

Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry >
Preparation of Aggregation-Induced Emission Nucleic Acid Probes and Study of Their Nucleic Acid Sensing Principles
Received date: 2024-03-31
Revised date: 2024-05-17
Online published: 2024-07-15
Supported by
National Natural Science Foundation of China(21975077); Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province(2022B1515020084); Open Fund of Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Luminescence from Molecular Aggregates(South China University of Technology, No. 2019B030301003); Independent Research Project of State Key Lab of Luminescent Materials and Devices (SCUT)(Skllmd-2022-01); Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation(2023B1515040003); Key Project of Yunnan Provincial Department of Science and Technology(202303AC100021)
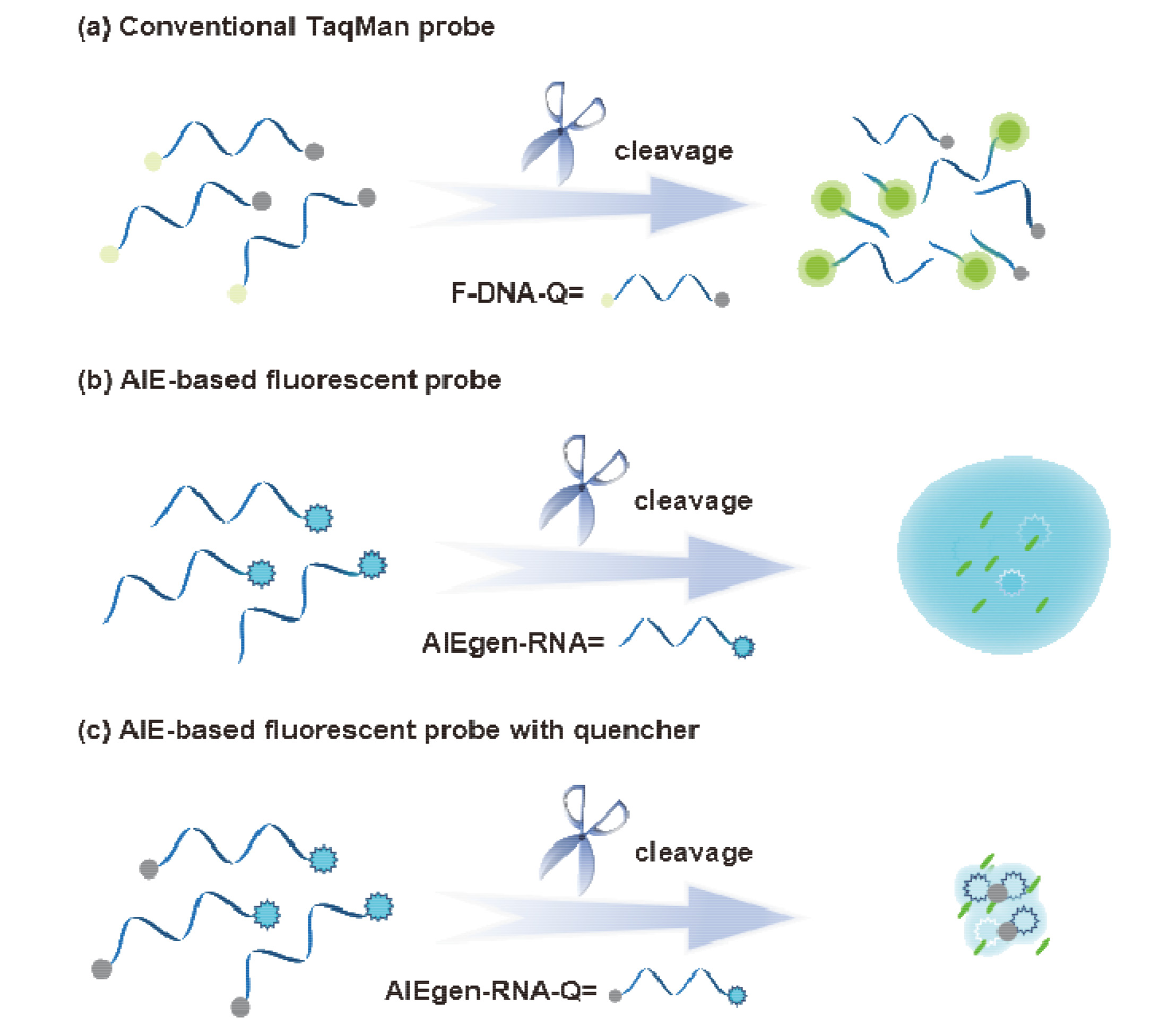
Nucleic acid detection is one of the most precise methods in biomedicine and medical diagnostics. Among these techniques, the widely employed polymerase chain reaction (PCR) utilizes the fluorescence signal output of TaqMan probes to achieve highly sensitive quantitative analysis of trace target sequences. This study systematically accomplishes the modification of the aggregation-induced emission (AIE) moiety—tetraphenylethylene (TPE) with phosphoramidite, and designs and synthesizes a series of single-labeled nucleic acid probes specific to particular RNA sequences, laying the foundation for the efficient preparation of various AIE nucleic acid probes using automatic oligonucleotide synthesizer. By specifically cleaving the water-soluble RNA segment within the TPE-RNA1 probe using the RNase A enzyme, various characterization techniques including transmission electron microscopy, fluorescence spectroscopy, mass spectrometry, etc., demonstrate changes in probe solubility induced by enzymatic cleavage, accompanied by hydrophobic aggregation. Through the optimization of parameters such as probe concentration, reaction time, and sequence length, a 34.7-fold enhancement in fluorescence under the AIE effect was achieved. This study replaces the traditional dual-labeled strategy of fluorescence-quencher moieties in probes with the AIE principle, expanding the design strategy of nucleic acid probes. It systematically characterizes and discusses the aggregation process of AIE-type nucleic acid probes, aiming to promote more efficient and sensitive nucleic acid detection probes and expand their applications in the field of biochemical detection.
Yan Ou , Lin Lan , Zhengxiong Wang , Zhiming Wang , BenZhong Tang . Preparation of Aggregation-Induced Emission Nucleic Acid Probes and Study of Their Nucleic Acid Sensing Principles[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024 , 44(8) : 2554 -2562 . DOI: 10.6023/cjoc202403057
| [1] | Hua, Y.; Ma, J.; Li, D.; Wang, R. Biosensor. 2022, 12, 183. |
| [2] | Samanta, D.; Ebrahimi, S. B.; Mirkin, C. A. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1901743. |
| [3] | Tian, R.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Jiang, Q.; Ding, B. Aggregat. 2021, 2, 133. |
| [4] | Quan, K.; Yi, C.; Yang, X.; He, X.; Huang, J.; Wang, K. TrA., Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 124, 115784. |
| [5] | Saccà, B.; Niemeyer, C. M. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 5910. |
| [6] | Zhang, X.; Chen, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y. Innovatio. 2024, 5, 100538. |
| [7] | Fei, X.; Gu, Y. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2009, 19, 1. |
| [8] | Tyagi, S.; Kramer, F. R. Nat. Biotechnol. 1996, 14, 303. |
| [9] | Gibson, U. E.; Heid, C. A.; Williams, P. M. Genome Res. 1996, 6, 995. |
| [10] | Zhang, H.; Huang, F.; Cai, G.; Li, Y.; Lin, J. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 9736. |
| [11] | Tran, T.; Kostecki, R.; Catton, M.; Druce, J. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, e00360-18. |
| [12] | Tabatabaei, M. S.; Islam, R.; Ahmed, M. Anal. Chim. Act. 2021, 1143, 250. |
| [13] | Oxnard, G. R.; Paweletz, C. P.; Kuang, Y.; Mach, S. L.; O'Connell, A.; Messineo, M. M.; Luke, J. J.; Butaney, M.; Kirschmeier, P.; Jackman, D. M.; J?nne, P. A. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 1698. |
| [14] | Venkatesan, N.; Jun Seo, Y.; Hyean Kim, B. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 648. |
| [15] | Hwang, G. T.; Seo, Y. J.; Kim, B. H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 6528. |
| [16] | Heinlein, T.; Knemeyer, J.-P.; Piestert, O.; Sauer, M. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 7957. |
| [17] | Nazarenko, I.; Lowe, B.; Darfler, M.; Ikonomi, P.; Schuster, D.; Rashtchian, A. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, e37. |
| [18] | Yang, C.; Abbas, F.; Rhouati, A.; Sun, Y.; Chu, X.; Cui, S.; Sun, B.; Xue, C. Biosensor. 2022, 12, 297. |
| [19] | Nikiforov, T. T. Anal. Biochem. 2014, 461, 67. |
| [20] | Knemeyer, J.-P.; Marmé, N.; Sauer, M. Anal. Chem. 2000, 72, 3717. |
| [21] | Sobek, J.; Schlapbach, R. Molecule. 2020, 25, 5369. |
| [22] | Luo, J.; Xie, Z.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Cheng, L.; Chen, H.; Qiu, C.; Kwok, H. S.; Zhan, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, D.; Tang, B. Z. Chem. Commun. 2001, 18, 1740. |
| [23] | Gui, Y.; Chen, K.; Sun, Y.; Tan, Y.; Luo, W.; Zhu, D.; Xiong, Y.; Yan, D.; Wang, D.; Tang, B. Z. Chin. J. Chem. 2023, 41, 1249. |
| [24] | Lu, H.; Ma, L.; Ma, H. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2023, 43, 4075 (in Chinese). |
| [24] | (鲁会名, 马拉毛草, 马恒昌, 有机化学, 2023, 43, 4075.) |
| [25] | Xu, H.; Han, P.; Qin, A.; Tang, B. Z. Acta Chim. Sinic. 2023, 81, 1420 (in Chinese). |
| [25] | (徐赫, 韩鹏博, 秦安军, 唐本忠, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 1420.) |
| [26] | Feng, X.; Zhu, L.; Yue, B. Acta Chim. Sinic. 2022, 80, 647 (in Chinese). |
| [26] | (冯锡成, 朱亮亮, 岳兵兵, 化学学报, 2022, 80, 647.) |
| [27] | Zhao, Y.; Chen, P.; Li, G.; Niu, Z.; Wang, E. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2023, 43, 2156 (in Chinese). |
| [27] | (赵洋, 陈盼盼, 李高楠, 钮智刚, 王恩举, 有机化学, 2023, 43, 2156.) |
| [28] | Zhang, Y.; Nie, F.; Zhou, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Huo, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhao, Z. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2023, 43, 3876 (in Chinese). |
| [28] | (张越华, 聂飞, 周路, 王晓烽, 刘源, 霍延平, 陈文铖, 赵祖金, 有机化学, 2023, 43, 3876.) |
| [29] | Zhu, L.; Zhou, J.; Xu, G.; Li, C.; Ling, P.; Liu, B.; Ju, H.; Lei, J. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 2559. |
| [30] | Ma, K.; Zhang, F.; Sayyadi, N.; Chen, W.; Anwer, A. G.; Care, A.; Xu, B.; Tian, W.; Goldys, E. M.; Liu, G. ACS Sens. 2018, 3, 320. |
| [31] | Wang, X.; Dai, J.; Min, X.; Yu, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Huang, K.; Yang, J.; Yi, X.; Lou, X.; Xia, F. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 8162. |
| [32] | Chen, J.; Jiang, H.; Zhou, H.; Hu, Z.; Niu, N.; Shahzad, S. A.; Yu, C. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 2398. |
| [33] | Lu, D.; He, L.; Wang, Y.; Xiong, M.; Hu, M.; Liang, H.; Huan, S.; Zhang, X.-B.; Tan, W. Talant. 2017, 167, 550. |
| [34] | Min, X.; Zhuang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Jia, Y.; Hakeem, A.; Zheng, F.; Cheng, Y.; Tang, B. Z.; Lou, X.; Xia, F. ACS Appl. Mater. Interface. 2015, 7, 16813. |
| [35] | Li, Y.; Kwok, R. T. K.; Tang, B. Z.; Liu, B. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 10135. |
| [36] | Chen, Z.; Wei, Z.; Xiao, F.; Chao, Z.; Lu, J.; Wang, Z.; Tian, L. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2207845. |
| [37] | Beaucage, S. L.; Caruthers, M. H. Tetrahedron Lett. 1981, 22, 1859. |
| [38] | Krotz, A. H.; Rentel, C.; Gorman, D.; Olsen, P.; Gaus, H. J.; McArdle, J. V.; Scozzari, A. N. Nucleoside., Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 2004, 23, 767. |
| [39] | Takamoto, K.; He, Q.; Morris, S.; Chance, M. R.; Brenowitz, M. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2002, 9, 928. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |