Acta Chimica Sinica ›› 2021, Vol. 79 ›› Issue (5): 614-627.DOI: 10.6023/A20120564 Previous Articles Next Articles
Special Issue: 分子探针、纳米生物学与生命分析化学
Review
李琛琛a, 陈慧燕b, 董月红b, 罗细亮a,*( ), 胡娟c,*(
), 胡娟c,*( ), 张春阳b,*(
), 张春阳b,*( )
)
投稿日期:2020-12-10
发布日期:2021-01-25
通讯作者:
罗细亮, 胡娟, 张春阳
作者简介: |
李琛琛, 2020年于山东师范大学获得分析化学博士学位, 现为青岛科技大学化学与分子工程学院副教授. 研究方向为生化分析和单分子检测. |
 |
陈慧燕, 山东师范大学化学化工与材料科学学院2018级硕士研究生, 研究方向为生物分析化学和单分子检测技术. |
 |
董月红, 山东师范大学化学化工与材料科学学院2018级硕士研究生, 主要研究方向为生化分析和化学发光检测. |
 |
罗细亮, 教授, 博士生导师, 国家优秀青年基金获得者, 山东省泰山学者特聘教授. 2005年于南京大学获得分析化学博士学位, 随后在爱尔兰都柏林城市大学、美国亚利桑那州立大学和匹兹堡大学从事博士后研究. 先后获批为欧盟玛丽居里学者、匹兹堡大学研究助理教授. 2011年加入青岛科技大学, 现任化学与分子工程学院院长、光电传感与生命分析教育部重点实验室主任. 主要研究方向为生化分析、光电传感和纳米生物复合材料. |
 |
胡娟, 上岗研究员, 硕士生导师. 2019年在山东师范大学获博士学位. 2009~2020年先后在中国科学院深圳先进技术研究院和山东师范大学工作, 现在东南大学化学化工学院工作. 主要研究方向为生物传感和单分子检测. |
 |
张春阳, 教授, 博士生导师, 中国科学院“百人计划”入选者, 国家杰出青年科学基金获得者, 国家“万人计划”科技创新领军人才, 国务院政府特殊津贴专家. 1999年在北京大学获博士学位, 随后在清华大学完成博士后研究. 2001年赴美, 先后在埃默里大学、约翰霍普金斯大学和纽约城市大学工作. 2009年回国加入中国科学院深圳先进技术研究院, 现为山东师范大学化学化工与材料科学学院院长. 主要研究方向为生化分析、生物纳米技术、单分子检测与成像. |
基金资助:
Chen-chen Lia, Hui-yan Chenb, Yue-hong Dongb, Xiliang Luoa,*( ), Juan Huc,*(
), Juan Huc,*( ), Chun-yang Zhangb,*(
), Chun-yang Zhangb,*( )
)
Received:2020-12-10
Published:2021-01-25
Contact:
Xiliang Luo, Juan Hu, Chun-yang Zhang
About author:Supported by:Share
Chen-chen Li, Hui-yan Chen, Yue-hong Dong, Xiliang Luo, Juan Hu, Chun-yang Zhang. Advances in Detection of Epigenetic Modification—5-Hydroxymethylcytosine[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(5): 614-627.
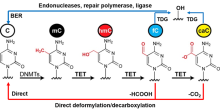
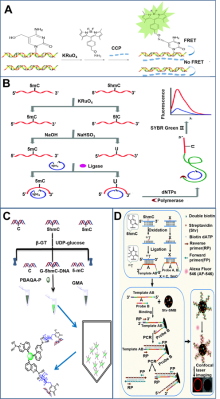

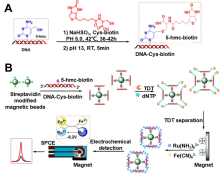
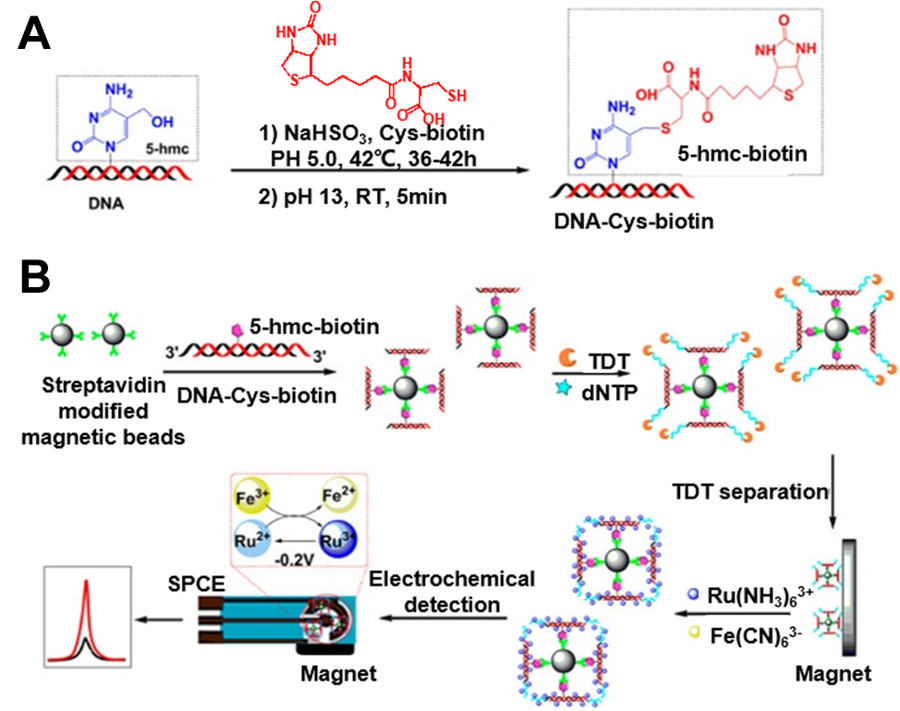
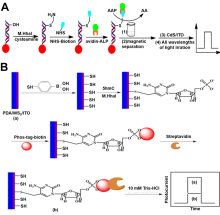




| 检测方法 | 适用目标 | 优点 | 缺点 | 参考文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 液相色谱-质谱联用法 | 检测5hmC总量 | 定量准确、可提供各个组分组成和结构信息 | 无法实现单碱基分辨、需要专业操作经验 | [ | |
| 荧光法 | 定量检测基因组DNA中的5hmC | 灵敏度高、操作简单 | 无法提供空间定位信息 | [ | |
| 电化学法 | 定量检测基因组DNA中的5hmC | 设备简单、成本低廉、易于微型化、背景信号低、灵敏度高 | 选择性较差、耗时长 | [ | |
| 电致化学发光法 | 5hmC的定量 | 化学势可控、灵敏度高、背景信号低、重现性好, 响应快速 | 存在电极表面污染问题、背景信号高、耗时长 | [ | |
| 光电化学法 | 5hmC的定量 | 成本低、操作简单、背景电流小、检测灵敏度高 | 不能检测人体基因组中的5hmC | [ | |
| 沉淀法 | GLIB | 5hmC DNA片段的分离和富集 | 不需要PCR扩增 | 反应时间较长、测序价格昂贵 | [ |
| CMS | 富集5hmC、全基因组定位 | 对5hmC丰度依赖性较低 | 需亚硫酸氢盐处理和特异性抗体、无法实现单碱基分辨 | [ | |
| JBP1 | 全基因组定位、解析5hmC在基因序列中的分布 | 简单直接、快速、高效 | 捕获效率低、灵敏度差 | [ | |
| hMeDIP | 全基因组定位、解析5hmC在基因序列中的分布 | 不需要PCR 扩增、单分子实时测序、成本低 | 有一定的序列偏好、无法实现单碱基分辨 | [ | |
| 亚硫酸氢盐测序及其衍生法 | BS-Seq | 全局和局部量化 | 适用于基因组的分析 | 亚硫酸氢盐处理可能导致DNA降解、不能区分5hmC和5mC | [ |
| TAB-Seq | 全基因组测序和位点特异性测序 | 高效、单碱基分辨率 | 依赖于苛刻的化学反应, 导致DNA损失较多; 将所有未甲基化的C转换为U会严重降低序列复杂性, 导致测序质量差、定位率低、基因组覆盖不均、测序成本高 | [ | |
| oxBS-Seq | 解析5hmC在基因序列中的精确定位 | 单碱基分辨率、可确定 5hmC和5mC精确位置、可与测序平台兼容 | 依赖于苛刻的化学反应, 导致DNA损失较多; 将所有未甲基化的C转换为U会严重降低序列复杂性, 导致测序质量差、定位率低、基因组覆盖不均、测序成本高 | [ | |
| 检测方法 | 适用目标 | 优点 | 缺点 | 参考文献 | |
| TAPS | 全基因组碱基水平分辨率的5hmC检测 | 非破坏性、高灵敏度和特异性 | 依赖于TET的活性; TET不是100%有效, 且成本高 | [ | |
| CAM-Seq | 定量检测基因组DNA中的5hmC | 不使用亚硫酸氢盐、具有单碱基分辨率的能力 | 氧化条件非常苛刻 | [ | |
| hmC-CATCH | 定量检测基因组DNA中的5hmC | 反应条件温和、无DNA降解发生、成本低 | 具有PCR偏向性 | [ | |
| 其他 | 5hmC在基因组中的分布 | 无位置倾向性、灵敏度高, 适用于微量样本和低丰度胞嘧啶修饰的分析 | 准确度差 | [ | |
| 单分子检测技术 | SMRT | 解析5hmC在基因序列中的精确定位、全局定量分析 | 不需要扩增DNA、有效降低了扩增反应对修饰位点的影响 | 碱基识别错误率较高、测序价格昂贵 | [ |
| 纳米孔传感 | 解析5hmC在基因序列中的精确定位、全局定量分析 | 不需要限制性内切酶、不需要羟甲基化位点的序列信息、可在样本序列信息未知的情况下检测DNA中任意5hmC | 没有应用于定量基因组DNA样品中的5hmC | [ | |
| 单分子成像 | 解析5hmC在基因序列中的精确定位、全局定量分析 | 可以提供空间定位信息 | 需要标记技术 | [ | |
| 检测方法 | 适用目标 | 优点 | 缺点 | 参考文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 液相色谱-质谱联用法 | 检测5hmC总量 | 定量准确、可提供各个组分组成和结构信息 | 无法实现单碱基分辨、需要专业操作经验 | [ | |
| 荧光法 | 定量检测基因组DNA中的5hmC | 灵敏度高、操作简单 | 无法提供空间定位信息 | [ | |
| 电化学法 | 定量检测基因组DNA中的5hmC | 设备简单、成本低廉、易于微型化、背景信号低、灵敏度高 | 选择性较差、耗时长 | [ | |
| 电致化学发光法 | 5hmC的定量 | 化学势可控、灵敏度高、背景信号低、重现性好, 响应快速 | 存在电极表面污染问题、背景信号高、耗时长 | [ | |
| 光电化学法 | 5hmC的定量 | 成本低、操作简单、背景电流小、检测灵敏度高 | 不能检测人体基因组中的5hmC | [ | |
| 沉淀法 | GLIB | 5hmC DNA片段的分离和富集 | 不需要PCR扩增 | 反应时间较长、测序价格昂贵 | [ |
| CMS | 富集5hmC、全基因组定位 | 对5hmC丰度依赖性较低 | 需亚硫酸氢盐处理和特异性抗体、无法实现单碱基分辨 | [ | |
| JBP1 | 全基因组定位、解析5hmC在基因序列中的分布 | 简单直接、快速、高效 | 捕获效率低、灵敏度差 | [ | |
| hMeDIP | 全基因组定位、解析5hmC在基因序列中的分布 | 不需要PCR 扩增、单分子实时测序、成本低 | 有一定的序列偏好、无法实现单碱基分辨 | [ | |
| 亚硫酸氢盐测序及其衍生法 | BS-Seq | 全局和局部量化 | 适用于基因组的分析 | 亚硫酸氢盐处理可能导致DNA降解、不能区分5hmC和5mC | [ |
| TAB-Seq | 全基因组测序和位点特异性测序 | 高效、单碱基分辨率 | 依赖于苛刻的化学反应, 导致DNA损失较多; 将所有未甲基化的C转换为U会严重降低序列复杂性, 导致测序质量差、定位率低、基因组覆盖不均、测序成本高 | [ | |
| oxBS-Seq | 解析5hmC在基因序列中的精确定位 | 单碱基分辨率、可确定 5hmC和5mC精确位置、可与测序平台兼容 | 依赖于苛刻的化学反应, 导致DNA损失较多; 将所有未甲基化的C转换为U会严重降低序列复杂性, 导致测序质量差、定位率低、基因组覆盖不均、测序成本高 | [ | |
| 检测方法 | 适用目标 | 优点 | 缺点 | 参考文献 | |
| TAPS | 全基因组碱基水平分辨率的5hmC检测 | 非破坏性、高灵敏度和特异性 | 依赖于TET的活性; TET不是100%有效, 且成本高 | [ | |
| CAM-Seq | 定量检测基因组DNA中的5hmC | 不使用亚硫酸氢盐、具有单碱基分辨率的能力 | 氧化条件非常苛刻 | [ | |
| hmC-CATCH | 定量检测基因组DNA中的5hmC | 反应条件温和、无DNA降解发生、成本低 | 具有PCR偏向性 | [ | |
| 其他 | 5hmC在基因组中的分布 | 无位置倾向性、灵敏度高, 适用于微量样本和低丰度胞嘧啶修饰的分析 | 准确度差 | [ | |
| 单分子检测技术 | SMRT | 解析5hmC在基因序列中的精确定位、全局定量分析 | 不需要扩增DNA、有效降低了扩增反应对修饰位点的影响 | 碱基识别错误率较高、测序价格昂贵 | [ |
| 纳米孔传感 | 解析5hmC在基因序列中的精确定位、全局定量分析 | 不需要限制性内切酶、不需要羟甲基化位点的序列信息、可在样本序列信息未知的情况下检测DNA中任意5hmC | 没有应用于定量基因组DNA样品中的5hmC | [ | |
| 单分子成像 | 解析5hmC在基因序列中的精确定位、全局定量分析 | 可以提供空间定位信息 | 需要标记技术 | [ | |
| [1] |
Wolffe, A. P.; Matzke, M. A. Science 1999, 286,481.
doi: 10.1126/science.286.5439.481 |
| [2] |
Jaenisch, R.; Bird, A. Nat. Genet. 2003, 33,245.
doi: 10.1038/ng1089 |
| [3] |
Prins, G. S.; Ye, S. H.; Birch, L.; Zhang, X.; Cheong, A.; Lin, H.; Calderon-Gierszal, E.; Groen, J.; Hu, W. Y.; Ho, S. M.; van Breemen, R. B. Environ. Health Perspect. 2017, 125,077007.
doi: 10.1289/EHP1050 |
| [4] |
Portela, A.; Esteller, M. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28,1057.
doi: 10.1038/nbt.1685 |
| [5] |
Tahara, T.; Tahara, S.; Horiguchi, N.; Kawamura, T.; Okubo, M.; Yamada, H.; Yoshida, D.; Ohmori, T.; Maeda, K.; Komura, N.; Ikuno, H.; Jodai, Y.; Kamano, T.; Nagasaka, M.; Nakagawa, Y.; Tsukamoto, T.; Urano, M.; Shibata, T.; Kuroda, M.; Ohmiya, N. Clin. Exp. Med. 2018, 18,215.
doi: 10.1007/s10238-017-0471-4 |
| [6] |
Moruzzi, S.; Guarini, P.; Udali, S.; Ruzzenente, A.; Guglielmi, A.; Conci, S.; Pattini, P.; Martinelli, N.; Olivieri, O.; Tammen, S. A.; Choi, S. W.; Friso, S. PLoS One 2017, 12,e0185792.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0185792 |
| [7] |
Iwata, A.; Nagata, K.; Hatsuta, H.; Takuma, H.; Bundo, M.; Iwamoto, K.; Tamaoka, A.; Murayama, S.; Saido, T.; Tsuji, S. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23,648.
doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddt451 |
| [8] |
Lee, J.; Hagerty, S.; Cormier, K. A.; Kim, J.; Kung, A. L.; Ferrante, R. J.; Ryu, H. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2008, 17,1774.
doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddn067 |
| [9] |
Begum, G.; Davies, A.; Stevens, A.; Oliver, M.; Jaquiery, A.; Challis, J.; Harding, J.; Bloomfield, F.; White, A. Endocrinology 2013, 154,4560.
doi: 10.1210/en.2013-1693 |
| [10] |
Baserga, M.; Kaur, R.; Hale, M. A.; Bares, A.; Yu, X.; Callaway, C. W.; McKnight, R. A.; Lane, R. H. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2010,299,R334.
doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00122.2010 |
| [11] |
Baserga, M.; Hale, M. A.; Wang, Z. M.; Yu, X.; Callaway, C. W.; McKnight, R. A.; Lane, R. H. Am. J. Physiol-Reg I. 2007, 292,R1943.
|
| [12] |
Masuyama, H.; Hiramatsu, Y. Endocrinology 2012, 153,2823.
doi: 10.1210/en.2011-2161 pmid: 22434078 |
| [13] |
Li, D.; Tian, Y. J.; Guo, J.; Sun, W. P.; Lun, Y. Z.; Guo, M.; Luo, N.; Cao, Y.; Cao, J. M.; Gong, X. J.; Zhou, S. S. Br. J. Nutr. 2013, 110,2156.
doi: 10.1017/S0007114513001815 |
| [14] |
Zhao, C.; Wang, H. L. Acta Chim. Sinica 2013, 71,26. (in Chinese).
doi: 10.6023/A12110891 |
|
( 赵超, 汪海林, 化学学报, 2013, 71,26.)
doi: 10.6023/A12110891 |
|
| [15] |
Cheng, X.; Roberts, R. J. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29,3784.
doi: 10.1093/nar/29.18.3784 |
| [16] |
Smith, Z. D.; Meissner, A. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2013, 14,204.
doi: 10.1038/nrg3354 |
| [17] |
Wood, R. J.; McKelvie, J. C.; Maynard-Smith, M. D.; Roach, P. L. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38,e107.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq047 |
| [18] |
Xu, H.; Jia, P.; Zhao, Z. Brief Bioinform. 2020,doi: 10.1093/bib/bbaa099.
|
| [19] |
Xiao, C. L.; Zhu, S.; He, M. H.; Chen, D.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Yu, G. L.; Liu, J. B.; Xie, S. Q.; Luo, F.; Liang, Z.; Wang, D. P.; Bo, X. C.; Gu, X. F.; Wang, K.; Yan, G. R. Mol. Cell 2018, 71,306.
doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.06.015 |
| [20] |
Stains, C. I.; Furman, J. L.; Segal, D. J.; Ghosh, I. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128,9761.
pmid: 16866532 |
| [21] |
Costello, J. F.; Fruhwald, M. C.; Smiraglia, D. J.; Rush, L. J.; Robertson, G. P.; Gao, X.; Wright, F. A.; Feramisco, J. D.; Peltomaki, P.; Lang, J. C.; Schuller, D. E.; Yu, L.; Bloomfield, C. D.; Caligiuri, M. A.; Yates, A.; Nishikawa, R.; Huang, H. J. S.; Petrelli, N. J.; Zhang, X. L.; O'Dorisio, M. S.; Held, W. A.; Cavenee, W. K.; Plass, C. Nat. Genet. 2000, 24,132.
pmid: 10655057 |
| [22] |
Bernstein, B. E.; Meissner, A.; Lander, E. S. Cell 2007, 128,669.
pmid: 17320505 |
| [23] |
Zhang, Q.; Wu, Y.; Xu, Q.; Ma, F.; Zhang, C. Y. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 171,112712.
doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2020.112712 |
| [24] |
Song, C. X.; Szulwach, K. E.; Fu, Y.; Dai, Q.; Yi, C.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, C. H.; Zhang, W.; Jian, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Looney, T. J.; Zhang, B.; Godley, L. A.; Hicks, L. M.; Lahn, B. T.; Jin, P.; He, C. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29,68.
doi: 10.1038/nbt.1732 |
| [25] |
Scarano, M. I.; Strazzullo, M.; Matarazzo, M. R.; D'Esposito, M. J. Cell. Physiol. 2005, 204,21.
pmid: 15648089 |
| [26] |
Robertson, K. D. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2005, 6,597.
pmid: 16136652 |
| [27] |
Iwan, K.; Rahimoff, R.; Kirchner, A.; Spada, F.; Schroder, A. S.; Kosmatchev, O.; Ferizaj, S.; Steinbacher, J.; Parsa, E.; Muller, M.; Carell, T. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2018, 14,72.
doi: 10.1038/nchembio.2531 |
| [28] |
Wu, S. C.; Zhang, Y. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Bio. 2010, 11,607.
doi: 10.1038/nrm2950 |
| [29] |
Huang, W.; Lan, M. D.; Qi, C. B.; Zheng, S. J.; Wei, S. Z.; Yuan, B. F.; Feng, Y. Q. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7,5495.
doi: 10.1039/c6sc01589a pmid: 30034689 |
| [30] |
Crawford, D. J.; Liu, M. Y.; Nabel, C. S.; Cao, X. J.; Garcia, B. A.; Kohli, R. M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138,730.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.5b10554 |
| [31] |
Chen, S.; Dou, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Li, F.; Su, J.; Fan, C.; Song, S. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88,3476.
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.6b00230 |
| [32] |
Zhang, L.; Yu, M.; He, C. Acta Chim. Sinica 2012, 70,2123. (in Chinese).
doi: 10.6023/A12090619 |
|
( 张良, 于淼, 何川, 化学学报, 2012, 70,2123.)
doi: 10.6023/A12090619 |
|
| [33] |
Liutkeviciute, Z.; Kriukiene, E.; Licyte, J.; Rudyte, M.; Urbanaviciute, G.; Klimasauskas, S. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136,5884.
doi: 10.1021/ja5019223 |
| [34] |
Kohli, R. M.; Zhang, Y. Nature 2013, 502,472.
doi: 10.1038/nature12750 |
| [35] |
Kagiwada, S.; Kurimoto, K.; Hirota, T.; Yamaji, M.; Saitou, M. EMBO J. 2013, 32,340.
doi: 10.1038/emboj.2012.331 |
| [36] |
Ginno, P. A.; Gaidatzis, D.; Feldmann, A.; Hoerner, L.; Imanci, D.; Burger, L.; Zilbermann, F.; Peters, A. H. F. M.; Edenhofer, F.; Smallwood, S. A.; Krebs, A. R.; Schubeler, D. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11,2680.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16354-x |
| [37] |
Shukla, A.; Sehgal, M.; Singh, T. R. Gene 2015, 564,109.
doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2015.03.075 |
| [38] |
Munzel, M.; Globisch, D.; Carell, T. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2011, 50,6460.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v50.29 |
| [39] |
Tahiliani, M.; Koh, K. P.; Shen, Y.; Pastor, W. A.; Bandukwala, H.; Brudno, Y.; Agarwal, S.; Iyer, L. M.; Liu, D. R.; Aravind, L.; Rao, A. Science 2009, 324,930.
doi: 10.1126/science.1170116 |
| [40] |
Kriaucionis, S.; Heintz, N. Science 2009, 324,929.
doi: 10.1126/science.1169786 |
| [41] |
Mellen, M.; Ayata, P.; Dewell, S.; Kriaucionis, S.; Heintz, N. Cell 2012, 151,1417.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.11.022 |
| [42] |
Szulwach, K. E.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Song, C. X.; Han, J. W.; Kim, S.; Namburi, S.; Hermetz, K.; Kim, J. J.; Rudd, M. K.; Yoon, Y. S.; Ren, B.; He, C.; Jin, P. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7,e1002154.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002154 |
| [43] |
Pfeifer, G. P.; Kadam, S.; Jin, S. G. Epigenetics Chromatin 2013, 6,10.
doi: 10.1186/1756-8935-6-10 |
| [44] |
Jin, S. G.; Jiang, Y.; Qiu, R.; Rauch, T. A.; Wang, Y.; Schackert, G.; Krex, D.; Lu, Q.; Pfeifer, G. P. Cancer Res. 2011, 71,7360.
doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-2023 |
| [45] |
Kato, T.; Iwamoto, K. Neuropharmacology 2014, 80,133.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.12.019 |
| [46] |
Wen, L.; Tang, F. Genomics 2014, 104,341.
doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2014.08.020 pmid: 25205307 |
| [47] |
Yang, Y.; Yang, G.; Chen, H.; Zhang, H.; Feng, J. J.; Cai, C. Analyst 2018, 143,2051.
doi: 10.1039/c7an02049j pmid: 29629447 |
| [48] |
Jin, S. G.; Kadam, S.; Pfeifer, G. P. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38,e125.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq223 |
| [49] |
Nestor, C.; Ruzov, A.; Meehan, R. R.; Dunican, D. S. Biotechniques 2010, 48,317.
doi: 10.2144/000113403 pmid: 20569209 |
| [50] |
Ito, S.; D'Alessio, A. C.; Taranova, O. V.; Hong, K.; Sowers, L. C.; Zhang, Y. Nature 2010, 466,1129.
doi: 10.1038/nature09303 |
| [51] |
Huang, Y.; Pastor, W. A.; Shen, Y. H.; Tahiliani, M.; Liu, D. R.; Rao, A. PLoS One 2010, 5,e8888.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008888 |
| [52] |
Flusberg, B. A.; Webster, D. R.; Lee, J. H.; Travers, K. J.; Olivares, E. C.; Clark, T. A.; Korlach, J.; Turner, S. W. Nat. Methods 2010, 7,461.
doi: 10.1038/NMETH.1459 |
| [53] |
Munzel, M.; Globisch, D.; Bruckl, T.; Wagner, M.; Welzmiller, V.; Michalakis, S.; Muller, M.; Biel, M.; Carell, T. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2010, 49,5375.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v49:31 |
| [54] |
Yin, R. C.; Mo, J. Z.; Lu, M. L.; Wang, H. L. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87,1846.
doi: 10.1021/ac5038895 |
| [55] |
Krais, A. M.; Park, Y. J.; Plass, C.; Schmeiser, H. H. Epigenetics 2011, 6,560.
doi: 10.4161/epi.6.5.15678 |
| [56] |
Hong, T.; Wang, T.; Guo, P.; Xing, X.; Ding, F.; Chen, Y.; Wu, J.; Ma, J.; Wu, F.; Zhou, X. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85,10797.
doi: 10.1021/ac4020676 |
| [57] |
Pastor, W. A.; Pape, U. J.; Huang, Y.; Henderson, H. R.; Lister, R.; Ko, M.; McLoughlin, E. M.; Brudno, Y.; Mahapatra, S.; Kapranov, P.; Tahiliani, M.; Daley, G. Q.; Liu, X. S.; Ecker, J. R.; Milos, P. M.; Agarwal, S.; Rao, A. Nature 2011, 473,394.
doi: 10.1038/nature10102 |
| [58] |
Ko, M.; Huang, Y.; Jankowska, A. M.; Pape, U. J.; Tahiliani, M.; Bandukwala, H. S.; An, J.; Lamperti, E. D.; Koh, K. P.; Ganetzky, R.; Liu, X. S.; Aravind, L.; Agarwal, S.; Maciejewski, J. P.; Rao, A. Nature 2010, 468,839.
doi: 10.1038/nature09586 |
| [59] |
Nestor, C. E.; Ottaviano, R.; Reddington, J.; Sproul, D.; Reinhardt, D.; Dunican, D.; Katz, E.; Dixon, J. M.; Harrison, D. J.; Meehan, R. R. Genome Res. 2012, 22,467.
doi: 10.1101/gr.126417.111 |
| [60] |
Voigt, P.; Tee, W. W.; Reinberg, D. Genes Dev. 2013, 27,1318.
doi: 10.1101/gad.219626.113 |
| [61] |
Plongthongkum, N.; Diep, D. H.; Zhang, K. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2014, 15,647.
|
| [62] |
Tang, Y.; Chu, J. M.; Huang, W.; Xiong, J.; Xing, X. W.; Zhou, X.; Feng, Y. Q.; Yuan, B. F. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85,6129.
doi: 10.1021/ac4010869 |
| [63] |
He, Y. F.; Li, B. Z.; Li, Z.; Liu, P.; Wang, Y.; Tang, Q.; Ding, J.; Jia, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, L.; Sun, Y.; Li, X.; Dai, Q.; Song, C. X.; Zhang, K.; He, C.; Xu, G. L. Science 2011, 333,1303.
doi: 10.1126/science.1210944 |
| [64] |
Le, T.; Kim, K. P.; Fan, G.; Faull, K. F. Anal. Biochem. 2011, 412,203.
doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2011.01.026 |
| [65] |
Liu, S.; Wang, J.; Su, Y.; Guerrero, C.; Zeng, Y.; Mitra, D.; Brooks, P. J.; Fisher, D. E.; Song, H.; Wang, Y. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41,6421.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt360 |
| [66] |
Yuan, F.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, Y. L.; Zhang, X. X. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92,1605.
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.9b04920 |
| [67] |
Shahal, T.; Koren, O.; Shefer, G.; Stern, N.; Ebenstein, Y. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1038,87.
doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2018.08.035 |
| [68] |
Wang, Z. Y.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C. Y. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54,8602.
doi: 10.1039/C8CC03938K |
| [69] |
Chen, H. Y.; Wei, J. R.; Pan, J. X.; Zhang, W.; Dang, F. Q.; Zhang, Z. Q.; Zhang, J. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 91,328.
doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2016.12.039 |
| [70] |
Cui, L.; Hu, J.; Wang, M.; Li, C. C.; Zhang, C. Y. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91,1232.
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.8b04663 |
| [71] |
Wang, H.; Liu, M. Z.; Bai, W. Q.; Sun, H. P.; Li, Y.; Deng, H. Q. Sens. Actuators B 2019, 284,236.
doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2018.12.132 |
| [72] |
Ma, S.; Sun, H.; Li, Y.; Qi, H.; Zheng, J. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88,9934.
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.6b01265 |
| [73] |
Zhou, Y. L.; Yin, H. S.; Sui, C. J.; Wang, Y.; Ai, S. Y. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 357,94.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.09.138 |
| [74] |
Sui, C.; Li, F.; Wu, H.; Yin, H.; Zhang, S.; Waterhouse, G. I. N.; Wang, J.; Zhu, L.; Ai, S. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 142,111516.
doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2019.111516 |
| [75] |
Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wu, F.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, X. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10,447.
doi: 10.1039/C8SC04272A |
| [76] |
Hu, L.; Liu, Y.; Han, S.; Yang, L.; Cui, X.; Gao, Y.; Dai, Q.; Lu, X.; Kou, X.; Zhao, Y.; Sheng, W.; Gao, S.; He, X.; He, C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141,8694.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b02512 |
| [77] |
Liu, Y.; Siejka-Zielinska, P.; Velikova, G.; Bi, Y.; Yuan, F.; Tomkova, M.; Bai, C.; Chen, L.; Schuster-Bockler, B.; Song, C. X. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37,424.
doi: 10.1038/s41587-019-0041-2 |
| [78] |
Song, C. X.; Clark, T. A.; Lu, X. Y.; Kislyuk, A.; Dai, Q.; Turner, S. W.; He, C.; Korlach, J. Nat. Methods 2012, 9,75.
doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1779 |
| [79] |
Gilat, N.; Tabachnik, T.; Shwartz, A.; Shahal, T.; Torchinsky, D.; Michaeli, Y.; Nifker, G.; Zirkin, S.; Ebenstein, Y. Clin. Epigenetics. 2017, 9,70.
doi: 10.1186/s13148-017-0368-9 pmid: 28725280 |
| [80] |
Cui, L.; Chung, T. H.; Tan, D.; Sun, X.; Jia, X. Y. Genomics 2014, 104,368.
doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2014.08.023 |
| [81] |
Hofer, A.; Liu, Z. J.; Balasubramanian, S. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141,6420.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b01915 |
| [82] |
Lichtman, J. W.; Conchello, J. A. Nat. Methods 2005, 2,910.
pmid: 16299476 |
| [83] |
Hall, T. Science 1961, 134,449.
doi: 10.1126/science.134.3477.449 |
| [84] |
Zhang, Z.; Yan, J.; Li, Z. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56,3111.
doi: 10.1039/D0CC00167H |
| [85] |
Shahal, T.; Gilat, N.; Michaeli, Y.; Redy-Keisar, O.; Shabat, D.; Ebenstein, Y. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86,8231.
doi: 10.1021/ac501609d |
| [86] |
Beyer, S.; Nickels, P.; Simmel, F. C. Nano Lett. 2005, 5,719.
doi: 10.1021/nl050155a |
| [87] |
Baner, J.; Nilsson, M.; Mendel-Hartvig, M.; Landegren, U. Nucleic Acids Res. 1998, 26,5073.
doi: 10.1093/nar/26.22.5073 |
| [88] |
Zhang, Z. H.; Shan, X.; Zhang, P. B.; Liu, W. L.; Yan, J. L.; Li, Z. P. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2019, 17,9849.
doi: 10.1039/C9OB02429H |
| [89] |
Yin, H. S.; Yang, Z. Q.; Wang, H. Y.; Zhou, Y. L.; Ai, S. Y. Sens. Actuators B 2017, 243,602.
doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2016.12.029 |
| [90] |
Tang, Z. W.; Huang, J.; He, H. L.; Ma, C. B.; Wang, K. M. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2020, 415,213317.
doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2020.213317 |
| [91] |
Povedano, E.; Montiel, V. R.; Valverde, A.; Navarro-Villoslada, F.; Yanez-Sedeno, P.; Pedrero, M.; Montero-Calle, A.; Barderas, R.; Pelaez-Garcia, A.; Mendiola, M.; Hardisson, D.; Feliu, J.; Camps, J.; Rodriguez-Tomas, E.; Joven, J.; Arenas, M.; Campuzano, S.; Pingarron, J. M. ACS Sens. 2019, 4,227.
doi: 10.1021/acssensors.8b01339 |
| [92] |
Povedano, E.; Ruiz-Valdepenas Montiel, V.; Gamella, M.; Pedrero, M.; Barderas, R.; Pelaez-Garcia, A.; Mendiola, M.; Hardisson, D.; Feliu, J.; Yanez-Sedeno, P.; Campuzano, S.; Pingarron, J. M. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92,5604.
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.0c00628 |
| [93] |
Liu, C. Y.; Bard, A. J. Nat. Mater. 2008, 7,505.
doi: 10.1038/nmat2160 |
| [94] |
Li, L. L.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, J. J. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89,358.
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.6b04675 |
| [95] |
Xu, S. J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, T. H.; Li, J. H. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82,9566.
doi: 10.1021/ac102296g |
| [96] |
Tang, X.; Zhao, D.; He, J.; Li, F.; Peng, J.; Zhang, M. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85,1711.
doi: 10.1021/ac303025y |
| [97] |
Sun, H.; Ma, S.; Li, Y.; Qi, H.; Ning, X.; Zheng, J. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 79,92.
doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2015.11.068 |
| [98] |
Sun, H.; Wang, H.; Bai, W.; Bao, L.; Lin, J.; Li, Y. Talanta 2019, 191,350.
doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2018.08.070 |
| [99] |
Zhao, W. W.; Xu, J. J.; Chen, H. Y. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114,7421.
doi: 10.1021/cr500100j |
| [100] |
Zhao, W. W.; Xu, J. J.; Chen, H. Y. Trac-Trend Anal. Chem. 2016, 82,307.
doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2016.06.020 |
| [101] |
Yang, Z. Q.; Shi, Y. H.; Liao, W. R.; Yin, H. S.; Ai, S. Y. Sens. Actuators B 2016, 223,621.
doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2015.09.159 |
| [102] |
Wang, M.; Yin, H.; Zhou, Y.; Sui, C.; Wang, Y.; Meng, X.; Waterhouse, G. I. N.; Ai, S. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 128,137.
doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2018.12.048 |
| [103] |
Zang, Y.; Lei, J.; Hao, Q.; Ju, H. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 77,557.
doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2015.10.010 |
| [104] |
Tan, Y.; Li, M. S.; Ye, X. X.; Wang, Z. G.; Wang, Y. Y.; Li, C. Y. Sens. Actuators B 2018, 262,982.
doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2018.02.066 |
| [105] |
Lan, F.; Liang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Ren, N.; Yan, M.; Ge, S.; Yu, J. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9,37839.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.7b12338 |
| [106] |
Okoth, O. K.; Yan, K.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 86,636.
doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2016.07.037 |
| [107] |
Li, L.; Wang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, C.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, X.; Liu, H.; Chen, X.; Yu, J. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10,14594.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.8b03632 |
| [108] |
Sui, C.; Wang, T.; Zhou, Y.; Yin, H.; Meng, X.; Zhang, S.; Waterhouse, G. I. N.; Xu, Q.; Zhuge, Y.; Ai, S. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 127,38.
doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2018.11.054 |
| [109] |
Pastor, W. A.; Huang, Y.; Henderson, H. R.; Agarwal, S.; Rao, A. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7,1909.
doi: 10.1038/nprot.2012.104 |
| [110] |
Huang, Y.; Pastor, W. A.; Zepeda-Martinez, J. A.; Rao, A. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7,1897.
doi: 10.1038/nprot.2012.103 pmid: 23018193 |
| [111] |
Tan, L.; Xiong, L.; Xu, W.; Wu, F.; Huang, N.; Xu, Y.; Kong, L.; Zheng, L.; Schwartz, L.; Shi, Y.; Shi, Y. G. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41,e84.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt091 |
| [112] |
Casanello, P.; Krause, B. J.; Castro-Rodriguez, J. A.; Uauy, R. Rev. Chil. Pediatr. 2016, 87,335.
doi: S0370-41062016000500002 pmid: 27692574 |
| [113] |
Booth, M. J.; Marsico, G.; Bachman, M.; Beraldi, D.; Balasubramanian, S. Nat. Chem. 2014, 6,435.
doi: 10.1038/nchem.1893 |
| [114] |
Raiber, E. A.; Hardisty, R.; van Delft, P.; Balasubramanian, S. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2017, 1,0069.
doi: 10.1038/s41570-017-0069 |
| [115] |
Yu, M.; Hon, G. C.; Szulwach, K. E.; Song, C. X.; Zhang, L.; Kim, A.; Li, X.; Dai, Q.; Shen, Y.; Park, B.; Min, J. H.; Jin, P.; Ren, B.; He, C. Cell 2012, 149,1368.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.04.027 |
| [116] |
Booth, M. J.; Branco, M. R.; Ficz, G.; Oxley, D.; Krueger, F.; Reik, W.; Balasubramanian, S. Science 2012, 336,934.
doi: 10.1126/science.1220671 |
| [117] |
Tanaka, K.; Okamoto, A. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007, 17,1912.
pmid: 17276678 |
| [118] |
Zeng, H.; He, B.; Xia, B.; Bai, D.; Lu, X.; Cai, J.; Chen, L.; Zhou, A.; Zhu, C.; Meng, H.; Gao, Y.; Guo, H.; He, C.; Dai, Q.; Yi, C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140,13190.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.8b08297 |
| [119] |
Sun, Z.; Dai, N.; Borgaro, J. G.; Quimby, A.; Sun, D.; Correa, I. R. Jr.; Zheng, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Guan, S. Mol. Cell. 2015, 57,750.
doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.12.035 |
| [120] |
Fang, K.; Zhang, K. X.; Wang, J.; Fu, Z. M.; Zhao, X. H. Yi Chuan 2016, 38,206. (in Chinese).
|
|
( 方科, 张凯翔, 王建, 付志猛, 赵湘辉, 遗传, 2016, 38,206.)
|
|
| [121] |
Li, C. C.; Liu, W. X.; Hu, J.; Zhang, C. Y. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10,8675.
doi: 10.1039/C9SC02137J |
| [122] |
Ma, F.; Li, Y.; Tang, B.; Zhang, C. Y. Acc. Chem. Res. 2016, 49,1722.
doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.6b00237 |
| [123] |
Eid, J.; Fehr, A.; Gray, J.; Luong, K.; Lyle, J.; Otto, G.; Peluso, P.; Rank, D.; Baybayan, P.; Bettman, B.; Bibillo, A.; Bjornson, K.; Chaudhuri, B.; Christians, F.; Cicero, R.; Clark, S.; Dalal, R.; Dewinter, A.; Dixon, J.; Foquet, M.; Gaertner, A.; Hardenbol, P.; Heiner, C.; Hester, K.; Holden, D.; Kearns, G.; Kong, X.; Kuse, R.; Lacroix, Y.; Lin, S.; Lundquist, P.; Ma, C.; Marks, P.; Maxham, M.; Murphy, D.; Park, I.; Pham, T.; Phillips, M.; Roy, J.; Sebra, R.; Shen, G.; Sorenson, J.; Tomaney, A.; Travers, K.; Trulson, M.; Vieceli, J.; Wegener, J.; Wu, D.; Yang, A.; Zaccarin, D.; Zhao, P.; Zhong, F.; Korlach, J.; Turner, S. Science 2009, 323,133.
doi: 10.1126/science.1162986 |
| [124] |
Kasianowicz, J. J.; Brandin, E.; Branton, D.; Deamer, D. W. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1996,93,13770.
pmid: 8943010 |
| [125] |
Clarke, J.; Wu, H. C.; Jayasinghe, L.; Patel, A.; Reid, S.; Bayley, H. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 4,265.
doi: 10.1038/nnano.2009.12 pmid: 19350039 |
| [126] |
Cherf, G. M.; Lieberman, K. R.; Rashid, H.; Lam, C. E.; Karplus, K.; Akeson, M. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30,344.
doi: 10.1038/nbt.2147 |
| [127] |
Manrao, E. A.; Derrington, I. M.; Laszlo, A. H.; Langford, K. W.; Hopper, M. K.; Gillgren, N.; Pavlenok, M.; Niederweis, M.; Gundlach, J. H. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30,349.
doi: 10.1038/nbt.2171 |
| [128] |
Wendell, D.; Jing, P.; Geng, J.; Subramaniam, V.; Lee, T. J.; Montemagno, C.; Guo, P. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 4,765.
doi: 10.1038/nnano.2009.259 pmid: 19893523 |
| [129] |
Howorka, S.; Siwy, Z. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38,2360.
doi: 10.1039/b813796j pmid: 19623355 |
| [130] |
Venkatesan, B. M.; Bashir, R. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6,615.
doi: 10.1038/nnano.2011.129 pmid: 21926981 |
| [131] |
Haque, F.; Li, J.; Wu, H. C.; Liang, X. J.; Guo, P. Nano Today 2013, 8,56.
doi: 10.1016/j.nantod.2012.12.008 |
| [132] |
Wanunu, M.; Cohen-Karni, D.; Johnson, R. R.; Fields, L.; Benner, J.; Peterman, N.; Zheng, Y.; Klein, M. L.; Drndic, M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133,486.
doi: 10.1021/ja107836t |
| [133] |
Li, W. W.; Gong, L. Z.; Bayley, H. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2013, 52,4350.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201300413 |
| [134] |
Zeng, T.; Liu, L.; Li, T.; Li, Y.; Gao, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, H. C. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6,5628.
doi: 10.1039/c5sc01436k pmid: 28757950 |
| [135] |
Gabrieli, T.; Sharim, H.; Nifker, G.; Jeffet, J.; Shahal, T.; Arielly, R.; Levi-Sakin, M.; Hoch, L.; Arbib, N.; Michaeli, Y.; Ebenstein, Y. ACS Nano 2018, 12,7148.
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.8b03023 pmid: 29924591 |
| [136] |
Chen, F.; Xue, J.; Zhang, J.; Bai, M.; Yu, X.; Fan, C.; Zhao, Y. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142,2889.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b11393 |
| [137] |
Song, C. X.; Diao, J.; Brunger, A. T.; Quake, S. R. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2016,113,4338.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1600223113 |
| [138] |
Szulwach, K. E.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Song, C. X.; Wu, H.; Dai, Q.; Irier, H.; Upadhyay, A. K.; Gearing, M.; Levey, A. I.; Vasanthakumar, A.; Godley, L. A.; Chang, Q.; Cheng, X.; He, C.; Jin, P. Nat. Neurosci. 2011, 14,1607.
doi: 10.1038/nn.2959 |
| [139] |
Li, C. C.; Dong, Y. H.; Zou, X.; Luo, X.; Shen, D.; Hu, J.; Zhang, C. Y. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93,1939.
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.0c05419 |
| [140] |
Walker, G. T.; Fraiser, M. S.; Schram, J. L.; Little, M. C.; Nadeau, J. G.; Malinowski, D. P. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992, 20,1691.
pmid: 1579461 |
| [141] |
Ma, F.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, C. Y. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86,6006.
doi: 10.1021/ac5017369 |
| [142] |
Zhao, W.; Ali, M. M.; Brook, M. A.; Li, Y. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2008, 47,6330.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v47:34 |
| [143] |
Ma, F.; Liu, M.; Zhang, C. Y. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55,8963.
doi: 10.1039/C9CC04369A |
| [144] |
Barany, F. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1991,88,189.
pmid: 1986365 |
| [145] |
Ma, F.; Liu, H.; Li, C. C.; Zhang, C. Y. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54,12638.
doi: 10.1039/C8CC07843B |
| [146] |
Yin, B. C.; Liu, Y. Q.; Ye, B. C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134,5064.
doi: 10.1021/ja300721s |
| [147] |
Ma, F.; Liu, W. J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, C. Y. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53,10596.
doi: 10.1039/C7CC06290G |
| [148] |
Zhang, Y.; Li, C. C.; Tang, B.; Zhang, C. Y. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89,7684.
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.7b01655 |
| [149] |
Li, C. C.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, B.; Zhang, C. Y. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54,5839.
doi: 10.1039/C8CC01695J |
| [150] |
Bi, S.; Yue, S.; Zhang, S. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46,4281.
doi: 10.1039/C7CS00055C |
| [151] |
Jiang, Y. S.; Li, B.; Milligan, J. N.; Bhadra, S.; Ellington, A. D. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135,7430.
doi: 10.1021/ja4023978 |
| [152] |
Ma, F.; Wei, S. H.; Zhang, C. Y. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91,7505.
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.9b01617 |
| [153] |
Lu, X.; Song, C. X.; Szulwach, K.; Wang, Z.; Weidenbacher, P.; Jin, P.; He, C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135,9315.
doi: 10.1021/ja4044856 |
| [154] |
Xia, B.; Han, D. L.; Lu, X. Y.; Sun, Z. Z.; Zhou, A. K.; Yin, Q. Z.; Zeng, H.; Liu, M. H.; Jiang, X.; Xie, W.; He, C.; Yi, C. Q. Nat. Methods 2015, 12,1047.
doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3569 |
| [155] |
Ma, F.; Liu, M.; Wang, Z. Y.; Zhang, C. Y. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52,1218.
doi: 10.1039/C5CC08797J |
| [156] |
Zhang, H. D.; Huang, X. D.; Liu, J. W.; Liu, B. H. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11,3812.
doi: 10.1039/D0SC00580K |
| [157] |
Miyata, K.; Naito, M.; Miyata, T.; Mokuda, S.; Asahara, H. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1668,3.
|
| [1] | Ma Qiulin, Feng Nan, Ju Huangxian. Advances in Analytical Methodology of Prostate Cancer Markers [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2020, 78(11): 1213-1222. |
| [2] | Zhao Chao, Wang Hailin. The Progress on Sequencing and Detection of Hydroxymethylated DNA [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2013, 71(01): 26-35. |
| [3] | Zhang Liang, Yu Miao, He Chuan. Mouse Tet1 Protein can Oxidize 5mC to 5hmC and 5caC on Single-stranded DNA [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2012, 70(20): 2123-2126. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||