; Jiang, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, S.; Wang, H.; Sun, B.; Su, Y.; He, Y. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 6631.
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.5b00676 |
| [32] |
Li, W.; Li, J.; Qiang, W.; Xu, J.; Xu, D. Analyst 2013, 138, 760.
doi: 10.1039/C2AN36374G |
| [33] |
Ou, L. J.; Jin, P. Y.; Chu, X.; Jiang, J. H.; Yu, R. Q. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 6015.
doi: 10.1021/ac100907g |
| [34] |
Yang, H.; Xiao, M.; Lai, W.; Wan, Y.; Li, L.; Pei, H. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 4990.
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.9b05149 |
| [35] |
Zhang, Y.; Jiao, J.; Wei, Y.; Wang, D.; Yang, C.; Xu, Z. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 15244.
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.0c04136 |
| [36] |
Cai, Y.; Zhu, H.; Zhou, W.; Qiu, Z.; Chen, C.; Qileng, A.; Li, K.; Liu, Y. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 7275.
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.1c00616 |
| [37] |
Yao, G.; Pei, H.; Li, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Huang, Q.; Fan, C. NPG Asia Materials 2015, 7, e159.
|
| [38] |
Lu, W.; Wang, L.; Li, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Shi, J.; Zuo, X.; Pan, D. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10158.
doi: 10.1038/srep10158 |
| [39] |
Nourisaeid, E.; Mousavi, A.; Arpanaei, A. Physica E 2016, 75, 188.
doi: 10.1016/j.physe.2015.09.018 |
| [40] |
Xie, Y.; Huang, Y.; Tang, D.; Cui, H.; Cao, H. Mikrochim. Acta 2018, 185, 534.
doi: 10.1007/s00604-018-3067-0 |
| [41] |
Yin, J.; Wang, J.; Yang, X.; Wu, T.; Wang, H.; Zhou, X. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 18728.
doi: 10.1039/C9RA03041G |
| [42] |
Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Dai, X.; Ding, L.; Chen, J.; Yao, G.; Liu, X.; Luo, S.; Shi, J.; Wang, L.; Nechushtai, R.; Pikarsky, E.; Willner, I.; Fan, C.; Li, J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 6311.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.1c13116 |
| [43] |
Zhang, Z.; Ma, J.; Zhang, G.; Ding, X.; Zhang, R.; Zhou, T.; Wang, X.; Wang, F. Langmuir 2020, 36, 10989.
doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.0c01821 |
| [44] |
Wu, Z.; Ke, J.; Liu, Y.; Sun, P.; Hong, M. Acta Chim. Sinica 2022, 80, 542. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A21120571 |
|
(吴志芬, 柯建熙, 刘永升, 孙蓬明, 洪茂椿, 化学学报, 2022, 80, 542.)
doi: 10.6023/A21120571 |
|
| [45] |
Zhao, L.-D.; Zuo, P.; Yin, B.-C.; Hong, C.-L.; Ye, B.-C. Acta Chim. Sinica 2020, 78, 1076. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A20060235 |
|
(赵丽东, 左鹏, 尹斌成, 洪成林, 叶邦策, 化学学报, 2020, 78, 1076.)
doi: 10.6023/A20060235 |
|
| [46] |
Huang, Y.; Yang, H. Y.; Ai, Y. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 9132.
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.5b03037 |
| [47] |
Zhang, P.; Chang, L.; Niu, C.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Liu, J. ACS Appl. Polym. 2022, 4, 6211.
|
| [48] |
Chen, L.; Chao, J.; Qu, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, D.; Su, S.; Aldalbahi, A.; Wang, L.; Pei, H. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 8014.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.6b16764 |
| [49] |
Ye, T.; Zhu, D.; Hao, L.; Yuan, M.; Cao, H.; Wu, X.; Yin, F.; Xu, F. Mikrochim. Acta 2022, 189, 151.
doi: 10.1007/s00604-022-05235-3 |
| [50] |
Zhu, D.; Pei, H.; Chao, J.; Su, S.; Aldalbahi, A.; Rahaman, M.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Huang, W.; Fan, C.; Zuo, X. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 18671.
doi: 10.1039/C5NR05366H |
| [51] |
Zhu, D.; Zhao, D.; Huang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Chao, J.; Su, S.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Shi, J.; Zuo, X.; Weng, L.; Li, Q.; Wang, L. Nanomedicine 2018, 14, 1797.
|
| [52] |
Zheng, D.; Seferos, D. S.; Giljohann, D. A.; Patel, P. C.; Mirkin, C. A. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 3258.
doi: 10.1021/nl901517b pmid: 19645478 |
| [53] |
Liu, M.; Li, Q.; Liang, L.; Li, J.; Wang, K.; Li, J.; Lv, M.; Chen, N.; Song, H.; Lee, J.; Shi, J.; Wang, L.; Lal, R.; Fan, C. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15646.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms15646 |
| [54] |
Qian, Q.; He, G.; Wang, C.; Li, S.; Zhao, X.; Xu, Y.; Mi, X. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 3705.
doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-07210-w |
| [55] |
Jiao, K.; Yan, Q.; Guo, L.; Qu, Z.; Cao, S.; Chen, X.; Li, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Fan, C.; Wang, F. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 14438.
doi: 10.1002/anie.202017039 pmid: 33851770 |
| [56] |
Wang, S.; Zhang, H.; Li, W.; Birech, Z.; Ma, L.; Li, D.; Li, S.; Wang, L.; Shang, J.; Hu, J. Mikrochim. Acta 2019, 187, 20.
doi: 10.1007/s00604-019-4003-7 |
| [57] |
Chen, Q.; Tian, R.; Liu, G.; Wen, Y.; Bian, X.; Luan, D.; Wang, H.; Lai, K.; Yan, J. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 207, 114187.
doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2022.114187 |
| [58] |
Zhou, Y.; Fang, W.; Lai, K.; Zhu, Y.; Bian, X.; Shen, J.; Li, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhang, W.; Yan, J. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 141, 111419.
doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2019.111419 |
| [59] |
Lim, D. K.; Jeon, K. S.; Hwang, J. H.; Kim, H.; Kwon, S.; Suh, Y. D.; Nam, J. M. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 452.
doi: 10.1038/nnano.2011.79 |
| [60] |
Zhao, B.; Shen, J.; Chen, S.; Wang, D.; Li, F.; Mathur, S.; Song, S.; Fan, C. Chem. Sci. 2014, 5, 4460.
doi: 10.1039/C4SC01792G |
| [61] |
Zhu, Y.; Jiang, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, S.; Wang, H.; Sun, B.; Su, Y.; He, Y. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 6631.
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.5b00676 |
| [62] |
Wang, H.; Halas, N. J. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 820.
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1521-4095 |
| [63] |
Guo, J.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Ju, H. Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 9332.
doi: 10.1002/chem.v23.39 |
| [64] |
Zhou, X.; Sun, Z.; Su, X.; Zheng, K.; Zou, X.; Zhang, W. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 1916.
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.2c04031 |
| [65] |
Khodadoust, A.; Nasirizadeh, N.; Taheri, R. A.; Dehghani, M.; Ghanei, M.; Bagheri, H. Mikrochim. Acta 2022, 189, 213.
doi: 10.1007/s00604-022-05301-w pmid: 35513513 |
| [66] |
Wang, M.; Cui, H.; Hong, N.; Shu, Q.; Wang, X.; Hu, Y.; Wei, G.; Fan, H.; Zhang, J. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 358.
|
| [67] |
Koo, K. M.; Carrascosa, L. G.; Shiddiky, M. J.; Trau, M. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 2000.
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.5b04795 |
| [68] |
Wang, Q.; Weng, Y.; Liang, W.; Li, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhu, H.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, J.; Jia, N.; Deng, W.; Liu, G. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 9277.
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.9b02175 |
| [69] |
Wang, L.; Wen, Y.; Yang, X.; Xu, L.; Liang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Ding, M.; Ren, S.; Yang, Z.; Lv, M.; Zhang, J.; Ma, K.; Liu, G. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 16002.
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.9b04757 |
| [1] | Liwei Hu, Xianhu Liu, Chuntai Liu, Yanlin Song, Mingzhu Li. Self-assembly Fabrication and Applications of Photonic Crystal Structure Color Materials★ [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(7): 809-819. |
| [2] | Ziyu Zhu, Axin Liang, Ruilin Haotian, Shanshan Tang, Miao Liu, Bingteng Xie, Aiqin Luo. Application of Biosensors in the Detection of SARS-CoV-2 [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(3): 253-263. |
| [3] | Xu Pu, Zejuan Li, Junqiu Shi, Yunqing Zhu, Jianzhong Du. Recent Advances in Organ-Targeting Polymeric Delivery Vectors for Nucleic Acids★ [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(10): 1438-1446. |
| [4] | Jamshid Kadirkhanov, Feng Zhong, Wenjian Zhang, Chunyan Hong. Preparation of Multi-chambered Vesicles by Polymerization-induced Self-assembly and the Influence of Solvophilic Fragments in the Core-forming Blocks [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(7): 913-920. |
| [5] | Zhiqin Wang, Bo Xiang, Xiaoyu Huang, Guolin Lu. Effect of Phosphotungstic Acid on Self-seeding of Oligo(p-phenylenevinylene)-b-poly(2-vinylpyridine)※ [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(3): 297-302. |
| [6] | Ruilin Haotian, Ziyu Zhu, Yanhui Cai, Wei Wang, Zhen Wang, Axin Liang, Aiqin Luo. Application of Covalent Organic Framework-Based Electrochemical Biosensors in Biological Sample Detection [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(11): 1524-1535. |
| [7] | Dong Yin, Hongyi Shang, Wenhao Yu, Shikai Xiang, Ping Hu, Keqing Zhao, Chun Feng, Biqin Wang. Synthesis, Mesomorphism and Gelation Properties of Triazole-Modified Triphenylene 2,3-Dicarboxylic Esters and 2,3-Dicarboxyimides [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(10): 1376-1384. |
| [8] | Yao Shi, Qianfeng Xia, Zhengqing He, Huangxian Ju. Biosensing Technology for Dengue Virus Detection [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(1): 69-79. |
| [9] | Yanmei Jin, Ye Meng, Yuan Li, Jianhua Shi, Lei Deng. Supramolecular Self-assembly of Symmetric Dicyclohexanocucurbit[6]uril and Nicotinic Hydrazide [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(1): 44-48. |
| [10] | Xusheng Wang, Xu Yang, Chunhui Chen, Hongfang Li, Yuanbiao Huang, Rong Cao. Graphene Quantum Dots Supported on Fe-based Metal-Organic Frameworks for Efficient Photocatalytic CO2 Reduction※ [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(1): 22-28. |
| [11] | Xu Yang, Zeying Zhang, Meng Su, Yanlin Song. Research Progress on Nano Photonics Technology-based SARS-CoV-2 Detection※ [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(1): 80-88. |
| [12] | Weihua Li. “Bridge” Makes Differences to the Self-assembly of Block Copolymers [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(2): 133-138. |
| [13] | Ni Liao, Xia Zhong, Wen-Bin Liang, Ruo Yuan, Ying Zhuo. Metal-organic Frameworks (MOF)-based Novel Electrochemiluminescence Biosensing Platform for Quantification of H2O2 Releasing from Tumor Cells [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(10): 1257-1264. |
| [14] | Hui He, Lingli Zhou, Zhen Liu. Advances in Protein Biomarker Assay via the Combination of Molecular Imprinting and Surface-enhanced Raman Scattering [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(1): 45-57. |
| [15] | Zhao Jingjing, Zhang Zhengzhong, Chen Xiaolang, Wang Bei, Deng Jinyuan, Zhang Dieqing, Li Hexing. Microwave-induced Assembly of CuS@MoS2 Core-shell Nanotubes and Study on Their Photocatalytic Fenton-like Reactions [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2020, 78(9): 961-967. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||