1 引言
2 结果与讨论
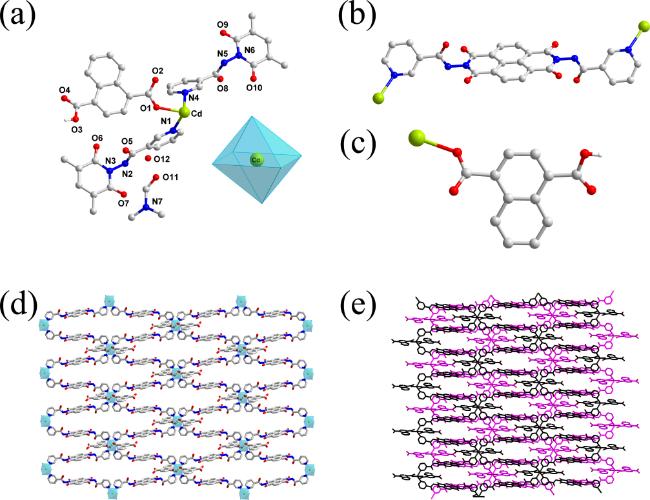
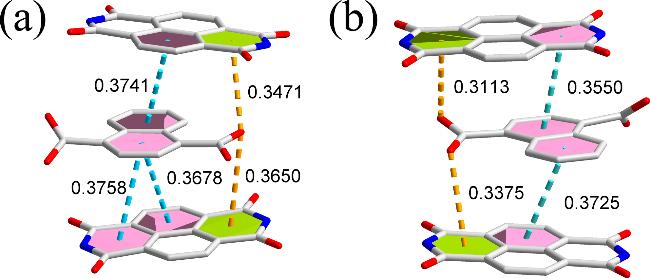
2.1 配合物1和2的晶体结构分析
图2 配合物1的晶体结构. (a)非对称结构基元图; (b)金属离子的配位模式; (c) 3-DPNDI分子的配位模式; (d)辅助配体的配位模式; (e) 2D层状结构; (f) 3D超分子网络Figure 2 The crystal structure of 1. (a) The asymmetric structure; (b) The coordination mode of metal ions; (c) The coordination mode of 3-DPNDI; (d) The coordination mode of auxiliary ligand; (e) The 2D layer; (f) The 3D supermolecular network |
图3 配合物2的晶体结构. (a)非对称结构基元图(内插图: 金属离子的配位环境); (b) 3-PANDI分子的配位模式; (c)辅助配体的配位模式; (d) 2D 层状结构; (e) 3D超分子网络Figure 3 The crystal structure of 2. (a) The asymmetric structure (insert: the coordination environment of metal ions); (b) The coordination mode of 3-PANDI; (c) The coordination mode of auxiliary ligand; (d) The 2D layer; (e) The 3D supermolecular network |
2.2 粉末X-射线衍射(PXRD)和热重分析(TGA)
2.3 紫外-可见吸收光谱(UV-vis)及电子顺磁共振分析(EPR)
图4 动力学曲线. (a)基于604 nm吸收峰, 配合物1的动力学曲线; (b)基于609 nm吸收峰, 配合物2的动力学曲线; (c)基于780 nm吸收峰, 配合物1的动力学曲线; (d)基于791 nm吸收峰, 配合物2的动力学曲线Figure 4 The kinetics curves. (a) The kinetics of 1 (based on absorption peak at 604 nm); (b) The kinetics of 2 (based on absorption peak at 609 nm); (c) The kinetics of 1 (based on absorption peak at 780 nm); (d) The kinetics of 2 (based on absorption peak at 791 nm) |
图5 紫外-可见吸收光谱和电子顺磁共振谱. (a)配合物1的紫外-可见吸收光谱(内插图: 配合物1的光致变色行为); (b)配合物2的紫外-可见吸收光谱(内插图: 配合物2的光致变色行为); (c)配合物1和1P的电子顺磁共振谱; (d)配合物2和2P的电子顺磁共振谱Figure 5 UV-vis and EPR pattern (a) UV-vis absorption spectra of 1 (insert: photochromic behaviors of 1); (b) UV-vis absorption spectra of 2 (insert: photochromic behaviors of 2); (c) EPR spectra of 1 and 1P; (d) EPR spectra of 2 and 2P |