Acta Chimica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 83 ›› Issue (5): 510-517.DOI: 10.6023/A25020041 Previous Articles Next Articles
Article
投稿日期:2025-02-14
发布日期:2025-04-22
基金资助:
Xiaogai Penga, Zhubin Hua,*( ), Haitao Suna,b,*(
), Haitao Suna,b,*( )
)
Received:2025-02-14
Published:2025-04-22
Contact:
* E-mail: Supported by:Share
Xiaogai Peng, Zhubin Hu, Haitao Sun. Theoretical Study on Dihydrogen Bond Interaction Dominated Dodecaborate-Solvent Molecular Clusters[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2025, 83(5): 510-517.
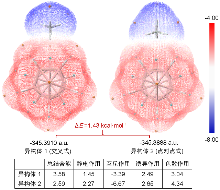
| 团簇 | 实验值 | 计算值 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PBE0 | IP-EOM-DLPNO-CCSD | ||
| 乙酸 | — | 1.88 | 1.90 |
| 硝基甲烷 | — | 1.74 | 1.75 |
| 乙腈 | 1.56 a | 1.70 | 1.71 |
| 乙醛 | — | 1.63 | 1.65 |
| 水 | 1.46 b | 1.63 | 1.62 |
| 甲醇 | — | 1.57 | 1.57 |
| 甲胺 | — | 1.49 | 1.52 |
| 氟代甲烷 | — | 1.53 | 1.53 |
| 乙烷 | — | 1.39 | 1.39 |
| 甲烷 | — | 1.35 | 1.36 |
| 裸硼烷 | 1.15 b | 1.30 | 1.31 |
| 团簇 | 实验值 | 计算值 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PBE0 | IP-EOM-DLPNO-CCSD | ||
| 乙酸 | — | 1.88 | 1.90 |
| 硝基甲烷 | — | 1.74 | 1.75 |
| 乙腈 | 1.56 a | 1.70 | 1.71 |
| 乙醛 | — | 1.63 | 1.65 |
| 水 | 1.46 b | 1.63 | 1.62 |
| 甲醇 | — | 1.57 | 1.57 |
| 甲胺 | — | 1.49 | 1.52 |
| 氟代甲烷 | — | 1.53 | 1.53 |
| 乙烷 | — | 1.39 | 1.39 |
| 甲烷 | — | 1.35 | 1.36 |
| 裸硼烷 | 1.15 b | 1.30 | 1.31 |







| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
|
(王海燕, 曾艳丽, 郑世钧, 孟令鹏, 物理化学学报, 2007, 23, 1131.)
|
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpca.4c00911 pmid: 38598527 |
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
doi: 10.1021/ct200751e pmid: 26592877 |
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
doi: 10.1021/ct800575z pmid: 26609710 |
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.jctc.7b00174 pmid: 28489372 |
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
doi: 10.1016/0263-7855(96)00018-5 pmid: 8744570 |
| [1] | Ning Li, Lina Xu, Guoyong Fang, Yingjin Ma. Fault-tolerant Coded Quantum Chemical Distributed Calculation [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(2): 138-145. |
| [2] | Huang Rongyi, Shen Qiong, Zhang Chao, Zhang Shaoyong, Xu Heng. Studies on the Mechanism of the Transition Metal-Catalyzed Reaction of Organonitrile with Sodium Azide [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2020, 78(6): 565-571. |
| [3] | Li Wuyang, Xu Lejin. Research Methods for the Degradation Mechanism of Organic Pollutants in Wastewater [J]. Acta Chim. Sinica, 2019, 77(8): 705-716. |
| [4] | Wu Youxiong, Ren Hongyang, Wu Yifang, Wang Bingxi. Theoretical Study of Energy Gaps for Naphthalimide-based Charge Transfer Compounds [J]. Acta Chim. Sinica, 2015, 73(1): 53-59. |
| [5] | FENG Li-Juan, YANG Huai-Yu, WANG Fu-Hui. Inhibition Behavior of Ascorbic Benzoate for Steel Rebar in Alkaline Solution [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2011, 69(20): 2359-2367. |
| [6] | SUN Xiao-Hong, LI Jun-Feng, LIU Yuan-Fa, MA Hai-Xia. Synthesis, Crystal Structure and Quantum Chemical Calculation of Pyrimethanil [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2011, 69(16): 1909-1914. |
| [7] | ZHANG Hao, YU Jian-Kang, SUN Jia-Zhong. Ab-initio Investigation on the Ion-associated Species and Process in Mg(ClO4)2 Solution [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2010, 68(14): 1363-1369. |
| [8] | CHOU Yi-Xiang, LI Jia, WANG Shu-Guang. Theoretical Investigations on Ligand-stabilized Binary Transition- metal Cluster [PdAu8(PR3)8]2+ (R=Me, OMe, H, F, Cl, CN) [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2010, 68(07): 611-616. |
| [9] | . A Quantum-Chemical Study on Charge Transport Properties of Triphenylene Discotic Crystals Substituted with Ester or Amide Functional Groups [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2008, 66(7): 738-744. |
| [10] | LIU Hong*,1; CHEN Yan-Qin ;WANG Yi-Bo2 . Nature and Structural Property of Complexes of Silicane with Hydrogen Halides [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2008, 66(3): 301-307. |
| [11] | . Density Functional Theory Study on Carbonyl Insertion into RhI—C Bond in Heterobimetallic Rh-M (M=Cr, Mo, W) Species [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2008, 66(20): 2193-2198. |
| [12] |
KONG, Rui-Hong a SHAN, Xiao-Bin a WANG, Si-Sheng a,b ZHANG, Yun-Wu a LIU, Fu-Yi *,a SHENG, Liu-Si a HAO, Li-Qing c WANG, Zhen-Ya c . Experimental and Theoretical Study of Kr and Kr2 [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2008, 66(13): 1508-1512. |
| [13] | LI Xiao-Tong; PANG Si-Ping*,2; YU Yong-Zhong; LUO Yun-Jun. Synthesis and Theoretical Studies of 3,6-Diazido-1,2,4,5-tetrazine [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2007, 65(10): 971-976. |
| [14] | YUAN Wei-Feng, RUAN Wen-Juan*, ZHANG Ying-Hui, NAN Jing, ZHU Zhi-Ang. Study on Molecular Recognition of New Dinuclear Chiral Salen Zn(II) Complex [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2006, 64(6): 475-482. |
| [15] | ZENG Yu-Xiang1,2, BEI Feng-Li, WANG Chao3, YANG Xu-Jie, LU Lu-De, WANG Xin*,1. Synthesis and Quantum Chemical Calculation of N-(4-Sulfophenyl)maleimide and Its Polymer [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2006, 64(10): 1079-1084. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||