

Photochemical Degradation of Perfluorocarboxylic Acids Induced by Ferric Ion:Effects of pH and Carbon Chain
Received date: 2014-02-13
Online published: 2014-05-27
Supported by
Project supported by Guizhou University Talent Introduction Project (No.2010009), Natural Science Foundation of Guizhou Province (No.20112066), State Environmental Protection Key Laboratory of Sources and Control of Air Pollution Complex (No.SCAPC201302) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.21267006).
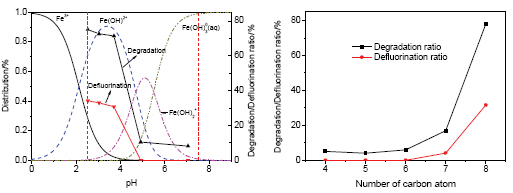
Perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA), as a typical perfluorinated compounds, is one kind of emerging persistent pollutants appearing in natural water.The existence of ferric ion in aquatic system improves the degradation of PFOA under the irradiation of 254 nm UV light.pH is an important factor for not only the distribution of photo activity species of ferric ion but also the degradation of PFOA.When the initial pH of reaction solution was 2.53, 3.04 and 3.71, respectively, PFOA was decomposed effectively and no obvious difference was observed whether for the degradation ratio of PFOA or for its corresponding defluorination ratio.On the contrary, when pH was 4.92 and 7.05, respectively, the degradation and defluorination of PFOA was inhibited markedly, which further confirmed that dissoluble iron played a key role in the decomposition of PFOA.And Fe(OH)2+ was the dominant species of the hydroxy complexes of Fe3+.At the same time, the degradation of short chain PFCAs bearing C4~C7 caused by ferric ions under the irradiation of 254 nm UV light was also investigated.As for PFCAs with C6~C8, the degradation ratio at 240 min was as follows: PFOA > PFHpA > PFHxA, which showed that the longer the carbon chain was, the easier the degradation of PFCAs was.While, for PFCAs with the number of carbon element less than 6, their degradation ratio at 240 min was as follows: PFHxA > PFBA > PFPeA.The relationship between the degradation of PFCAs and the length of carbon chain of PFCAs was not clear.More short chain PFCAs were identified by LC/MS as the primary intermediates of these short chain PFCAs.Based on these, it was proposed that the degradation of PFCAs bearing C4~C8 was mainly caused by the formation of complexes between ferric ion and PFCAs, and then hydroxyl radical formed from photolysis of Fe(OH)2+ and the redox cycle of Fe2+/Fe3+ further improved their degradation.As a result, PFCAs were decomposed step by step.
Wang Yuan , Shi Xiaoyan . Photochemical Degradation of Perfluorocarboxylic Acids Induced by Ferric Ion:Effects of pH and Carbon Chain[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2014 , 72(6) : 682 -688 . DOI: 10.6023/A14020101
[1] Rayne, S.; Forest, K.J.Environ.Sci.Heal.C 2009, 44, 1145.
[2] Holzer, J.; Midasch, O.; Rauchfuss, K.; Kraft, M.; Reupert, R.; Angerer, J.; Kleeschulte, P.P.; Marschall, N.; Wilhelm, M.Environ.Health Persp.2008, 116, 651.
[3] Lynda, A.N.; John, M.N.; Frances, S.S.; Nancy, V.R.; Edward, A.E.Reprod.Toxicol.2009, 27, 231.
[4] Lindstrom, A.B.; Strynar, M.J.; Libelo, E.L.Environ.Sci.Technol.2011, 45, 7954.
[5] Schroder, H.F.; Meesters, R.J.W.J.Chromatogr.A 2005, 1082, 110.
[6] Dillert, R.; Bahnemann, D.; Hidaka, H.Chemosphere 2007, 67, 785.
[7] Song, C.; Chen, P.; Wang, C.; Zhu, L.Chemosphere 2012, 86, 853.
[8] Park, H.; Vecitis, C.D.; Cheng, J.; Choi, W.; Mader, B.T.; Hoffmann, M.R.J.Phys.Chem.A 2009, 113, 690.
[9] Yamamoto, T.; Noma, Y.; Sakai, S.; Shibata, Y.Environ.Sci.Technol.2007, 41, 5660.
[10] Wang, Y.; Zhang, P.Y.; Pan, G.; Chen, H.J.Hazard.Mater.2008, 160, 181.
[11] Wang, Y.; Zhang, P.Y.J.Hazard.Mater.2011, 192, 1869.
[12] Wang, Y.; Zhang, P.Y.Acta Chim.Sinica 2010, 68, 345.(王媛, 张彭义, 化学学报, 2010, 68, 345).
[13] Dillert, R.; Bahnemann, D.; Hidaka, H.Chemosphere 2007, 67, 785.
[14] Panchangam, S.C.; Lin, A.Y.C.; Shaik, K.L.; Lin, C.F.Chemosphere 2009, 77, 242.
[15] Lee, Y.C.; Lo, S.I.; Kuo, J.; Hsieh, C.H.Front.Environ.Sci.Eng.2012, 6, 17.
[16] Deng, N.S.; Wu, F.Environmental Photochemistry, Chemical Industry Press, Beijing, 2003, pp.83~101.(邓南圣, 吴锋, 环境光化学, 化学工业出版社, 北京, 2003, pp.83~101).
[17] Martin, J.W.; Mabury, S.A.; Solomon, K.R.; Muir, D.C.G.Environ.Toxicol.Chem.2003, 22, 189.
[18] Rebecca, R.Environ.Sci.Technol.2006, 40, 12.
[19] Sun, H.W.; Li, F.S.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, X.Z.; He, N.; Song, Q.; Zhao, L.J.; Sun, L.N.; Sun, T.H.Water Res.2011, 45, 4483.
[20] Quinete, N.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, T.; Yun, S.H.; Moreira, I.; Kannan, K.Chemosphere 2009, 77, 863.
[21] Naile, J.E.; Khim, J.S.; Wang, T.Y.; Chen, C.L.; Luo, W.; Kwon, B.; Park, J.; Koh, C.H.; Jones, P.D.; Lu, Y.L.; Giesy, J.P.Environ.Pollut.2010, 158, 1237.
[22] Mak, Y.L.; Taniyasu, S.; Yeung, L.W.Y.; Lu, G.H.; Jin, L.; Yang, Y.L.; Lam, P.K.S.; Kannan, K.; Yamashita, N.Environ.Sci.Technol.2009, 43, 4824.
[23] Stefannson, A.Environ.Sci.Technol.2007, 41, 6117.
[24] Dean, J.A.Lange’s Handbook of Chemistry, 15th ed., McGraw-Hill Inc., New York, 1999, p.1195.
[25] Vecitis, C.D.; Park, H.; Cheng, J.; Mader, B.T.; Hoffmann, M.R.Front.Environ.Sci.Eng.2009, 3, 129.
[26] Niu, J.F.; Lin, H.; Gong, C.; Sun, X.M.Environ.Sci.Technol.2013, 47, 14341.
[27] Niu, J.F.; Lin, H.; Gong, C.; Sun, X.M.Environ.Sci.Technol.2012, 46, 10191.
[28] Zhuo, Q.F.; Deng, S.B.; Yang, B.; Huang, J.; Wang, B.; Zhang, T.T.; Yu, G.Electrochim.Acta 2012, 77, 17.
[29] Taniyasu, S.; Yamashita, N.; Yamazaki, E.; Petrick, G.; Kannan, K.Chemosphere 2013, 90, 1686.
[30] Hori, H.; Yamamoto, A.; Koike, K.; Kutsuna, S.; Osaka, I.; Arakawa, R.Chemosphere 2007, 68, 572.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |