

Click Chemistry-based Synchrotron X-ray Imaging Tags★
Received date: 2023-03-02
Online published: 2023-04-12
Supported by
National Key Research and Development Program of China(2022YFA1603600); National Natural Science Foundation of China(22022410); National Natural Science Foundation of China(82050005); 2022 Shanghai “Science and Technology Innovation Action Plan” Fundamental Research Project(22JC1401203); Youth Innovation Promotion Association CAS(2016236)
One of the basic goals of cell biology is to identify multiple biological molecules within cells and understand the complex interactions between biological molecules in cellular life activities. Synchrotron-based X-ray microscopy has high spatial resolution and good energy (element) resolution, which has great application potential in the recognition and imaging of intracellular biomolecules. At present, the probes that have been developed for synchrotron-based X-ray microscopy are mainly immunostaining probes and genetic labeling probes. Immunostaining probes are prone to lead to cross-reactions due to their dependence on antigen-antibody reactions. The genetic labeling probes, based on gene coding tags, catalyze the generation of X-ray sensitive polymers. However, the polymers used to provide X-ray imaging signals have no fixed morphology. When it is applied to cell imaging, the positioning accuracy will be reduced due to the diffusion of tags in cells, which is an inherent defect of such imaging tags. In addition, there are few existing systems that can express each other independently and step by step for this type of probe. Therefore, both types of X-ray probes mentioned above are difficult to achieve simultaneous high-resolution imaging observation of multiple biological target molecules in cellular life activities. In this research paper, by using the characteristics of X-ray that has good energy resolution and does not interfere with each other between element spectra, we can synthesize polydopamine (PDA) nanoparticles in a controlled manner, modify azide groups on PDA nanoparticles and chelate metal ions, develop a click chemistry based synchronous X-ray imaging tag (PDA-N3-Metal), and conduct synchrotron radition X-ray imaging on the tag with an imaging resolution of 30 nm. The research results lay a good foundation for further preparation of X-ray probes based on click chemistry, and for realizing the specific recognition and imaging of multiple biological molecules in cells at the same time.
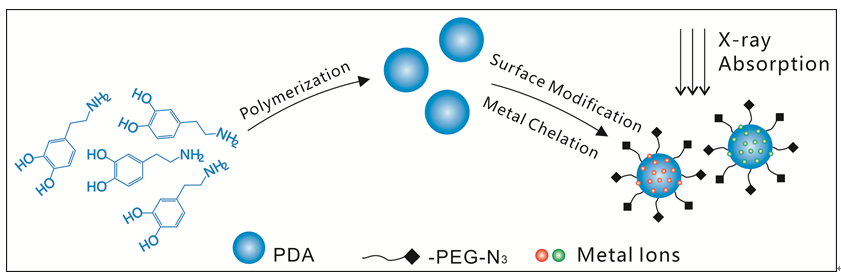
Key words: polydopamine; click chemistry; synchrotron-based X-ray; metal; imaging tag
Qiaowei Tang , Xiaoqing Cai , Dapeng Yin , Huating Kong , Xiangzhi Zhang , Jichao Zhang , Qinglong Yan , Ying Zhu , Chunhai Fan . Click Chemistry-based Synchrotron X-ray Imaging Tags★[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023 , 81(5) : 441 -444 . DOI: 10.6023/A23030061
| [1] | Kong, H. T.; Zhang, J. C.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Shin, H. J.; Tai, R. Z.; Yan, Q. L.; Xia, K.; Hu, J.; Wang, L. H.; Zhu, Y.; Fan, C. H. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2020, 7, 1218. |
| [2] | Zhu, Y.; Zhang, J. C.; Li, A. G.; Zhang, Y. Q.; Fan, C. H. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2017, 39, 11. |
| [3] | Gao, J.; Gu, Z. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2021, 8, nwaa206. |
| [4] | Liu, Z. C.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, L. M.; Jiang, W. P.; Liu, Y. W.; Tang, Q. W.; Cai, X. Q.; Li, J.; Wang, L. H.; Tao, C. L.; Yin, X. Z.; Li, X. W.; Hou, S. G.; Jiang, D. W.; Liu, K.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, H. J.; Liu, M. L.; Fan, C. H.; Tian, Y. Sci. China: Chem. 2023, 66, 324. |
| [5] | Yan, X.; Cai, X. Q.; Tang, Q. W.; Zhou, F.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, L. H.; Hu, J. Nuclear Techniques 2022, 45, 040103. (in Chinese) |
| [5] | (燕鑫, 蔡小青, 汤乔伟, 周峰, 诸颖, 王丽华, 胡钧, 核技术, 2022, 45, 040103.) |
| [6] | Tian, T.; Zhang, J. C.; Lei, H. Z.; Zhu, Y.; Shi, J. Y.; Hun, J.; Huang, Q.; Fan, C. H.; Sun, Y. H. Nucl. Sci. Tech. 2015, 26, 030506. |
| [7] | Lai, H. M.; Tang, Y. M.; Lau, Z.; Campbell, R.; Yau, J.; Chan, Y.; Chan, W.; Wong, T.; Wong, H.; Yan, L.; Wu, W.; Wong, S.; Kwok, K. W.; Wing, Y. K.; Lam, H.; Ng, H. K.; Mrsic-Flogel, T.; Mok, V.; Chan, J.; Ko, H. Nat. Methods 2022, 19, 1137. |
| [8] | Yan, M. L.; Zuo, T. T.; Zhang, J. C.; Wang, Y. Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, L. H.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, Y. H. Chem. Commun. 2022, 58, 713. |
| [9] | Rhee, H. W.; Zou, P.; Udeshi, N. D.; Martell, J. D.; Mootha, V. K.; Carr, S. A.; Ting, A. Y. Science 2013, 339, 1328. |
| [10] | Kolb, H. C.; Sharpless, K. B. Drug Discov. Today 2003, 8, 1128. |
| [11] | Kolb, H. C.; Finn, M. G.; Sharpless, K. B. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2001, 40, 2004. |
| [12] | Lai, C. W.; Sun, Y.; Yang, H.; Zhang, X. Q.; Lin, B. P. Acta Chim. Sinica 2013, 71, 1201. (in Chinese) |
| [12] | (来常伟, 孙莹, 杨洪, 张雪勤, 林保平, 化学学报, 2013, 71, 1201.) |
| [13] | Best, M. D. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 6571. |
| [14] | Xie, R.; Dong, L.; Du, Y. F.; Zhu, Y. T.; Hua, R.; Zhang, C.; Chen, X. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2016, 113, 5173. |
| [15] | Sawa, M.; Hsu, T.-L.; Itoh, T.; Sugiyama, M.; Hanson, S. R.; Vogt, P. K.; Wong, C.-H. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2006, 103, 12371. |
| [16] | Fan, Q. L.; Cheng, K.; Hu, X.; Ma, X. W.; Zhang, R. P.; Yang, M.; Lu, X. M.; Xing, L.; Huang, W.; Gambhir, S. S.; Cheng, Z. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 15185. |
| [17] | Lee, H.; Dellatore, S. M.; Miller, W. M.; Messersmith, P. B. Science 2007, 318, 426. |
| [18] | Qi, C.; Fu, L.-H.; Xu, H.; Wang, T.-F.; Lin, J.; Huang, P. Sci. China: Chem. 2019, 62, 162. |
| [19] | Huang, L.; Liu, M. Y.; Huang, H. Y.; Wen, Y. Q.; Zhang, X. Y.; Wei, Y. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 1858. |
| [20] | Liu, Y. L.; Ai, K. L.; Lu, L. H. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 5057. |
| [21] | Cheng, W.; Zeng, X. W.; Chen, H. Z.; Li, Z. M.; Zeng, W. F.; Mei, L.; Zhao, Y. L. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 8537. |
| [22] | Zhang, X. Z.; Xu, Z. J.; Zhen, X. J.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Yan, R.; Chang, R.; Zhou, R. R.; Tai, R. Z. Acta Phys. Sin. 2010, 59, 4535. (in Chinese) |
| [22] | (张祥志, 许子健, 甄香君, 王勇, 郭智, 严睿, 常睿, 周冉冉, 邰仁忠, 物理学报, 2010, 59, 4535.) |
| [23] | Hell, S. W. Science 2007, 316, 1153. |
| [24] | Blom, H.; Widengren, J. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 7377. |
| [25] | G?ttfert, F.; Wurm, C. A.; Mueller, V.; Berning, S.; Cordes, V. C.; Honigmann, A.; Hell, S. W. Biophys. J. 2013, 105, L01. |
| [26] | Samanta, S.; Gong, W.; Li, W.; Sharma, A.; Shim, I.; Zhang, W.; Das, P.; Pan, W.; Liu, L.; Yang, Z.; Qu, J.-l.; Kim, J. S. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 380, 17. |
| [27] | Samanta, S.; He, Y.; Sharma, A.; Kim, J.; Pan, W.; Yang, Z.; Li, J.; Yan, W.; Liu, L.; Qu, J.; Kim, J. S. Chem 2019, 5, 1697. |
| [28] | Heintzmann, R.; Huser, T. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 13890. |
| [29] | Laughlin, S. T.; Bertozzi, C. R. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 2930. |
| [30] | Flors, C. J. Microsc. 2013, 251, 1. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |