

Iron Phosphorus Clusters with N-Heterocyclic Carbene Ligation
Online published: 2024-07-22
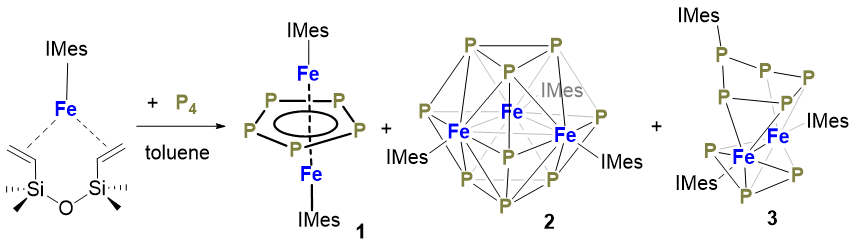
Three iron phosphorus clusters with N-heterocyclic carbene ligation have been synthesized from the reactions of low-coordinate iron(0) complexes [(NHC)Fe(η2:η2-dvtms)] (NHC=N-heterocyclic carbene, dvtms=divinyltetramethyl- isiloxane) with white phosphorus and characterized by spectroscopic methods. The iron phosphorus clusters [(IMes)2Fe2(μ- η5:η5-cyclo-P5)] (1), [(IMes)3Fe3(μ-η6:η6:η6-P9)] (2) and [(IMes)2Fe2(μ-η2:η2-cyclo-P4P(IMes))(μ-η3:η3-P3)] (3) were isolated from the equimolar reaction of [(IMes)Fe(η2:η2-dvtms)] (IMes=1,3-dimesitylimidazol-2-ylidene) with P4 at low temperature (-30 ℃ to room temperature) upon recrystallization. Complexes 1 and 3 can be synthesized in 18% and 32% isolated yields, respectively, from the reactions of [(IMes)Fe(η2:η2-dvtms)] with P4 at different reaction temperature (80 ℃ and -30 ℃ to room temperature, respectively). Complex 2 can only be obtained in trace amount from the low-temperature reaction. The three iron phosphorus clusters 1~3 have been characterized by single-crystal X-ray diffraction studies. Complex 1 shows an anti-sandwich type structure with the Fe…Fe distance of 0.2515(1) nm and the μ-η5:η5-P5 ligand in disorder. Analogous com-plex [(IDep)2Fe2(μ-η5:η5-P5)] [4, IDep=1,3-di(2',6'-diethylphenyl)imidazol-2-ylidene] can be synthesized from the reaction of [(IDep)Fe(η2:η2-dvtms)] with P4. Its molecular structure established by X-ray diffraction study does not exhibit disorder in the μ-η5:η5-P5 ligand and the two iron centers show nearly identical coordination environment. The zero-field 57Fe Mössbauer spectrum of 1 measured at 80 K shows a quadrupole doublet with the isomer shift δ=0.32 mm•s−1 and quadrupole splitting |ΔEQ|=0.61 mm•s−1. Magnetic susceptibility measurements point out a doublet state (S=1/2) for 1. The characterization data suggests that 1 and 4 can be described as the III-type mixed valence complex based on the Robin-Day Models. Complex 2 represents the first example of metal complexes featuring a P9 ligand. The polyphosphide ligand contains two paralleling P3 triangles and three boat-shaped P6 faces. Each P6 face is coordinating with a Fe(IMes) fragment in η6-fashion. The three Fe atoms form a Fe3 triangle with the Fe…Fe distances close to each other [0.2626(1) nm in average]. Complex 3 features a μ-η2:η2-cyclo-P4P(IMes) ligand and a μ-η3:η3-P3 ligand. The bond distances and angles of the two polyphosphide ligands in 3 are close to those of the counterparts in [(IMes)2Co2(μ-η2:η2-cyclo-P4P(iPr2Im))(μ-η3:η3-P3)]. The 1H NMR and 31P NMR spectra of 3 are indicative of its diamagnetic nature. The 57Fe Mössbauer quadrupole doublet of 3 measured at 80 K has a isomer shift δ=0.26 mm•s-1 and quadrupole splitting |ΔEQ|=0.91 mm•s-1.
Key words: N-heterocyclic carbene; iron; white phosphorus; cluster compound; polyphosphide
Mu Du , Chengbo Yang , Qi Chen , Liang Deng . Iron Phosphorus Clusters with N-Heterocyclic Carbene Ligation[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024 , 82(9) : 932 -939 . DOI: 10.6023/A24060203
| [1] | Von Schnering H. G.; Hoenle W. Chem. Rev. 1988, 88, 243. |
| [2] | Geeson M. B.; Cummins C. C. ACS. Cent. Sci. 2020, 6, 848. |
| [3] | Scott D. J. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202205019 |
| [4] | Huangfu X.; Wang Z.; Chen Y.; Wei J.; Liu W.; Zhang W.-X. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2024, 11, nwae162 |
| [5] | Ginsberg A. P.; Lindsell W. E. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1971, 93, 2082. |
| [6] | Peruzzini M.; Abdreimova R. R.; Budnikova Y.; Romerosa A.; Scherer O. J.; Sitzmann H. J. Organomet. Chem. 2004, 689, 4319. |
| [7] | Cossairt B. M.; Piro N. A.; Cummins C. C. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 4164. |
| [8] | Scheer M.; Balazs G.; Seitz A. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 4236. |
| [9] | Caporali M.; Gonsalvi L.; Rossin A.; Peruzzini M. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 4178. |
| [10] | Fang W.; Douair I.; Hauser A.; Li K.; Zhao Y.; Roesky P. W.; Wang S.; Maron L.; Zhu C. CCS Chem. 2022, 4, 2630. |
| [11] | Gardner B. M.; Tuna F.; McInnes E. J. L.; McMaster J.; Lewis W.; Blake A. J.; Liddle S. T. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 7068. |
| [12] | Du S.; Chai Z.; Hu J.; Zhang W.-X.; Xi Z. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2019, 39, 2338 (in Chinese). |
| [12] | (杜山山, 柴正祺, 胡静远, 张文雄, 席振峰, 有机化学, 2019, 39, 2338.) |
| [13] | Du S.; Hu J.; Chai Z.; Zhang W.-X.; Xi Z. Chin. J. Chem. 2019, 37, 71. |
| [14] | Du S.; Yang J.; Hu J.; Chai Z.; Luo G.; Luo Y.; Zhang W.-X.; Xi Z. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 6843. |
| [15] | Zhang F.; Han K.; Cai J.; Ye Z.; Zhang J.; Zhou X.; Li Z. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2024, 11, 478. |
| [16] | Arduengo A. J.; Gamper S. F.; Calabrese J. C.; Davidson F. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1994, 116, 4391. |
| [17] | Fantasia S.; Nolan S. P. Chem.-Eur. J. 2008, 14, 6987. |
| [18] | Liu Y.; Cheng J.; Deng L. Acc. Chem. Res. 2020, 53, 244. |
| [19] | Zhang H.; Ouyang Z.; Liu Y.; Zhang Q.; Wang L.; Deng L. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 8432. |
| [20] | Zhang L.; Liu Y.; Deng L. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 15525. |
| [21] | Cheng J.; Chen Q.; Leng X.; Ouyang Z.; Wang Z.; Ye S.; Deng L. Chem 2018, 4, 2844. |
| [22] | Marko I. E.; Sterin S.; Buisine O.; Mignani G.; Branlard P.; Tinant B.; Declercq J. P. Science 2002, 298, 204. |
| [23] | Jackstell R.; Harkal S.; Jiao H.; Spannenberg A.; Borgmann C.; Rottger D.; Nierlich F.; Elliot M.; Niven S.; Cavell K.; Navarro O.; Viciu M. S.; Nolan S. P.; Beller M. Chem.-Eur. J. 2004, 10, 3891. |
| [24] | Wu J.; Faller J. W.; Hazari N.; Schmeier T. J. Organometallics 2012, 31, 806. |
| [25] | Zarzycki B.; Zell T.; Schmidt D.; Radius U. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 2013, 2051. |
| [26] | Hierlmeier G.; Coburger P.; van Leest N. P.; de Bruin B.; Wolf R. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 14148. |
| [27] | Yang C.; Jiang X.; Chen Q.; Leng X.; Xiao J.; Ye S.; Deng L. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 20785. |
| [28] | Cordero B.; Gomez V.; Platero-Prats A. E.; Reves M.; Echeverria J.; Cremades E.; Barragan F.; Alvarez S. Dalton Trans. 2008, 2832. |
| [29] | Reiners M.; Baabe D.; Zaretzke M. K.; Freytag M.; Walter M. D. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 7274. |
| [30] | Scherer O. J.; Brück T.; Wolmersh?user G. Chem. Ber. 1989, 122, 2049. |
| [31] | Loginov D. A.; Vinogradov M. M.; Starikova Z. A.; Petrovskii P. V.; Holub J.; Kudinov A. R. Collect. Czech. Chem. Commun. 2010, 75, 981. |
| [32] | Riesinger C.; R?hner D.; Krossing I.; Scheer M. Chem. Commun. 2023, 59, 4495. |
| [33] | Evans D. F. J. Chem. Soc. 1959, 2003. |
| [34] | Robin M. B.; Day P. Adv. Inorg. Chem. Radiochem. 1968, 10, 247. |
| [35] | Scherer O. J.; Schwalb J.; Wolmersh?user G.; Kaim W.; Gross R. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 1986, 25, 363. |
| [36] | Song B.; Cao P.; Zhao W.; Li B. Phys. Status Solidi 2001, 226, 305. |
| [37] | Chen M. D.; Huang R. B.; Zheng L. S.; Au C. T. J. Mol. Struct.: THEOCHEM. 2000, 499, 195. |
| [38] | Fr?tschel-Rittmeyer J.; Holthausen M.; Friedmann C.; R?hner D.; Krossing I.; Weigand J. J. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabq8613 |
| [39] | Madl E.; Butovskii M. V.; Balazs G.; Peresypkina E. V.; Virovets A. V.; Seidl M.; Scheer M. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 7643. |
| [40] | Riedlberger F.; Todisco S.; Mastrorilli P.; Timoshkin A. Y.; Seidl M.; Scheer M. Chem.-Eur. J. 2020, 26, 16251. |
| [41] | Scherer O. J.; Hilt T.; Wolmersh?user G. Organometallics 1998, 17, 4110. |
| [42] | Yao S.; Lindenmaier N.; Xiong Y.; Inoue S.; Szilvasi T.; Adelhardt M.; Sutter J.; Meyer K.; Driess M. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 1250. |
| [43] | Spitzer F.; Grassl C.; Balazs G.; Madl E.; Keilwerth M.; Zolnhofer E. M.; Meyer K.; Scheer M. Chem.-Eur. J. 2017, 23, 2716. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |