Acta Chimica Sinica ›› 2026, Vol. 84 ›› Issue (1): 109-118.DOI: 10.6023/A25090300 Previous Articles Next Articles
Article
覃其品a,b,*( ), 李秋明a, 张菊梅a, 谭明雄a,b, 梁宏b
), 李秋明a, 张菊梅a, 谭明雄a,b, 梁宏b
投稿日期:2025-09-06
发布日期:2025-10-10
基金资助:
Qipin Qina,b,*( ), Qiuming Lia, Jumei Zhanga, Mingxiong Tana,b, Hong Liangb
), Qiuming Lia, Jumei Zhanga, Mingxiong Tana,b, Hong Liangb
Received:2025-09-06
Published:2025-10-10
Contact:
* E-mail: qpqin2018@126.com
Supported by:Share
Qipin Qin, Qiuming Li, Jumei Zhang, Mingxiong Tan, Hong Liang. Synthesis and Evaluation of in vitro and in vivo Anticancer Activities of 8-Hydroxyquinoline-modified Platinum(II) Polypyridyl Complexes[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2026, 84(1): 109-118.
| Entrya | A549 | A549/DDP | MDA-MB- 231 | HL-7702 | SIb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Py | >50.0 | >50.0 | >50.0 | >50.0 | ca. 1.0 |
| IQ-OH | >50.0 | >50.0 | >50.0 | >50.0 | ca. 1.0 |
| cis-[PtCl2- (DMSO)2] | >50.0 | >50.0 | >50.0 | >50.0 | ca. 1.0 |
| PtIQ | 7.2±0.5 | 6.1±0.9 | 9.0±0.1 | 35.5±0.4 | 4.0 |
| PyPt | 1.0±0.2 | 0.9±0.3 | 0.05±0.04 | >50.0 | >980.4 |
| PtIQ+Py | 7.0±0.5 | 6.0±0.1 | 8.8±0.4 | 36.2±0.7 | 4.2 |
| 顺铂 | 13.0±0.6 | >50.0 | 11.1±0.3 | 15.6±0.2 | 1.4 |
| Entrya | A549 | A549/DDP | MDA-MB- 231 | HL-7702 | SIb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Py | >50.0 | >50.0 | >50.0 | >50.0 | ca. 1.0 |
| IQ-OH | >50.0 | >50.0 | >50.0 | >50.0 | ca. 1.0 |
| cis-[PtCl2- (DMSO)2] | >50.0 | >50.0 | >50.0 | >50.0 | ca. 1.0 |
| PtIQ | 7.2±0.5 | 6.1±0.9 | 9.0±0.1 | 35.5±0.4 | 4.0 |
| PyPt | 1.0±0.2 | 0.9±0.3 | 0.05±0.04 | >50.0 | >980.4 |
| PtIQ+Py | 7.0±0.5 | 6.0±0.1 | 8.8±0.4 | 36.2±0.7 | 4.2 |
| 顺铂 | 13.0±0.6 | >50.0 | 11.1±0.3 | 15.6±0.2 | 1.4 |
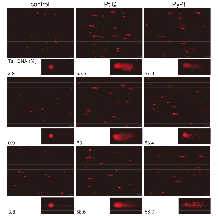
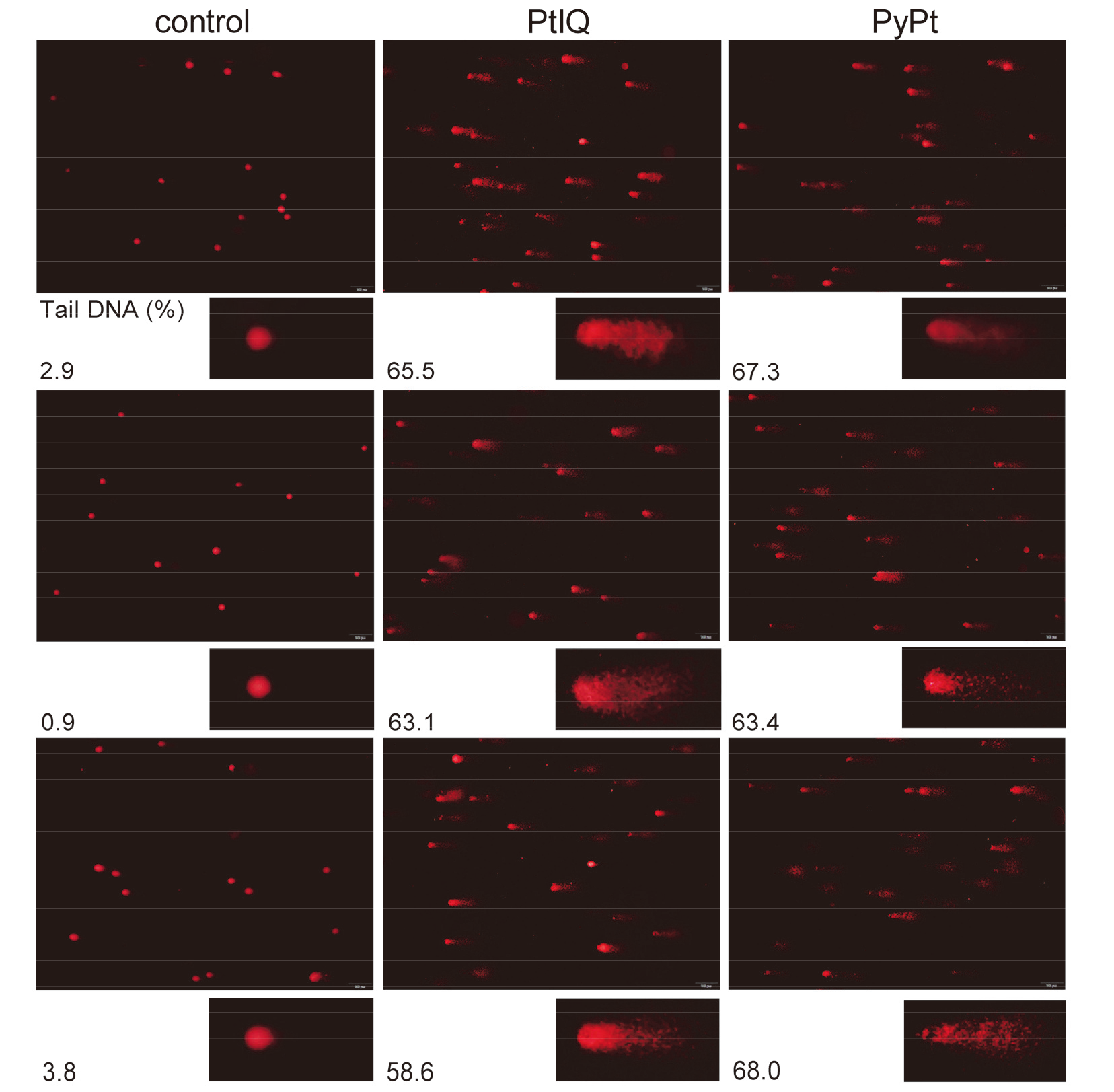
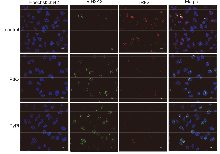
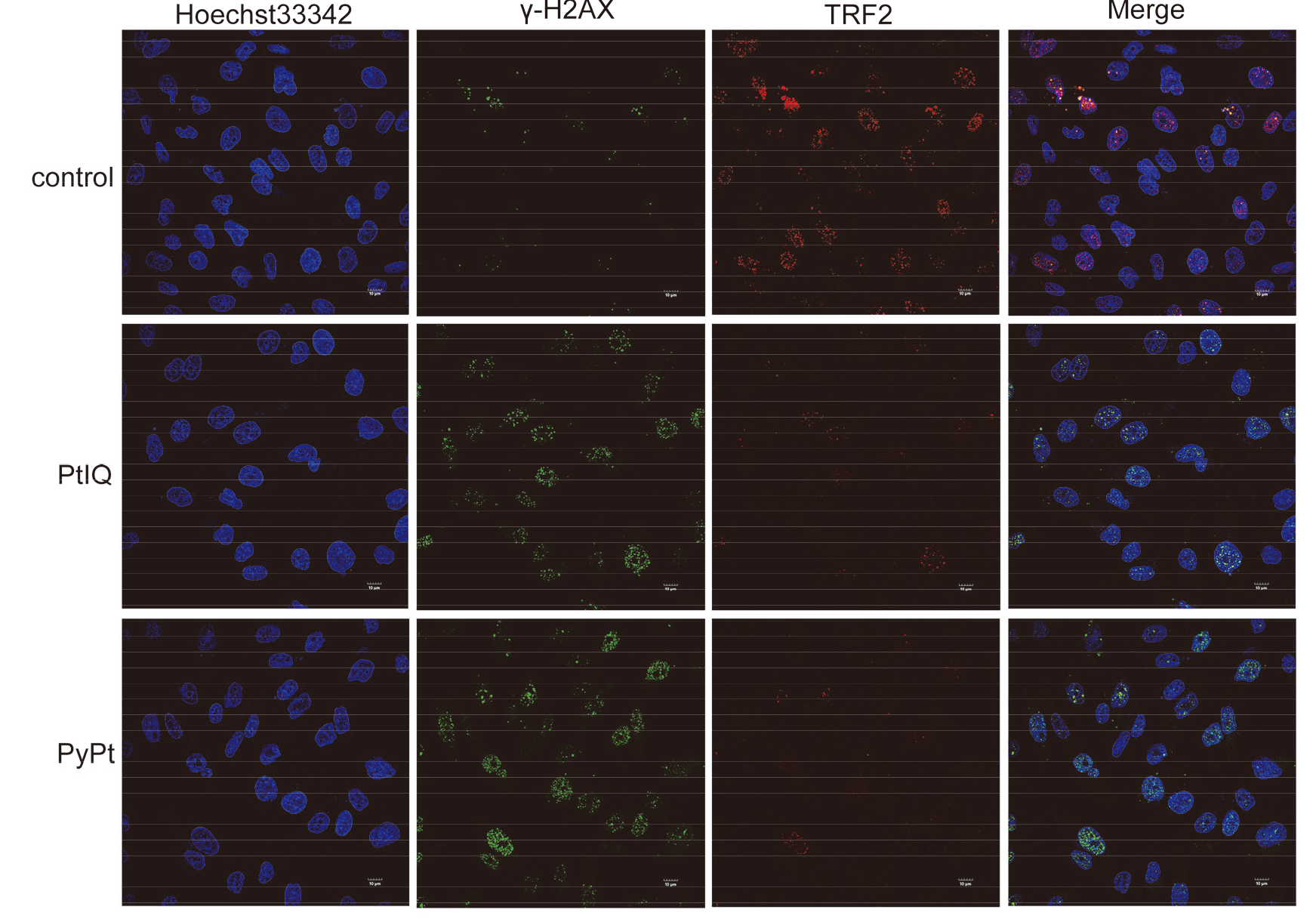
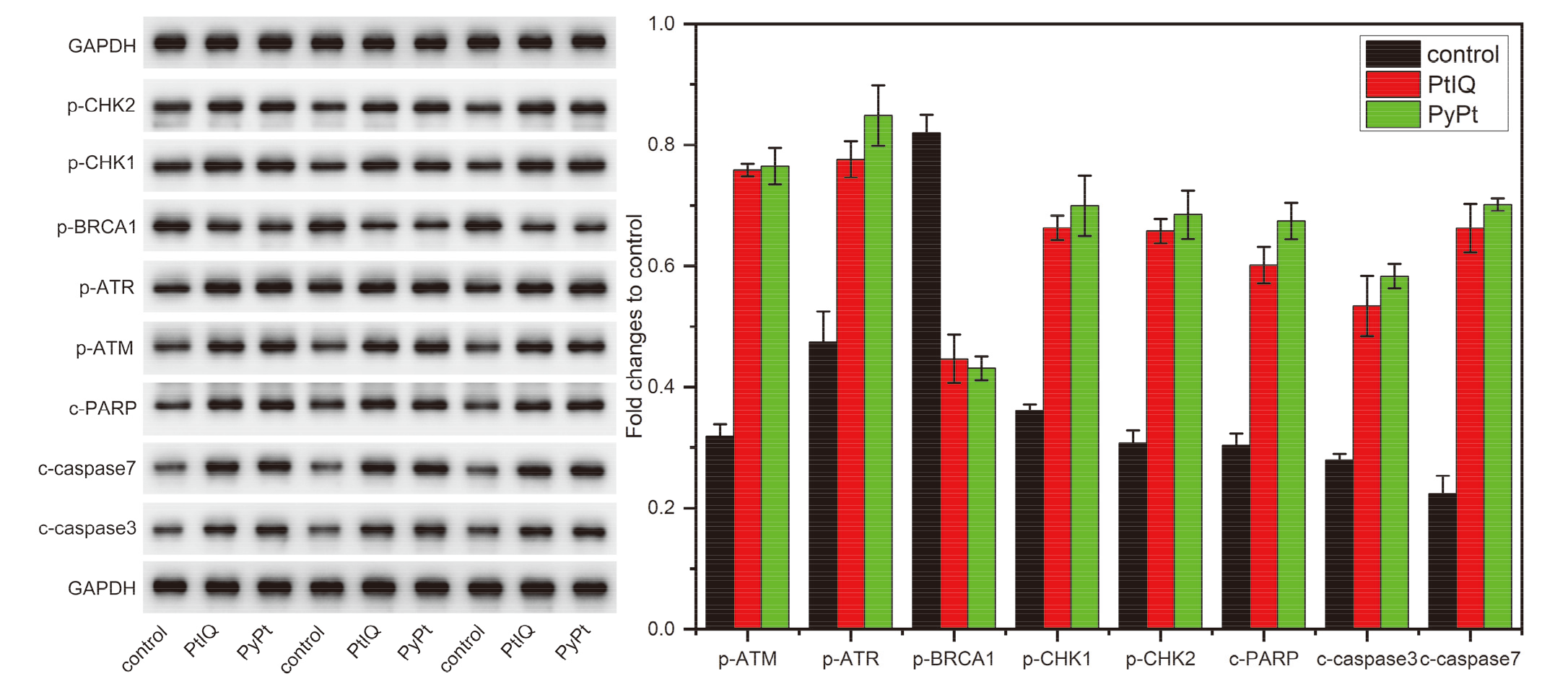
| [1] |
doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2023.215578 |
| [2] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.4c02509 |
| [3] |
doi: 10.1002/anie.v62.44 |
| [4] |
doi: 10.1039/D4QI00459K |
| [5] |
doi: 10.1039/D4QI00386A |
| [6] |
(a)
doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.1c01763 pmid: 25575314 |
|
(b)
doi: S0223-5234(18)30921-8 pmid: 25575314 |
|
|
(c)
doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2014.12.052 pmid: 25575314 |
|
| [7] |
doi: 10.1039/D0NJ04753H |
| [8] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2023.112152 |
| [9] |
doi: 10.1039/D4NJ04292A |
| [10] |
(a)
doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c01895 pmid: 36891739 |
|
(b)
doi: 10.1039/C6MD00201C pmid: 36891739 |
|
|
(c)
doi: 10.1016/j.poly.2013.07.008 pmid: 36891739 |
|
| [11] |
doi: 10.1039/c3dt51720a |
| [12] |
doi: 10.1039/C7QI00299H |
| [13] |
doi: 10.1002/asia.v6.12 |
| [14] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jorganchem.2011.07.003 |
| [15] |
(a)
doi: 10.1007/s00044-021-02739-0 |
|
(b)
doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.4c00285 |
|
| [16] |
doi: S0223-5234(18)30780-3 pmid: 30205260 |
| [17] |
doi: 10.1039/C7MD00472A |
| [18] |
doi: 10.1039/D4DT01794C |
| [19] |
(a)
doi: 10.1039/D2DT01765B |
|
(b)
doi: 10.1080/00958972.2018.1548703 |
|
| [20] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c00603 |
| [21] |
(a)
doi: 10.1002/anie.v63.31 |
|
(b)
doi: 10.1039/D3DT03197G |
|
|
(c)
doi: 10.6023/A21060282 |
|
|
(赵添堃, 王鹏, 姬明宇, 李善家, 杨明俊, 蒲秀瑛, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 1385.)
doi: 10.6023/A21060282 |
|
|
(d)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201704006 |
|
|
(张磊, 李文赟, 刘来, 郑诚月, 王杨, 徐应淑, 史大斌, 聂绪强, 国佳莹, 朱春媛, 王京, 有机化学, 2017, 37, 1721.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201704006 |
|
|
(e)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202401013 |
|
|
(胡健灵, 张超, 朱文达, 何业谱, 彭姝羚, 陈振强, 李明月, 刘志军, 陈河如, 有机化学, 2024, 44, 1870.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202401013 |
|
| [22] |
(a)
doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.4c00060 pmid: 28657713 |
|
(b)
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.7b00131 pmid: 28657713 |
|
|
(c)
doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.0c00417 pmid: 28657713 |
|
| [23] |
(a)
doi: 10.6023/A19110403 |
|
(刘启雁, 蔡戴宏, 戚永育, 乐学义, 化学学报, 2020, 78, 263.)
doi: 10.6023/A19110403 |
|
|
(b)
|
|
|
(王晓星, 顾彦, 陈登霞, 方艳芬, 黄应平, 化学学报, 2010, 68, 2463.)
|
|
| [24] |
doi: 10.1002/anie.v61.33 |
| [25] |
doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1048691 |
| [26] |
pmid: 10660911 |
| [27] |
(a)
|
|
(b)
doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c00318 |
|
| [28] |
(a)
doi: 10.1038/35022514 |
|
(b)
doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2025.108507 |
|
|
(c)
doi: 10.6023/A23040154 |
|
|
(秦沛, 马海, 张发光, 马军安, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 697.)
doi: 10.6023/A23040154 |
| [1] | WANG Xiao-Xing, GU Yan, CHEN Deng-Xia, FANG Yan-Fen, HUANG Ying-Ping. Effect of Superoxide Dismutase on the DNA Damage by TiO2 under UV [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2010, 68(23): 2463-2470. |
| [2] | REN Yun-Feng1,2; CHENG Kang-Min1,2; LIU Gui-Feng1,2; SUN Yan-Hong; SHEN Yu-Mei*,1. Synthesis, Radiosynthesis and Anticancer Activity of β-Elemene Tricarbonyl Rhenium Complex [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2008, 66(4): 459-464. |
| [3] | LIU Shu-Na; WU Ping; ZHOU Bo; ZHOU Yao-Ming; CAI Chen-Xin*. Immobilization, Characterization of DNA on the Surface of Carbon Nanotube and Electrochemical Detection of DNA Damage [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2008, 66(4): 424-432. |
| [4] | . Photochemical Activities of Chromium(III) Complex [Cr(III)(4-ASA)(en)2]Cl [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2008, 66(21): 2353-2359. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||