化学学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 79 ›› Issue (2): 146-157.DOI: 10.6023/A20090412 上一篇 下一篇
综述
投稿日期:2020-09-07
发布日期:2020-12-01
通讯作者:
章福祥
作者简介: |
詹溯, 2017年于大连海事大学载运工具运用工程专业获得工学博士学位, 2018年加入中国科学院大连化学物理研究所章福祥课题组, 目前主要研究方向为常温常压光电催化合成氨. |
 |
章福祥, 中国科学院大连化物所研究员/博导; 国家杰出青年基金获得者; 英国皇家化学会会士. 1999和2004年分别获得南开大学理学学士学位和博士学位, 同年留校任教至2007年8月, 2007年9月至2008年6月获法国CNRS博士后基金支持于巴黎第六大学做访问学者, 2008年7月至2011年9月在东京大学做博士后和特任助理教授, 2011年10月至今在中国科学院大连化学物理研究所工作. 目前主要从事宽光谱捕光催化剂全分解水制氢研究, 研究内容涉及宽光谱捕光光催化材料设计合成, 高效光生电荷分离体系构建以及光催化表面/界面反应机制等方面. 已在包括Nat. Commun., Nature Catal., Joule, J. Am. Chem. Soc., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., Adv. Mater., Adv. Energy Mater.等刊物上发表学术论文百余篇. |
基金资助:Received:2020-09-07
Published:2020-12-01
Contact:
Fuxiang Zhang
Supported by:文章分享
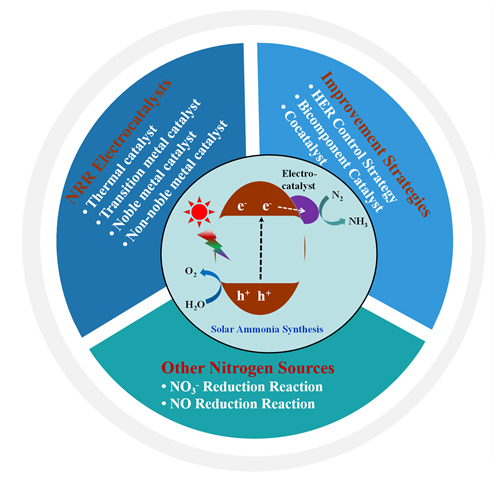
氨不仅是重要的化肥化工原料, 还是理想的清洁能源载体. 目前人工氨合成主要基于Haber-Bosch过程, 但该方法存在能耗大、转化率低、大量排放温室气体等问题. 相比而言, 利用太阳能催化转化N2和H2O等制NH3是一条实现太阳能至化学能转化的绿色制氢储氢一体化路线, 受到世界各国科学家的高度关注. 但当前该技术路线的氮还原(NRR)转化率和法拉第效率均较低, 开发高效NRR电催化剂并将其与捕光材料耦合是实现高效太阳能催化合成氨的关键. 本综述将首先介绍太阳能催化合成氨的一些基本原理、主要技术路线和基本检测方法, 然后分类介绍传统热催化剂、过渡金属催化剂、贵金属催化剂和非贵金属催化剂等在电催化NRR领域中的应用, 以及提升NRR性能的主要策略和其它氮源(如: NO3 –和NO)电催化合成氨的研究进展, 最后就该方向存在的一些问题以及急需突破的方向进行了总结与展望.
詹溯, 章福祥. 常温常压电催化合成氨的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(2): 146-157.
Su Zhan, Fuxiang Zhang. Recent Progress on Electrocatalytic Synthesis of Ammonia Under Amibent Conditions[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(2): 146-157.
| 反应式 | 电位/V (vs. NHE), pH=0 | |
|---|---|---|
| N2+e–→N2 – | –4.16 | |
| N2+H++e–→N2H | –3.20 | |
| N2+2H++2e–→N2H2 | –1.10 | |
| N2+4H++4e–→N2H4 | –0.36 | |
| N2+5H++5e–→N2H5 + | –0.23 | |
| N2+8H++6e–→2NH4 + | 0.27 | |
| N2+6H++6e–→NH3 | 0.55 | |
| 反应式 | 电位/V (vs. NHE), pH=0 | |
|---|---|---|
| N2+e–→N2 – | –4.16 | |
| N2+H++e–→N2H | –3.20 | |
| N2+2H++2e–→N2H2 | –1.10 | |
| N2+4H++4e–→N2H4 | –0.36 | |
| N2+5H++5e–→N2H5 + | –0.23 | |
| N2+8H++6e–→2NH4 + | 0.27 | |
| N2+6H++6e–→NH3 | 0.55 | |
| 检测方法 | 检测范围 | 特点 | 注意事项 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 纳氏试剂显色法 | 0.025~5.0 mg/L | 操作简便 | 试剂中含汞, 毒性高, 对环境危害大, 试剂寿命短, 需要注意Fe2+、Cu2+、Ca2+等离子对显色效果干扰 |
| 水杨酸-次氯酸显色法 | 0.01~1.0 mg/L | 操作简便、低毒性 | 溶液pH应大于11, 否则将影响显色化合物生成, 需要注意Fe2+离子对显色效果干扰 |
| 离子色谱 | 0.02~40 mg/L | 重现性好、灵敏度高、检测时间短 | 注意电解液中Na+浓度, 减少对NH4 +检测的干扰 |
| 15N同位素-核磁共振NMR | 5~10 μmol/L | 为生成氨的真实来源提供直接证据 | 需保证15N2气体的纯度 |
| 检测方法 | 检测范围 | 特点 | 注意事项 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 纳氏试剂显色法 | 0.025~5.0 mg/L | 操作简便 | 试剂中含汞, 毒性高, 对环境危害大, 试剂寿命短, 需要注意Fe2+、Cu2+、Ca2+等离子对显色效果干扰 |
| 水杨酸-次氯酸显色法 | 0.01~1.0 mg/L | 操作简便、低毒性 | 溶液pH应大于11, 否则将影响显色化合物生成, 需要注意Fe2+离子对显色效果干扰 |
| 离子色谱 | 0.02~40 mg/L | 重现性好、灵敏度高、检测时间短 | 注意电解液中Na+浓度, 减少对NH4 +检测的干扰 |
| 15N同位素-核磁共振NMR | 5~10 μmol/L | 为生成氨的真实来源提供直接证据 | 需保证15N2气体的纯度 |
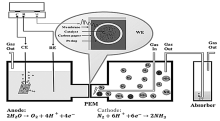



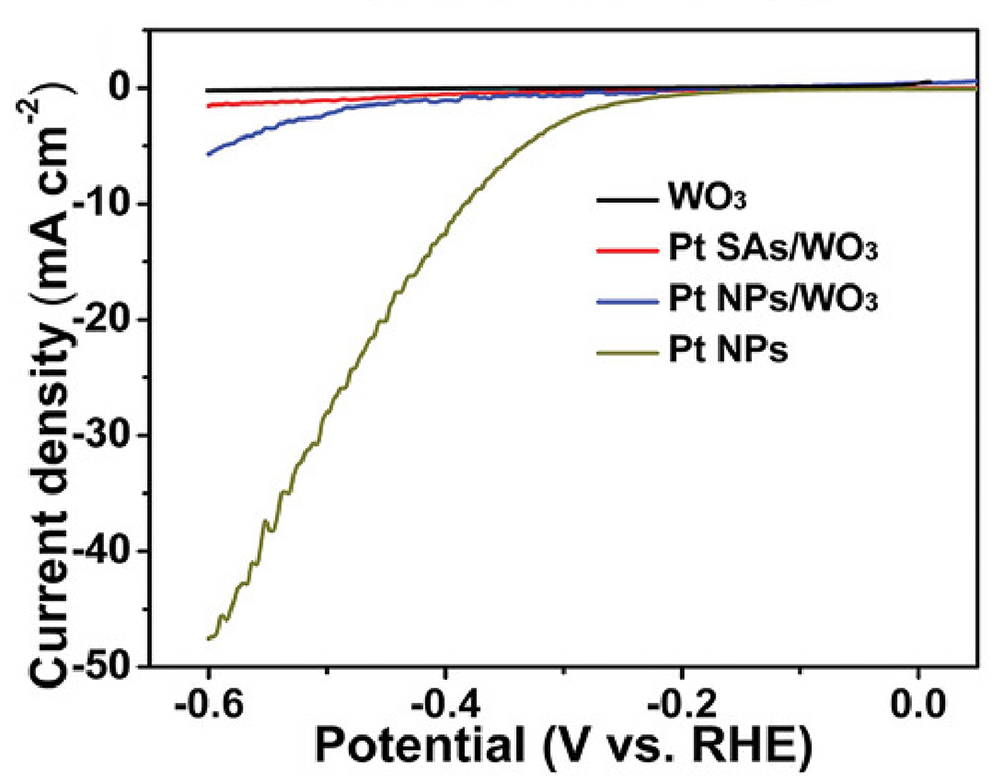
| 催化剂 | 电解液 | NH3产率 | 法拉第效率/% | 文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 传统热催化剂 | Fe2O3/CNT | KHCO3 | 2.18×10–3 gNH3•m–2•h–1 (–2.0 V vs. Ag/AgCl) | 0.025 | [ |
| Fe-(O-C2)4 | 0.1 mol/L KOH | 32.1 μg•h –1•mgcat.–1 (–0.1 V vs. RHE) | 29.3 | [ | |
| Fe-N4-C | 0.1 mol/L KOH | 7.48 μg•h –1•mg–1 (0.0 V vs. RHE) | 56.55 | [ | |
| Fe-W18O49 | 0.25 mol/L LiClO4 | 24.7 μg•h –1•mgcat. –1 (–0.15 V vs. RHE) | 20.0 | [ | |
| Ru-Mo2CTx | 0.5 mol/L K2SO4 | 40.57 μg•h –1•mg–1 (–0.3 V vs. RHE) | 25.77 | [ | |
| RuSAs/N-C | 0.05 mol/L H2SO4 | 120.9 μg NH3•mgcat. –1•h–1 (–0.3 V vs. RHE) | 29.6 | [ | |
| 生物固氮酶同组分催化剂(Mo、V) | MoS2 | 0.1 mol/L Na2SO4 | 8.08×10–11 mol•s–1•cm–2 (–0.3 V vs. RHE) | 1.17 | [ |
| Mo2N | 0.1 mol/L HCl | 78.4 μg•h –1•mgcat. –1 (–0.3 V vs. RHE) | 4.5 | [ | |
| SA-Mo/NPC | 0.1 mol/L KOH | 34.0 μg•h –1•gcat. –1 (–0.3 V vs. RHE) | 14.6 | [ | |
| Mo3Fe3C | 0.1 mol/L Li2SO4 | 72.5 μg•h –1•cm–2 (–0.05 V vs. RHE) | 43.6 | [ | |
| V8C7 | 0.1 mol/L HCl | 34.62 μg•h –1•cm–2 (–0.4 V vs. RHE) | 12.20 | [ | |
| VN | 0.1 mol/L HCl | 2.48×10-10 mol–1•s–1•cm–2 (–0.3 V vs. RHE) | 3.58 | [ | |
| VO2 | 0.1 mol/L Na2SO4 | 14.85 μg•h –1•gcat. –1 (–0.7 V vs. RHE) | 3.97 | [ | |
| P-V2O3/C | 0.1 mol/L Na2SO4 | 22.4 μg•h –1•mgcat. –1 (–0.35 V vs. RHE) | 13.78 | [ | |
| 贵金属催化剂 | Au纳米棒 | 0.1 mol/L KOH | 1.648 μg•h –1•cm–2 (–0.2 V vs. RHE) | 4.02 | [ |
| Au | 0.1 mol/L HCl | 21.4 μgh –1•mgcat. –1 (–0.2 V vs. RHE) | 8.11 | [ | |
| 单原子Au | 5 mmol/L H2SO4 | 1305 μg•h –1•mgAu –1 (–0.1 V vs. RHE) | 11.1 | [ | |
| 单原子Pt | 0.1 mol/L K2SO4 | 342.4 μg•h –1•mgPt –1 (–0.2 V vs. RHE) | 31.3 | [ | |
| PdCu | 0.1 mol/L KOH | 2.8 μg•h –1•mgcat. –1 (–0.2 V vs. RHE) | 0.6 | [ | |
| 非贵金属催化剂 | Cu-TiO2 | 0.5 mol/L LiClO4 | 21.31 μg•h –1•mgcat. –1 (–0.55 V vs. RHE) | 21.99 | [ |
| Sn枝晶 | 0.1 mol/L PBS | 5.66×10–11 mol–1•s–1•cm–2 (–0.6 V vs. RHE) | 3.67 | [ | |
| Cr2O3/rGO | 0.1 mol/L HCl | 33.3 μg•h –1•mgcat. –1 (–0.7 V vs. RHE) | 7.33 | [ | |
| LiMn2O4 | 0.1 mol/L HCl | 15.83 μg•h –1•mgcat. –1 (–0.5 V vs. RHE) | 7.44 | [ | |
| LaFeO3 | 0.1 mol/L HCl | 18.59 μg•h –1•mgcat. –1 (–0.55 V vs. RHE) | 8.77 | [ | |
| Bi纳米片 | 0.1 mol/L HCl | 6.89×10–11 mol–1•s–1•cm–2 (–0.5 V vs. RHE) | 10.26 | [ |
| 催化剂 | 电解液 | NH3产率 | 法拉第效率/% | 文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 传统热催化剂 | Fe2O3/CNT | KHCO3 | 2.18×10–3 gNH3•m–2•h–1 (–2.0 V vs. Ag/AgCl) | 0.025 | [ |
| Fe-(O-C2)4 | 0.1 mol/L KOH | 32.1 μg•h –1•mgcat.–1 (–0.1 V vs. RHE) | 29.3 | [ | |
| Fe-N4-C | 0.1 mol/L KOH | 7.48 μg•h –1•mg–1 (0.0 V vs. RHE) | 56.55 | [ | |
| Fe-W18O49 | 0.25 mol/L LiClO4 | 24.7 μg•h –1•mgcat. –1 (–0.15 V vs. RHE) | 20.0 | [ | |
| Ru-Mo2CTx | 0.5 mol/L K2SO4 | 40.57 μg•h –1•mg–1 (–0.3 V vs. RHE) | 25.77 | [ | |
| RuSAs/N-C | 0.05 mol/L H2SO4 | 120.9 μg NH3•mgcat. –1•h–1 (–0.3 V vs. RHE) | 29.6 | [ | |
| 生物固氮酶同组分催化剂(Mo、V) | MoS2 | 0.1 mol/L Na2SO4 | 8.08×10–11 mol•s–1•cm–2 (–0.3 V vs. RHE) | 1.17 | [ |
| Mo2N | 0.1 mol/L HCl | 78.4 μg•h –1•mgcat. –1 (–0.3 V vs. RHE) | 4.5 | [ | |
| SA-Mo/NPC | 0.1 mol/L KOH | 34.0 μg•h –1•gcat. –1 (–0.3 V vs. RHE) | 14.6 | [ | |
| Mo3Fe3C | 0.1 mol/L Li2SO4 | 72.5 μg•h –1•cm–2 (–0.05 V vs. RHE) | 43.6 | [ | |
| V8C7 | 0.1 mol/L HCl | 34.62 μg•h –1•cm–2 (–0.4 V vs. RHE) | 12.20 | [ | |
| VN | 0.1 mol/L HCl | 2.48×10-10 mol–1•s–1•cm–2 (–0.3 V vs. RHE) | 3.58 | [ | |
| VO2 | 0.1 mol/L Na2SO4 | 14.85 μg•h –1•gcat. –1 (–0.7 V vs. RHE) | 3.97 | [ | |
| P-V2O3/C | 0.1 mol/L Na2SO4 | 22.4 μg•h –1•mgcat. –1 (–0.35 V vs. RHE) | 13.78 | [ | |
| 贵金属催化剂 | Au纳米棒 | 0.1 mol/L KOH | 1.648 μg•h –1•cm–2 (–0.2 V vs. RHE) | 4.02 | [ |
| Au | 0.1 mol/L HCl | 21.4 μgh –1•mgcat. –1 (–0.2 V vs. RHE) | 8.11 | [ | |
| 单原子Au | 5 mmol/L H2SO4 | 1305 μg•h –1•mgAu –1 (–0.1 V vs. RHE) | 11.1 | [ | |
| 单原子Pt | 0.1 mol/L K2SO4 | 342.4 μg•h –1•mgPt –1 (–0.2 V vs. RHE) | 31.3 | [ | |
| PdCu | 0.1 mol/L KOH | 2.8 μg•h –1•mgcat. –1 (–0.2 V vs. RHE) | 0.6 | [ | |
| 非贵金属催化剂 | Cu-TiO2 | 0.5 mol/L LiClO4 | 21.31 μg•h –1•mgcat. –1 (–0.55 V vs. RHE) | 21.99 | [ |
| Sn枝晶 | 0.1 mol/L PBS | 5.66×10–11 mol–1•s–1•cm–2 (–0.6 V vs. RHE) | 3.67 | [ | |
| Cr2O3/rGO | 0.1 mol/L HCl | 33.3 μg•h –1•mgcat. –1 (–0.7 V vs. RHE) | 7.33 | [ | |
| LiMn2O4 | 0.1 mol/L HCl | 15.83 μg•h –1•mgcat. –1 (–0.5 V vs. RHE) | 7.44 | [ | |
| LaFeO3 | 0.1 mol/L HCl | 18.59 μg•h –1•mgcat. –1 (–0.55 V vs. RHE) | 8.77 | [ | |
| Bi纳米片 | 0.1 mol/L HCl | 6.89×10–11 mol–1•s–1•cm–2 (–0.5 V vs. RHE) | 10.26 | [ |


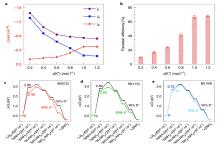
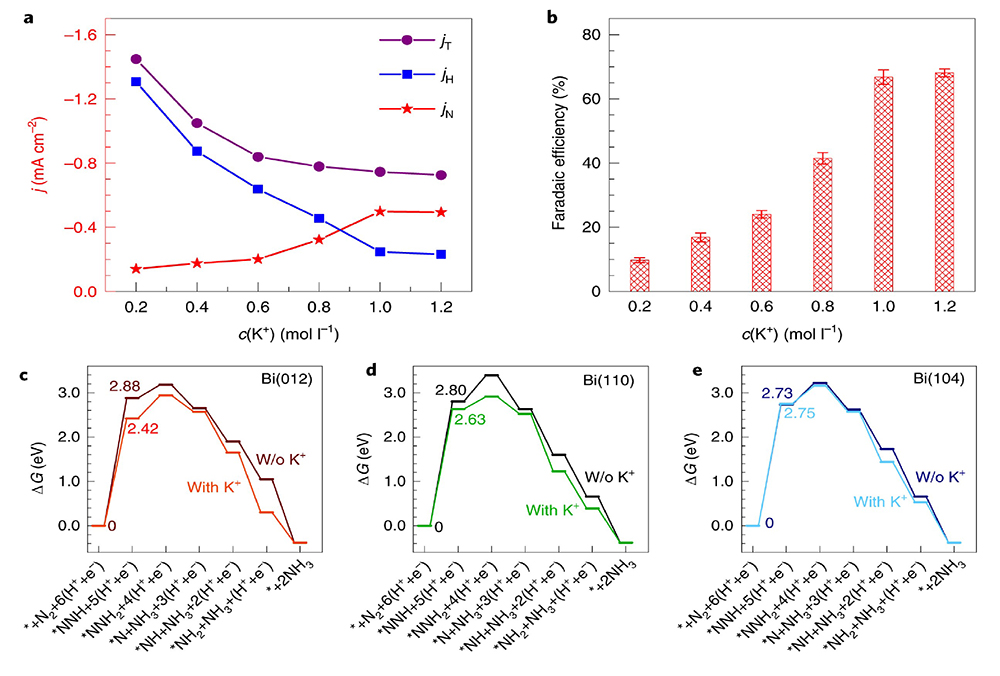

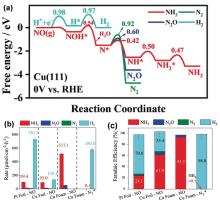

| [1] |
(a) Erisman J.W. ; Sutton M.A. ; Galloway J. ; Klimont Z. ; Winiwarter W. Nat. Geosci. 2008, 1, 636.
|
|
(b) Ertl G. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 3524.
|
|
| [2] |
(a) Li X.B. ; Tung C.H. ; Wu L.Z. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 10804.
|
|
(b) Zamfirescu C. ; Dincer I. J. Power Sources 2008, 185, 459.
|
|
|
(c) Foster S.L. ; Perez Bakovic S.I. ; Duda R.D. ; Maheshwari S. ; Milton R.D. ; Minteer S.D. ; Janik M.J. ; Renner J.N. ; Greenlee L.F. Nat. Catal. 2018, 1, 490.
|
|
|
(d) Guo J.P. ; Chen P. Chem 2017, 3, 709.
|
|
| [3] |
Schuth F. ; Palkovits R. ; Schlogl R. ; Su D.S. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 6278.
|
| [4] |
Liu H. ; Chin J. J. Catal. 2014, 35, 1619.
|
| [5] |
Rafiqul I. ; Weber C. ; Lehmann B. ; Voss A. Energy 2005, 30, 2487.
|
|
Qiu W.B. ; Xie X.Y. ; Qiu J.D. ; Fang W.H. ; Liang R.P. ; Ren X. ; Ji X.Q. ; Cui G.W. ; Asiri A.M. ; Cui G.L. ; Tang B. ; Sun X.P. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3485.
|
|
| [6] |
(a) Nishibayashi Y. ; Saito M. ; Uemura S. ; Takekuma S. ; Takekuma H. ; Yoshida Z. Nature 2004, 428, 279.
|
|
(b) Li H. ; Shang J. ; Ai Z. ; Zhang L. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 6393.
|
|
|
(c) Hao Y. ; Dong X. ; Zhai S. ; Ma H. ; Wang X. ; Zhang X. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 18722.
|
|
|
(d) Schrock R.R. Acc. Chem. Res. 2005, 38, 955.
|
|
|
(e) Sun S. ; An Q. ; Wang W. ; Zhang L. ; Liu J. ; Goddard W.A. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 201.
|
|
|
(f) Sun S. ; Li X. ; Wang W. ; Zhang L. ; Sun X. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2017, 200, 323.
|
|
|
(g) Banerjee A. ; Yuhas B.D. ; Margulies E.A. ; Zhang Y. ; Shim Y. ; Wasielewski M.R. ; Kanatzidis M.G. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 2030.
|
|
|
(h) Liu J. ; Kelley M.S. ; Wu W. ; Banerjee A. ; Douvalis A.P. ; Wu J. ; Zhang Y. ; Schatz G.C. ; Kanatzidis M.G. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2016, 113, 5530.
|
|
|
(i) Oshikiri T. ; Ueno K. ; Misawa H. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 9802.
|
|
|
(j) Pickett C.J. ; Talarmin J. Nature 1985, 317, 652.
|
|
|
(k) Kordali V. ; Kyriacou G. ; Lambrou C.H. Chem. Commun. 2000, 0, 1673.
|
|
|
(l) Yu X.M. ; Han P. ; Wei Z.X. ; Huang L.S. ; Gu Z.X. ; Peng S.J. ; Ma J.M. ; Zheng G.F. Joule 2018, 2, 1610.
|
|
|
(m) Lv C. ; Qian Y.M. ; Yan C.S. ; Ding Y. ; Liu Y.Y. ; Chen G. ; Yu G.H. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 10246.
|
|
|
(n) Zhang L.L. ; Ding L.X. ; Chen G.F. ; Yang X.F. ; Wang H.H. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 131, 2612.
|
|
| [7] |
Walter M.G. ; Warren E.L. ; Mckone J.R. ; Boettcher S.W. ; Mi Q.X. ; Santori E.A. ; Lewis N.S. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 6446.
|
| [8] |
Chen J.G. ; Crooks R.M. ; Seefeldt L.C. ; Bren K.L. ; Bullock R.M. ; Darensbourg M.Y. ; Holland P.L. ; Hoffman B. ; Janik M.J. ; Jones A.K. ; Kanatzidis M.G. ; King P. ; Lancaster K.M. ; Lymar S.V. ; Pfromm P. ; Schneider W.F. ; Schrock R.R. Science 2018, 360, 873.
|
| [9] |
Shilov A.E. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2003, 52, 2555.
|
| [10] |
(a) Singh A.R. ; Rohr B.A. ; Schwalbe J.A. ; Cargnello M. ; Chan K. ; Jaramillo T.F. ; Chorkendorff I.B. ; Norskov J.K. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 106.
|
|
(b) Skulason E. ; Bligaard T. ; Gudmundsdottir S. ; Studt F. ; Rossmeisl J. ; Abild-Pedersen F. ; Vegge T. ; Jonsson H. ; Norskov J.K. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2012, 14, 1235.
|
|
| [11] |
(a) Shipman M.A. ; Symes M.D. Catal. Today 2017, 286, 57.
|
|
(b) Xu H. ; Inthisuphalap K. ; Li Y. ; Mukherjee S. ; Lattimer J. ; Soloveichik G. ; Wu G. Nano Energy 2020, 69, 104469.
|
|
| [12] |
Urabe K. ; Aika K.I. ; Ozaki A. J. Catal. 1974, 11, 108.
|
| [13] |
Ithisuphalap K. ; Zhang H. ; Guo L. ; Yang Q. ; Yang H. ; Wu G. Small Methods 2019, 3, 1800352.
|
| [14] |
Huang Y.W. ; Zhang N. ; Wu Z.J. ; Xie X.Q. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 4978.
|
| [15] |
(a) Furuya N. ; Yoshiba H.J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem. 1989, 263, 171.
|
|
(b) Lan R. ; Irvine J.T.S. ; Tao S. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1145.
|
|
| [16] |
(a) Kugler K. ; Luhn M. ; Schramm J.A. ; Rahimi K. ; Wessling M. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 3768.
|
|
(b) Yang D. ; Chen T. ; Wang Z. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 18967.
|
|
|
(c) Zhao Z.M. ; Luo S. ; Ma P. ; Luo Y.T. ; Wu W. ; Long Y. ; Ma J.T. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 8814.
|
|
| [17] |
Gibert R. ; Rioux R. ; Saheb E. Anal. Chem. 1984, 56, 106.
|
| [18] |
(a) Lazouski N. ; Chung M.J. ; Williams K. ; Gala M.L. ; Manthiram K. Nat. Catal. 2020, 3, 463.
|
|
(b) Liu D.N. ; Wang J.H. ; Bian S. ; Liu Q. ; Gao Y.H. ; Wang X. ; Chu P.K. ; Yu X.F. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 2002731.
|
|
| [19] |
Zhou L. ; Boyd C.E. Aquaculture 2016, 450, 187.
|
| [20] |
Cui X.Y. ; Tang C. ; Zhang Q. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 1800369.
|
| [21] |
Hodgetts R.Y. ; Kiryutin A.S. ; Nichols P. ; Du H.L. ; Bakker J.M. ; Macfarlane D.R. ; Simonov A.N. ACS Energy Lett. 2020, 5, 736.
|
| [22] |
Suryanto B.H.R. ; Du H.L. ; Wang D.B. ; Chen J. ; Simonov A.N. ; MacFarlane D.R. Nat. Catal. 2019, 2, 290.
|
| [23] |
Shi M.M. ; Bao D. ; Wulan B.R. ; Li Y.H. ; Zhang Y.F. ; Yan J.M. ; Jiang Q. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1606550.
|
| [24] |
Schlesinger W.H. ; Hartley A.E. Biogeocemistry 1992, 15, 191.
|
| [25] |
Turner C. ; Spanel P. ; Smith D.A. Physiol. Meas. 2006, 27, 321.
|
| [26] |
Andersen S.Z. ; Colic V. ; Yang S. ; Schwalbe J.A. ; Nielander A.C. ; McEnaney J.M. ; Enemark-Rasmussen K. ; Baker J.G. ; Singh A.R. ; Rohr B.A. ; Statt M.J. ; Blair S.J. ; Mezzavilla S. ; Kibsgaard J. ; Vesborg P.C.K. ; Cargnello M. ; Bent S.F. ; Jaramillo T.F. ; Stephens I.E.L. ; Norskov J.K. ; Chorkendorff I. Nature 2019, 570, 504.
|
| [27] |
(a) Aika K. ; Hori H. ; Ozaki A. J. Catal. 1972, 27, 424.
|
|
(b) Gong Y.T. ; Wu J.Z. ; Kitano M. ; Wang J.J. ; Ye T.N. ; Li J. ; Kobayashi Y. ; Kishida K. ; Abe H. ; Niwa Y. ; Yang H.S. ; Tada T. ; Hosono H. Nat. Catal. 2018, 1, 178.
|
|
| [28] |
Imbihl R. ; Behm R.J. ; Etrl G. ; Moritz W. Surf. Sci. 1982, 123, 129.
|
| [29] |
Somorjai G. ; Materer N. Top. Catal. 1994, 1, 215.
|
| [30] |
Zheng J.W. ; Liao F.L. ; Wu S. ; Jones G. ; Chen T.Y. ; Fellowes J. ; Sudmeier T. ; McPherson I.J. ; Wilkinson I. ; Tsang S.C.E. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 17335.
|
| [31] |
Chen S.M. ; Perathoner S. ; Ampelli C. ; Mebrahtu C. ; Su D.S. ; Centi G. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 2699.
|
| [32] |
Qiao B.T. ; Wang A.Q. ; Yang X.F. ; Allard L.F. ; Jiang Z. ; Cui Y.T. ; Liu J.Y. ; Li J. ; Zhang T. Nat. Chem. 2011, 3, 634.
|
| [33] |
Zhang S.B. ; Jin M. ; Shi T.F. ; Han M.M. ; Sun Q. ; Lin Y. ; Ding Z.H. ; Zheng L.R. ; Wang G.Z. ; Zhang Y.X. ; Zhang H.M. ; Zhao H.J. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 13423.
|
| [34] |
Wang M.F. ; Liu S.S. ; Qian T. ; Liu J. ; Zhou J.Q. ; Ji H.Q. ; Xiong J. ; Zhong J. ; Yan C.L. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 341.
|
| [35] |
Kitano M. ; Inoue Y. ; Yamazaki Y. ; Hayashi F. ; Kanbara S. ; Matsuishi S. ; Yokoyama T. ; Kim S.W. ; Hara M. ; Hosono H. Nat. Chem. 2012, 4, 934.
|
| [36] |
Dahl S. ; Logadottir A. ; Egeberg R.C. ; Larsen J.H. ; Chorkendorff I. ; Tornqvist E. ; Norskov J.K. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1999, 83, 1814.
|
| [37] |
(a) Szmigiel D. ; Rarog-Pilecka W. ; Miskiewicz E. ; Glinski M. ; Kielak M. ; Kaszkur M. ; Kowalczyk Z. Appl. Catal. A-Gen. 2004, 273, 105.
|
|
(b) Rarog-Pilecka W. ; Miskiewicz E. ; Szmigiel D. ; Kowalczyk Z. J. Catal. 2005, 231, 11.
|
|
| [38] |
Peng W. ; Luo M. ; Xu X.D. ; Jiang K. ; Peng M. ; Chen D.C. ; Chan T.S. ; Tan Y.W. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 2001364.
|
| [39] |
Geng Z.G. ; Liu Y. ; Kong X.D. ; Li P. ; Li K. ; Liu Z.Y. ; Du J.J. ; Shu M. ; Si R. ; Zeng J. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1803498.
|
| [40] |
Gronberg K.L.C. ; Gormal C.A. ; Durrant M.C. ; Smith B.E. ; Henderson R.A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 10613.
|
| [41] |
Sippel D. ; Rohde M. ; Netzer J. ; Trncik C. ; Gies J. ; Grunau K. ; Djurdjevic I. ; Decamps L. ; Andrade S.L.A. ; Einsle O. Science 2018, 359, 1484.
|
| [42] |
Zhao J.X. ; Chen Z.F. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 12480.
|
| [43] |
Han L.L. ; Liu X.J. ; Chen J.P. ; Lin R.Q. ; Liu H.X. ; Lu F. ; Bak S. ; Liang Z.X. ; Zhao S.Z. ; Stavitski E. ; Luo J. ; Adzic R.R. ; Xin H.L. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 2321.
|
| [44] |
Huang Y. ; Yang T.T. ; Yang L. ; Liu R. ; Zhang G.Z. ; Jiang J. ; Luo Y. ; Lian P. ; Tang S.B. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 15173.
|
| [45] |
Feng J. ; Zhu X.J. ; Chen Q.Y. ; Xiong W. ; Cheng X. ; Luo Y.L. ; Alshehri A.A. ; Alzahrani K.A. ; Jiang Z.J. ; Li W. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 26227.
|
| [46] |
Zhang X.P. ; Kong R.M. ; Du H.T. ; Xia L. ; Qu F.L. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 5323.
|
| [47] |
Du H.L. ; Gengenbach T.R. ; Hodgetts R. ; MacFarlane D.R. ; Simonov A.N. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 6839.
|
| [48] |
Shi M.M. ; Bao D. ; Li S.J. ; Wulan B.R. ; Yan J.M. ; Jiang Q. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1800124.
|
| [49] |
(a) Haruta M. ; Kobayashi T. ; Sano H. ; Yamada N. Chem. Lett. 1987, 16, 405.
|
|
(b) Ciriminna R. ; Falletta E. ; Della Pina C. ; Teles J.H. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 14210.
|
|
| [50] |
Bao D. ; Zhang Q. ; Meng F.L. ; Zhong H.X. ; Shi M.M. ; Zhang Y. ; Yan J.M. ; Jiang Q. ; Zhang X.B. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1604799.
|
| [51] |
Wang X.Q. ; Wang W.Y. ; Qiao M. ; Wu G. ; Chen W.X. ; Yuan T.W. ; Xu Q. ; Chen M. ; Zhang Y. ; Wang X.L. ; Wang J. ; Ge J.J. ; Hong X. ; Li Y.F. ; Wu Y. ; Li Y.D. Sci. Bull. 2018, 63, 1246.
|
| [52] |
(a) Dehcheshmeh M.M. ; Shervedani R.K. ; Torabi M. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 327, 134895.
|
|
(b) Li D. ; Chen X.F. ; Lv Y.Z. ; Zhang G.Y. ; Huang Y. ; Liu W. ; Li Y. ; Chen R.S. ; Nuckolls C. ; Ni H.W. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2020, 269, 118824.
|
|
|
(c) Luo Y.P. ; Huang D.K. ; Li M. ; Xiao X. ; Shi W.N. ; Wang M.K. ; Su J. ; Shen Y. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 219, 187.
|
|
| [53] |
Hao R. ; Sun W.M. ; Liu Q. ; Liu X.L. ; Chen J.L. ; Lv X.W. ; Li W. ; Liu Y.P. ; Shen Z.R. Small 2020, 16, 2000015.
|
| [54] |
(a) Wu T.W. ; Zhao H.T. ; Zhu X.J. ; Xing Z. ; Liu Q. ; Liu T. ; Gao S.Y. ; Liu S.Y. ; Chen G. ; Asiri A.M. ; Zhang Y.N. ; Sun X.P. Adv. Mater. 2020, 2000299.
|
|
(b) Lv X. ; Wang F.Y. ; Du J. ; Liu Q. ; Luo Y.S. ; Lu S.Y. ; Chen G. ; Gao S.Y. ; Zheng B.Z. Sun X.P. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2020, 4, 4469.
|
|
|
(c) Xia L. ; Li B.H. ; Zhang Y. ; Zhang R. ; Ji L. ; Chen H.Y. ; Cui G.W. ; Zheng H.G. ; Sun X.P. ; Xie F.Y. ; Liu Q. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 58, 2257.
|
|
|
(d) Li C.B. ; Yu J.L. ; Yang L. ; Zhao J.X. ; Kong W. H. ; Wang T. ; Asiri A.M. ; Li Q. ; Sun X.P. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 58, 15, 9597.
|
|
|
(e) Li C.B. ; Ma D.W. ; Mou S.Y. ; Luo Y.S. ; Ma B.Y. ; Lu S.Y. ; Cui G.W. ; Li Q. ; Liu Q. ; Sun X.P. J. Energy Chem. 2020, 50, 402.
|
|
| [55] |
Li L.Q. ; Tang C. ; Xia B.Q. ; Jin H.Y. ; Zheng Y. ; Qiao S.Z. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 2902.
|
| [56] |
Zhang R. ; Ji L. ; Kong W.H. ; Wang H.B. ; Zhao R.B. ; Chen H.Y. ; Li T.S. ; Li B.H. ; Luo Y.L. ; Sun X.P. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 5263.
|
| [57] |
Han Z. ; Choi C. ; Hong S. ; Wu T. ; Soo Y. ; Yung Y. ; Qiu J. ; Sun Z. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2019, 257, 117896.
|
| [58] |
(a) Zhang Y.Q. ; Ouyang B. ; Xu J. ; Chen S. ; Rawat R.S. ; Fan H.J. Adv. Energy Mater. 2016, 6, 1600221.
|
|
(b) Hammer B. ; Norskov J.K. Nature 1995, 376, 238.
|
|
| [59] |
Zhang L. ; Ji X.Q. ; Ren X. ; Ma Y.J. ; Shi X.F. ; Tian Z.Q. ; Asiri A.M. ; Chen L. ; Tang B. ; Sun. X. P. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1800191.
|
| [60] |
Ren X. ; Cui G.W. ; Chen L. ; Xie F.Y. ; Wei Q. ; Tian Z.Q. ; Sun X.P. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 8474.
|
| [61] |
Zhang R. ; Guo H.R. ; Yang L. ; Wang Y. ; Niu Z.G. ; Huang H. ; Chen H.Y. ; Xia L. ; Li T.S. ; Shi X.F. ; Sun X.P. ; Li B.H. ; Liu Q. ChemElectroChem 2019, 6, 1014.
|
| [62] |
Cheng X. ; Wang J.W. ; Xiong W. ; Wang T. ; Wu T.W. ; Lu S.Y. ; Chen G. ; Gao S.Y. ; Shi X.F. ; Jiang Z.J. ; Niu X.B. ; Sun X.P. ChemNanoMat 2020, 6, 1315.
|
| [63] |
(a) Wang Y.H. ; Cui X.Q. ; Zhang Y.Y. ; Zhang L.J. ; Gong X.G. ; Zheng G.F. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 7626.
|
|
(b) Chen G.F. ; Cao X.R. ; Wu S.Q. ; Zeng X.Y. ; Ding L.X. ; Zhu M. ; Wang H.H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 9771.
|
|
| [64] |
Lee H.K. ; Koh C.S.L. ; Lee Y.H ; Liu C. ; Phang I.Y. ; Han X.M. ; Tsung C.K. ; Ling X.Y. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, 3208.
|
| [65] |
Tong Y.Y. ; Guo H.P. ; Liu D.L. ; Yan X. ; Su P.P. ; Liang J. ; Zhou S. ; Liu J. ; Lu G.Q. ; Dou S.X. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 132, 7356.
|
| [66] |
Tao H.C. ; Choi C. ; Ding L.X. ; Jiang Z. ; Hang Z.S. ; Jia M.W. ; Fan Q. ; Gao Y.N. ; Wang H.H. ; Robertson A.W. ; Hong S. ; Jung Y.S. ; Liu S.Z. ; Sun Z.Y. Chem 2019, 5, 204.
|
| [67] |
Vojvodic A. ; Medford A.J. ; Studt F. ; Abild-Pedersen F. ; Khan T.S. ; Bligaard T. ; Norskov J.K. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2014, 598, 108.
|
| [68] |
(a) Nazemi M. ; El-Sayed M.A. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 11422.
|
|
(b) Manjuatha R. ; Schechter A. Electrochem. Commun. 2018, 90, 96.
|
|
|
(c) Chang B. ; Deng L.Q. ; Wang S.Z. ; Shi D. ; Ai Z.Z. ; Jiang H.H. ; Shao Y.L. ; Zhang L. ; Shen J.X. ; Wu Y.Z. ; Hao X.P. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 91.
|
|
| [69] |
Qin B.H. ; Li Y.H. ; Zhang Q. ; Yang G.X. ; Liang H. ; Peng F. Nano Energy 2020, 68, 104374.
|
| [70] |
(a) Kowalczyk Z. ; Sentek J. ; Jodzis S. ; Muhler M. ; Hinrichsen O. J. Catal. 1997, 169, 407.
|
|
(b) Kowalczyk Z. Catal. Lett. 1996, 37, 173.
|
|
|
(c) Narasimharao K. ; Seetharamulu P. ; Rao K.S.R. ; Basahel S.N. J. Mol. Catal. A-Chem. 2016, 411, 157.
|
|
| [71] |
Hao Y.C. ; Guo Y. ; Chen L.W. ; Shu M. ; Wang X.Y. ; Bu T.A. ; Gao W.Y. ; Zhang N. ; Su X. ; Feng X. ; Zhou J.W. ; Wang B. ; Hu C.W. ; Yin A.X. ; Si R. ; Zhang Y.W. ; Yan C.H. Nat. Catal. 2019, 2, 448.
|
| [72] |
(a) Su L. ; Han D.D. ; Zhu G.J. ; Xu H. ; Luo W. ; Wang L.J. ; Jiang W. ; Dong A.G. ; Yang J.P. Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 5423.
|
|
(b) Guillette L.J. ; Edwards T.M. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2005, 45, 19.
|
|
| [73] |
(a) Dima G.E. ; Beltramo G.L. ; Koper M.T.M. Electrochim. Acta 2005, 50, 4318.
|
|
(b) DeVooy A.C.A. ; Koper M.T.M. ; Van Santen R.A .; Van Veen J. A.R . J. Electroanal. Chem. 2001, 506, 127.
|
|
|
(c) Ye T. ; Durkin D.P. ; Banek N.A. ; Wagner M.J. ; Shuai D.M. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 27421.
|
|
|
(d) Zhang R. ; Shuai D. ; Guy K.A. ; Shapley J.R. ; Strathmann T.J. ; Werth C.J. ChemCatChem 2013, 5, 313.
|
|
| [74] |
Zhang X. ; Wang Y.T. ; Liu C.B. ; Yu Y.F. ; Liu S.Y. ; Zhang B. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 403, 126269.
|
| [75] |
Wang Y.T. ; Zhou W. ; Jia R.R. ; Yu Y.F. ; Zhang B. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 5350.
|
| [76] |
Li J. ; Zhan G.M. ; Yang J.H. ; Quan F.J. ; Mao C.L. ; Liu Y. ; Wang B. ; Lei F.C. ; Li L.J. ; Chan A.W.M. ; Xu L.P. ; Shi Y.B. ; Du Y. ; Hao W.C. ; Wong P.K. ; Wang J.F. ; Dou S.X. ; Zhang L.Z. ; Yu J.C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 7036.
|
| [77] |
Wang Y.T. ; Yu Y.F. ; Jia R.R. ; Zhang C. ; Zhang B. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2019, 6, 730.
|
| [78] |
(a) Zhu L. ; Zhang L. ; Qu H.X ,; Zhong Q. J. Mol. Catal. A-Chem. 2015, 409, 207.
|
|
(b) Fritz A. ; Pitchon V. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 1997, 13, 1.
|
|
| [79] |
(a) Koebel M. ; Elsener M. ; Madia G. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2001, 40, 52.
|
|
(b) Koebel M. J. Catal. 2002, 209, 159.
|
|
| [80] |
Long J. ; Chen S.M. ; Zhang Y.L. ; Guo C.X. ; Fu X.Y. ; Deng D.H. ; Xiao J.P. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 9711.
|
| [81] |
(a) Li R.G. ; Zhang F.X. ; Wang D.G. ; Yang J.X. ; Li M.R. ; Zhu J. ; Zhou X. ; Han H.X. ; Li C. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1432.
|
|
(b) Dong B.B. ; Cui J.Y. ; Gao Y.Y. ; Qi Y. ; Zhang F.X. ; Li C. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1808185.
|
| [1] | 李珊, 路俊欣, 刘杰, 蒋绿齐, 易文斌. 氟烷基亚磺酸钠盐电化学合成α-氟烷基酮[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(2): 110-114. |
| [2] | 刘建川, 李翠艳, 刘耀祖, 王钰杰, 方千荣. 高稳定二维联咔唑sp2碳共轭共价有机框架材料用于高效电催化氧还原★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(8): 884-890. |
| [3] | 杨镇鸿, 干晓娟, 王书哲, 段君元, 翟天佑, 刘友文. 金属性Ni3N纳米粒子的制备与乙二醇电氧化性能★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(11): 1471-1477. |
| [4] | 闫绍兵, 焦龙, 何传新, 江海龙. ZIF-67/石墨烯复合物衍生的氮掺杂碳限域Co纳米颗粒用于高效电催化氧还原[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(8): 1084-1090. |
| [5] | 何家伟, 焦柳, 程雪怡, 陈光海, 吴强, 王喜章, 杨立军, 胡征. 金属有机框架衍生的空心碳纳米笼的结构调控与锂硫电池性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(7): 896-902. |
| [6] | 马行宇, 孙晖, 李江, 刘之洋, 周红军. 基于Li-N2电池体系的“连续式”氮气还原合成氨[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(7): 861-866. |
| [7] | 蒋银龙, 李国超, 陈青松, 徐忠宁, 林姗姗, 郭国聪. 富晶格位错的多孔铋纳米花高效电还原二氧化碳制甲酸盐※[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(6): 703-707. |
| [8] | 王丹, 封波, 张晓昕, 刘亚楠, 裴燕, 乔明华, 宗保宁. 基于热解ZIF-8的氮掺杂碳电化学氧还原合成过氧化氢催化剂[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(6): 772-780. |
| [9] | 张谭, 余钟亮, 余嘉祺, 万慧凝, 包成宇, 涂文强, 杨颂. 基于高性能负载型钼基载氮体的化学链合成氨性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(6): 788-796. |
| [10] | 祁育, 章福祥. 太阳能光催化分解水制氢※[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(6): 827-838. |
| [11] | 应霞薇, 浮建军, 曾敏, 刘文, 张天宇, 沈培康, 张信义. 基于BiOCl-Fe2O3@TiO2介孔复合材料的光电化学合成氨性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(4): 503-509. |
| [12] | 李泽洋, 杨宇森, 卫敏. 二氧化碳还原电催化剂的结构设计及性能研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(2): 199-213. |
| [13] | 安攀, 张庆慧, 杨状, 武佳星, 张佳颖, 王雅君, 李宇明, 姜桂元. 双碳目标下太阳能制氢技术的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(12): 1629-1642. |
| [14] | 王金格, 周伟, 李佳轶, 丁雅妮, 高继慧. 脉冲电催化的研究进展及性能强化机制[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(11): 1555-1568. |
| [15] | 熊昆, 陈伽瑶, 杨娜, 蒋尚坤, 李莉, 魏子栋. 理论探究水溶液条件对TMNxCy催化氮还原性能的增强机制[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(9): 1138-1145. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
