Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (6): 2014-2026.DOI: 10.6023/cjoc202311022 Previous Articles Next Articles
ARTICLES
邱雪梅a, 胡伟男a, 王文航a, 覃丽清a, 祝丹雪a, 杨孟芝a, 邵利辉a,b, 谭画元a, 王钦a, 李洙锐a,b, 陈丹萍a,*( ), 王贞超a,b,c,*(
), 王贞超a,b,c,*( )
)
收稿日期:2023-11-22
修回日期:2023-12-31
发布日期:2024-02-19
基金资助:
Xuemei Qiua, Weinan Hua, Wenhang Wanga, Liqing Qina, Danxue Zhua, Mengzhi Yanga, Lihui Shaoa,b, Huayuan Tana, Qin Wanga, Zhurui Lia,b, Danping Chena,*( ), Zhenchao Wanga,b,c,*(
), Zhenchao Wanga,b,c,*( )
)
Received:2023-11-22
Revised:2023-12-31
Published:2024-02-19
Contact:
* E-mail: Supported by:Share
Xuemei Qiu, Weinan Hu, Wenhang Wang, Liqing Qin, Danxue Zhu, Mengzhi Yang, Lihui Shao, Huayuan Tan, Qin Wang, Zhurui Li, Danping Chen, Zhenchao Wang. Synthesis, Antibacterial Activity and Mechanism Research of 1,3,4-Oxadiazole and 1,2,4-Triazole Derivatives Containing Disulfide Bond[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(6): 2014-2026.
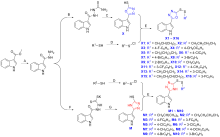

| Compd. | Toxic regression equation | R2 | EC50a/(μg•mL–1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | y=2.8392x+3.8619 | 0.9133 | 2.52±0.33 |
| X2 | y=3.5872x+3.0149 | 0.9512 | 3.58±0.12 |
| X3 | y=2.6741x+4.1261 | 0.9595 | 2.12±0.37 |
| X4 | y=2.6796x+2.1937 | 0.9795 | 11.15±3.78 |
| X5 | y=4.1284x+2.4310 | 0.9106 | 4.19±0.17 |
| X6 | y=1.8622x+3.8906 | 0.9673 | 3.94±0.43 |
| X7 | y=1.8761x+3.1762 | 0.9624 | 9.38±0.56 |
| X8 | y=1.2684x+4.0827 | 0.9499 | 5.29±0.35 |
| X9 | y=2.2436x+3.4254 | 0.9899 | 5.03±0.24 |
| X10 | y=3.6527x+3.0943 | 0.9015 | 2.72±0.35 |
| X11 | y=0.9789x+3.8225 | 0.9324 | 15.95±1.12 |
| X12 | y=1.7160x+3.4499 | 0.9789 | 8.00±0.37 |
| X13 | y=2.1875x+4.2470 | 0.9530 | 2.21±0.86 |
| X14 | y=1.5112x+4.3272 | 0.9826 | 2.79±0.22 |
| X15 | y=4.1328x+1.3607 | 0.9298 | 7.60±1.61 |
| X16 | y=2.9360x+4.3037 | 0.9705 | 1.73±0.40 |
| M1 | y=2.9499x+4.4688 | 0.9781 | 1.51±0.24 |
| M2 | y=3.0540x+4.1412 | 0.9920 | 1.91±0.05 |
| M3 | y=3.8150x+2.4660 | 0.9945 | 4.61±0.11 |
| M4 | y=3.5955x+3.8988 | 0.9878 | 2.02±0.17 |
| M5 | y=2.1930x+3.7662 | 0.9677 | 3.65±0.56 |
| M6 | y=2.4115x+3.7829 | 0.9754 | 3.19±0.11 |
| M7 | y=3.5519x+1.5782 | 0.9669 | 9.19±1.22 |
| M8 | y=2.6874x+3.1483 | 0.8722 | 4.89±0.19 |
| M9 | y=3.4748x+4.2098 | 0.9654 | 1.69±0.62 |
| M10 | y=2.3466x+3.7859 | 0.9328 | 3.29±0.22 |
| BTb | y=4.0040x–2.3086 | 0.9381 | 66.88±4.06 |
| TCb | y=4.4997x–3.7491 | 0.9942 | 87.97±4.79 |
| Compd. | Toxic regression equation | R2 | EC50a/(μg•mL–1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | y=2.8392x+3.8619 | 0.9133 | 2.52±0.33 |
| X2 | y=3.5872x+3.0149 | 0.9512 | 3.58±0.12 |
| X3 | y=2.6741x+4.1261 | 0.9595 | 2.12±0.37 |
| X4 | y=2.6796x+2.1937 | 0.9795 | 11.15±3.78 |
| X5 | y=4.1284x+2.4310 | 0.9106 | 4.19±0.17 |
| X6 | y=1.8622x+3.8906 | 0.9673 | 3.94±0.43 |
| X7 | y=1.8761x+3.1762 | 0.9624 | 9.38±0.56 |
| X8 | y=1.2684x+4.0827 | 0.9499 | 5.29±0.35 |
| X9 | y=2.2436x+3.4254 | 0.9899 | 5.03±0.24 |
| X10 | y=3.6527x+3.0943 | 0.9015 | 2.72±0.35 |
| X11 | y=0.9789x+3.8225 | 0.9324 | 15.95±1.12 |
| X12 | y=1.7160x+3.4499 | 0.9789 | 8.00±0.37 |
| X13 | y=2.1875x+4.2470 | 0.9530 | 2.21±0.86 |
| X14 | y=1.5112x+4.3272 | 0.9826 | 2.79±0.22 |
| X15 | y=4.1328x+1.3607 | 0.9298 | 7.60±1.61 |
| X16 | y=2.9360x+4.3037 | 0.9705 | 1.73±0.40 |
| M1 | y=2.9499x+4.4688 | 0.9781 | 1.51±0.24 |
| M2 | y=3.0540x+4.1412 | 0.9920 | 1.91±0.05 |
| M3 | y=3.8150x+2.4660 | 0.9945 | 4.61±0.11 |
| M4 | y=3.5955x+3.8988 | 0.9878 | 2.02±0.17 |
| M5 | y=2.1930x+3.7662 | 0.9677 | 3.65±0.56 |
| M6 | y=2.4115x+3.7829 | 0.9754 | 3.19±0.11 |
| M7 | y=3.5519x+1.5782 | 0.9669 | 9.19±1.22 |
| M8 | y=2.6874x+3.1483 | 0.8722 | 4.89±0.19 |
| M9 | y=3.4748x+4.2098 | 0.9654 | 1.69±0.62 |
| M10 | y=2.3466x+3.7859 | 0.9328 | 3.29±0.22 |
| BTb | y=4.0040x–2.3086 | 0.9381 | 66.88±4.06 |
| TCb | y=4.4997x–3.7491 | 0.9942 | 87.97±4.79 |
| Compd. | Curative effect | Protective effect | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Morbidity/% | Disease index/% | Control efficiencya/% | Morbidity/% | Disease index/% | Control efficiencya/% | ||
| M1 | 100 | 54.49 | 42.37 | 100 | 58.02 | 38.64 | |
| BT | 100 | 59.11 | 37.49 | 100 | 60.00 | 36.55 | |
| CKb | 100 | 94.56 | — | 100 | 94.56 | — | |
| Compd. | Curative effect | Protective effect | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Morbidity/% | Disease index/% | Control efficiencya/% | Morbidity/% | Disease index/% | Control efficiencya/% | ||
| M1 | 100 | 54.49 | 42.37 | 100 | 58.02 | 38.64 | |
| BT | 100 | 59.11 | 37.49 | 100 | 60.00 | 36.55 | |
| CKb | 100 | 94.56 | — | 100 | 94.56 | — | |
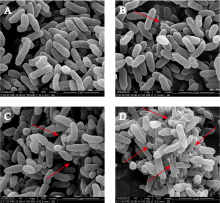

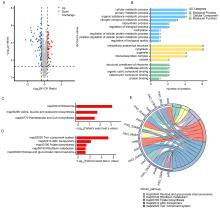

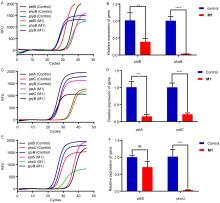

| [1] |
Mansfield, J.; Genin, S.; Magori, S.; Citovsky, V.; Sriariyanum, M.; Ronald, P.; Dow, M.; Verdier, V.; Beer, S. V.; Machado, M. A. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2012, 13, 614.
|
| [2] |
Ray, M.; Ray, A.; Dash, S.; Mishra, A.; Achary, K. G.; Nayak, S.; Singh, S. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 87, 708.
|
| [3] |
Strange, R. N.; Scott, P. R. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2005, 43, 83.
|
| [4] |
Deng, Y.; Liu, H. B.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Q. L.; Li, X. H.; Wang, S. P. Mol. Breed. 2018, 38. 18.
|
| [5] |
Scholthof, K. B.; Adkins, S.; Czosnek, H.; Palukaitis, P.; Jacquot, E.; Hohn, T.; Hohn, B.; Saunders, K.; Candresse, T.; Ahlquist, P. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2011, 12, 938.
|
| [6] |
Silva, A. R.; Andrade Neto, J. B.; Silva, C. R.; Sousa Campos, R.; Costa Silva, R. A.; Freitas, D. D.; Nascimento, F. B.; Andrade, L. N. D.; Sampaio, L. S.; Grangeiro, T. B. Antimicrob. Agents Chemo- ther. 2016, 60, 3551.
|
| [7] |
Wang, L. L.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y. Y.; Qiao, C. H.; Ye, Y. H. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 8632.
|
| [8] |
Zhang, J.; Peng, J. F.; Wang, T.; Kang, Y.; Jing, S. S.; Zhang, Z. T. Mol. Diversity 2017, 21, 317.
|
| [9] |
Li, L. X.; Jiao, J.; Wang, X. B.; Chen, M.; Fu, X. C.; Si, W. J.; Yang, C. L. Molecules 2018, 23, 746.
|
| [10] |
Song, B. A. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2018, 147, 1.
|
| [11] |
Xu, W. M.; Han, F. F.; He, M.; Hu, D. Y.; He, J.; Yang, S.; Song, B. A. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 1036.
|
| [12] |
Yuan, W. C.; Yu, Z. W.; Song, W. Q.; Li, Y. N.; Fang, Z. Y.; Zhu, B. Z.; Li, X. M.; Wang, H.; Hong, W.; Sun, N. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 2283.
|
| [13] |
Labriere, C.; Gong, H.; Finlay, B. B.; Reiner, N. E.; Young, R. N. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 125, 1.
|
| [14] |
Jiang, L. L.; Tan, Y.; Zhu, X. L.; Wang, Z. F.; Zuo, Y.; Chen, Q.; Xi, Z.; Yang, G. F. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 2643.
|
| [15] |
Kandemir, H.; Ma, C.; Kutty, S. K.; Black, D. S.; Griffith, R.; Lewis, P. J.; Kumar, N. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2014, 22, 1672.
|
| [16] |
Siwach, A.; Verma, P. K. BMC Chem. 2020, 14, 70.
|
| [17] |
Zhou, L.; Wang, P. Y.; Zhou, J.; Shao, W. B.; Fang, H. S.; Wu, Z. B. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2017, 21, 852.
|
| [18] |
Fan, Z. J.; Shi, J.; Bao, X. P. Mol. Diversity 2018, 22, 657.
|
| [19] |
Gao, F.; Wang, T.; Xiao, J.; Huang, G. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 173, 274.
|
| [20] |
Shang, J.; Wang, W. M.; Li, Y. H.; Song, H. B.; Li, Z. M.; Wang, J. G. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 8286.
|
| [21] |
Wang, J. R.; Hu, Y. M.; Zhou, H.; Li, A. P.; Zhang, S. Y.; Luo, X. F.; Zhang, B. Q.; An, J. X.; Zhang, Z. J.; Liu, Y. Q. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 11782.
|
| [22] |
Tian, K.; Li, X. Q.; Zhang, L.; Gan, Y. Y.; Meng, J.; Wu, S. Q.; Wan, J. L.; Xu, Y.; Cai, C. T.; Ouyang, G. P. Chem. Pap. 2018, 73, 17.
|
| [23] |
Wei, Z. Y.; Cui, B. R.; Cui, X.; Wu, Y. L.; Fu, Y.; Liu, L. P.; Piao, H. R. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2017, 89, 47.
|
| [24] |
Fong, J.; Yuan, M. J.; Jakobsen, T. H.; Mortensen, K. T.; Delos Santos, M. M.; Chua, S. L.; Yang, L.; Tan, C. H.; Nielsen, T. E.; Givskov, M. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 215.
|
| [25] |
Huang, Y. Y.; Xu, Y. X.; Song, R. R.; Ni, S. S.; Liu, J. Q.; Xu, Y. H.; Ren, Y. L.; Rao, L.; Wang, Y. J.; Wei, L.; Feng, L. L.; Su, C.; Peng, C.; Li, J.; Wan, J. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 6238.
|
| [26] |
Li, P.; Hu, D. Y.; Xie, D. D.; Chen, J. X.; Jin, L. H.; Song, B. A. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 3093.
|
| [27] |
Wang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Breslawec, A. P.; Liang, T.; Deng, Z.; Kuperman, L. L.; Yu, Q. npj Biofilms Microbiomes 2023, 9, 63.
|
| [28] |
Wuichet, K.; Cantwell, B. J.; Zhulin, I. B. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2010, 13, 219.
|
| [29] |
Lewis, V. G.; Ween, M. P.; McDevitt, C. A. Protoplasma 2012, 249, 919.
|
| [30] |
Yuan, Z. C.; Zaheer, R.; Finan, T. M. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 1089.
|
| [31] |
Spira, B.; Aguena, M.; de Castro Oliveira, J. V.; Yagil, E. Mol. Genet. Genomics 2010, 284, 489.
|
| [32] |
Hudek, L.; Premachandra, D.; Webster, W. A.; Brau, L. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 6344.
|
| [33] |
Neznansky, A.; Blus-Kadosh, I.; Yerushalmi, G.; Banin, E.; Opatowsky, Y. FASEB J. 2014, 28, 5223.
|
| [34] |
Vuppada, R. K.; Hansen, C. R.; Strickland, K. A. P.; Kelly, K. M.; McCleary, W. R. BMC Microbiol. 2018, 18. 8.
|
| [35] |
Tan, Y.; Ma, S.; Leonhard, M.; Moser, D.; Haselmann, G. M.; Wang, J.; Eder, D.; Schneider-Stickler, B. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 200, 35.
|
| [36] |
Ajiboye, T. O.; Aliyu, M.; Isiaka, I.; Haliru, F. Z.; Ibitoye, O. B.; Uwazie, J. N.; Muritala, H. F.; Bello, S. A. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2016, 258, 276.
|
| [37] |
Peng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zou, Y.; Song, H. Y.; Wang, S.; Cai, Q. F.; Chen, J. X.; Hu, D. Y. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2023, 193, 105457.
|
| [38] |
Wu, Q.; Cai, H.; Yuan, T.; Li, S. Y.; Gan, X. H.; Song, B. A. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 30, 127113.
|
| [39] |
Xiang, J.; Liu, D. Y.; Chen, J. X.; Hu, D. Y.; Song, B. A. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2020, 170, 104695.
|
| [40] |
Shi, J.; Ding, M. H.; Luo, N.; Wan, S. R.; Li, P. J.; Li, J. H.; Bao, X. P. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 9613.
|
| [41] |
Tao, Q. Q.; Liu, L.W.; Wang, P. Y.; Long, Q. S.; Zhao, Y. L.; Jin, L. H.; Xu, W. M.; Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; Yang, S. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 7626.
|
| [42] |
Habartova, K.; Havelek, R.; Seifrtova, M.; Kralovec, K.; Cahli- kova, L.; Chlebek, J.; Cermakova, E.; Mazankova, N.; Marikova, J.; Kunes, J. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4829.
|
| [43] |
Shafiei, S. N. S.; Ahmad, K.; Ikhsan, N. F. M.; Ismail, S. I.; Sijam, K. Braz. J. Biol. 2021, 81, 11.
|
| [44] |
Long, X. S.; Zhang, G. L.; Long, H. T.; Wang, Q.; Wang, C. Y.; Zhu, M.; Wang, W. H.; Li, C. P.; Wang, Z. C.; Ouyang, G. P. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10900.
|
| [45] |
Chakravortty, D.; Yu, X.; Liang, X.; Liu, K.; Dong, W.; Wang, J.; Zhou, M. G. Plos One 2015, 10, e0134237.
|
| [1] | Yannan Ma, Ya'ni Liu, Jinyan Wang, Xitong Chen, Hao Yin, Qiaona Chi, Shixi Jia, Shanshan Du, Yunkun Qi, Kewei Wang. DIC/Oxyma Based Efficient Synthesis and Activity Evaluation of Spider Peptide Toxin GsMTx4 [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2022, 42(2): 498-506. |
| [2] | Jinyan Wang, Liying Dong, Ya'ni Liu, Xitong Chen, Yannan Ma, Hao Yin, Shanshan Du, Yunkun Qi, Kewei Wang. Efficient Synthesis and Oxidative Folding Studies of Centipede Toxin RhTx [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2021, 41(7): 2800-2809. |
| [3] | LI Ling-Dong,b,TANG Wei,b,LIU Wu-Jun,b,ZHAO Zong-Bao*,a. Synthesis and Activity of the Photoaffinity-Labeled Functional Probe Based on Prenyl Side-Chain [J]. Chin. J. Org. Chem., 2008, 28(03): 489-493. |
| [4] | HUANG Xiao-Yi, WANG Tao, XIA Chuan-Qin, YU Xiao-Qi, XIE Ru-Gang. Synthesis of Novel Disulfide Bond-Bearing Cyclopeptides [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2004, 24(12): 1629-1632. |
| [5] | Jiang Hui;Zhong Mingnai;Chen Jisheng;Miao Zhenwei. The advances in the synthesis of multiple disulfide bond-containing peptides [J]. Chin. J. Org. Chem., 1999, 19(3): 214-223. |
| [6] | Wang Liangyou;Pan Heping;Chen Zhengying. Methods of disulfide formation in peptide synthesis [J]. Chin. J. Org. Chem., 1998, 18(6): 576-580. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||