化学学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 79 ›› Issue (7): 853-868.DOI: 10.6023/A21030106 上一篇 下一篇
综述
龚陈祥a,b, 程书平a, 孟祥川a,b, 胡笑添a,b,*( ), 陈义旺a,b,c,*(
), 陈义旺a,b,c,*( )
)
投稿日期:2021-03-22
发布日期:2021-04-27
通讯作者:
胡笑添, 陈义旺
作者简介: |
龚陈祥, 南昌大学化学学院2019 级在读硕士生. 主要研究方向为导电聚合物形貌调控和大面积柔性钙钛矿太阳电池的制备研究. |
 |
胡笑添, 南昌大学特聘研究员, 中国科学院化学研究所理学博士. 主要代表性成果: 自主设计研发“卷对卷”光电器件印刷系统, 并实现大面积柔性透明电极和新型薄膜光伏器件制备; 利用柔性仿生设计, 首次实现印刷可穿戴钙钛矿太阳能电源. |
 |
陈义旺, 南昌大学和江西师范大学教授, 博士生导师, 国家杰出青年科学基金获得者, 江西师范大学副校长, 南昌大学高分子及能源化学研究院院长. 主要从事太阳电池、纳米材料、功能高分子材料等领域研究. |
基金资助:
Chenxiang Gonga,b, Shuping Chenga, Xiangchuan Menga,b, Xiaotian Hua,b( ), Yiwang Chena,b,c(
), Yiwang Chena,b,c( )
)
Received:2021-03-22
Published:2021-04-27
Contact:
Xiaotian Hu, Yiwang Chen
Supported by:文章分享
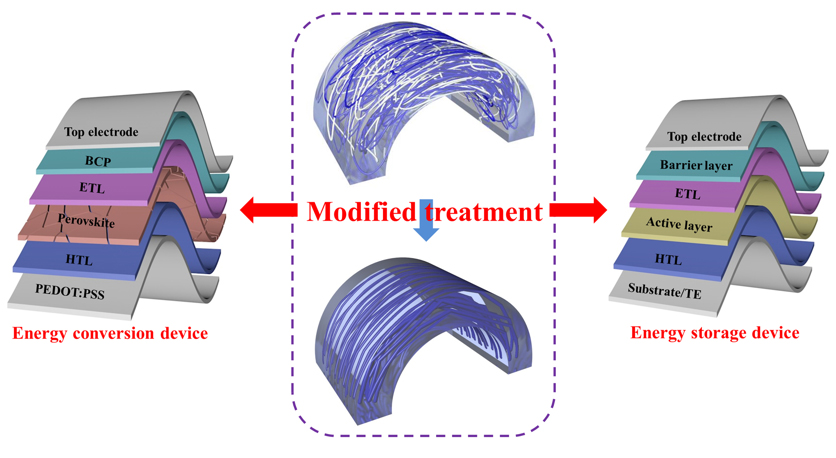
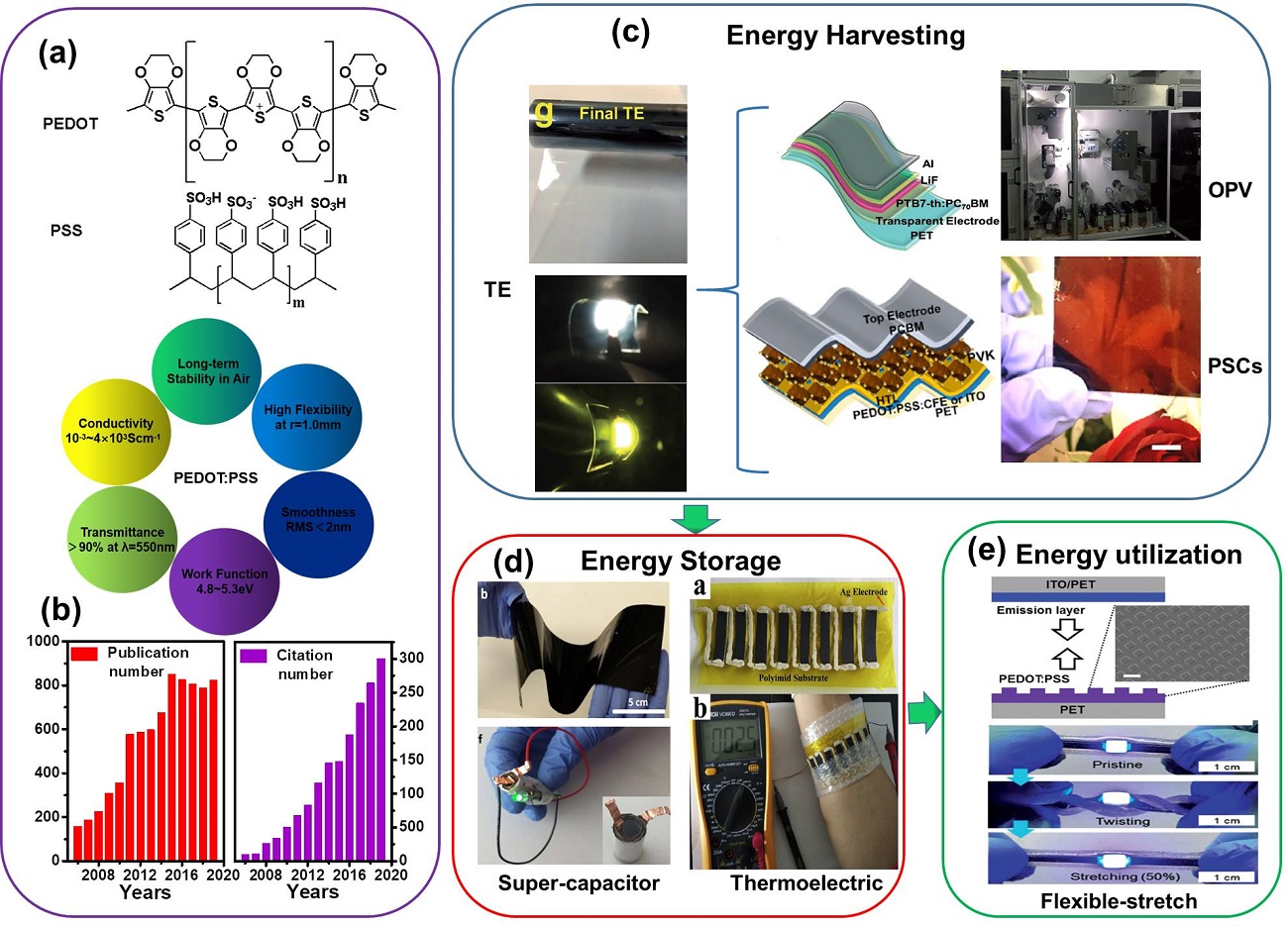
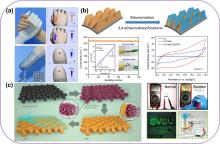
近年来, 柔性有机和钙钛矿光伏器件、有机薄膜晶体管和医用传感器等因其具有可穿戴性、柔性、半透明性等优点, 成为科学研究的热门领域. 利用具有优异力学性能的导电聚合物是实现这些高性能器件的有效途径之一. 在导电聚合物中, 3,4-亚乙基二氧噻吩(PEDOT)及其水性分散液3,4-亚乙基二氧噻吩:聚苯乙烯磺酸盐(PEDOT:PSS)已经被证明是最有前途替代传统金属氧化物的柔性材料, 其在器件中可作为透明电极、空穴传输层、互连器、电活性层或运动传感导体等. 综述了PEDOT及PEDOT:PSS应用柔性器件的研究现状, 包括提高电导率、机械耐受性和长期稳定性的各种策略, 揭示了性能增强的潜在机理. 最后, 论述了导电聚合物在器件制备中亟待解决的问题和未来发展方向. 本工作讨论了导电聚合物薄膜形貌的重要性, 并展望了它们在下一代柔性电子器件中的广阔前景.
龚陈祥, 程书平, 孟祥川, 胡笑添, 陈义旺. PEDOT导电高分子在柔性能量转化与存储器件的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(7): 853-868.
Chenxiang Gong, Shuping Cheng, Xiangchuan Meng, Xiaotian Hu, Yiwang Chen. Recent Advances of PEDOT in Flexible Energy Conversion and Storage Devices[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(7): 853-868.


| Scheme | Type | Solvent | σ/(S•cm-1) | T/% | Rsh/(Ω•sq-1) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EG | Doping | Baytron P | 200 | — | — | [ |
| DMSO | Doping | Baytron PH500 | 550 | 95 | 190 | [ |
| EG | Doping | PH1000 | 1330 | 86 | 60 | [ |
| EG, MSA | Doping | PH1000 | 3560 | 92.5 | 43 | [ |
| Doping | PH1000 | 3100 | 96 | 59 | [ | |
| EG | Doping | PH1000 | 5012 | 73 | 36 | [ |
| H2SO4 | Soaking (1 mol/L) | PH1000 | 3065 | 81 | 39 | [ |
| Soaking (1 mol/L) | PH1000 | 3065 | 87 | 67 | [ | |
| Soaking (100%) | PH1000 | 4200 | 90 | 46 | [ | |
| Soaking (98%) | PH1000 | 3210 | 92 | 79 | [ | |
| H2SO4 | Transfer-printing | PH1000 | 4000 | 90 | 45 | [ |
| Transfer-printing | PH1000 | 4000 | 86.5 | 33 | [ | |
| HNO3 | Soaking | PH1000 | 4100 | — | 14 | [ |
| MSA | Soaking | PH1000 | 2540 | 92 | 50 | [ |
| H2SO4 | Post-treatment | PH1000 and 4083 | 1700 | 89 | — | [ |
| H2SO4 | Post-treatment | PH1000 and 4083 | 3000 | — | — | [ |
| HCOOH | Post-treatment | PH1000 and 4083 | 1362 | — | — | [ |
| Scheme | Type | Solvent | σ/(S•cm-1) | T/% | Rsh/(Ω•sq-1) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EG | Doping | Baytron P | 200 | — | — | [ |
| DMSO | Doping | Baytron PH500 | 550 | 95 | 190 | [ |
| EG | Doping | PH1000 | 1330 | 86 | 60 | [ |
| EG, MSA | Doping | PH1000 | 3560 | 92.5 | 43 | [ |
| Doping | PH1000 | 3100 | 96 | 59 | [ | |
| EG | Doping | PH1000 | 5012 | 73 | 36 | [ |
| H2SO4 | Soaking (1 mol/L) | PH1000 | 3065 | 81 | 39 | [ |
| Soaking (1 mol/L) | PH1000 | 3065 | 87 | 67 | [ | |
| Soaking (100%) | PH1000 | 4200 | 90 | 46 | [ | |
| Soaking (98%) | PH1000 | 3210 | 92 | 79 | [ | |
| H2SO4 | Transfer-printing | PH1000 | 4000 | 90 | 45 | [ |
| Transfer-printing | PH1000 | 4000 | 86.5 | 33 | [ | |
| HNO3 | Soaking | PH1000 | 4100 | — | 14 | [ |
| MSA | Soaking | PH1000 | 2540 | 92 | 50 | [ |
| H2SO4 | Post-treatment | PH1000 and 4083 | 1700 | 89 | — | [ |
| H2SO4 | Post-treatment | PH1000 and 4083 | 3000 | — | — | [ |
| HCOOH | Post-treatment | PH1000 and 4083 | 1362 | — | — | [ |
| PEDOT:PSS | Device structure | Scheme | PCE/% | JSC/ (mA•cm-2) | FF/% | VOC/V | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transparency electrode | PET/PH1000/ZnO/Perovskite/Spiro- OMeTAD/PH1000 | Nitric acid annealed | 10.3 | 17.3 | 60 | 0.99 | [ |
| PET/PH1000/Perovskite/PCBM/PTCDI/ Cr2O3/Cr/Au/Polyurethane | Solvent treatment | 12 | 17.5 | 76 | 0.93 | [ | |
| PET/PH1000/MAPbI3/TiO2/Al | Solvent doping | 7.60 | 15.0 | 60.0 | 0.80 | [ | |
| PET/PH1000/PEI/MAPbI3/Spiro-OMeTAD/ Au | Solvent doping | 9.73 | 17.2 | 59.7 | 0.95 | [ | |
| NOA63/PH1000/MAPbI3/PCBM/Eutectic Ga-In blends | — | 10.75 | 16.6 | 70.5 | 0.92 | [ | |
| PET/PEDOT:PSS:CFE/PEDOT:PSS/ Perovskite/PCBM/Ag | Surfactant treatment | 19.0 | 22.38 | 0.79 | 1.08 | [ | |
| Hole transport layer | PET/ITO/NC-PEDOT:PSS/Perovskite/PCBM/Ag | Nanocellular scaffold | 19.66 | 22.47 | 0.81 | 1.08 | [ |
| PET/ITO/PEDOT:EVA/Perovskite/PCBM/ BCP/Ag | — | 19.87 | 21.26 | 0.79 | 1.18 | [ | |
| PDMS/PEDOT:PSS/Perovskite//PCBM/PEI/ PEDOT:PSS/PDMS | — | 15.61 | 18.70 | 0.78 | 1.07 | [ | |
| PET/PH1000/PEDOT:PSS/Perovskite/PCBM/Rhodamine/C60 /Rhodamine/LiF/Ag | Solvent treatment | 8.6 | 17.2 | 57 | 0.86 | [ | |
| PET/Ag-mesh/PH1000/PEDOT:PSS/ Perovskite/PCBM/Al | Auxiliary electrode | 14 | 19.5 | 80 | 0.91 | [ | |
| PEN/Graphene-Mo/PEDOT:PSS/MAPbI3/C60/BCP/LiF/Al | — | 16.80 | 21.7 | 80 | 1.0 | [ | |
| PEN/ITO/PEDOT:PSS/MAPbI3/C60/BCP/LiF/Al | Metal oxide doping | 17.30 | 21.5 | 83.0 | 0.97 | [ |
| PEDOT:PSS | Device structure | Scheme | PCE/% | JSC/ (mA•cm-2) | FF/% | VOC/V | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transparency electrode | PET/PH1000/ZnO/Perovskite/Spiro- OMeTAD/PH1000 | Nitric acid annealed | 10.3 | 17.3 | 60 | 0.99 | [ |
| PET/PH1000/Perovskite/PCBM/PTCDI/ Cr2O3/Cr/Au/Polyurethane | Solvent treatment | 12 | 17.5 | 76 | 0.93 | [ | |
| PET/PH1000/MAPbI3/TiO2/Al | Solvent doping | 7.60 | 15.0 | 60.0 | 0.80 | [ | |
| PET/PH1000/PEI/MAPbI3/Spiro-OMeTAD/ Au | Solvent doping | 9.73 | 17.2 | 59.7 | 0.95 | [ | |
| NOA63/PH1000/MAPbI3/PCBM/Eutectic Ga-In blends | — | 10.75 | 16.6 | 70.5 | 0.92 | [ | |
| PET/PEDOT:PSS:CFE/PEDOT:PSS/ Perovskite/PCBM/Ag | Surfactant treatment | 19.0 | 22.38 | 0.79 | 1.08 | [ | |
| Hole transport layer | PET/ITO/NC-PEDOT:PSS/Perovskite/PCBM/Ag | Nanocellular scaffold | 19.66 | 22.47 | 0.81 | 1.08 | [ |
| PET/ITO/PEDOT:EVA/Perovskite/PCBM/ BCP/Ag | — | 19.87 | 21.26 | 0.79 | 1.18 | [ | |
| PDMS/PEDOT:PSS/Perovskite//PCBM/PEI/ PEDOT:PSS/PDMS | — | 15.61 | 18.70 | 0.78 | 1.07 | [ | |
| PET/PH1000/PEDOT:PSS/Perovskite/PCBM/Rhodamine/C60 /Rhodamine/LiF/Ag | Solvent treatment | 8.6 | 17.2 | 57 | 0.86 | [ | |
| PET/Ag-mesh/PH1000/PEDOT:PSS/ Perovskite/PCBM/Al | Auxiliary electrode | 14 | 19.5 | 80 | 0.91 | [ | |
| PEN/Graphene-Mo/PEDOT:PSS/MAPbI3/C60/BCP/LiF/Al | — | 16.80 | 21.7 | 80 | 1.0 | [ | |
| PEN/ITO/PEDOT:PSS/MAPbI3/C60/BCP/LiF/Al | Metal oxide doping | 17.30 | 21.5 | 83.0 | 0.97 | [ |



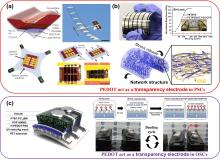



| PEDOT:PSS | Device structure | Scheme | PCE/% | JSC/ (mA•cm-2) | FF/% | VOC/V | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transparency electrode | PET/Ag-grid/PEDOT:PSS(PH1000)/ PTB7:PC71BM/LiF/Al | Hybrid electrode | 5.85 | 13.7 | 61 | 0.7 | [ |
| PET/Ag-grid/PEDOT:PSS(PH1000)/ZnO/ PFN/Active layer/MoO3/Ag | Acid treatment | 6.01 | 13.9 | 60 | 0.72 | [ | |
| PEN/H2SO4-PEDOT:PSS(PH1000)/ PTB7-Th:PC71BM/Ca/Al | Solvent doping | 7.6 | 14.2 | 69 | 0.77 | [ | |
| PEN/PEI/Ag/PEDOT:PSS(PH1000)/ PTB7-Th:PC71BM/MoO3/Ag | Anti-reflection layer | 9.9 | 16.9 | 74 | 0.79 | [ | |
| Hole transport layer | PET/Ag-mesh/H-PEDOT:PSS/PEDOT:PSS/ PTB7:PC71BM/TiO x/Al | Hybrid electrode | 6.94 | 14.2 | 67.1 | 0.73 | [ |
| PET/Ag-grid/PH1000/ZnO/PTB7-Th:PC71BM/MoO3/Al | Auxiliary electrode | 6.58 | 14.3 | 59 | 0.78 | [ | |
| PET/Acid-PH1000/PEDOT:PSS/P3HT:PCBM/Ca/Al | Acid treatment | 3.92 | 10.2 | 65 | 0.595 | [ | |
| PET/Acid-PH1000/PEDOT:PSS/ PBDB-T:IT-M/Ca/Al | Acid treatment | 10.12 | 15.5 | 70.3 | 0.93 | [ | |
| PET/PH1000/PEDOT:PSS/Active layer/ PDINO/Al | — | 14.06 | 23.57 | 72.0 | 0.83 | [ | |
| PET/Ag-mesh/PH1000/PEDOT:PSS/ Photoactive layer/PDINO/Ag | — | 10.20 | 20.48 | 67.5 | 0.74 | [ |
| PEDOT:PSS | Device structure | Scheme | PCE/% | JSC/ (mA•cm-2) | FF/% | VOC/V | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transparency electrode | PET/Ag-grid/PEDOT:PSS(PH1000)/ PTB7:PC71BM/LiF/Al | Hybrid electrode | 5.85 | 13.7 | 61 | 0.7 | [ |
| PET/Ag-grid/PEDOT:PSS(PH1000)/ZnO/ PFN/Active layer/MoO3/Ag | Acid treatment | 6.01 | 13.9 | 60 | 0.72 | [ | |
| PEN/H2SO4-PEDOT:PSS(PH1000)/ PTB7-Th:PC71BM/Ca/Al | Solvent doping | 7.6 | 14.2 | 69 | 0.77 | [ | |
| PEN/PEI/Ag/PEDOT:PSS(PH1000)/ PTB7-Th:PC71BM/MoO3/Ag | Anti-reflection layer | 9.9 | 16.9 | 74 | 0.79 | [ | |
| Hole transport layer | PET/Ag-mesh/H-PEDOT:PSS/PEDOT:PSS/ PTB7:PC71BM/TiO x/Al | Hybrid electrode | 6.94 | 14.2 | 67.1 | 0.73 | [ |
| PET/Ag-grid/PH1000/ZnO/PTB7-Th:PC71BM/MoO3/Al | Auxiliary electrode | 6.58 | 14.3 | 59 | 0.78 | [ | |
| PET/Acid-PH1000/PEDOT:PSS/P3HT:PCBM/Ca/Al | Acid treatment | 3.92 | 10.2 | 65 | 0.595 | [ | |
| PET/Acid-PH1000/PEDOT:PSS/ PBDB-T:IT-M/Ca/Al | Acid treatment | 10.12 | 15.5 | 70.3 | 0.93 | [ | |
| PET/PH1000/PEDOT:PSS/Active layer/ PDINO/Al | — | 14.06 | 23.57 | 72.0 | 0.83 | [ | |
| PET/Ag-mesh/PH1000/PEDOT:PSS/ Photoactive layer/PDINO/Ag | — | 10.20 | 20.48 | 67.5 | 0.74 | [ |

| [1] |
Lipomi, D. J.; Bao, Z. N. MRS Bull. 2017, 42, 93.
doi: 10.1557/mrs.2016.325 |
| [2] |
Hammock, M. L.; Chortos, A.; Tee, B. C.-K.; Tok, J. B.-H.; Bao, Z. N. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 5997.
doi: 10.1002/adma.201302240 |
| [3] |
(a) Someya, T.; Bao, Z. N.; Malliaras, G. G. Nature 2016, 540, 379.
doi: 10.1038/nature21004 |
|
(b) Oh, J. Y.; Kim, S.; Baik, H.; Jeong, U. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 4455.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v28.22 |
|
| [4] |
Kim, D.-H.; Ahn, J.-H.; Choi, W. M.; Kim, H.-S.; Kim, T.-H.; Song, J. Z.; Huang, Y. Y.; Liu, Z.; Lu, C.; Rogers, J. A. Science 2008, 320, 507.
doi: 10.1126/science.1154367 |
| [5] |
Lipomi, D. J.; Vosgueritchian, M.; Tee, B. C.-K.; Hellstrom, S. L.; Lee, J. A.; Fox, C. H.; Bao, Z. N. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 788.
doi: 10.1038/nnano.2011.184 |
| [6] |
Cheng, Y.-B.; Pascoe, A.; Huang, F.; Peng, Y. Nature 2016, 539, 488.
doi: 10.1038/539488a |
| [7] |
Son, D.; Lee, J.; Qiao, S. T.; Ghaffari, R.; Kim, J.; Lee, J. E.; Song, C.; Kim, S. J.; Lee, D. J.; Jun, S. W.; Yang, S. X.; Park, M.; Shin, J.; Do, K.; Lee, M.; Kang, K.; Hwang, C. S.; Lu, N. S.; Hyeon, T.; Kim, D.-H. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2014, 9, 397.
doi: 10.1038/nnano.2014.38 |
| [8] |
Kim, D.-H.; Lee, Y. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2015, 10, 570.
doi: 10.1038/nnano.2015.129 |
| [9] |
Minev, I. R.; Musienko, P.; Hirsch, A.; Barraud, Q.; Wenger, N.; Moraud, E. M.; Gandar, J.; Capogrosso, M.; Milekovic, T.; Asboth, L.; Torres, R. F.; Vachicouras, N.; Liu, Q. H.; Pavlova, N.; Duis, S.; Larmagnac, A.; Vörös, J.; Micera, S.; Suo, Z. G.; Courtine, G.; Lacour, S. P. Science 2015, 347, 159.
doi: 10.1126/science.1260318 pmid: 25574019 |
| [10] |
Larson, C.; Peele, B.; Li, S.; Robinson, S.; Totaro, M.; Beccai, L.; Mazzolai, B.; Shepherd, R. Science 2016, 351, 1071.
doi: 10.1126/science.aac5082 pmid: 26941316 |
| [11] |
Ouyang, J. Y. Displays 2013, 34, 423.
doi: 10.1016/j.displa.2013.08.007 |
| [12] |
Shi, H.; Liu, C. C.; Jiang, Q. L.; Xu, J. K. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2015, 1, 1500017.
doi: 10.1002/aelm.201500017 |
| [13] |
Hu, X. T.; Huang, Z. Q.; Zhou, X.; Li, P. W.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Z. D.; Su, M.; Ren, W. J.; Li, F. Y.; Li, M. Z.; Chen, Y. W.; Song, Y. L. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1703236.
doi: 10.1002/adma.201703236 |
| [14] |
Li, D. D.; Lai, W.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-Z.; Huang, W. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1704738.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v30.10 |
| [15] |
(a) Fan, X.; Nie, W. Y.; Tsai, H.; Wang, N. X.; Huang, H. H.; Cheng, Y. J.; Wen, R. J.; Ma, L. J.; Yan, F.; Xia, Y. G. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1900813.
doi: 10.1002/advs.v6.19 |
|
(b) Bayer, A. G. Eur.Patent DE3813589, 1988.
|
|
|
(c) Jonas, F.; Schrader, L. Synth. Met. 1991, 831, 41.
|
|
|
(d) Heywang, G.; Jonas, F. Adv. Mater. 1992, 4, 116.
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1521-4095 |
|
|
(e) Winter, I.; Reece, C.; Hormes, J.; Heywang, G.; Jonas, F. Chem. Phys. 1995, 194, 207.
doi: 10.1016/0301-0104(95)00026-K |
|
|
(f) Dietrich, M.; Heinze, J.; Heywang, G.; Jonas, F. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1994, 369, 87.
doi: 10.1016/0022-0728(94)87085-3 |
|
|
(g) Bayer, A. G. Eur. Patent EP0440957, 1991.
|
|
|
(h) Gevaert, A. Eur. Patent EP93104866, 1993.
|
|
|
(i) Jonas, F.; Krafft, W.; Muys, B. Macromol. Symp. 1995, 100, 169.
doi: 10.1002/masy.19951000128 |
|
|
(j) Groenendaal, L.; Jonas, F.; Freitag, D.; Pielartzik, H.; Reynolds, J. R. Adv. Mater. 2000, 12, 481.
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1521-4095 |
|
| [16] |
(a) Seo, K.-W.; Lee, J.; Jo, J.; Cho, C.; Lee, J.-Y. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1902447.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v31.36 |
|
(b) Mao, L.; Chen, Q.; Li, Y. W.; Li, Y.; Cai, J. H.; Su, W. M.; Bai, S.; Jin, Y. Z.; Ma, C.-Q.; Cui, Z.; Chen, L. W. Nano Energy 2014, 10, 259.
doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2014.09.007 |
|
|
(c) Wang, J.; Fei, F.; Luo, Q.; Nie, S. H.; Wu, N.; Chen, X. L.; Su, W. M.; Li, Y. J.; Ma, C.-Q. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 7834.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.6b16341 |
|
|
(d) Li, T. F.; Zhan, X. W. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 257. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A20110502 |
|
|
(李腾飞, 占肖卫, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 257.)
doi: 10.6023/A20110502 |
|
| [17] |
Zhang, J. W.; Xu, G. Y.; Tao, F.; Zeng, G.; Zhang, M. Y.; Yang, Y. (M.); Li, Y. W.; Li, Y. F. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1807159.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v31.10 |
| [18] |
(a) Fukuda, K.; Yu, K.; Someya, T. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 2000765.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.v10.25 |
|
(b) Hu, X. T.; Meng, X. C.; Xiong, J.; Huang, Z. Q.; Yang, X.; Tan, L. C.; Chen, Y. W. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2017, 2, 1700138.
doi: 10.1002/admt.201700138 |
|
|
(c) Kee, S.; Kim, N.; Park, B.; Kim, B. S.; Hong, S.; Lee, J.-H.; Jeong, S.; Kim, A.; Jang, S.-Y.; Lee, K. Adv. Mater. 2017, 30, 1703437.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v30.3 |
|
| [19] |
Wan, Z. F.; Streed, E. W.; Lobino, M.; Wang, S. J.; Sang, R. T.; Cole, I. S.; Thiel, D. V.; Li, Q. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2018, 3, 1700315.
doi: 10.1002/admt.v3.4 |
| [20] |
Han, Y. W.; Jeon, S. J.; Lee, H. S.; Park, H.; Kim, K. S.; Lee, H.-W.; Moon, D. K. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1902065.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.v9.42 |
| [21] |
Kang, H.; Jung, S.; Jeong, S.; Kim, G.; Lee, K. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6503.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms7503 |
| [22] |
Cui, Y.; Yang, C. Y.; Yao, H. F.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Y. M.; Jia, G. X.; Gao, F.; Hou, J. H. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1703080.
doi: 10.1002/adma.201703080 |
| [23] |
(a) Li, Z.; Wu, S. F.; Zhang, J.; Lee, K. C.; Lei, H.; Lin, F.; Wang, Z. L.; Zhu, Z. L.; Jen, A. K. Y. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 2000361.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.v10.18 |
|
(b) Hu, X. T.; Huang, Z. Q.; Zhou, X.; Li, P. W.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Z. D.; Su, M.; Ren, W. J.; Li, F. Y.; Li, M. Z.; Chen, Y. W.; Song, Y. L. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1703236.
doi: 10.1002/adma.201703236 |
|
|
(c) Hu, X. T.; Huang, Z. Q.; Li, F. Y.; Su, M.; Huang, Z. D.; Zhao, Z. P.; Cai, Z. R.; Yang, X.; Meng, X. C.; Li, P. W.; Wang, Y.; Li, M. Z.; Chen, Y. W.; Song, Y. L. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 979.
doi: 10.1039/C8EE01799A |
|
| [24] |
(a) Kim, Y. Y.; Yang, T.-Y.; Suhonen, R.; Välimäki, M.; Maaninen, T.; Kemppainen, A.; Jeon, N. J.; Seo, J. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1802094.
doi: 10.1002/advs.v6.7 |
|
(b) Nazeeruddin, M. K.; Bolink, H. J. Nature Photon. 2014, 8, 128.
doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2013.341 |
|
| [25] |
(a) Zhang, Y. K.; Wu, Z. W.; Li, P.; Ono, L. K.; Qi, Y. B.; Zhou, J. X.; Shen, H.; Surya, C.; Zheng, Z. J. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1701569.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.v8.1 |
|
(b) Li, Y. W.; Meng, L.; Yang, Y.(M.); Xu, G. Y.; Hong, Z. R.; Chen, Q.; You, J. B.; Li, G.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y. F.. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10214.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms10214 |
|
|
(c) Yang, Y.; Zhu, C. T.; Lin, F. Y.; Chen, T.; Pan, D. Q.; Guo, X. Y. Acta Chim. Sinica 2019, 77, 964. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A19040143 |
|
|
(杨英, 朱从潭, 林飞宇, 陈甜, 潘德群, 郭学益, 化学学报, 2019, 77, 964.)
doi: 10.6023/A19040143 |
|
| [26] |
Pandey, M.; Wang, Z.; Kapil, G.; Baranwal, A. K.; Hirotani, D.; Hamada, K.; Hayase, S. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2019, 21, 1900288.
doi: 10.1002/adem.v21.8 |
| [27] |
(a) Poorkazem, K.; Liu, D. Y.; Kelly, T. L. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 9241.
doi: 10.1039/C5TA00084J |
|
(b) Lee, M.; Jo, Y.; Kim, D. S.; Jeong, H. Y.; Jun, Y. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 14592.
doi: 10.1039/C5TA03240G |
|
|
(c) Yoon, J.; Sung, H.; Lee, G.; Cho, W.; Ahn, N.; Jung, H. S.; Choi, M. Energy Environ. Sci. 2017, 10, 337.
doi: 10.1039/C6EE02650H |
|
| [28] |
(a) Yu, J. C.; Hong, J. A.; Jung, E. D.; Kim, D. B.; Baek, S.-M.; Lee, S.; Cho, S.; Park, S. S.; Choi, K. J.; Song, M. H. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1070.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-19612-7 |
|
(b) Xue, Q. F.; Liu, M. Y.; Li, Z. C.; Yan, L.; Hu, Z. C.; Zhou, J. W.; Li, W. Q.; Jiang, X.-F.; Xu, B. M.; Huang, F.; Li, Y.; Yip, H.-L.; Cao, Y. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1707444.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.v28.18 |
|
|
(c) Elbohy, H.; Bahrami, B.; Mabrouk, S.; Reza, K. M.; Gurung, A.; Pathak, R.; Liang, M.; Qiao, Q. Q.; Zhu, K. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 29, 1806740.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.v29.47 |
|
| [29] |
Zhou, L.; Yu, M. J.; Chen, X. L.; Nie, S. H.; Lai, W. Y.; Su, W. M.; Cui, Z.; Huang, W. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1705955.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.v28.11 |
| [30] |
Xie, C. C.; Zhao, X. F.; Ong, E. W. Y.; Tan, Z.-K. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4213.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-18110-7 |
| [31] |
Nakanotani, H.; Higuchi, T.; Furukawa, T.; Masui, K.; Morimoto, K.; Numata, M.; Tanaka, H.; Sagara, Y.; Yasuda, T.; Adachi, C. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4016.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms5016 pmid: 24874292 |
| [32] |
Kaltenbrunner, M.; Adam, G.; Głowacki, E. D.; Drack, M.; Schwödiauer, R.; Leonat, L.; Apaydin, D. H.; Groiss, H.; Scharber, M. C.; White, M. S.; Sariciftci, N. S.; Bauer, S. Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 1032.
doi: 10.1038/nmat4388 pmid: 26301766 |
| [33] |
Li, W.; Li, Y.-Q.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, Y.-X.; Jin, T.-Y.; Chen, J.-D.; Zhang, X.-H.; Tang, J.-X. Adv. Optical Mater. 2019, 7, 1900985.
doi: 10.1002/adom.v7.21 |
| [34] |
Bae, H. W.; Kim, S. K.; Lee, S.; Song, M.-G.; Lampande, R.; Kwon, J. H. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2019, 5, 1900620.
doi: 10.1002/aelm.v5.10 |
| [35] |
Patrikar, K.; Jain, N.; Chakraborty, D.; Johari, P.; Rao, V. R.; Kabra, D. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1805878.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.v29.8 |
| [36] |
He, D. W.; Zhang, Y. H.; Wu, Q. S.; Xu, R.; Nan, H. Y.; Liu, J. F.; Yao, J. J.; Wang, Z. L.; Yuan, S. J.; Li, Y.; Shi, Y.; Wang, J. L.; Ni, Z. H.; He, L.; Miao, F.; Song, F. Q.; Xu, H. X.; Watanabe, K.; Taniguchi, T.; Xu, J.-B.; Wang, X. R. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5162.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms6162 |
| [37] |
Liao, C. Z.; Zhang, M.; Niu, L. Y.; Zheng, Z. J.; Yan, F. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 191.
doi: 10.1039/C3TB21079K |
| [38] |
Duan, S. M.; Gao, X.; Wang, Y.; Yang, F. X.; Chen, M. X.; Zhang, X. T.; Ren, X. C.; Hu, W. P. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1807975.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v31.16 |
| [39] |
Pak, K.; Choi, J.; Lee, C.; Im, S. G. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2019, 5, 1800799.
doi: 10.1002/aelm.v5.4 |
| [40] |
Hammock, M. L.; Knopfmacher, O.; Ng, T. N.; Tok, J. B.; Bao, Z. N. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 6138.
doi: 10.1002/adma.201401829 |
| [41] |
Casalini, S.; Leonardi, F.; Cramer, T.; Biscarini, F. Org. Electron. 2013, 14, 156.
doi: 10.1016/j.orgel.2012.10.027 |
| [42] |
Kergoat, L.; Herlogsson, L.; Braga, D.; Piro, B.; Pham, M. C.; Crispin, X.; Berggren, M.; Horowitz, G. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 2565.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v22:23 |
| [43] |
Muzaffar, M. U.; Zhang, S. H.; Cui, P.; He, J. Q.; Zhang, Z. Y. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2003162.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.v30.35 |
| [44] |
Choi, H.; Kim, Y. J.; Song, J.; Kim, C. S.; Lee, G. S.; Kim, S.; Park, J.; Yim, S. H.; Park, S. H.; Hwang, H. R.; Hong, M.-H.; Veluswamy, P.; Cho, B. J. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1901505.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.v29.20 |
| [45] |
Haque, M. A.; Kee, S.; Villalva, D. R.; Ong, W.-L.; Baran, D. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 1903389.
doi: 10.1002/advs.v7.10 |
| [46] |
Fan, Z.; Li, P. C.; Du, D. H.; Ouyang, J. Y. Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1602116.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.201602116 |
| [47] |
Liang, L. R.; Chen, G. M.; Guo, C.-Y. Mater. Chem. Front. 2017, 1, 380.
doi: 10.1039/C6QM00061D |
| [48] |
Taroni, P. J.; Santagiuliana, G.; Wan, K. N.; Calado, P.; Qiu, M. T.; Zhang, H.; Pugno, N. M.; Palma, M.; Stingelin-Stutzman, N.; Heeney, M.; Fenwick, O.; Baxendale, M.; Bilotti, E. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1704285.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.v28.15 |
| [49] |
Wang, C.; Sun, K.; Fu, J. H.; Chen, R.; Li, M.; Zang, Z. G.; Liu, X. X.; Li, B. C.; Gong, H.; Ouyang, J. Y. Adv. Sustainable Syst. 2018, 2, 1800085.
doi: 10.1002/adsu.v2.12 |
| [50] |
Kayser, L. V.; Lipomi, D. J. Adv. Mater. 2018, 31, 1806133.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v31.10 |
| [51] |
Han, M. G.; Foulger, S. H. Small 2006, 2, 1164.
doi: 10.1002/smll.v2:10 |
| [52] |
Jiang, F. X.; Yue, R. R.; Du, Y. K.; Xu, J. K.; Yang, P. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 44, 127.
doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2013.01.003 |
| [53] |
Yao, Y. Y.; Wen, Y. P.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z. F.; Zhang, H.; Xu, J. K. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 831, 38.
doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2014.04.059 |
| [54] |
Galán, T.; Prieto-Simón, B.; Alvira, M.; Eritja, R.; Götz, G.; Bäuerle, P.; Samitier, J. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 74, 751.
doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2015.07.037 |
| [55] |
Po, R.; Carbonera, C.; Bernardi, A.; Tinti, F.; Camaioni, N. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2012, 100, 97.
doi: 10.1016/j.solmat.2011.12.022 |
| [56] |
Feig, V. R.; Tran, H.; Lee, M.; Bao, Z. N. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5030.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07487-1 |
| [57] |
Zuo, Y. X.; Xu, J. X.; Zhu, X. F.; Duan, X. M.; Lu, L. M.; Gao, Y. S.; Xing, H. K.; Yang, T. T.; Ye, G.; Yu, Y. F. Synth. Met. 2016, 220, 14.
doi: 10.1016/j.synthmet.2016.05.022 |
| [58] |
Gharahcheshmeh, M. H.; Tavakoli, M. M.; Gleason, E. F.; Robinson, M. T.; Kong, J.; Gleason, K. K. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaay0414.
doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aay0414 |
| [59] |
Lu, Y.; Kacica, C.; Bansal, S.; Santino, L. M.; Acharya, S.; Hu, J. Y.; Izima, C.; Chrulski, K.; Diao, Y. F.; Wang, H. M.; Yang, H. R.; Biswas, P.; Schaefer, J.; D’Arcy, J. M. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 47320.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.9b15625 |
| [60] |
Zhang, F.; Johansson, M.; Andersson, M. R.; Hummelen, J. C.; Inganäs, O. Adv. Mater. 2002, 14, 662.
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1521-4095 |
| [61] |
Kim, J. Y.; Jung, J. H.; Lee, D. E.; Joo, J. Synth. Met. 2002, 126, 311.
doi: 10.1016/S0379-6779(01)00576-8 |
| [62] |
Lee, I.; Kim, G.; Yang, M.; Kim, T.-S. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 302.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.5b08753 |
| [63] |
Ouyang, J. Y.; Chu, C.-W.; Chen, F.-C.; Xu, Q.; Yang, Y. J. Macromol. Sci. Part A 2004, 41, 1497.
doi: 10.1081/MA-200035426 |
| [64] |
Ouyang, J.; Chu, C. W.; Chen, F. C.; Xu, Q. F.; Yang, Y. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2005, 15, 203.
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1616-3028 |
| [65] |
Sun, K.; Zhang, S. P.; Li, P. C.; Xia, Y. J.; Zhang, X.; Du, D. H.; Isikgor, F. H.; Ouyang, J. Y. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2015, 26, 4438.
doi: 10.1007/s10854-015-2895-5 |
| [66] |
Ouyang, J. Y.; Xu, Q. F.; Chu, C.-W.; Yang, Y.; Li, G.; Shinar, J. Polymer 2004, 45, 8443.
doi: 10.1016/j.polymer.2004.10.001 |
| [67] |
Sankir, N. D. Circuit World 2008, 34, 32.
|
| [68] |
Fan, X.; Wang, J. Z.; Wang, H. B.; Liu, X.; Wang, H. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 16287.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.5b02830 |
| [69] |
Kim, N.; Kee, S.; Lee, S. H.; Lee, B. H.; Kahng, Y. H.; Jo, Y.-R.; Kim, B.-J.; Lee, K. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 2268.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v26.14 |
| [70] |
Kim, N.; Kang, H.; Lee, J.-H.; Kee, S.; Lee, S. H.; Lee, K. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 2317.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v27.14 |
| [71] |
Fan, X.; Xu, B. G.; Liu, S. H.; Cui, C. H.; Wang, J. Z.; Yan, F. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 14029.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.6b01389 |
| [72] |
Xia, Y. J.; Sun, K.; Ouyang, J. Y. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 2436.
doi: 10.1002/adma.201104795 |
| [73] |
Yeon, C.; Yun, S. J.; Kim, J.; Lim, J. W. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2015, 1, 1500121.
doi: 10.1002/aelm.201500121 |
| [74] |
Bießmann, L.; Saxena, N.; Hohn, N.; Hossain, M. A.; Veinot, J. G. C.; Müller-Buschbaum, P. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2019, 5, 1800654.
doi: 10.1002/aelm.v5.2 |
| [75] |
Li, P. C.; Sun, K.; Ouyang, J. Y. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 18415.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.5b04492 |
| [76] |
Vosgueritchian, M.; Lipomi, D. J.; Bao, Z. N. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 421.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.201101775 |
| [77] |
Lim, J.-E.; Lee, S.-M.; Kim, S.-S.; Kim, T.-W.; Koo, H.-W.; Kim, H.-K. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14685.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-14951-3 |
| [78] |
Mannayil, J.; Raman, S. M.; Sankaran, J.; Raman, R.; Ezhuthachan, J. M. K. Phys. Status Solidi A 2018, 215, 1701003.
|
| [79] |
Kaltenbrunner, M.; White, M. S.; Glowacki, E. D.; Sekitani, T.; Someya, T.; Sariciftci, N. S.; Bauer, S. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 770.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms1772 pmid: 22473014 |
| [80] |
Schausberger, S. E.; Kaltseis, R.; Drack, M.; Cakmak, U.; Major, Z.; Bauer, S. IEEE Access 2015, 3, 556.
doi: 10.1109/Access.6287639 |
| [81] |
Yin, D.; Jiang, N.-R.; Liu, Y. F.; Zhang, X. L.; Li, A. W.; Feng, J.; Sun, H. B. Light Sci. Appl. 2018, 7, 35.
doi: 10.1038/s41377-018-0041-x |
| [82] |
Wang, Y.; Zhu, C. X.; Pfattner, R.; Yan, H. P.; Jin, L. H.; Chen, S. C.; Molina-Lopez, F.; Lissel, F.; Liu, J.; Rabiah, N. I.; Chen, Z.; Chung, J. W.; Linder, C.; Toney, M. F.; Murmann, B.; Bao, Z. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1602076.
doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1602076 |
| [83] |
Noh, J.-S. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 1857.
doi: 10.1039/C3RA46087H |
| [84] |
Hu, X. T.; Meng, X. C.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y. Y.; Cai, Z. R.; Huang, Z. Q.; Su, M.; Wang, Y.; Li, M. Z.; Li, F. Y.; Yao, X.; Wang, F. Y.; Ma, W.; Chen, Y. W.; Song, Y. L. Joule 2019, 3, 1.
doi: 10.1016/j.joule.2018.12.022 |
| [85] |
Kim, W.; Kim, S.; Kang, I.; Jung, M. S.; Kim, S. J.; Kim, J. K.; Cho, S. M.; Kim, J.-H.; Park, J. H. ChemSusChem 2016, 9, 1042.
doi: 10.1002/cssc.201600070 |
| [86] |
Li, J. P.; Qi, S. H.; Liang, J. J.; Li, L.; Xiong, Y.; Hu, W.; Pei, Q. B. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 14140.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.5b03482 |
| [87] |
Oh, J. Y.; Rondeau-Gagné, S.; Chiu, Y.-C.; Chortos, A.; Lissel, F.; Wang, G. -J. N.; Schroeder, B. C.; Kurosawa, T.; Lopez, J.; Katsumata, T.; Xu, J.; Zhu, C. X.; Gu, X. D.; Bae, W.-G.; Kim, Y.; Jin, L. H.; Chung, J. W.; Tok, J. B. H.; Bao, Z. N. Nature 2016, 539, 411.
doi: 10.1038/nature20102 |
| [88] |
Yang, W.; Park, B.; Jung, E.; Jeon, N.; Kim, Y.; Lee, D.; Shin, S.; Seo, J.; Kim, E.; Noh, J.; Seok, S. Science 2017, 356, 1376.
doi: 10.1126/science.aan2301 |
| [89] |
National Renewable Energy Laboratory: Best research-cell efficiency chart, https://www.nrel.gov/pv/assets/images/efficiency-chart.png (2019)
|
| [90] |
Vaagensmith, B.; Reza, K. M.; Hasan, M.; Elbohy, H.; Adhikari, N.; Dubey, A.; Kantack, N.; Gaml, E.; Qiao, Q. Q. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 35861.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.7b10987 |
| [91] |
Sun, K.; Li, P. C.; Xia, Y. J.; Chang, J. J.; Ouyang, J. Y. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 15314.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.5b03171 |
| [92] |
Hanmandlu, C.; Liu, C.-C.; Chen, C.-Y.; Boopathi, K.; Wu, S.-H.; Singh, M.; Mohapatra, A.; Lin, H.-W.; Chang, Y.-C.; Chang, Y.-C.; Lai, C.-S.; Chu, C.-W. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 17973.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.8b04329 |
| [93] |
Du, X. Y.; Lytken, O.; Killian, M.; Cao, J. M.; Stubhan, T.; Turbiez, M.; Schmuki, P.; Steinrück, H.-P.; Ding, L. M.; Fink, R. H.; Li, N.; Brabec, C. J. Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1601959.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.201601959 |
| [94] |
Kim, Y. H.; Cho, H.; Heo, J. H.; Kim, T. S.; Myoung, N. S.; Lee, C. L.; Im, S. H.; Lee, T. W. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 1248.
doi: 10.1002/adma.201403751 |
| [95] |
Chen, P.; Xiong, Z. Y.; Wu, X. Y.; Shao, M.; Meng, Y.; Xiong, Z.-H.; Gao, C. H. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 3961.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.7b01562 |
| [96] |
Kim, D. B.; Yu, J. C.; Nam, Y. S.; Kim, D. W.; Jung, E. D.; Lee, S. Y.; Lee, S.; Park, J. H.; Lee, A.-Y.; Lee, B. R.; Nuzzo, D. D.; Friend, R. H.; Song, M. H. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 8161.
doi: 10.1039/C6TC02099B |
| [97] |
Zuo, C. T.; Ding, L. M. Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1601193.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.201601193 |
| [98] |
Meng, X. C.; Cai, Z. R.; Zhang, Y. Y.; Hu, X. T.; Xing, Z.; Huang, Z. Q.; Huang, Z. D.; Cui, Y. J.; Hu, T.; Su, M.; Liao, X. F.; Zhang, L.; Wang, F. Y.; Song, Y. L.; Chen, Y. W. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3016.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16831-3 |
| [99] |
Song, C.; Zhong, Z. M.; Hu, Z. H.; Wang, J. H.; Wang, L.; Ying, L.; Wang, J.; Cao, Y. Org. Electron. 2016, 28, 252.
doi: 10.1016/j.orgel.2015.10.039 |
| [100] |
Jönsson, S. K. M.; Birgerson, J.; Crispin, X.; Greczynski, G.; Osikowicz, W.; Denier van der Gon, A. W. W.; Salaneck, R.; Fahlman, M. Synth. Met. 2003, 139, 1.
doi: 10.1016/S0379-6779(02)01259-6 |
| [101] |
Wang, J. H.; Song, C.; He, Z. W.; Mai, C. H.; Xie, G. C.; Mu, L.; Cun, Y. K.; Li, J. L.; Wang, J.; Peng, J. B.; Cao, Y. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1804137.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v30.39 |
| [102] |
Na, S. I.; Kim, S. S.; Jo, J.; Kim, D. Y. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 4061.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v20:21 |
| [103] |
Song, W.; Fan, X.; Xu, B. G.; Yan, F.; Cui, H. Q.; Wei, Q.; Peng, R. X.; Hong, L.; Huang, J. M.; Ge, Z. Y. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1800075.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v30.26 |
| [104] |
Liu, Z. K.; Li, J. H.; Yan, F. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 4296.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v25.31 |
| [105] |
Liu, Z. K.; Li, J. H.; Sun, Z.-H.; Tai, G. A.; Lau, S. P.; Yan, F. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 810.
doi: 10.1021/nn204675r |
| [106] |
Yan, T. T.; Song, W.; Huang, J. M.; Peng, R. X.; Huang, L. K.; Ge, Z. Y. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1902210.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v31.39 |
| [107] |
Fan, Z.; Ouyang, J. Y. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2019, 5, 1800769.
doi: 10.1002/aelm.v5.11 |
| [108] |
(a) Zhang, Q.; Sun, Y. M.; Xu, W.; Zhu, D. B. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 6829.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v26.40 |
|
(b) Song, H. J.; Cai, K. F. Energy 2017, 125, 519.
doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2017.01.037 |
|
| [109] |
Bubnova, O.; Crispin, X. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 9345.
doi: 10.1039/c2ee22777k |
| [110] |
Chen, Y. N.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, Z. Q. Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 401.
doi: 10.1039/C4EE03297G |
| [111] |
Yang, J. H.; Yip, H.-L.; Jen, A. K. Y. Adv. Energy Mater. 2013, 3, 549.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.v3.5 |
| [112] |
Wang, X. Z.; Kyaw, A. K. K.; Yin, C. L.; Wang, F.; Zhu, Q.; Tang, T.; Yee, P. I.; Xu, J. W. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 18334.
doi: 10.1039/C8RA02058B |
| [113] |
Lee, S. H.; Park, H.; Kim, S.; Son, W.; Cheong, I. W.; Kim, J. H. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 7288.
doi: 10.1039/C4TA00700J |
| [114] |
Zhang, F. J.; Zang, Y. P.; Huang, D. Z.; Di, C.-A.; Zhu, D. B. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8356.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms9356 |
| [115] |
(a) Chen, D.; Jiang, K.; Huang, T. T.; Shen, G. Z. Adv. Mater. 2019, 32, 1901806.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v32.5 |
|
(b) Liu, Y. Q.; Weng, B.; Razal, J. M.; Xu, Q.; Zhao, C.; Hou, Y. Y.; Seyedin, S.; Jalili, R.; Wallace, G. G.; Chen, J. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17045.
doi: 10.1038/srep17045 |
|
| [116] |
Diao, Y. F.; Lu, Y.; Yang, H. R.; Wang, H. M.; Chen, H. Z.; D’Arcy, J. M. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2003394.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.v30.32 |
| [117] |
Jia, Y. F.; Yuan, Y.; Sun, J.; Dang, L. Q.; Liu, Z. H.; Lei, Z. B. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 12696.
doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c04791 |
| [118] |
Zhang, X. Y.; Wu, S. W.; Deng, S. J.; Wu, W. X.; Zeng, Y. X.; Xia, X. H.; Pan, G. X.; Tong, Y. X.; Lu, X. H. Small Methods 2019, 3, 1900525.
doi: 10.1002/smtd.v3.12 |
| [119] |
Wang, H. M.; Diao, Y. F.; Lu, Y.; Yang, H. R.; Zhou, Q. J.; Chrulski, K.; D’Arcy, J. M. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3882.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-17708-1 |
| [1] | 张冠华, 杨子涵, 马越. 混合工艺对氧化物/硫化物复合固态电解质电化学性能的影响[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(10): 1387-1393. |
| [2] | 王赫男, 张安歌, 张仲, 田洪瑞, 岳倩, 赵雪, 鹿颖, 刘术侠. 基于稀土阳离子和多酸阴离子的系列纯无机离子液体的合成及性质[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(7): 920-924. |
| [3] | 赵伟辰, 徐鑫, 白慧娟, 张劲, 卢善富, 相艳. 自交联聚乙烯亚胺-聚砜高温质子交换膜研究[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(1): 69-75. |
| [4] | 陆霞, 吴仁香, 李波波, 朱云峰, 李李泉. 用于聚合物镍氢电池的新型PVA/SiO2碱性微孔聚合物电解质[J]. 化学学报, 2013, 71(03): 427-432. |
| [5] | 黄先威, 邓继勇, 许律, 沈平, 赵斌, 谭松庭. 聚合物/TiO2杂化纳米纤维微孔膜的制备及其在染料敏化太阳能电池中的应用[J]. 化学学报, 2012, 70(15): 1604-1610. |
| [6] | 肖秋实, 许青青, 李良超, 仇海珍, 陈海峰, 许峰. Zn0.6Mn0.2Ni0.2Fe2O4/聚邻甲基苯胺复合物的制备和电磁性能[J]. 化学学报, 2012, 70(06): 728-734. |
| [7] | 高建生, 徐学诚. 氯掺杂提高多壁碳纳米管的电导率[J]. 化学学报, 2011, 69(12): 1403-1407. |
| [8] | 李良琼, 陈金伟, 鲁惠, 姜春萍, 高山, 杨鑫, 练晓娟, 刘效疆, 王瑞林. 不同磺化度下的磺化聚醚醚酮对全钒储能液流电池性质影响的研究[J]. 化学学报, 2009, 67(24): 2785-2790. |
| [9] | 崔孟忠, 李竹云, 张洁, 冯圣玉. 含硅氢键聚二硅氧烷/聚醚共混聚合物电解质 II. PSEMH对PEO结晶性能及离子电导率的影响[J]. 化学学报, 2009, 67(24): 2851-2856. |
| [10] | 崔孟忠, 李竹云, 张洁, 冯圣玉. 含硅氢键聚二硅氧烷/聚醚共混聚合物电解质 I. 离子电导率研究[J]. 化学学报, 2009, 67(22): 2624-2628. |
| [11] | 庄全超, 魏涛, 魏国祯, 董全峰, 孙世刚. 尖晶石LiMn2O4中锂离子嵌入脱出过程的电化学阻抗谱研究[J]. 化学学报, 2009, 67(19): 2184-2192. |
| [12] | 张玉香, 霍志鹏, 张昌能, 戴松元. 基于偏氟乙烯-六氟丙烯共聚物凝胶电解质的染料敏化太阳电池光电性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2009, 67(19): 2253-2257. |
| [13] | 林晓敏,闫石,朱丽丽,李莉萍,苏文辉. Ce1-xPrxO2-δ (x=0.05~0.30)固溶体的合成及其性质研究[J]. 化学学报, 2009, 67(12): 1389-1394. |
| [14] | 谷威,李志强,朱申敏,张荻. 高能球磨法固相掺杂制备樟脑磺酸掺杂聚苯胺[J]. 化学学报, 2008, 66(9): 1097-1101. |
| [15] | Polymer Electrolytes Based on P(VAc-MMA). P(VAc-MMA)为基体的聚合物电解质研究[J]. 化学学报, 2008, 66(8): 975-979. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||