Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (8): 2554-2562.DOI: 10.6023/cjoc202403057 Previous Articles Next Articles
ARTICLES
欧彦a, 蓝琳b, 王正雄b, 王志明a,b,*( ), 唐本忠a,b
), 唐本忠a,b
收稿日期:2024-03-31
修回日期:2024-05-17
发布日期:2024-06-07
基金资助:
Yan Oua, Lin Lanb, Zhengxiong Wangb, Zhiming Wanga,b( ), BenZhong Tanga,b
), BenZhong Tanga,b
Received:2024-03-31
Revised:2024-05-17
Published:2024-06-07
Contact:
E-mail: Supported by:Share
Yan Ou, Lin Lan, Zhengxiong Wang, Zhiming Wang, BenZhong Tang. Preparation of Aggregation-Induced Emission Nucleic Acid Probes and Study of Their Nucleic Acid Sensing Principles[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(8): 2554-2562.
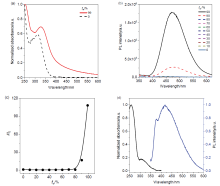
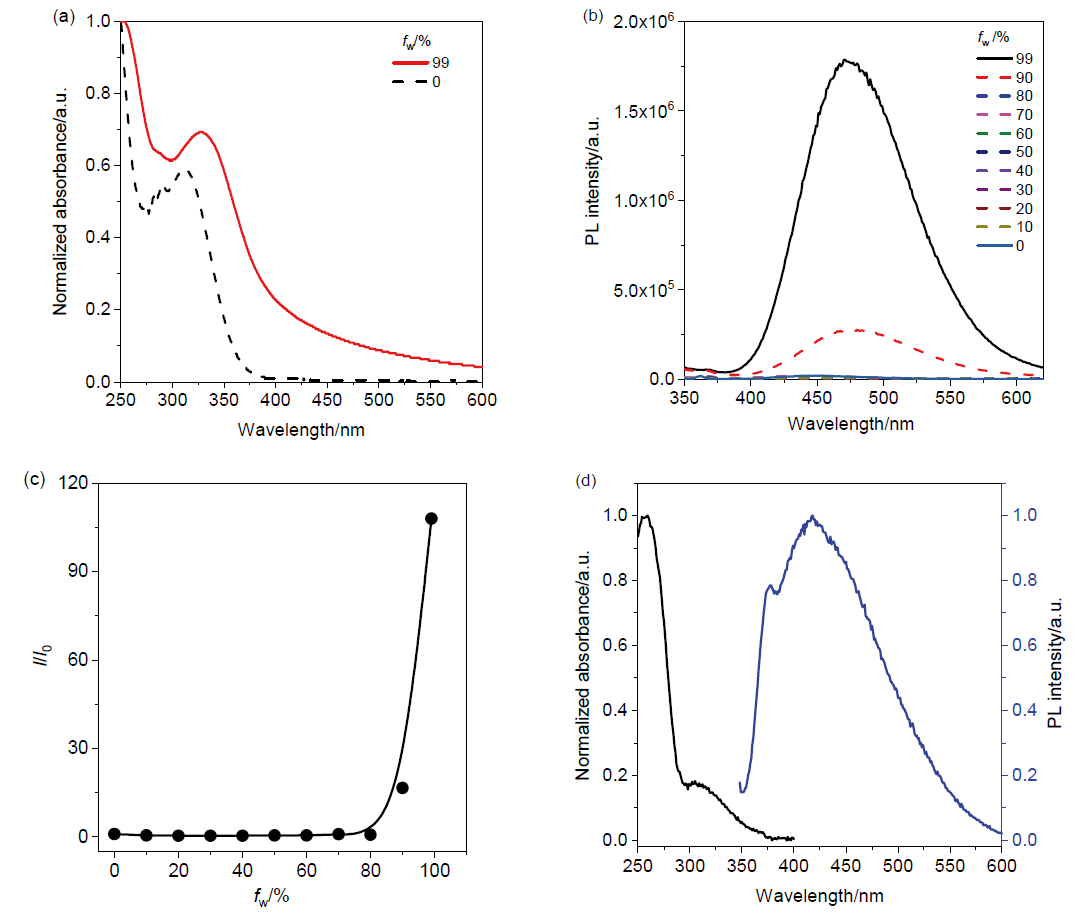
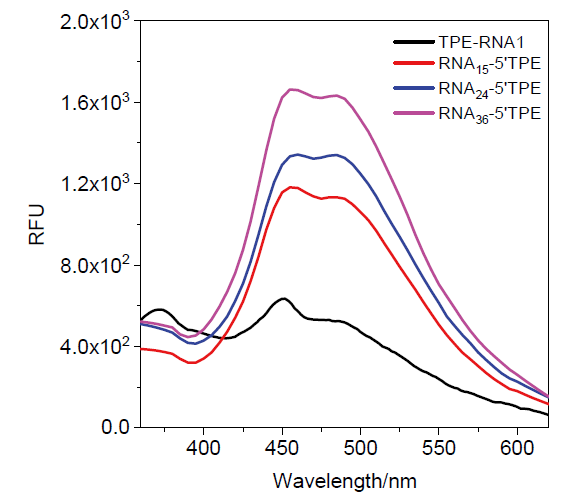
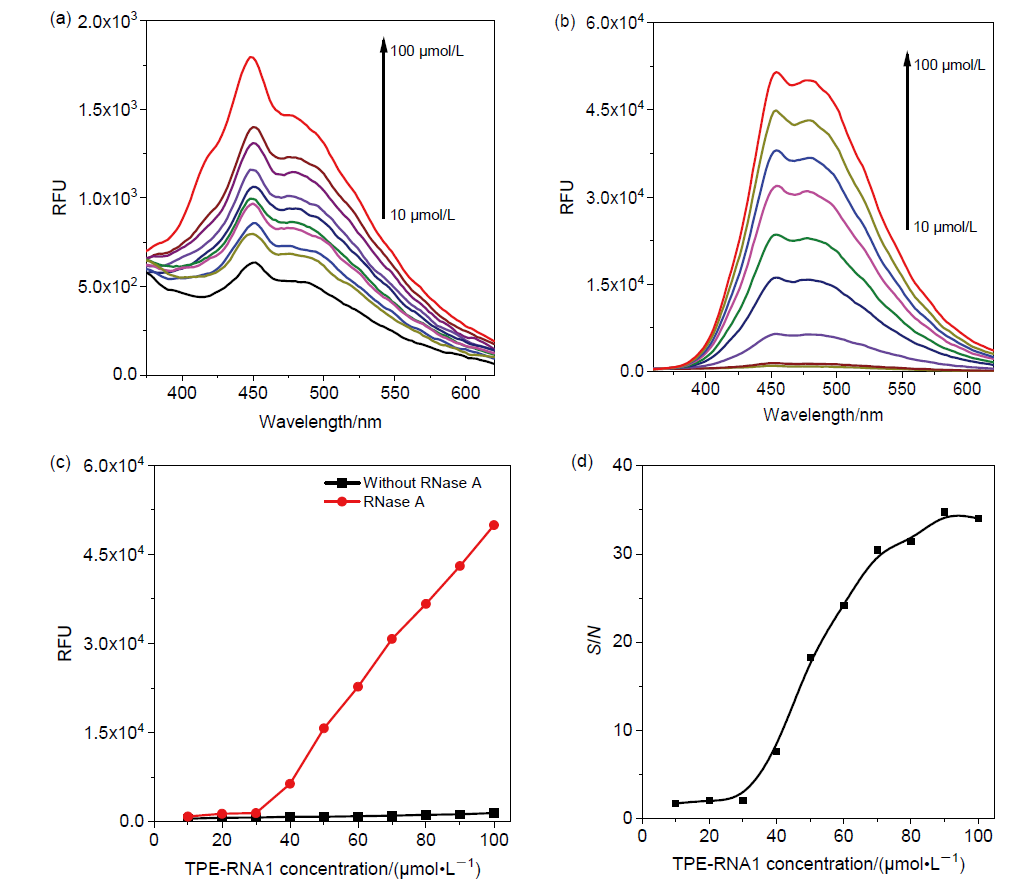
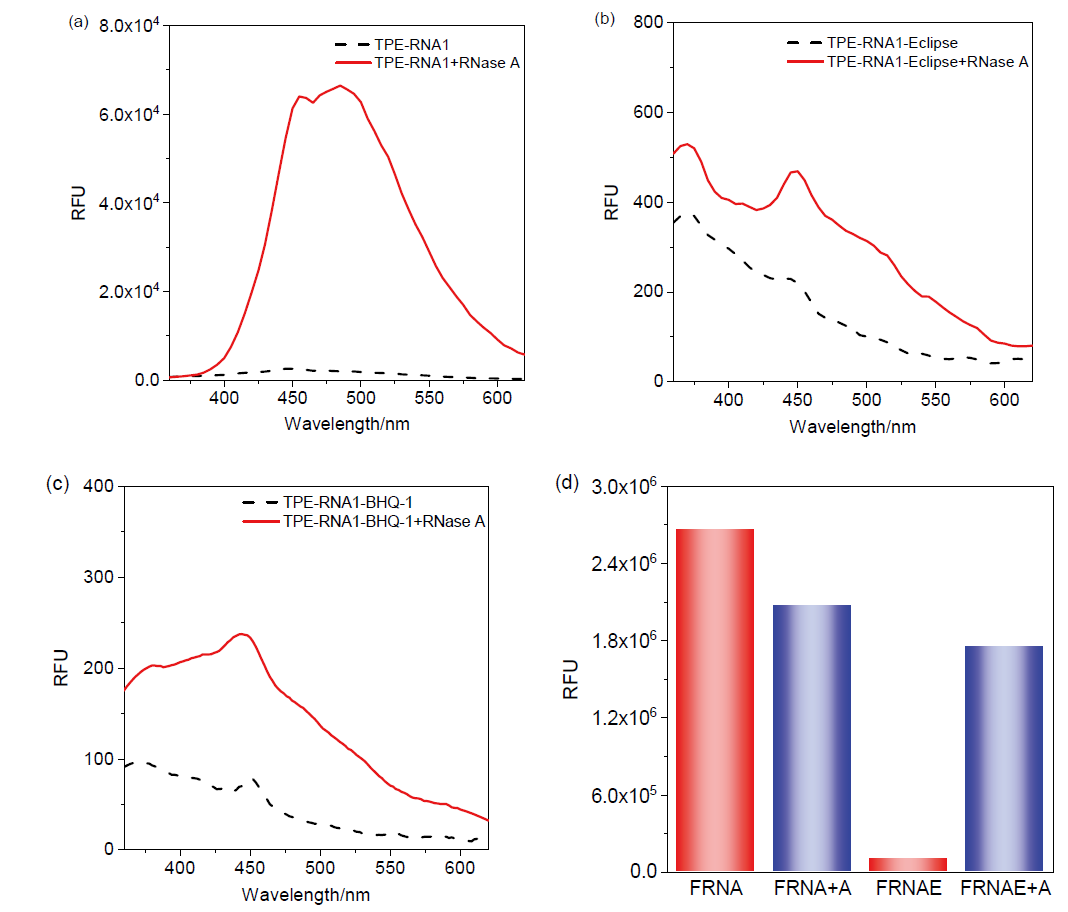
| [1] |
Hua, Y.; Ma, J.; Li, D.; Wang, R. Biosensor. 2022, 12, 183.
|
| [2] |
Samanta, D.; Ebrahimi, S. B.; Mirkin, C. A. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1901743.
|
| [3] |
Tian, R.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Jiang, Q.; Ding, B. Aggregat. 2021, 2, 133.
|
| [4] |
Quan, K.; Yi, C.; Yang, X.; He, X.; Huang, J.; Wang, K. TrA., Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 124, 115784.
|
| [5] |
Saccà, B.; Niemeyer, C. M. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 5910.
|
| [6] |
Zhang, X.; Chen, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y. Innovatio. 2024, 5, 100538.
|
| [7] |
Fei, X.; Gu, Y. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2009, 19, 1.
|
| [8] |
Tyagi, S.; Kramer, F. R. Nat. Biotechnol. 1996, 14, 303.
doi: 10.1038/nbt0396-303 pmid: 9630890 |
| [9] |
Gibson, U. E.; Heid, C. A.; Williams, P. M. Genome Res. 1996, 6, 995.
doi: 10.1101/gr.6.10.995 pmid: 8908519 |
| [10] |
Zhang, H.; Huang, F.; Cai, G.; Li, Y.; Lin, J. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 9736.
|
| [11] |
Tran, T.; Kostecki, R.; Catton, M.; Druce, J. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, e00360-18.
|
| [12] |
Tabatabaei, M. S.; Islam, R.; Ahmed, M. Anal. Chim. Act. 2021, 1143, 250.
|
| [13] |
Oxnard, G. R.; Paweletz, C. P.; Kuang, Y.; Mach, S. L.; O'Connell, A.; Messineo, M. M.; Luke, J. J.; Butaney, M.; Kirschmeier, P.; Jackman, D. M.; Jänne, P. A. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 1698.
|
| [14] |
Venkatesan, N.; Jun Seo, Y.; Hyean Kim, B. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 648.
doi: 10.1039/b705468h pmid: 18362974 |
| [15] |
Hwang, G. T.; Seo, Y. J.; Kim, B. H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 6528.
pmid: 15161261 |
| [16] |
Heinlein, T.; Knemeyer, J.-P.; Piestert, O.; Sauer, M. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 7957.
|
| [17] |
Nazarenko, I.; Lowe, B.; Darfler, M.; Ikonomi, P.; Schuster, D.; Rashtchian, A. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, e37.
|
| [18] |
Yang, C.; Abbas, F.; Rhouati, A.; Sun, Y.; Chu, X.; Cui, S.; Sun, B.; Xue, C. Biosensor. 2022, 12, 297.
|
| [19] |
Nikiforov, T. T. Anal. Biochem. 2014, 461, 67.
doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2014.05.027 pmid: 24907506 |
| [20] |
Knemeyer, J.-P.; Marmé, N.; Sauer, M. Anal. Chem. 2000, 72, 3717.
pmid: 10959954 |
| [21] |
Sobek, J.; Schlapbach, R. Molecule. 2020, 25, 5369.
|
| [22] |
Luo, J.; Xie, Z.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Cheng, L.; Chen, H.; Qiu, C.; Kwok, H. S.; Zhan, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, D.; Tang, B. Z. Chem. Commun. 2001, 18, 1740.
|
| [23] |
Gui, Y.; Chen, K.; Sun, Y.; Tan, Y.; Luo, W.; Zhu, D.; Xiong, Y.; Yan, D.; Wang, D.; Tang, B. Z. Chin. J. Chem. 2023, 41, 1249.
|
| [24] |
Lu, H.; Ma, L.; Ma, H. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2023, 43, 4075 (in Chinese).
|
|
(鲁会名, 马拉毛草, 马恒昌, 有机化学, 2023, 43, 4075.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202305010 |
|
| [25] |
Xu, H.; Han, P.; Qin, A.; Tang, B. Z. Acta Chim. Sinic. 2023, 81, 1420 (in Chinese).
|
|
(徐赫, 韩鹏博, 秦安军, 唐本忠, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 1420.)
doi: 10.6023/A23050232 |
|
| [26] |
Feng, X.; Zhu, L.; Yue, B. Acta Chim. Sinic. 2022, 80, 647 (in Chinese).
|
|
(冯锡成, 朱亮亮, 岳兵兵, 化学学报, 2022, 80, 647.)
doi: 10.6023/A22010015 |
|
| [27] |
Zhao, Y.; Chen, P.; Li, G.; Niu, Z.; Wang, E. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2023, 43, 2156 (in Chinese).
|
|
(赵洋, 陈盼盼, 李高楠, 钮智刚, 王恩举, 有机化学, 2023, 43, 2156.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202210002 |
|
| [28] |
Zhang, Y.; Nie, F.; Zhou, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Huo, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhao, Z. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2023, 43, 3876 (in Chinese).
|
|
(张越华, 聂飞, 周路, 王晓烽, 刘源, 霍延平, 陈文铖, 赵祖金, 有机化学, 2023, 43, 3876.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202303022 |
|
| [29] |
Zhu, L.; Zhou, J.; Xu, G.; Li, C.; Ling, P.; Liu, B.; Ju, H.; Lei, J. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 2559.
|
| [30] |
Ma, K.; Zhang, F.; Sayyadi, N.; Chen, W.; Anwer, A. G.; Care, A.; Xu, B.; Tian, W.; Goldys, E. M.; Liu, G. ACS Sens. 2018, 3, 320.
|
| [31] |
Wang, X.; Dai, J.; Min, X.; Yu, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Huang, K.; Yang, J.; Yi, X.; Lou, X.; Xia, F. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 8162.
|
| [32] |
Chen, J.; Jiang, H.; Zhou, H.; Hu, Z.; Niu, N.; Shahzad, S. A.; Yu, C. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 2398.
|
| [33] |
Lu, D.; He, L.; Wang, Y.; Xiong, M.; Hu, M.; Liang, H.; Huan, S.; Zhang, X.-B.; Tan, W. Talant. 2017, 167, 550.
|
| [34] |
Min, X.; Zhuang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Jia, Y.; Hakeem, A.; Zheng, F.; Cheng, Y.; Tang, B. Z.; Lou, X.; Xia, F. ACS Appl. Mater. Interface. 2015, 7, 16813.
|
| [35] |
Li, Y.; Kwok, R. T. K.; Tang, B. Z.; Liu, B. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 10135.
|
| [36] |
Chen, Z.; Wei, Z.; Xiao, F.; Chao, Z.; Lu, J.; Wang, Z.; Tian, L. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2207845.
|
| [37] |
Beaucage, S. L.; Caruthers, M. H. Tetrahedron Lett. 1981, 22, 1859.
|
| [38] |
Krotz, A. H.; Rentel, C.; Gorman, D.; Olsen, P.; Gaus, H. J.; McArdle, J. V.; Scozzari, A. N. Nucleoside., Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 2004, 23, 767.
|
| [39] |
Takamoto, K.; He, Q.; Morris, S.; Chance, M. R.; Brenowitz, M. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2002, 9, 928.
|
| [1] | Yujie Yang, Wei Cao, Jikai Yu, Zhixia Zhang, Li Xu, Hua Wang. Synthesis of Donor-Acceptor (D-A) Typed Phenylcyclooctatetrathiophenes and Their Performances on Aggregation Induced Emission and High Pressure Luminescence [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(8): 2495-2503. |
| [2] | Jidong Zhang, Yao Yang, Jie Zhang, Wei She. Detection of Zn(II) by Tetraphenylethyene Fluorescent Probe Based on Aggregation-Induced Emission (AIE)-Excited State Intramolecular Proton Transfer (ESIPT) Effect [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(4): 1337-1342. |
| [3] | Chongyang Zeng, Ping Hu, Biqin Wang, Wenyan Fang, Keqing Zhao. Cyanostilbene Bridged Triphenylene Dyad Stimuli-Responsive Discotic Liquid Crystal: Synthesis, Properties and Applications [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2023, 43(9): 3287-3296. |
| [4] | Yang Zhao, Panpan Chen, Lizhi Han, Enju Wang. Aggregation-Induced Emission and Cell Imaging of Triphenylimidazole Derivatives [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2023, 43(7): 2454-2461. |
| [5] | Yuehua Zhang, Fei Nie, Lu Zhou, Xiaofeng Wang, Yuan Liu, Yanping Huo, Wencheng Chen, Zujin Zhao. Synthesis and Optoelectronic Studies of Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence Materials Based on Benzothiazolyl Ketones [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2023, 43(11): 3876-3887. |
| [6] | Meng Liu, Yanru Huang, Xiaofei Sun, Lijun Tang. An “Aggregation-Induced Emission+Excited-State Intramolecular Proton Transfer” Mechanisms-Based Benzothiazole Derived Fluorescent Probe and Its ClO– Recognition [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2023, 43(1): 345-351. |
| [7] | Yangyang Li, Xiaofei Sun, Xiaoling Hu, Yuanyuan Ren, Keli Zhong, Xiaomei Yan, Lijun Tang. Synthesis of Triphenylamine Derivative and Its Recognition for Hg2+ with “OFF-ON” Fluorescence Response Based on Aggregation-Induced Emission (AIE) Mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2023, 43(1): 320-325. |
| [8] | Jidong Zhang, Wanlin Yan, Wenqiang Hu, Dian Guo, Dalong Zhang, Xiaoxin Quan, Xianpan Bu, Siyu Chen. Design and Synthesis of a Zn2+ Fluorescent Probe Based on Aggregation Induced Luminescence Properties [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2023, 43(1): 326-331. |
| [9] | Zhaohua Chen, Xiying Cao, Sihong Chen, Shiwei Yu, Yanlan Lin, Shuting Lin, Zhaoyang Wang. Design, Synthesis and Application of Trisubstituted Olefinic Aggregation-Induced Emission Molecules [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2022, 42(8): 2355-2363. |
| [10] | Ze Guo, Di Wu, Lili Wang, Zheng Duan. BF3•Et2O Promoted Dienone-Phenol Type Rearrangement to Synthesize Phosphepine with Aggregation Induced Luminescence (AIE) Effect [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2022, 42(8): 2481-2487. |
| [11] | Yuetian Guo, Yongxin Pan, Lijun Tang. Progresses in Reactive Fluorescent Probes with Fused Aggregation- Induced Emission (AIE) and Excited State Intramolecular Proton Transfer (ESIPT) Structures [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2022, 42(6): 1640-1650. |
| [12] | Sihong Chen, Jiamin Xu, Yuemei Li, Baoru Peng, Lingyu Luo, Huiye Feng, Zhaohua Chen, Zhaoyang Wang. Research Progress of Aggregation-Caused Quenching (ACQ) to Aggregation-Induced Emission (AIE) Transformation Based on Organic Small Molecules [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2022, 42(6): 1651-1666. |
| [13] | Jiang Qian, Wang Zhonglong, Li Mingxin, Yang Yiqin, Xu Xu, Xu Haijun, Wang Shifa. Nopinone-Based Difluoroboron β-Diketonate Complex: Aggregation-Induced Emission and Solvatochromism [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2020, 40(12): 4290-4297. |
| [14] | Liu Ruijiao, Zeng Jing. Study on a Novel Colorimetric and Off-On Fluorescent Chemosensor with Aggregation-Induced Emission Effect for Detection of Fe3+ in Aqueous Solution [J]. Chin. J. Org. Chem., 2017, 37(12): 3274-3281. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||