Acta Chimica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 83 ›› Issue (12): 1561-1575.DOI: 10.6023/A25060215 Previous Articles Next Articles
Special Issue: “中国青年化学家”合辑
Review
王润泽a, 储著银b, 陈俊艺c, 徐梦欣a, 李献华b, 刘志博a,c,d,e,*
投稿日期:2025-06-12
发布日期:2025-08-18
作者简介: |
王润泽, 本科毕业于北京师范大学化学学院, 2024年博士毕业于荷兰代尔夫特理工大学, 博士导师为代尔夫特理工大学核反应堆研究所Antonia Denkova教授和Hubert Wolterbeek教授, 同年加入昌平实验室进行博士后研究, 合作导师为刘志博教授. 研究方向为新型放射性核素制备, 靶向核药物研发. |
 |
储著银, 中国科学院地质与地球物理研究所研究员. 1992本科毕业于安徽大学化学系, 1995年于中国科学技术大学获应用化学硕士学位, 1998年博士毕业于中国科学院地质研究所. 1998年至今一直任职于中国科学院地质与地球物理研究所, 研究方向为同位素地球化学. 主持多项国家自然科学基金项目, 作为技术骨干参与国家重点研发计划项目, 发表EPSL和AC等Nature Index期刊论文5篇. 曾赴MIT高精度U-Pb地质年代学实验室交流访问. |
 |
陈俊艺, 北京大学化学与分子工程学院应用化学系博雅博士后, 本科毕业于南京大学化学化工学院, 2022年博士毕业于北京大学化学与分子工程学院应用化学系, 导师为刘志博教授. 负责北京大学回旋加速器平台与辐照平台的管理运行工作. 研究方向包括放射性药物与核素制备, 核技术应用. |
 |
徐梦欣, 现任昌平实验室助理研究员, 2022年博士毕业于北京大学化学与分子工程学院应用化学系, 师从刘志博教授. 2022年到2024年在北京大学从事博士后工作, 2024年加入昌平实验室. 主要研究方向为肿瘤靶向放射性药物的开发与临床转化. |
 |
李献华, 中国科学院地质与地球物理研究所研究员, 中国科学院院士. 1983年本科毕业于中国科学技术大学地球化学专业, 1988年在中国科学院地球化学研究所研究生毕业, 获博士学位. 长期从事大陆形成演化和矿产资源同位素年代学和地球化学研究及微区同位素分析新技术方法研发与应用. |
 |
刘志博, 北京大学化学与分子工程学院教授, 副院长, 应用化学系主任, 北大-清华生命科学联合中心研究员, 昌平实验室领衔科学家. 获北京市自然科学一等奖(第一完成人)、国家杰出青年基金、新基石基金会科学探索奖、九三学社全国青年科技英才等项目资助或荣誉. 2010年在南京大学获学士学位, 2014年在英属哥伦比亚大学获博士学位, 2014~2016年在美国国立卫生研究院开展博士后研究. 主要从事放射性药物、中子俘获治疗药物和核辐射驱动的物质转化研究. |
★ “中国青年化学家”专辑.
基金资助:Runze Wanga, Zhuyin Chub, Junyi Chenc, Mengxin Xua, Xianhua Lib, Zhibo Liua,c,d,e,*
Received:2025-06-12
Published:2025-08-18
Contact:
* E-mail: zbliu@pku.edu.cn
About author:★ For the VSI “Rising Stars in Chemistry”.
Supported by:Share
Runze Wang, Zhuyin Chu, Junyi Chen, Mengxin Xu, Xianhua Li, Zhibo Liu. Bridging the Gap: Lead Isotopes for Interdisciplinary Research★[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2025, 83(12): 1561-1575.
| 放射性铅同位素 | 半衰期 | 衰变模式 | 应用领域 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 202Pb | 5.25×104年 | EC | 地质年代学研究 |
| 203Pb | 51.9小时 | EC | 核医学癌症诊断 |
| 205Pb | 1.7×107年 | EC | 地质年代学研究 |
| 210Pb | 22.2年 | β- | 环境科学与地球化学研究 |
| 212Pb | 10.6小时 | β- | 核医学癌症治疗 |
| 放射性铅同位素 | 半衰期 | 衰变模式 | 应用领域 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 202Pb | 5.25×104年 | EC | 地质年代学研究 |
| 203Pb | 51.9小时 | EC | 核医学癌症诊断 |
| 205Pb | 1.7×107年 | EC | 地质年代学研究 |
| 210Pb | 22.2年 | β- | 环境科学与地球化学研究 |
| 212Pb | 10.6小时 | β- | 核医学癌症治疗 |
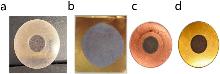
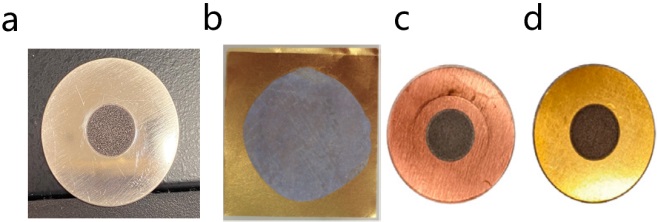
| 靶片材料 | 电镀液组成 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|
| 金片 | 1 g [natTl]Tl2O3, 0.5 mol/L EDTA, 0.4 mol/L NaOH, 300 µL 20% BRIJ-35, 1.9 mL 35%水合肼, 33.1 mL超纯水 | [ |
| 金片或铜片 | 250 mg [natTl]Tl2O3或[205Tl]Tl2O3, 300 μL水合肼, 1 g NaOH, 1.5 g EDTA, 10 mL超纯水 | [ |
| 银片 | 21 g EDTA, 5 g NaOH, 2.53 mL水合肼, 250 µL BRIJ-35, 90 mL去离子水, 溶解后加入额外2.35 mL 水合肼与250 µL BRIJ-35, 混匀后加至8.475 g [natTl]Tl2SO4或8.949 g of [natTl]TlNO3中, 待固体完全溶解后加入额外250 µL水合肼 | [ |
| 靶片材料 | 电镀液组成 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|
| 金片 | 1 g [natTl]Tl2O3, 0.5 mol/L EDTA, 0.4 mol/L NaOH, 300 µL 20% BRIJ-35, 1.9 mL 35%水合肼, 33.1 mL超纯水 | [ |
| 金片或铜片 | 250 mg [natTl]Tl2O3或[205Tl]Tl2O3, 300 μL水合肼, 1 g NaOH, 1.5 g EDTA, 10 mL超纯水 | [ |
| 银片 | 21 g EDTA, 5 g NaOH, 2.53 mL水合肼, 250 µL BRIJ-35, 90 mL去离子水, 溶解后加入额外2.35 mL 水合肼与250 µL BRIJ-35, 混匀后加至8.475 g [natTl]Tl2SO4或8.949 g of [natTl]TlNO3中, 待固体完全溶解后加入额外250 µL水合肼 | [ |
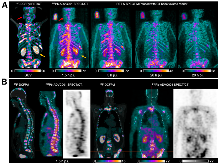

| 核反应 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|
| 192Os(14C,xn)202Pb | [ |
| 198Pt(9Be,xn)202Pb | [ |
| 204Pb(p,xpyn)202Pb | [ |
| 238UCx(p,yn)202Pb | [ |
| natTl(p,xn)201/202/203/204/205Pb | [ |
| 203Tl(p,2n)202Pb | 在研 |
| 核反应 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|
| 192Os(14C,xn)202Pb | [ |
| 198Pt(9Be,xn)202Pb | [ |
| 204Pb(p,xpyn)202Pb | [ |
| 238UCx(p,yn)202Pb | [ |
| natTl(p,xn)201/202/203/204/205Pb | [ |
| 203Tl(p,2n)202Pb | 在研 |
| 放射性铅同位素 | 制备设施/方法 | 核反应/衰变链 |
|---|---|---|
| 202Pb | 回旋加速器 | 203Tl(p,2n)202Pb |
| 203Pb | 回旋加速器 | 203Tl(p,n)203Pb或205Tl(p,3n)203Pb |
| 205Pb | 回旋加速器 | 206Pb(p,2n)205Bi(EC)205Pb |
| 210Pb | 226Ra衰变生成 | 226Ra(α)222Rn(α)218Po(α)214Pb(β-)214Bi(β-)214Po(α)210Pb |
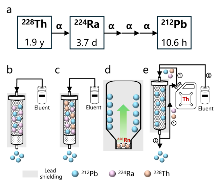
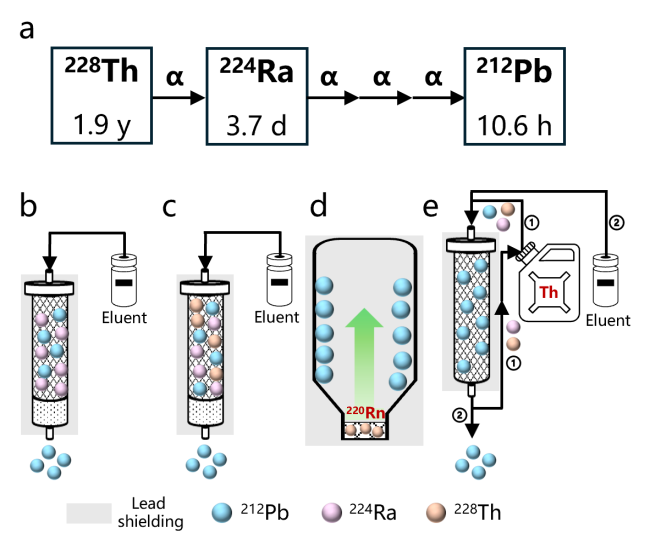
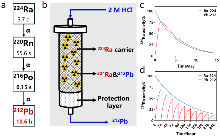
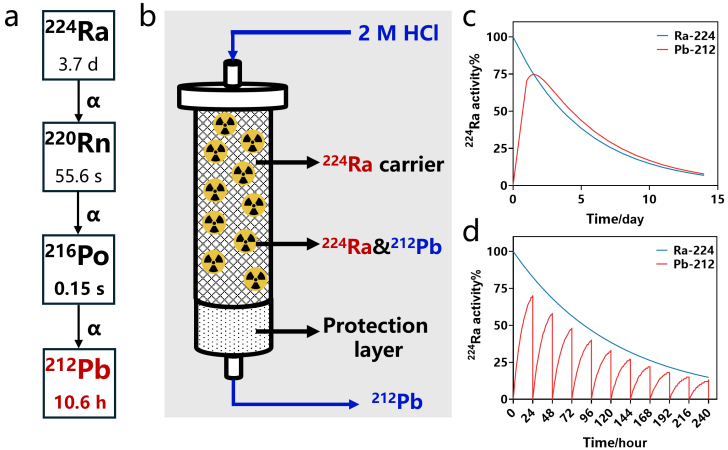
| 212Pb | 核反应堆 | 226Ra(n,γ)227Ra(β-)227Ac(n,γ)228Ac(β-)228Th(α)224Ra(α)220Rn(α)216Po(α)212Pb |
| 核废料分离 | 232U(α)228Th(α)224Ra(α)220Rn(α)216Po(α)212Pb | |
| 天然钍分离 | 232Th(α)228Ra(β-)228Ac(β-)228Th(α)224Ra(α)220Rn(α)216Po(α)212Pb |
| 放射性铅同位素 | 制备设施/方法 | 核反应/衰变链 |
|---|---|---|
| 202Pb | 回旋加速器 | 203Tl(p,2n)202Pb |
| 203Pb | 回旋加速器 | 203Tl(p,n)203Pb或205Tl(p,3n)203Pb |
| 205Pb | 回旋加速器 | 206Pb(p,2n)205Bi(EC)205Pb |
| 210Pb | 226Ra衰变生成 | 226Ra(α)222Rn(α)218Po(α)214Pb(β-)214Bi(β-)214Po(α)210Pb |
| 212Pb | 核反应堆 | 226Ra(n,γ)227Ra(β-)227Ac(n,γ)228Ac(β-)228Th(α)224Ra(α)220Rn(α)216Po(α)212Pb |
| 核废料分离 | 232U(α)228Th(α)224Ra(α)220Rn(α)216Po(α)212Pb | |
| 天然钍分离 | 232Th(α)228Ra(β-)228Ac(β-)228Th(α)224Ra(α)220Rn(α)216Po(α)212Pb |
| [1] |
|
|
(王庆铸, 郭俊峰, 陈建立, 刘思然, 房振, 李铭, 方辉, 考古, 2021, 7, 106.)
|
|
| [2] |
|
|
(程文斌, 郎兴海, 欧阳辉, 彭义伟, 谢富伟, 王勇, 彭强, 杨超, 陈翠华, 向芳, 地质论评, 2023, 69, 2247.)
|
|
| [3] |
doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.134.062502 |
| [4] |
doi: 10.1186/s13550-022-00896-w |
| [5] |
doi: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2022.01.002 |
| [6] |
doi: 10.1007/s00259-021-05212-7 |
| [7] |
doi: 10.1007/s00259-024-06600-5 |
| [8] |
doi: 10.1186/s13550-024-01069-7 |
| [9] |
doi: 10.1038/s41573-020-0073-9 |
| [10] |
doi: 10.2967/jnumed.120.254532 |
| [11] |
doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-07461-6 |
| [12] |
doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-24-0897 |
| [13] |
doi: 10.1007/s00259-023-06300-6 |
| [14] |
doi: 10.1007/s00259-023-06230-3 |
| [15] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5c00837 |
| [16] |
doi: 10.1021/cbmi.3c00067 |
| [17] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.2c00579 |
| [18] |
|
|
(陈俊艺, 刘宇, 徐梦欣, 刘志博, 中华核医学与分子影像杂志, 2022, 42, 330.)
|
|
| [19] |
|
|
(陈俊艺, 李银龙, 王峰, 张天爵, 刘志博, 化学通报, 2021, 84, 1210.)
|
|
| [20] |
doi: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2022.03.001 |
| [21] |
doi: 10.1016/j.apradiso.2017.05.006 |
| [22] |
pmid: 2364380 |
| [23] |
doi: 10.1515/ract-2019-0005 |
| [24] |
doi: 10.1524/ract.91.2.109.19988 |
| [25] |
doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-2300 pmid: 17363549 |
| [26] |
doi: 10.1002/jlcr.v67.11 |
| [27] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.3c00456 |
| [28] |
doi: 10.2967/jnumed.107.048553 |
| [29] |
doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14010189 |
| [30] |
doi: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2024.108990 |
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
doi: 10.1016/S0969-8043(97)00234-0 |
| [33] |
doi: 10.3390/ph16070985 |
| [34] |
pmid: 7828627 |
| [35] |
pmid: 7085191 |
| [36] |
doi: 10.1016/0883-2889(88)90016-0 |
| [37] |
doi: 10.1021/ac60177a041 |
| [38] |
doi: 10.2967/jnumed.121.263230 |
| [39] |
doi: 10.1016/j.apradiso.2022.110238 |
| [40] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.iecr.0c04084 |
| [41] |
doi: 10.1186/s41181-021-00121-4 |
| [42] |
doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-37313-8 |
| [43] |
doi: 10.1021/ed036p296 |
| [44] |
doi: 10.2967/jnumed.122.264009 |
| [45] |
doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/1099/1/012003 |
| [46] |
doi: 10.1016/S0969-8043(00)00372-9 |
| [47] |
IAEA World Distribution of Thorium Deposits, International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna, 2021.
|
| [48] |
doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2022.02.012 |
| [49] |
doi: 10.1039/D3DT04166B |
| [50] |
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2024.157971 |
| [51] |
doi: 10.2174/0929867327999200727190423 |
| [52] |
doi: 10.1016/j.apradiso.2024.111190 |
| [53] |
doi: 10.1016/s0378-4274(98)00126-x pmid: 9801025 |
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
doi: 10.2967/jnumed.123.265976 |
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
doi: 10.1016/j.apradiso.2016.04.015 |
| [58] |
doi: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2023.108314 |
| [59] |
pmid: 2712112 |
| [60] |
pmid: 2599463 |
| [61] |
|
| [62] |
|
| [63] |
doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-0619 |
| [64] |
doi: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2013.01.010 |
| [65] |
|
| [66] |
doi: 10.1002/cam4.2013.2.issue-5 |
| [67] |
doi: 10.4161/19420862.2014.985160 pmid: 25587678 |
| [68] |
doi: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2016.04.001 |
| [69] |
doi: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2017.12.004 |
| [70] |
|
| [71] |
doi: 10.2967/jnumed.114.143842 |
| [72] |
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1607427 |
| [73] |
doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30198-0 |
| [74] |
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2107322 |
| [75] |
doi: 10.1007/s00259-025-07269-0 |
| [76] |
doi: 10.2967/jnumed.123.267189 |
| [77] |
doi: 10.1002/jlcr.v63.3 |
| [78] |
doi: 10.3390/cancers13153676 |
| [79] |
|
| [80] |
|
| [81] |
doi: 10.2967/jnumed.124.268101 |
| [82] |
National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine A Vision for NSF Earth Sciences 2020-2030: Earth in Time, The National Academies Press, Washington, DC, 2020.
|
| [83] |
doi: 10.1016/S0301-9268(02)00208-5 |
| [84] |
doi: 10.1130/G23193A.1 |
| [85] |
doi: 10.1016/j.cretres.2012.03.014 |
| [86] |
doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-04100-2 |
| [87] |
|
| [88] |
doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2015.05.026 |
| [89] |
doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2015.02.040 |
| [90] |
doi: 10.1039/D1JA00116G |
| [91] |
doi: 10.1360/N972015-01048 |
|
(储著银, 许俊杰, 陈知, 李潮峰, 李向辉, 贺怀宇, 李献华, 郭敬辉, 科学通报, 2016, 61, 1121.)
|
|
| [92] |
doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1955)66[1131:ICADOL]2.0.CO;2 |
| [93] |
|
| [94] |
doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(73)90213-5 |
| [95] |
|
| [96] |
|
| [97] |
|
| [98] |
doi: 10.1016/0029-554X(76)90660-1 |
| [99] |
|
| [100] |
doi: 10.1016/0375-9474(95)00305-K |
| [101] |
doi: 10.1007/s100500070032 |
| [102] |
doi: 10.1524/ract.1994.65.3.151 |
| [103] |
doi: 10.1140/epja/i2017-12345-y |
| [104] |
doi: 10.1016/0020-708X(78)90128-X |
| [105] |
pmid: 1110421 |
| [106] |
pmid: 8996297 |
| [107] |
doi: 10.1016/0020-708X(79)90138-8 |
| [108] |
doi: 10.1016/0025-3227(79)90039-2 |
| [109] |
doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(80)90134-9 |
| [110] |
doi: 10.1017/jog.2020.19 |
| [111] |
doi: 10.1007/BF00028424 |
| [112] |
doi: 10.1016/S0341-8162(78)80002-2 |
| [113] |
doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(75)90198-2 |
| [114] |
doi: 10.3189/172756500781833098 |
| [115] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.04.028 |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||