Acta Chimica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 83 ›› Issue (4): 332-340.DOI: 10.6023/A25010018 Previous Articles Next Articles
Article
投稿日期:2025-01-13
发布日期:2025-03-24
基金资助:
Jianhua Chen, Lan Jiang, Yang Zeng, Songhai Xie, Yan Pei, Minghua Qiao( )
)
Received:2025-01-13
Published:2025-03-24
Contact:
E-mail: Supported by:Share
Jianhua Chen, Lan Jiang, Yang Zeng, Songhai Xie, Yan Pei, Minghua Qiao. Effect of Crystal Phase Ratio of Bi-Phase Titania on Structure and Catalytic Performance of Pt-WOx/TiO2 Catalyst in Glycerol Hydrogenolysis[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2025, 83(4): 332-340.

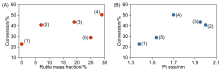
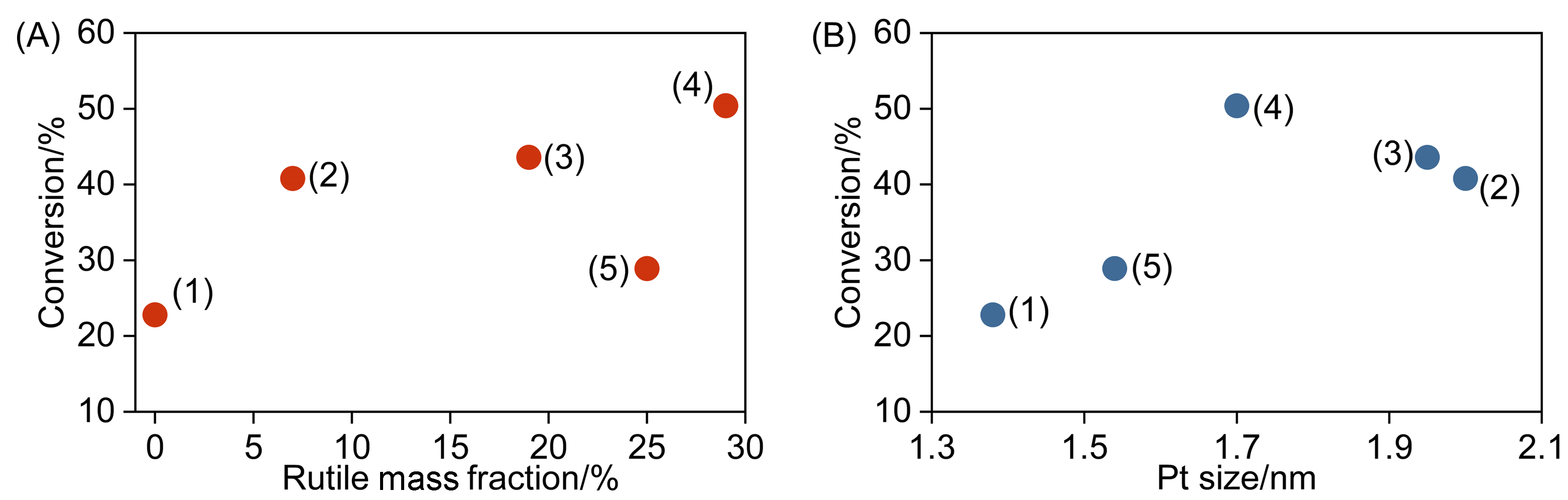
| Catalyst | wAa/% | wRa/% | DPtb/% | SPtb/(m2•gPt-1) | dPtb/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pt-WOx/bp-TiO2(1) | 100 | 0 | 25 | 62 | 4.5 |
| Pt-WOx/bp-TiO2(2) | 93 | 7 | 5 | 12 | 23.0 |
| Pt-WOx/bp-TiO2(3) | 81 | 19 | 14 | 34 | 8.1 |
| Pt-WOx/bp-TiO2(4) | 71 | 29 | 21 | 51 | 5.5 |
| Pt-WOx/bp-TiO2(5) | 75 | 25 | 26 | 64 | 4.3 |
| Catalyst | wAa/% | wRa/% | DPtb/% | SPtb/(m2•gPt-1) | dPtb/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pt-WOx/bp-TiO2(1) | 100 | 0 | 25 | 62 | 4.5 |
| Pt-WOx/bp-TiO2(2) | 93 | 7 | 5 | 12 | 23.0 |
| Pt-WOx/bp-TiO2(3) | 81 | 19 | 14 | 34 | 8.1 |
| Pt-WOx/bp-TiO2(4) | 71 | 29 | 21 | 51 | 5.5 |
| Pt-WOx/bp-TiO2(5) | 75 | 25 | 26 | 64 | 4.3 |
| Catalyst | w(Pt)a/% | w(W)a/% | SBETb/(m2•g-1) | Vporeb/(cm3•g-1) | dporeb/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pt-WOx/bp-TiO2(1) | 1.8 | 6.7 | 190 | 0.33 | 6.9 |
| Pt-WOx/bp-TiO2(2) | 1.9 | 6.8 | 149 | 0.45 | 12.2 |
| Pt-WOx/bp-TiO2(3) | 1.9 | 7.0 | 141 | 0.32 | 9.4 |
| Pt-WOx/bp-TiO2(4) | 2.0 | 6.9 | 161 | 0.32 | 7.9 |
| Pt-WOx/bp-TiO2(5) | 1.9 | 6.9 | 160 | 0.38 | 9.5 |
| Catalyst | w(Pt)a/% | w(W)a/% | SBETb/(m2•g-1) | Vporeb/(cm3•g-1) | dporeb/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pt-WOx/bp-TiO2(1) | 1.8 | 6.7 | 190 | 0.33 | 6.9 |
| Pt-WOx/bp-TiO2(2) | 1.9 | 6.8 | 149 | 0.45 | 12.2 |
| Pt-WOx/bp-TiO2(3) | 1.9 | 7.0 | 141 | 0.32 | 9.4 |
| Pt-WOx/bp-TiO2(4) | 2.0 | 6.9 | 161 | 0.32 | 7.9 |
| Pt-WOx/bp-TiO2(5) | 1.9 | 6.9 | 160 | 0.38 | 9.5 |



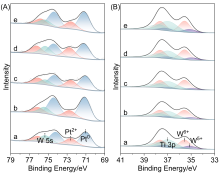

| Catalyst | 4f7/2 BE/eV | Pt2+/(Pt0+Pt2+) | W5+/(W6++W5+) | (Pt/Ti)a/% | (W/Ti)a/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pt2+ | Pt0 | W6+ | W5+ | |||||
| Pt-WOx/bp-TiO2(1) | 72.6 | 71.0 | 35.6 | 35.1 | 0.30 | 0.26 | 2.9 | 13.6 |
| Pt-WOx/bp-TiO2(2) | 72.8 | 71.1 | 35.6 | 35.0 | 0.23 | 0.18 | 2.9 | 13.7 |
| Pt-WOx/bp-TiO2(3) | 72.6 | 71.0 | 35.6 | 34.9 | 0.34 | 0.17 | 2.8 | 13.8 |
| Pt-WOx/bp-TiO2(4) | 72.8 | 71.2 | 35.6 | 34.9 | 0.36 | 0.22 | 3.1 | 14.4 |
| Pt-WOx/bp-TiO2(5) | 72.6 | 71.2 | 35.6 | 35.1 | 0.26 | 0.24 | 2.8 | 14.0 |
| Catalyst | 4f7/2 BE/eV | Pt2+/(Pt0+Pt2+) | W5+/(W6++W5+) | (Pt/Ti)a/% | (W/Ti)a/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pt2+ | Pt0 | W6+ | W5+ | |||||
| Pt-WOx/bp-TiO2(1) | 72.6 | 71.0 | 35.6 | 35.1 | 0.30 | 0.26 | 2.9 | 13.6 |
| Pt-WOx/bp-TiO2(2) | 72.8 | 71.1 | 35.6 | 35.0 | 0.23 | 0.18 | 2.9 | 13.7 |
| Pt-WOx/bp-TiO2(3) | 72.6 | 71.0 | 35.6 | 34.9 | 0.34 | 0.17 | 2.8 | 13.8 |
| Pt-WOx/bp-TiO2(4) | 72.8 | 71.2 | 35.6 | 34.9 | 0.36 | 0.22 | 3.1 | 14.4 |
| Pt-WOx/bp-TiO2(5) | 72.6 | 71.2 | 35.6 | 35.1 | 0.26 | 0.24 | 2.8 | 14.0 |
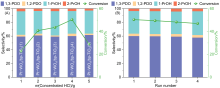

| Catalyst | wRa/% | Pt2+/(Pt0+Pt2+)b | dPt/nm | DPt/% | H/Pte | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TEMc | COd | COd | H2e | |||||
| Pt-WOx/bp-TiO2(1) | 0 | 0.30 | 1.38 | 4.5 | 25 | 22 | 0.86 | |
| Pt-WOx/bp-TiO2(4) | 29 | 0.36 | 1.70 | 5.5 | 21 | 51 | 2.03 | |
| Catalyst | wRa/% | Pt2+/(Pt0+Pt2+)b | dPt/nm | DPt/% | H/Pte | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TEMc | COd | COd | H2e | |||||
| Pt-WOx/bp-TiO2(1) | 0 | 0.30 | 1.38 | 4.5 | 25 | 22 | 0.86 | |
| Pt-WOx/bp-TiO2(4) | 29 | 0.36 | 1.70 | 5.5 | 21 | 51 | 2.03 | |
| [1] |
Hoekman, S. K.; Broch, A.; Robbins, C.; Ceniceros, E.; Natarajan, M. Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 143.
|
| [2] |
Attarbachi, T.; Kingsley, M. D.; Spallina, V. Fuel 2023, 340, 127485.
|
| [3] |
Kaur, G.; Srivastava, A. K.; Chand, S. Biochem. Eng. J. 2012, 64, 106.
|
| [4] |
Zhu, F.; Liu, D.; Chen, Z. Green Chem. 2022, 24, 1390.
|
| [5] |
Shrirame, B. S.; Varma, A. R.; Sahoo, S. S.; Gayen, K.; Maity, S. K. Biomass Bioenergy 2023, 177, 106943.
|
| [6] |
Bhowmik, S.; Darbha, S. Catal. Rev. 2021, 63, 639.
|
| [7] |
Yang, M.; Jiao, Y.; Ren, Y. Prog. Chem. 2024, 36, 256.
doi: 10.7536/PC230615 |
| [8] |
Wu, F.; Jiang, H.; Zhu, X.; Lu, R.; Shi, L.; Lu, F. ChemSusChem 2021, 14, 569.
|
| [9] |
Fan, Y.; Cheng, S.; Wang, H.; Tian, J.; Xie, S.; Pei, Y.; Qiao, M.; Zong, B. Appl. Catal., B 2017, 217, 331.
|
| [10] |
Zeng, Y.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, X.; Xie, S.; Pei, Y.; Zhou, G.; Hua, W.; Qiao, M.; Li, Z.; Zong, B. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 9532.
|
| [11] |
Wang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhao, L.; Xia, Q. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 1004925.
|
| [12] |
Zhou, G.; Dou, R.; Bi, H.; Xie, S.; Pei, Y.; Fan, K.; Qiao, M.; Sun, B.; Zong, B. J. Catal. 2015, 332, 119.
|
| [13] |
Feng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Ling, L.; Zhang, R.; Fan, M.; Hou, B.; Li, D.; Wang, B. ACS Catal. 2024, 14, 1874.
|
| [14] |
Zhang, W.; He, H.; Tian, Y.; Lan, K.; Liu, Q.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Elzatahry, A.; Che, R.; Li, W.; Zhao, D. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 1664.
doi: 10.1039/c8sc04155e pmid: 30842830 |
| [15] |
Zhang, H.; Banfield, J. F. J. Phys. Chem. B 2000, 104, 3481.
|
| [16] |
Ohsaka, T.; Izumi, F.; Fujiki, Y. J. Raman Spectrosc. 1978, 7, 321.
|
| [17] |
Deo, G.; Turek, A. M.; Wachs, I. E.; Machej, T.; Haber, J.; Das, N.; Eckert, H.; Hirt, A. M. Appl. Catal. A 1992, 91, 27.
|
| [18] |
Yan, J.; Wu, G.; Guan, N.; Li, L.; Li, Z.; Cao, X. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 10978.
|
| [19] |
Kim, D. S.; Ostromecki, M.; Wachs, I. E. J. Mol. Catal. A 1996, 106, 93.
|
| [20] |
Arribas, M. A.; Márquez, F.; Martínez, A. J. Catal. 2000, 190, 309.
|
| [21] |
Komornicki, S.; Radecka, M.; Sobas, P. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 2004, 15, 527.
|
| [22] |
Kim, T. Y.; Park, D. S.; Choi, Y.; Baek, J.; Park, J. R.; Yi, J. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 10021.
|
| [23] |
Ou, G.; Xu, Y.; Wen, B.; Lin, R.; Ge, B.; Tang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Yang, C.; Huang, K.; Zu, D.; Yu, R.; Chen, W.; Li, J.; Wu, H.; Liu, L.-M.; Li, Y. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1302.
|
| [24] |
He, J.; Burt, S. P.; Ball, M.; Zhao, D.; Hermans, I.; Dumesic, J. A.; Huber, G. W. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 1427.
|
| [25] |
Zhu, S.; Qiu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Hao, S.; Zheng, H.; Li, Y. Catal. Today 2013, 212, 120.
|
| [26] |
García-Fernández, S.; Gandarias, I.; Requies, J.; Güemez, M. B.; Bennici, S.; Auroux, A.; Arias, P. L. J. Catal. 2015, 323, 65.
|
| [27] |
Lauriol-Garbey, P.; Postole, G.; Loridant, S.; Auroux, A.; Belliere-Baca, V.; Rey, P.; Millet, J. M. M. Appl. Catal. B 2011, 106, 94.
|
| [28] |
Jiang, F.; Zeng, L.; Li, S.; Liu, G.; Wang, S.; Gong, J. ACS Catal. 2014, 5, 438.
|
| [29] |
Gong, L.; Lu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Lin, R.; Li, J.; Dong, W.; Wang, T.; Chen, W. Appl. Catal. A 2010, 390, 119.
|
| [30] |
Deng, C.; Duan, X.; Zhou, J.; Chen, D.; Zhou, X.; Yuan, W. Catal. Today 2014, 234, 208.
|
| [31] |
Zhao, B.; Liang, Y.; Liu, L.; He, Q.; Dong, J. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 8254.
|
| [32] |
Wen, Y.; Shen, W.; Li, Y.; Fang, Y. React. Kinet., Mech. Catal. 2021, 132, 219.
|
| [33] |
Chen, J.; Huang, H.; Pan, H.; Cao, Y.; Jiang, L.; Xia, Q.; Meng, X.; Qiu, J.; Zuilhof, H.; Liu, S. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 6242.
|
| [34] |
Cheng, S.; Zeng, Y.; Pei, Y.; Fan, K.; Qiao, M.; Zong, B. Acta Chim. Sinica 2019, 77, 1054. (in Chinese)
|
|
(成诗婕, 曾杨, 裴燕, 范康年, 乔明华, 宗保宁, 化学学报, 2019, 77, 1054.)
doi: 10.6023/A19060219 |
|
| [35] |
Zeng, Y.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, X.; Xie, S.; Pei, Y.; Qiao, M.; Li, Z.; Xu, H.; Fan, K.; Zong, B. Acta Chim. Sinica 2022, 80, 903. (in Chinese)
|
|
(曾杨, 姜兰, 张晓昕, 谢颂海, 裴燕, 乔明华, 李振华, 徐华龙, 范康年, 宗保宁, 化学学报, 2022, 80, 903.)
doi: 10.6023/A22020059 |
|
| [36] |
Jiang, L.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Pei, Y.; Yan, S.; Qiao, M.; Fan, K.; Zong, B. Acta Chim. Sinica 2023, 81, 231. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A22120509 |
|
(姜兰, 范义秋, 张晓昕, 裴燕, 闫世润, 乔明华, 范康年, 宗保宁, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 231.)
doi: 10.6023/A22120509 |
|
| [37] |
Wang, L.; Stuckert, A. N.; Chen, H.; Yang, R. T. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 4793.
|
| [38] |
Pevzner, S.; Pri-Bar, I.; Lutzky, I.; Ben-Yehuda, E.; Ruse, E.; Regev, O. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 27164.
|
| [39] |
Fan, Y.; Cheng, S.; Wang, H.; Ye, D.; Xie, S.; Pei, Y.; Hu, H.; Hua, W.; Li, Z. H.; Qiao, M.; Zong, B. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 2174.
|
| [40] |
Lei, N.; Zhao, X.; Hou, B.; Yang, M.; Zhou, M.; Liu, F.; Wang, A.; Zhang, T. ChemCatChem 2019, 11, 3903.
|
| [41] |
Zhou, W.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Ma, X. ChemCatChem 2016, 8, 3663.
|
| [42] |
Conner, W. C., Jr.; Falconer, J. L. Chem. Rev. 1995, 95, 759.
|
| [1] | Lan Jiang, Yiqiu Fan, Xiaoxin Zhang, Yan Pei, Shirun Yan, Minghua Qiao, Kangnian Fan, Baoning Zong. Effect of W Content on Structure and Catalytic Performance of Pt/GaWZrOx Catalysts in Glycerol Selective Hydrogenolysis [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(3): 231-238. |
| [2] | Yang Zeng, Lan Jiang, Xiaoxin Zhang, Songhai Xie, Yan Pei, Minghua Qiao, Zhen-Hua Li, Hualong Xu, Kangnian Fan, Baoning Zong. W-doped Hierarchically Porous Silica Nanosphere Supported Platinum for Catalytic Glycerol Hydrogenolysis to 1,3-Propanediol [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(7): 903-912. |
| [3] | Cheng, Shijie, Zeng, Yang, Pei, Yan, Fan, Kangnian, Qiao, Minghua, Zong, Baoning. Synthesis and Catalysis of Pt/W-s-SBA-15 Catalysts with Short Channel for Glycerol Hydrogenolysis to 1,3-Propanediol [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2019, 77(10): 1054-1062. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||