

High-efficiency Near Infrared Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence Based on Phenazine Acceptor
Received date: 2024-10-17
Online published: 2024-12-27
Supported by
National Key R&D Program of China(2020YFA0714604); National Natural Science Foundation of China(22005184); National Natural Science Foundation of China(62375193); International Science and Technology Innovation Cooperation/Hong Kong, Macao and Taiwan Science and Technology Innovation Cooperation Project of Jiangsu Province(BZ2023053)
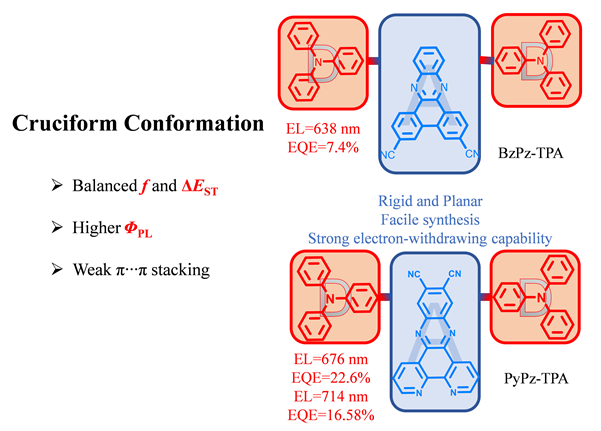
Two donor-acceptor-donor (D-A-D) type red thermally activated delayed fluorescence (TADF) materials 10,13- bis(4-(diphenylamino)phenyl)dibenzo[a,c]phenazine-3,6-dicarbonitrile (BzPz-TPA) and 10,13-bis(4-(diphenylamino)phenyl)- dipyrido[3,2-a:2',3'-c]phenazine-11,12-dicarbonitrile (PyPz-TPA) were designed and synthesized with dibenzophenazine and dipyridobenzazine as acceptor units and triphenylamine as donor units respectively. Two cyano groups were introduced into BzPz-TPA and PyPz-TPA to enhance the electron-withdrawing capability of the acceptor unit. Strong donor and acceptor units were introduced into the molecular skeletons of BzPz-TPA and PyPz-TPA, and steric hindrance between D and A units led to a twisted D-A configuration, thus achieving relatively small singlet-triplet energy gaps (ΔEST). In addition, the intramolecular hydrogen bonding interaction between donor and acceptor units can modulate the D-A molecular configuration and the overlap between the highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) and the lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO). In the BzPz-TPA molecule, the dihedral angle between the donor and acceptor units is 44°, and there is a twisted configuration between D-A, thereby achieving effective separation of HOMO and LUMO. HOMO is mainly located on the donor unit TPA, while LUMO is mainly located on the acceptor unit. In PyPz-TPA molecule, the dihedral angle between the donor and acceptor units is 52°, and the D-A twisted configuration effectively separates the HOMO and LUMO. The HOMO is mainly on the donor unit TPA, and the LUMO is mainly on the acceptor unit. Since BzPz-TPA and PyPz-TPA have the same donor unit, they have similar HOMO energy levels. Due to the rigid skeleton of two molecules and the smaller ΔEST, the BzPz-TPA is doped into the host material 4,4'-bis(9-carbazole)biphenyl (CBP) and resulted in the maximum external quantum efficiency (EQE) of 7.4% for the organic light-emitting diode (OLED) device emitting at 638 nm. When PyPz-TPA is doped into the host material CBP, the OLED device achieved the maximum EQE of 22.6% at 676 nm emission. Besides, the OLED of PyPz-TPA achieved the maximum EQE of 16.58% and near-infrared luminescence at an emission wavelength of 714 nm.
Jinzhu Ma , Yang Li , Shan Gao , Yue Zhao , Lei Ding , Dongying Zhou , Jian Fan . High-efficiency Near Infrared Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence Based on Phenazine Acceptor[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2025 , 83(1) : 17 -24 . DOI: 10.6023/A24100310
| [1] | Tang, C. W.; VanSlyke, S. A. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1987, 51, 913. |
| [2] | Ge, F.-J.; Zhang, K.-Z.; Cao, Q.-P.; Xu, H.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, W.-H.; Ban, X.-X.; Zhang, X.-B.; Li, N.; Zhu, P. Acta Chim. Sinica 2023, 81, 1157 (in Chinese). |
| [2] | ( 葛凤洁, 张开志, 曹清鹏, 徐慧, 周涛, 张文浩, 班鑫鑫, 张晓波, 李娜, 朱鹏, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 1157.) |
| [3] | Liu, Y. C.; Li, C. S.; Ren, Z. J.; Yan, S. K.; Bryce, M. R. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2018, 3, 18020. |
| [4] | Jeon, Y. M.; Choi, H. R.; Kwon, J. H.; Choi, S.; Nam, K. M.; Park, K. C.; Choi, K. C. Light Sci. Appl. 2019, 8, 114. |
| [5] | Zeng, X. Y.; Tang, Y. Q.; Cai, X. Y.; Tang, J. X.; Li, Y. Q. Mater. Chem. Front. 2023, 7, 1166. |
| [6] | Joo, W. J.; Kyoung, J.; Esfandyarpour, M.; Lee, S. H.; Koo, H.; Song, S. J.; Kwon, Y. N.; Song, S.; Bae, J. C.; Jo, A.; Kwon, M. J.; Han, S. H.; Kim, S. H.; Hwang, S. W.; Brongersma, M. L. Science 2020, 370, 459. |
| [7] | Zhao, S.-Y.; Zhang, X.; Lu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Q.-H. Mater. Rep. 2020, 34, 17155 (in Chinese). |
| [7] | ( 赵思宇, 张祥, 卢伶, 张义, 赵青华, 材料导报, 2020, 34, 17155.) |
| [8] | Wu, Z. G.; Han, H. B.; Yan, Z. P.; Luo, X. F.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, Y. X.; Zuo, J. L.; Pan, Y. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1900524. |
| [9] | Jeon, S. K.; Lee, H. L.; Yook, K. S.; Lee, J. Y. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1803524. |
| [10] | Wu, L.; Wang, K.; Wang, C.; Fan, X. C.; Shi, Y. Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S. L.; Ye, J.; Zheng, C. J.; Li, Y. Q.; Yu, J.; Ou, X. M.; Zhang, X. H. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 1495. |
| [11] | Liu, Z.-Y.; Rao, J.-F.; Zhu, S.-J.; Wang, B.-Y.; Yu, F.; Feng, Q.-Y.; Xie, L.-H. Acta Chim. Sinica 2023, 81, 820 (in Chinese). |
| [11] | ( 刘振宇, 饶俊峰, 祝守加, 王兵洋, 余帆, 冯全友, 解令海, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 820.) |
| [12] | Wei, Y. C.; Wang, S. F.; Hu, Y.; Liao, L. S.; Chen, D. G.; Chang, K. H.; Wang, C. W.; Liu, S. H.; Chan, W. H.; Liao, J. L.; Hung, W. Y.; Wang, T. H.; Chen, P. T.; Hsu, H. F.; Chi, Y.; Chou, P. T. Nat. Photonics 2020, 14, 570. |
| [13] | Wang, S. F.; Su, B. K.; Wang, X. Q.; Wei, Y. C.; Kuo, K. H.; Wang, C. H.; Liu, S. H.; Liao, L. S.; Hung, W. Y.; Fu, L. W.; Chuang, W. T.; Qin, M. C.; Lu, X. H.; You, C. F.; Chi, Y.; Chou, P. T. Nat. Photonics 2022, 16, 843. |
| [14] | Uoyama, H.; Goushi, K.; Shizu, K.; Nomura, H.; Adachi, C. Nature 2012, 492, 234. |
| [15] | Wang, S. P.; Yan, X. J.; Cheng, Z.; Zhang, H. Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 13068. |
| [16] | Yuan, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y. X.; Lin, J. D.; Wang, Y. K.; Jiang, Z. Q.; Liao, L. S.; Lee, S. T. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1700986. |
| [17] | Xue, J.; Liang, Q. X.; Wang, R.; Hou, J. Y.; Li, W. Q.; Peng, Q.; Shuai, Z. G.; Qiao, J. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1808242. |
| [18] | Congrave, D. G.; Drummond, B. H.; Conaghan, P. J.; Francis, H.; Jones, S.T.; Grey, C. P.; Greenham, N. C.; Credgington, D.; Bronstein, H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 18390. |
| [19] | Cheng, J. F.; Pan, Z. H.; Zhang, K.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, C. K.; Ding, L.; Fung, M. K.; Fan, J. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 132744. |
| [20] | Wang, X.-J.; Liu, Y.-X.; Li, Y.; Yang, C.-Z.; Fung, M.-K.; Fan, J. Chem. J. Chinese Universities 2023, 44, 10 (in Chinese). |
| [20] | ( 王霄靖, 刘艺霞, 李阳, 杨陈宗, 冯敏强, 樊健, 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44, 10.) |
| [21] | Xu, J. Y.; Dai, Y.; Zhang, J. Y.; Jia, Z.; Meng, Q. Y.; Qiao, J. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2024, 12, 2300989. |
| [22] | Feng, Z. Q.; Yu, Y. J.; Song, Z. Y.; Song, M.; Zuo, P.; Jiang, Z. Q.; Zhou, D. Y.; Liao, L. S. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 2403831. |
| [23] | Wang, Y. Y.; Zhang, Y. L.; Tong, K. N.; Ding, L.; Fan, J.; Liao, L. S. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 15301. |
| [24] | He, J.-C.; Wu, J.-Q.; Wang, J.-H.; Xu, J.-W.; Tang, B.-Z.; Zhao, Z.-J. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2024, 44, 2513 (in Chinese). |
| [24] | ( 何俊初, 武俊琪, 王江辉, 徐静文, 唐本忠, 赵祖金, 有机化学, 2024, 44, 2513.) |
| [25] | Yang, H.; Wang, W.-J.; Ji, J.-J.; Ding, Y.-Q.; Li, G.-H. J. Synth. Cryst. 2007, 36, 226 (in Chinese). |
| [25] | ( 杨辉, 王维洁, 季静佳, 丁玉强, 李果华, 人工晶体学报, 2007, 36, 226.) |
| [26] | Li, Y. Y.; Li, P. C.; Lu, Z. H. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1700414. |
| [27] | Gorse, A. D.; Pesquer, M. J. Phys. Chem. 1995, 99, 4039. |
| [28] | Wang, H. Q.; Zhao, B. J.; Qu, C.; Duan, C. B.; Li, Z.; Ma, P.; Chang, P.; Han, C. M.; Xu, H. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 436, 135080. |
| [29] | Tai, J. W.; Tang, Y. K.; Zhang, K.; Yang, C. Z.; Pan, Z. H.; Lin, Y. C.; Shih, Y. W.; Chen, C. H.; Chiu, T. L.; Lee, J. H.; Wang, C. K.; Wu, C. C.; Fan, J. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 452, 139534. |
| [30] | Zhao, T. X.; Jiang, S. S.; Wang, Y. S.; Hu, J. X.; Lin, F. L.; Meng, L. Y.; Gao, P.; Chen, X. L.; Lu, C. Z. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 30543. |
| [31] | Song, S.-F.; Zhao, D.-W.; Xu, Z.; Xu, X.-R. Chinese J. Lumin. 2006, 27, 675 (in Chinese). |
| [31] | ( 宋淑芳, 赵德威, 徐征, 徐叙瑢, 发光学报, 2006, 27, 675.) |
| [32] | Li, Z.; Yang, D. Z.; Han, C. M.; Zhao, B. J.; Wang, H. Q.; Man, Y.; Ma, P.; Chang, P.; Ma, D. G.; Xu, H. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 14846. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |