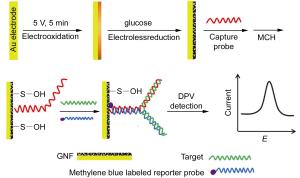
| [1] Heller, M. J. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2002, 4, 129.[2] Taton, T. A.; Mirkin, C. A.; Letsinger, R. L. Science 2000, 289,1757.[3] Boon, E. M.; Ceres, D. M.; Drummond, T. G.; Hill, M. G.; Barton,J. K. Nat. Biotechnol. 2000, 18, 1096.[4] Shan, Y.; Xu, J. J.; Chen, H. Y. Chem. Commun. 2009, 905[5] Fan, C. H.; Plaxco, K. W.; Heeger, A. J. Trends Biotechnol. 2005,23, 186.[6] Chen, Z. P.; Peng, Z. F.; Luo, Y.; Qu, B.; Jiang, J. H.; Zhang, X. B.;Shen, G. L.; Yu, R. Q. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 23, 485.[7] Park, S. J.; Taton, T. A.; Mirkin, C. A. Science 2002, 295, 1503.[8] Tombelli, S.; Mascini, R.; Braccini, L.; Anichini, M.; Turner, A. P.F. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2000, 15, 363.[9] Ye, M.; Zhang, Y. Y.; Li, H. T.; Zhang, Y. Q.; Tan, P.; Tang, H.;Yao, S. Z. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 2339.[10] Hu, K. C.; Lan, D. X.; Li, X. M.; Zhang, S. S. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80,9124.[11] Loaiza, O. A.; Campuzano, S.; Pedrero, M.; Pividori, M. I.; Garcia,P.; Pingarron, J. M. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 8239.[12] Miranda-Castro, R.; De-Los-Santos-Alvarez, P.; Lobo-Castanon, M.J.; Miranda-Ordieres, A. J.; Tunon-Blanco, P. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79,4050.[13] Ting, B. P.; Zhang, J.; Gao, Z. Q.; Ying, J. Y. Biosens. Bioelectron.2009, 25, 282.[14] Wang, J.; Liu, G. D.; Jan, M. R. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 3010.[15] Chen, S. T.; Zhang, X. L.; Zhang, Q. H.; Tan, W. H. Nanoscale Res.Lett. 2009, 4, 1159.[16] Dong, X. Y.; Mi, X. N.; Wang, B.; Xu, J. J.; Chen, H. Y. Talanta2011, 84, 531.[17] Dong, X. Y.; Mi, X. N.; Zhao, W. W.; Xu, J. J.; Chen, H. Y. Biosens.Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 3654.[18] Li, D.; Song, S. P.; Fan, C. H. Acc. Chem. Res. 2010, 43, 631.[19] Lubin, A. A.; Plaxco, K. W. Acc. Chem. Res. 2010, 43, 496.[20] Uzawa, T.; Cheng, R. R.; White, R. J.; Makarov, D. E.; Plaxco, K.W. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 16120.[21] Farjami, E.; Clima, L.; Gothelf, K.; Ferapontova, E. E. Anal. Chem.2011, 83, 1594.[22] Lubin, A. A.; Lai, R. Y.; Baker, B. R.; Heeger, A. J.; Plaxco, K. W.Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 5671.[23] Kang, D.; Zuo, X. L.; Yang, R. Q.; Xia, F.; Plaxco, K. W.; White, R. J. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 9109.[24] Xiao, Y.; Lubin, A. A.; Heeger, A. J.; Plaxco, K. W. Angew. Chem.,Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 5456.[25] Ricci, F.; Lai, R. Y.; Plaxco, K. W. Chem. Commun. 2007, 3768.[26] Immoos, C. E.; Lee, S. J.; Grinstaff, M. W. Chem. Biochem. 2004, 5,1100.[27] Liu, Y.; Tuleouva, N.; Ramanculov, E.; Revzin, A. Anal. Chem.2010, 82, 8131.[28] Fan, C. H.; Plaxco, K. W.; Heeger, A. J. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S.A. 2003, 100, 9134.[29] Lai, R. Y.; Plaxco, K. W.; Heeger, A. J. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 229.[30] Xiao, Y.; Qu, X. G.; Plaxco, K. W.; Heeger, A. J. J. Am. Chem. Soc.2007, 129, 11896.[31] Cash, K. J.; Heeger, A. J.; Plaxco, K. W.; Xiao, Y. Anal. Chem.2009, 81, 656.[32] Immoos, C. E.; Le, S. J.; Grinstaff, M. W. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004,126, 10814.[33] Zhang, Y. L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H. B.; Jiang, J. H.; Shen, G. L.; Yu,R. Q.; Li, J. H. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 1982.[34] Jin, Y.; Yao, X.; Liu, Q.; Li, J. H. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22,1126.[35] Zhao, W.; Xu, J. J.; Shi, C. G.; Chen, H. Y. Electrochem. Commun.2006, 8, 773. |