

Synergistic Treatment of Dye Wastewater by the Adsorption-Degradation of a Bifunctional Aerogel
Received date: 2023-01-12
Online published: 2023-02-27
Supported by
National Natural Science Foundation of China(22178324); National Natural Science Foundation of China(21908201); Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation(LY21B060011); China Postdoctoral Science Foundation(2020M671793)
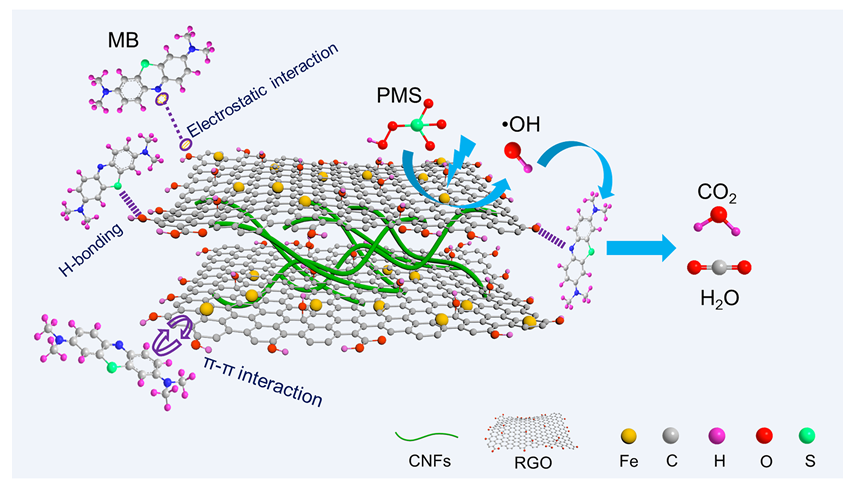
Dye wastewater with high toxicity and poor biodegradability poses a considerable threat to human health and the ecosystem. Although the adsorption effectively removes organic pollutants from wastewater, the pollutants are merely transferred from liquid phase to solid adsorbents. Destroying the adsorbed pollutants and regenerating adsorbents require additional treatments, which may cause secondary harm to the environment. In addition to the removal of organic pollutants by adsorption, the pollutants can be oxidatively degraded by oxidative radicals that are generated in peroxymonosulfate (PMS)-based advanced oxidation technology. However, the degradation efficiency of organic pollutants treated by advanced oxidation technology may be affected by complex components of dye wastewater. Herein, Fe-doped cellulose nanofiber/reduced graphene oxide aerogel (CNFs/RGO/Fe) was prepared and served as both adsorbent and catalyst in advanced oxidation process for dyes wastewater treatment. The morphology and chemical composition of the composite aerogel were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). It was proved that CNFs/RGO/Fe possessed layered porous structures, which are beneficial for the transport, diffusion, and adsorption of pollutants. The uniform loading of Fe0 and Fe3O4 particles on the aerogel skeleton contributed to the efficient activation of PMS. The results of the adsorption experiment showed that the CNFs/RGO/Fe exhibited excellent selective adsorption for cationic dyes. The maximum adsorption capacity of methylene blue (MB), rhodamine B (RhB), and crystal violet (CV) on CNFs/RGO/Fe were 655.1 mg/g, 696.5 mg/g, and 962.1 mg/g, respectively. The pseudo-second-order kinetic model and Langmuir isothermal model fitted well with the adsorption process of CNFs/RGO/Fe for cationic dyes. After adsorption, the CNFs/RGO/Fe was immersed in PMS solution separately to study the degradation performance for the adsorbate. The results showed that CNFs/RGO/Fe could promote the activation of PMS to generate a large amount of •OH, leading to the degradation of adsorbate and the regeneration of adsorbent. In addition, the synergistic adsorption-degradation process established by CNFs/RGO/Fe achieved over 75% removal of dyes even after 5 cycles, indicating CNFs/RGO/Fe had good repeatability. The study on the synergistic treatment of dye wastewater by adsorption-degradation is expected to provide a new perspective for the removal of organic pollutants in complex water.
Key words: adsorption; degradation; aerogel; advanced oxidation technology; dye wastewater
Wentao Wang , Xinting Lai , Shiquan Yan , Lei Zhu , Yuyuan Yao , Liming Ding . Synergistic Treatment of Dye Wastewater by the Adsorption-Degradation of a Bifunctional Aerogel[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023 , 81(3) : 222 -230 . DOI: 10.6023/A23010009
| [1] | Pavithra K. G.; Kumar P. S.; Jaikumar V.; Raian P. S. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 75, 1. |
| [2] | Vigneshwaran S.; Sirajudheen P.; Karthikeyan P.; Meenakshi S. Surf. Interfaces 2021, 23, 100920. |
| [3] | Fang J.; Zhao W. J.; Zhang M. H.; Fang Q. R. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 186.. (in Chinese) |
| [3] | (方婧, 赵文娟, 张明浩, 方千荣, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 186 ) |
| [4] | Zhang Y.; Hong X.; Cao X. W.; Huang X. Q.; Hu B.; Ding S. Y.; Lin H. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2021, 13, 6359. |
| [5] | Wang W.; Zhao Y. L.; Bai H. Y.; Zhang T. T.; Ibarra-Galvan V.; Song S. X. Carbohyd. Polym. 2018, 198, 518. |
| [6] | Liu Q. M.; Li Y. Y.; Chen H. F.; Lu J.; Yu G. S.; M?slang M.; Zhou Y. B. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 382, 121040. |
| [7] | Gao H.; Li H. F.; Jing C. Y.; Wang X. B. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2021, 319, 111068. |
| [8] | Kang W. W.; Cui Y.; Yang Y. Z.; Guo M. C.; Zhao Z. B.; Wang X. Z.; Liu X. G. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 417, 126160. |
| [9] | Xu R. Q.; Liu W. J.; Cai J. Y.; Li Z. H. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 257, 117876. |
| [10] | Zhao M. K.; Zhang S. F.; Fang G. G.; Huang C.; Wu T. Polymers 2020, 12, 2219. |
| [11] | Lee S.; Moon B. J.; Lee H. J.; Bae S.; Kim T.; Jung Y. C.; Park J. H.; Lee S. H. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2018, 10, 17335. |
| [12] | Ren F.; Li Z.; Tan W. Z.; Liu X. H.; Sun Z. F.; Ren P. G.; Yan D. X. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2018, 532, 58. |
| [13] | Xiao J. L.; Zhang J. F.; Lv W. Y.; Song Y. H.; Zheng Q. Carbon 2017, 123, 354. |
| [14] | Jegadeesan G. B.; Amirthavarshini S.; Divya J.; Gunarani G. I. Adv. Powder Technol. 2019, 30, 2890. |
| [15] | Yang L. M.; Chen W. D.; Sheng C. H.; Wu H. L.; Mao N. T.; Zhang H. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 549, 149300. |
| [16] | Oh W. D.; Ng C. Z.; Ng S. L.; Lim J. W.; Leong K. H. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 230, 115852. |
| [17] | Xiao S.; Cheng M.; Zhong H.; Liu Z. F.; Liu Y.; Yang X.; Liang Q. H. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 384, 123265. |
| [18] | Li X. R.; Liu Z. H.; Zhu Y. J.; Song L.; Dong Z. J.; Niu S.; Lyu C. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 749, 141466. |
| [19] | Zhang Y. P.; Peng X. S.; Tian J. Y.; Li F.; Fan X. T.; Ma L. R.; Zhang R. J. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106856. |
| [20] | Chen D.; Li Q.; Shao L.; Zhang F.; Qian G. R. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 1944. |
| [21] | Wang P.; Lou X. Y.; Chen Q. Q.; Liu Y. J.; Sun X. H.; Guo Y. G.; Zhang X. J.; Wang R. X.; Wang Z. H.; Chen S.; Zhang L.; Zhang R. Q.; Guan J. Environ. Res. 2022, 214, 113780. |
| [22] | Sinha S.; Andia K. C.; Devi N. A.; Swain B. P. B. Mater. Sci. 2022, 45. |
| [23] | Yang X. G.; Jin B. S.; Yu L. L.; Zhu F. H.; Xu Y. Y.; Liu R. J. Mater. Res. Express. 2021, 8, 025011. |
| [24] | Shi S. K.; Zhou X. Y.; Chen W. M.; Chen M. Z.; Nguyen T.; Wang X.; Zhang W. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 44632. |
| [25] | Ma Y. Y.; Lv X. F.; Xiong D. B.; Zhao X. S.; Zhang Z. H. Appl. Catal., B 2021, 284, 119720. |
| [26] | Ishtiaq F.; Bhatti H. N.; Khan A.; Iqbal M.; Kausar A. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 147, 217. |
| [27] | Alnajrani M. N.; Alsager O. A. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 794. |
| [28] | Wei Y. R.; Ma J.; Yuan T. T.; Jiang J. W.; Duan Y. L.; Xue J. Q. Acta Chim. Sinica 2022, 80, 494. (in Chinese) |
| [28] | (位亚茹, 马晶, 袁婷婷, 姜嘉伟, 段银利, 薛娟琴, 化学学报, 2022, 80, 494). |
| [29] | Manippady S. R.; Singh A.; Basavaraja B. M.; Samal A. K.; Srivastava S.; Saxena M. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 1571. |
| [30] | Li K. R.; Zhou M. H.; Liang L.; Jiang L. L.; Wang W. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2019, 546, 333. |
| [31] | Xu S. Z.; Lv Y. L.; Zeng X. F.; Cao D. P. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 323, 502. |
| [32] | Li Z. T.; Liu D. M.; Cai Y. D.; Wang Y. P.; Teng J. Fuel 2019, 257, 116031. |
| [33] | Lyu W.; Li J. Q.; Zheng L. L.; Liu H.; Chen J.; Zhang W. Y.; Liao Y. Z. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 414, 128931. |
| [34] | Joshi P.; Sharma O. P.; Ganguly S. K.; Srivastava M.; Khatri O. P. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2022, 608, 2870. |
| [35] | Pang X. N.; Sellaoui L.; Franco D.; Netto M. S.; Georgin J.; Luiz Dotto G.; Abu Shayeb M. K.; Belmabrouk H.; Bonilla-Petriciolet A.; Li Z. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 391, 123617. |
| [36] | Zhang M.; Xiao C. M.; Yan X.; Chen S. S.; Wang C. H.; Luo R.; Qi J. W.; Sun X. Y.; Wang L. J.; Li J. S. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 10289. |
| [37] | Suhan M. B. K.; Shuchi S. B.; Anis A.; Haque Z.; Islam M. S. Environ. Nanotechnol., Monit. Manage. 2020, 14, 100335. |
| [38] | Li Y. Y.; Cao P.; Wang S.; Xu X. L. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 347, 126691. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |