

Microcalorimetry Analysis of Thermal Runaway Process in Lithium-ion Batteries
Received date: 2023-11-14
Online published: 2024-01-17
Supported by
National Natural Science Foundation of China(22275059); Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province(2021A0505110001)
With the vigorous development and large-scale applications of the global new energy vehicles, lithium ion battery (LIB) as the key components of electric vehicles has attracted extensive attention and research. While many urgent problems such as increasing energy density of LIB to alleviate range anxiety, developing fast charging strategy to shorten the driver's waiting time and prolonging LIB cycle life are to be solved. Especially the frequent thermal runaway incidents of LIB electric vehicles seriously affect the safety of passengers and the promotion of new energy vehicles. In order to understand the complex thermal reactions during thermal runaway occurrence, scanning calorimeter (C80 microcalorimeter) has been proposed to analyze the thermal behavior of different full cell systems, including positive electrodes, negative electrodes, separator and electrolyte of LiFePO4 (LFP), Li[NiCoMn]O2 (NCM) and LFP/NCM hybrid LIB. A deconvolution method is used to calculate heat generation based on specific electrode according to the deconvoluted data. Anode-electrolyte biphasic system at different state of charge (SOC), anode single-phase system, cathode-electrolyte biphasic system and LFP/NCM hybrid full cells without electrolyte are also studied to reveal detailed steps and specific heat generation during thermal runaway mechanism. According to the analysis, thermal runaway reactions of LIB full cells are comprised by the anode-electrolyte (130~200 ℃), anode-NCM (200~240 ℃) and anode-LFP (240~300 ℃). Additionally, in the case of injection co-efficient of commercial LIB, electrolyte will be used up during anode-electrolyte reaction. Then the leftover Li in anode subsequently react with cathode and the remaining decomposition of cathode will stop producing heat. Although the residual positive electrode material may still release oxygen due to structural collapse, the heat will not increase significantly due to the lack of negative electrodes or electrolytes that react with it. These results are crucial to reveal the internal mechanism of thermal reactions in LIB, providing the foundation of different battery systems applying to electric car.
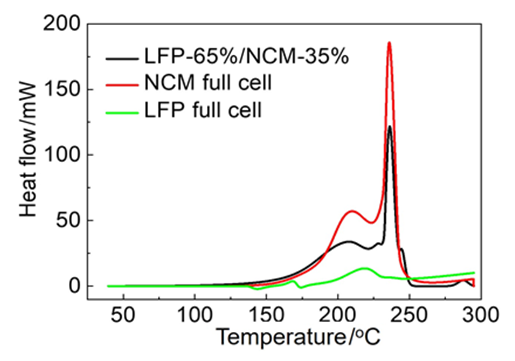
Key words: lithium-ion battery; microcalorimeter; heat production; Li[NiCoMn]O2; LiFePO4
Xiaoyu Gu , Jin Li , Qian Sun , Chaoyang Wang . Microcalorimetry Analysis of Thermal Runaway Process in Lithium-ion Batteries[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024 , 82(2) : 146 -151 . DOI: 10.6023/A23110498
| [1] | Li, M.; Lu, J.; Chen, Z.; Amine, K. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1800561. |
| [2] | Xu, J.; Cai, X.; Cai, S.; Shao, Y.; Hu, C.; Lu, S.; Ding, S. Energy Environ. Mater. 2023, 6, e12450. |
| [3] | Li, J.; Fleetwood, J.; Hawley, W. B.; Kays, W. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 903. |
| [4] | Yuan, Z.; Zhang, H.; Hu, S.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, J.; Cui, G. Acta Chim. Sinica 2023, 81, 1064. (in Chinese) |
| [4] | (苑志祥, 张浩, 胡思伽, 张波涛, 张建军, 崔光磊, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 1064.) |
| [5] | Yu, Q.; Nie, Y.; Peng, S.; Miao, Y.; Zhai, C.; Zhang, R.; Han, J.; Zhao, S.; Pecht, M. Appl. Energ. 2023, 349, 121674. |
| [6] | Cai, S.; Zhang, X.; Ji, J. J. Energy Storage 2023, 72, 108750. |
| [7] | Feng, X.; Ouyang, M.; Liu, X.; Lu, L.; Xia, Y.; He, X. Energy Storage Mater. 2018, 10, 246. |
| [8] | Wang, Q.; Ping, P.; Zhao, X.; Chu, G.; Sun, J.; Chen, C. J. Power Sources 2012, 208, 210. |
| [9] | Xu, Z.; Zhou, X.; Fu, J.; Li, Q.; Tan, Z.; Fan, X.; Wang, Z.; Tian, B.; Guo, X. Chinese Sci. Bull. 2023, 68, 4501. (in Chinese) |
| [9] | (徐振恒, 周晓燕, 付佳龙, 李秋桐, 谭则杰, 樊小鹏, 王志明, 田兵, 郭新, 科学通报, 2023, 68, 4501.) |
| [10] | Zheng, Y.; Che, Y.; Hu, X.; Sui, X.; Stroe, D. I.; Teodorescu, R. Prog. Energ. Combust. 2024, 100, 101120. |
| [11] | Khan, M. M.; Alkhedher, M.; Ramadan, M.; Ghazal, M. J. Energy Storage 2023, 73, 108775. |
| [12] | Ma, S.; Jiang, M.; Tao, P.; Song, C.; Wu, J.; Wang, J.; Deng, T.; Shang, W. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2018, 28, 653. |
| [13] | Ping, P.; Wang, Q.; Huang, P.; Sun, J.; Chen, C. Appl. Energ. 2014, 129, 261. |
| [14] | Ping, P. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, 2014. (in Chinese) |
| [14] | (平平, 博士论文,中国科学技术大学, 合肥, 2014.) |
| [15] | Huang, P. F. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, 2018. (in Chinese) |
| [15] | (黄沛丰, 博士论文, 中国科学技术大学, 合肥, 2018.) |
| [16] | Feng, X.; Zheng, S.; Ren, D.; He, X.; Wang, L.; Cui, H.; Liu, X.; Jin, C.; Zhang, F.; Xue, C.; Hsub, H.; Gao, S.; Chen, T.; Li, Y.; Wang, T.; Wang, H.; Li, M.; Ouyang, M. Appl. Energ. 2019, 246, 53. |
| [17] | Bak, S. M.; Hu, E. Y.; Zhou, Y. N.; Yu, X. Q.; Senanayake, S. D.; Cho, S. J.; Kim, K. B.; Chung, K. Y.; Yang, X. Q.; Nam, K. W. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 22594. |
| [18] | Li, C.; Wang, H. W.; Han, X. B.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y. J.; Feng, X. N.; Ouyang, M. G. J. Electrochem. Energy. 2021, 8, 021012. |
| [19] | Mao, B. B.; Liu, C. Q.; Yang, K.; Li, S.; Liu, P. J.; Zhang, M. J.; Meng, X. D.; Gao, F.; Duan, Q. L.; Wang, Q. S.; Sun, J. H. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2021, 139, 110717. |
| [20] | Wang, Q. S.; Jiang, L. H.; Yu, Y.; Sun, J. H. Nano Energy 2019, 55, 93. |
| [21] | Zhu, X.; Sun, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Lin, N.; Shan, C. J. Energy Storage 2023, 68, 107768. |
| [22] | Liang, C.; Zhang, W. H.; Wei, Z. S.; Wang, Z. Y.; Wang, Q. S.; Sun, J. H. J. Energy Chem. 2021, 59, 446. |
| [23] | Peng, Y.; Yang, L. Z.; Ju, X. Y.; Liao, B. S.; Ye, K.; Li, L.; Cao, B.; Ni, Y. J. Hazard Mater. 2020, 381, 120916. |
| [24] | Liang, C.; Jiang, L. H.; Ye, S. L.; Wang, Z. Y.; Wei, Z. S.; Wang, Q. S.; Sun, J. H. J. Energy Chem. 2021, 54, 332. |
| [25] | Duh, Y. S.; Lee, C. Y.; Chen, Y. L.; Kao, C. S. Thermochim. Acta 2016, 642, 88. |
| [26] | Jiang, L. H.; Wang, Q. S.; Sun, J. H. J. Hazard Mater. 2018, 351, 260. |
| [27] | Duan, J.; Tang, X.; Dai, H. F.; Yang, Y.; Wu, W. Y.; Wei, X. Z.; Huang, Y. H. Electrochem. Energ. Rev. 2020, 3, 1. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |