

Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry >
Polycyclic Tetramate Macrolactams from the Marine-Derived Actinoalloteichus cyanogriseus WH1-2216-6
Received date: 2017-03-28
Revised date: 2017-04-27
Online published: 2017-05-10
Supported by
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81561148012, 41376148) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China-Guangdong Fund Joint Project (No. U1501221).
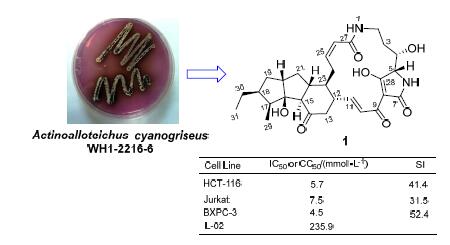
From the fermentation broth of the marine-derived Actinoalloteichus cyanogriseus WH1-2216-6, a new 5,5,6-polycyclic tetramate macrolactam (PTM) named 16-hydroxymaltophilin (1) was isolated and identified along with five known analouges, dihydromaltophilin (2), 4-deoxydihydromaltophilin (3), maltophilin (4), xanthobaccin C (5) and FI-2 (6), by means of UV-guided isolation as well as the spectroscopic identification. The cytotoxicities of compounds 1~5 were tested against the human normal hepatic cell line (L-02) and the seven human cancer cell lines, A549, MCF-7, Jurkat, BXPC-3, HCT-116, PANC-1 and K562. The results showed that compounds 1~5 were active against the above human cancer cell lines with the IC50 values of 0.1~9.7 μmol·L-1, among which the new compound 1 was the lowest toxic to L-02 cell and the most selective to Jurkat, HCT-116 and BXPC-3 cells with the selection index (SI) of 31.5, 41.4 and 52.4, respectively. The antifungal activities of 1~6 against Aspergillus fumigatus AF293 were also tested by two-fold dilution method. Compounds 2 and 4 were active against A. fumigatus AF293 with the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) values of 3.04 and 6.12 μmol·L-1, respectively. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first time to report the antifungal activity of 5,5,6-PTMs against A. fumigatus AF293. Apart from the cytotoxicity of compounds 2 and 3 against A549 and MCF-7 tumor cells lines, the other cytotoxicities were reported here for the first time, indicating the potential use of PTMs as the antitumor and antifungal lead compounds against A. fumigatus.
Mei Xiangui , Wang Liping , Wang Dongyang , Fan Jie , Zhu Weiming . Polycyclic Tetramate Macrolactams from the Marine-Derived Actinoalloteichus cyanogriseus WH1-2216-6[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2017 , 37(9) : 2352 -2360 . DOI: 10.6023/cjoc201703048
[1] Zhao, C.; Zhu, T.; Zhu, W. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 33, 1195(in Chinese). (赵成英, 朱统汉, 朱伟明, 有机化学, 2013, 33, 1195.)
[2] Blodgett, J. A.; Oh, D. C.; Cao, S.; Currie, C. R.; Kolter, R.; Clardy, J. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2010, 107, 11692.
[3] Zhang, G.; Zhang, W.; Saha, S.; Zhang, C. Curr. Top Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 1727.
[4] Jomon, K.; Kuroda, Y.; Ajisaka, M.; Sakai, H. J. Antibiot. 1972, 25, 271.
[5] Gunasekera, S. P.; Gunasekera, M.; McCarthy, P. J. Org. Chem. 1991, 56, 4830.
[6] Kanaxawa, S.; Fusetani, N.; Matsunaga, S. Tetrahedron Lett. 1993, 34, 1065.
[7] Jakobi, M.; Winkelmann, G.; Kaiser, D.; Kempter, C.; Jung, G.; Berg, G.; Bahl, H. J. Antibiot. 1996, 49, 1101.
[8] Graupner, P. R.; Hornburgh, S. T.; Mathiesonc, J. T.; Chapin, E. L.; Kemmitt, G. M.; Brown, J. M.; Snipes, C. E. J. Antibiot. 1997, 50, 1014.
[9] Yu, F.; Zaleta-Rivera, K.; Zhu, X.; Huffman, J.; Millet, J. C.; Harris, S. D.; Yuen, G.; Li, X. C.; Du, L. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 64.
[10] Nakayama, T.; Homma, Y.; Hashidoko, Y.; Mizutani, J.; Tahara, S. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 4334.
[11] Li, Y.; Huffman, J.; Li, Y.; Du, L.; Shen, Y. Med. Chem. Commun. 2012, 3, 982.
[12] Xu, L.; Wu, P.; Wright, S. J.; Du, L.; Wei, X. Y. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 1841.
[13] Saha, S.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, G.; Zhu, Y. G.; Chen, Y. C.; Liu, W.;Yuan, C. S.; Zhang, Q. B.; Zhang, H. B.; Zhang, L. P.; Zhnag, W. M.; Zhang, C. S. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 1607.
[14] Li, S.; Du, L.; Yuen, G.; Harris, S. D. Mol. Biol. Cell 2006, 17, 1218.
[15] Li, S.; Calvo, A. M.; Yuen, G. Y.; Du, L.; Harris, S. D. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2009, 56, 182.
[16] Li, S.; Jochum, C. C.; Yu, F.; Zaleta-Rivera, K.; Du, L.; Harris, S. D.; Yuen, G. Y. Phytopathology 2008, 98, 695.
[17] Qian, G.; Hu, B.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, F. Agric. Sci. China 2009, 8, 68.
[18] Lou, L.; Chen, H.; Cerny, R. L.; Li, Y.; Shen, Y.; Du, L. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 4.
[19] Lou, L.; Qian, G.; Xie, Y.; Hang, J.; Chen, H.; Zaleta-Rivera, K.; Li, Y.; Shen, Y.; Dussault, P. H.; Liu, F.; Du, L. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 643.
[20] Fu, P.; Wang, S.; Hong, K.; Li, X.; Liu, P.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, W. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 1751.
[21] Jia, H.-J.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, P.-P.; Zhu, W.-M. Chin. J. Mar. Drug. 2014, 33, 9(in Chinese). (贾海健, 王聪, 王乂, 刘培培, 朱伟明, 中国海洋药物, 2014, 33, 9.)
[22] Lacret, R.; Oves-Costales, D.; Gómez, C.; Díaz, C.; de la Cruz M; Pérez-Victoria, I.; Vicente, F.; Genilloud, O.; Reyes, F. Mar. Drugs 2014, 13, 128.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |