化学学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 79 ›› Issue (11): 1394-1400.DOI: 10.6023/A21080358 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
投稿日期:2021-08-01
发布日期:2021-09-10
通讯作者:
薛小松
基金资助:
Danqi Zhang, Yingbo Shao, Hanliang Zheng, Biying Zhou, Xiao-Song Xue( )
)
Received:2021-08-01
Published:2021-09-10
Contact:
Xiao-Song Xue
Supported by:文章分享
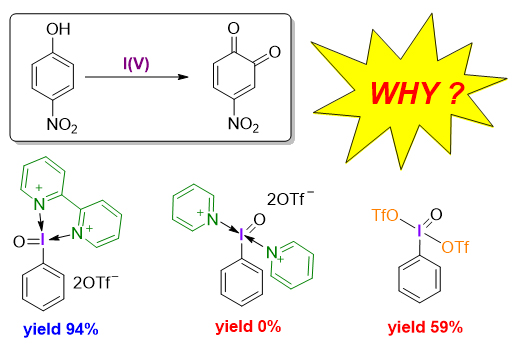
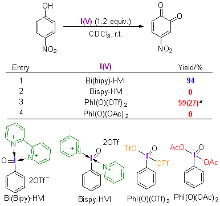
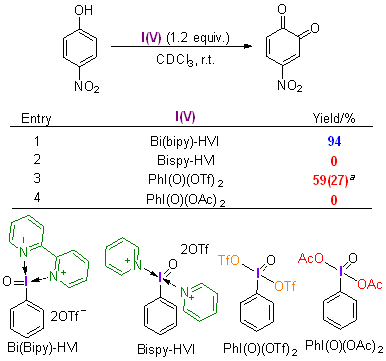
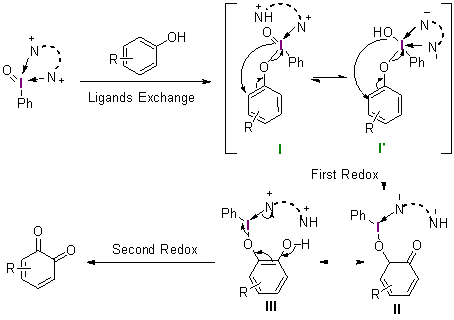
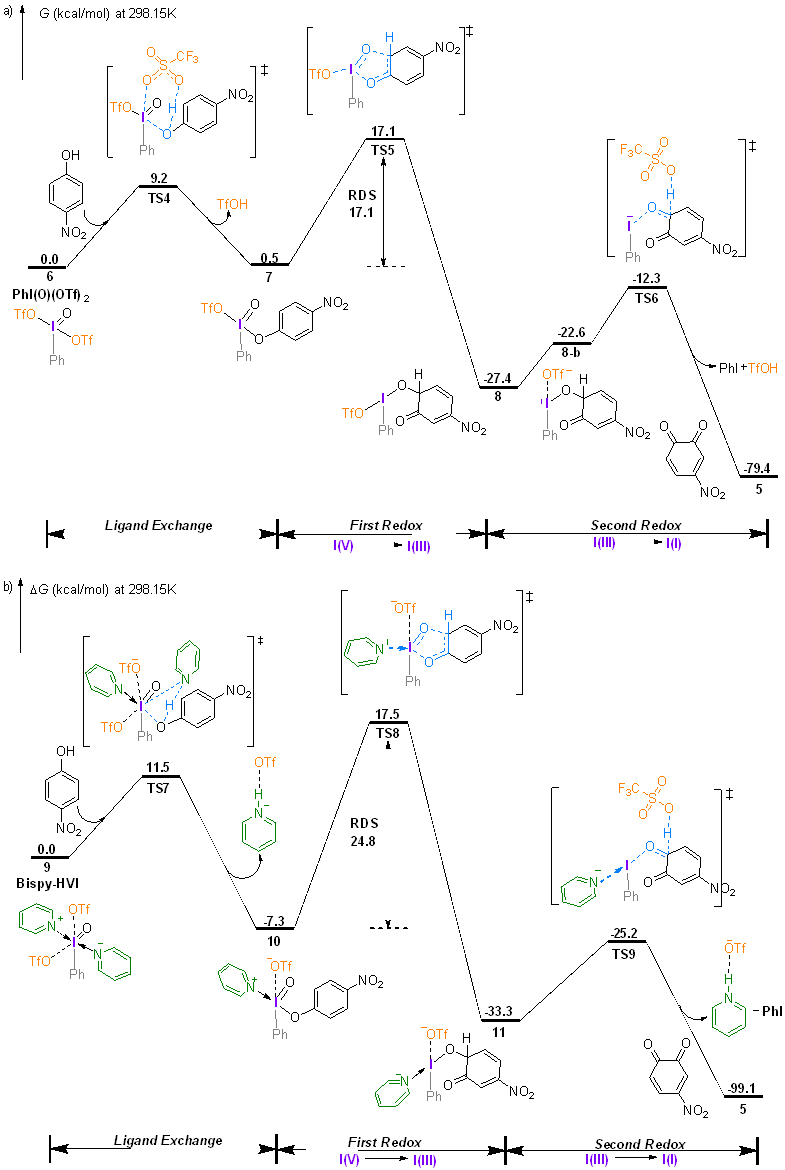
采用密度泛函理论方法研究了不同配体螯合五价碘试剂介导的苯酚氧化去芳构化反应机理以及配体对试剂活性的影响机制. 揭示了双齿氮配体具有双重作用: 一方面通过配位螯合作用增强五价碘试剂2-碘酰苯甲酸(2-iodoxybenzoic acid, IBX)的反应活性, 另一方面作为碱捕获反应中生成的强酸, 避免强酸与邻醌产物发生进一步反应, 从而提高反应的总收率. 研究结果将增加和深化对配体调控高价碘试剂反应性的认识和理解, 为理性设计与开发新配体和反应提供理论依据.
张丹琪, 邵英博, 郑汉良, 周碧莹, 薛小松. 双齿氮配体螯合五价碘试剂介导的苯酚氧化去芳构化机理的理论研究[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(11): 1394-1400.
Danqi Zhang, Yingbo Shao, Hanliang Zheng, Biying Zhou, Xiao-Song Xue. Mechanistic Study on the Bidentate Nitrogen-Ligated Iodine(V) Reagent Promoted Oxidative Dearomatization of Phenols[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(11): 1394-1400.

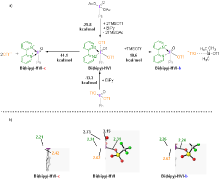
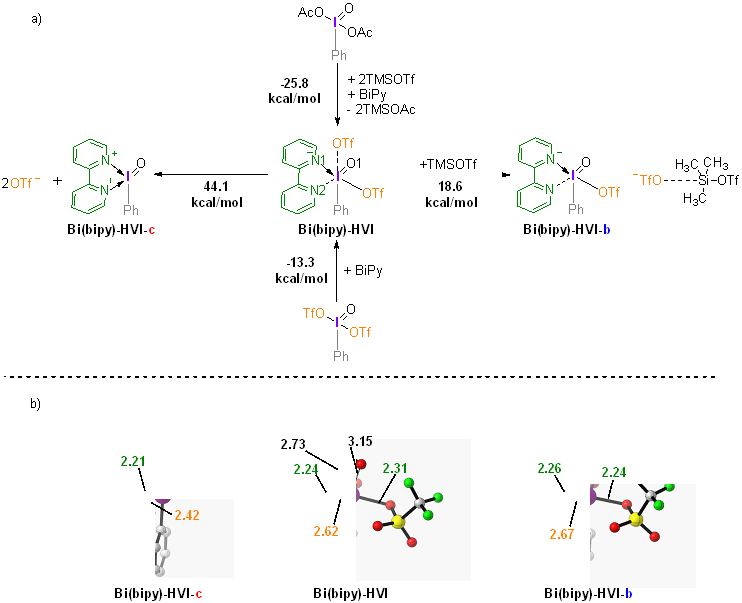
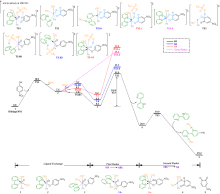

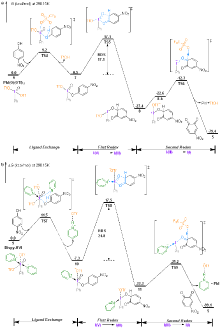
| [1] |
(a) Zhdankin V. V. Hypervalent Iodine Chemistry: Preparation, Structure, and Synthetic Applications of Polyvalent Iodine Compounds, Wiley, New York, 2013.
pmid: 26861673 |
|
(b) Chen J.; Qu H.; Peng J.; Chen C. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 35, 937. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201501004 pmid: 26861673 |
|
|
( 陈静, 曲红梅, 彭静, 陈超, 有机化学, 2015, 35, 937.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201501004 pmid: 26861673 |
|
|
(c) Duan Y.; Jiang S.; Han Y.; Sun B.; Zhang C. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 36, 1973. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201605007 pmid: 26861673 |
|
|
( 段亚南, 姜山, 韩永超, 孙博, 张弛, 有机化学, 2016, 36, 1973.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201605007 pmid: 26861673 |
|
|
(d) Yoshimura A.; Zhdankin V. V. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 3328.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00547 pmid: 26861673 |
|
|
(e) Zhang X.; Cong Y.; Lin G.; Guo X.; Cao Y.; Lei K.; Du Y. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 36, 2513. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201605034 pmid: 26861673 |
|
|
( 张翔, 丛颖, 林光宇, 郭旭亮, 曹阳, 雷坤华, 杜云飞, 有机化学, 2016, 36, 2513.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201605034 pmid: 26861673 |
|
|
(f) Ma J.; Chen L.; Yuan Z.; Cheng H. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 38, 1586. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201802021 pmid: 26861673 |
|
|
( 马姣丽, 陈立成, 袁中文, 程辉成, 有机化学, 2018, 38, 1586.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201802021 pmid: 26861673 |
|
|
(g) Parra A. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 12033.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.9b00338 pmid: 26861673 |
|
|
(h) Cai Q.; Ma H. Acta Chim. Sinica 2019, 77, 213. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A18110470 pmid: 26861673 |
|
|
( 蔡倩, 马浩文, 化学学报, 2019, 77, 213.)
doi: 10.6023/A18110470 pmid: 26861673 |
|
|
(i) Zhang B.; Li X.; Guo B.; Du Y. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 14119.
doi: 10.1039/D0CC05354F pmid: 26861673 |
|
|
(j) Yang X.; Hu Z.; Jia M.; Du F.; Zhang C. Synlett 2021, 32, 1289.
doi: 10.1055/a-1492-4943 pmid: 26861673 |
|
| [2] |
(a) Qin K.; Su G.; Rao W.; Tan G. M. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 26, 1623. (in Chinese)
|
|
( 覃开云, 苏桂发, 饶万平, 谭光明, 有机化学, 2006, 26, 1623.)
|
|
|
(b) Satam V.; Harad A.; Rajule R.; Pati H. Tetrahedron 2010, 66, 7659.
doi: 10.1016/j.tet.2010.07.014 |
|
|
(c) Duschek A.; Kirsch S. F. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 1524.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201000873 |
|
|
(d) Zhang S.; Wu H.; Tang Y. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 41, 490. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202007030 |
|
|
( 张书瑜, 吴昊天, 汤峨, 有机化学, 2021, 41, 490.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202007030 |
|
| [3] |
(a) Pierpont C. G. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2001, 216, 99.
|
|
(b) Kharisov B. I.; Méndez-Rojas M. A.; Garnovskii A. D.; Ivakhnenko E. P.; Ortiz-Méndez U. J. Coord. Chem. 2002, 55, 745.
doi: 10.1080/0095897022000001511 |
|
|
(c) Sun L.; Campbell M. G.; Dinca M. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 3566.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201506219 |
|
|
(d) Sato S.; Sakata K.; Hashimoto Y.; Takikawa H.; Suzuki K. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 12608.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v56.41 |
|
|
(e) Esguerra K. V. N.; Lumb J.-P. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 1514.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v57.6 |
|
|
(f) Zhang R.; Luo S. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2018, 29, 1193.
doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2018.02.009 |
|
| [4] |
(a) Magdziak D.; Rodriguez A. A.; Van De Water R. W.; Pettus T. R. Org. Lett. 2002, 4, 285.
pmid: 29236486 |
|
(b) Lebrasseur N.; Gagnepain J.; Ozanne-Beaudenon A.; Léger J. M.; Quideau S. J. Org. Chem. 2007, 72, 6280.
pmid: 29236486 |
|
|
(c) Wu A.; Duan Y.; Xu D.; Penning T. M.; Harvey R. G. Tetrahedron 2010, 66, 2111.
doi: 10.1016/j.tet.2009.12.022 pmid: 29236486 |
|
|
(d) Uyanik M., Mutsuga T., Ishihara K. Molecules 2012, 17, 8604.
doi: 10.3390/molecules17078604 pmid: 29236486 |
|
|
(e) Usui K.; Yamamoto K.; Shimizu T.; Okazumi M.; Mei B.; Demizu Y.; Kurihara M.; Suemune H. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 80, 6502.
doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.5b00759 pmid: 29236486 |
|
|
(f) Mishra A. K.; Moorthy J. N. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 81, 6472.
doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.6b01105 pmid: 29236486 |
|
|
(g) Uyanik M.; Mutsuga T.; Ishihara K. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 3956.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201612463 pmid: 29236486 |
|
|
(h) Pulvirenti L.; Muccilli V.; Cardullo N.; Spatafora C.; Tringali C. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 1648.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.7b00250 pmid: 29236486 |
|
|
(i) Bizzarri B. M.; Botta L.; Capecchi E.; Celestino I.; Checconi P.; Palamara A. T.; Nencioni L.; Saladino R. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 3247.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.7b00665 pmid: 29236486 |
|
|
(j) Stack D. E.; Mahmud B. Synth. Commun. 2018, 48, 161.
doi: 10.1080/00397911.2017.1390586 pmid: 29236486 |
|
| [5] |
(a) Xiao X.; Greenwood N. S.; Wengryniuk S. E. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2019, 131, 16327.
doi: 10.1002/ange.v131.45 |
|
(b) Xiao X.; Roth J. M.; Greenwood N. S.; Velopolcek M. K.; Aguirre J.; Jalali M.; Ariafard A.; Wengryniuk S. E. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 86, 6566.
doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.1c00375 |
|
| [6] |
(a) Weiss R.; Seubert J. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1994, 33, 891.
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1521-3773 |
|
(b) Zhdankin V. V.; Koposov A. Y.; Yashin N. V. Tetrahedron Lett. 2002, 43, 5735.
doi: 10.1016/S0040-4039(02)01192-9 |
|
| [7] |
(a) Zhou B.; Yan T.; Xue, X. S.; Cheng, J. P. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 6128.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.6b03134 |
|
(b) Yan T.; Zhou, B.; Xue, X. S.; Cheng, J. P. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 81, 9006.
doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.6b01642 |
|
|
(c) Zhou B.; Xue X. S.; Cheng J. P. Tetrahedron Lett. 2017, 58, 1287.
doi: 10.1016/j.tetlet.2017.02.040 |
|
|
(d) Zhou B.; Haj M. K.; Jacobsen E. N.; Houk K. N.; Xue X. S. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 15206.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.8b05935 |
|
|
(e) Zheng H.; Sang Y.; Houk K. N.; Xue X. S.; Cheng J. P. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 16046.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b08243 |
|
|
(f) Yang J.; Li M.; Xue X. S. Chin. J. Chem. 2019, 37, 359.
doi: 10.1002/cjoc.v37.4 |
|
|
(g) Zheng H.; Xue X. S. Curr. Org. Chem. 2020, 4, 1.
|
|
| [8] |
Frisch M. J.; Trucks G. W.; Schlegel H. B.; Scuseria G. E.; Robb M. A.; Cheeseman J. R.; Scalmani G.; Barone V.; Petersson G. A.; Nakatsuji H.; Li X.; Caricato M.; Marenich A. V.; Bloino J.; Janesko B. G.; Gomperts R.; Mennucci B.; Hratchian H. P.; Ortiz J. V.; Izmaylov A. F.; Sonnenberg J. L.; Williams-Young D.; Ding F.; Lipparini F. Egidi F.; Goings J.; Peng B.; Petrone A.; Henderson T.; Ranasinghe D.; Zakrzewski V. G.; Gao J.; Rega N.; Zheng G.; Liang W.; Hada M.; Ehara M.; Toyota K.; Fukuda R.; Hasegawa J.; Ishida M.; Nakajima T.; Honda Y.; Kitao O.; Nakai H.; Vreven T.; Throssell K.; Montgomery Jr., J. A.; Peralta J. E.; Ogliaro F.; Bearpark M. J.; Heyd J. J.; Brothers E. N.; Kudin K. N.; Staroverov V. N.; Keith T. A.; Kobayashi R.; Normand J.; Raghavachari K.; Rendell A. P.; Burant J. C.; Iyengar S. S.; Tomasi J.; Cossi M.; Millam J. M.; Klene M.; Adamo C.; Cammi R.; Ochterski J. W.; Martin R. L.; Morokuma K.; Farkas O.; Foresman J. B.; Fox D. J. Gaussian 16, Revision A.03, Gaussian, Inc., Wallingford CT, 2016.
|
| [9] |
Marenich A. V.; Cramer C. J.; Truhlar D. G. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 6378.
doi: 10.1021/jp810292n |
| [10] |
Zhao Y.; Truhlar D. G. Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 157.
doi: 10.1021/ar700111a |
| [11] |
Hay P. J.; Wadt W. R. J. Chem. Phys. 1985, 82, 299.
doi: 10.1063/1.448975 |
| [12] |
(a) Weigend F.; Furche F.; Ahlrichs R. J. Chem. Phys. 2003, 119, 12753.
doi: 10.1063/1.1627293 |
|
(b) Weigend F.; Ahlrichs R. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2005, 7, 3297.
doi: 10.1039/b508541a |
|
|
(c) Jiang H.; Sun T. Y.; Wang X.; Xie Y.; Zhang X.; Wu Y. D.; Schaefer III H. F. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 6502.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.7b03167 |
|
|
(d) Sun T.; Chen K.; Zhou H.; You T.; Yin P.; Wang X. J. Comput. Chem. 2021, 42, 470.
doi: 10.1002/jcc.v42.7 |
|
| [13] |
Legault C. Y. CYLview, 1.0b, Université de Sherbrooke, 2009;
|
| [14] |
The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, Version 2.0.4, Schrödinger, LLC.
|
| [15] |
Kaur A.; Ariafard A. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2020, 18, 1117.
doi: 10.1039/C9OB02650A |
| [16] |
(a) Feldman K. S.; Sambandam A.; Bowers K. E.; Appel H. M. J. Org. Chem. 1999, 64, 5794.
doi: 10.1021/jo982477n pmid: 17226982 |
|
(b) Mitchell J. S.; Wu Y.; Cook C. J.; Main L. Bioconjugate Chem. 2007, 18, 268.
pmid: 17226982 |
|
| [17] |
在审稿期间,Ariafard等人在有机化学杂志发表了相关反应的机理研究工作, 该工作得到了与我们工作相似的结论: Jalali M.; Bissember A. C.; Yates B. F..; Wengryniuk S. E.; Ariafard A. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 86, 12237.
|
| [1] | 王娟, 肖华敏, 谢丁, 郭元茹, 潘清江. 铜掺杂与氮化碳复合氧化锌材料结构和二氧化氮气体传感性质的密度泛函理论计算[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(11): 1493-1499. |
| [2] | 薄一凡, 刘玉玉, 常永正, 李银祥, 张效霏, 宋春元, 许卫锋, 曹洪涛, 黄维. 环状芴基张力半导体拉曼光谱理论与实验研究[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(5): 442-446. |
| [3] | 朱纯, 曹泽星. 高效金属双卟啉染料的计算设计及其敏化TiO2半导体复合体系的理论研究[J]. 化学学报, 2013, 71(11): 1527-1534. |
| [4] | 顾均, 丁祎, 柯俊, 张亚文, 严纯华. 基于软硬酸碱理论的单分散中重稀土硫氧化物纳米板的可控合成[J]. 化学学报, 2013, 71(03): 360-366. |
| [5] | 刘琼, 汪佩, 张干兵. OsO+氧化活化氢分子气相反应机理的密度泛函理论计算[J]. 化学学报, 2012, 70(12): 1337-1346. |
| [6] | 韦永勤, 吴克琛, 林晨升, 莽朝永, 刘萍, 张明昕, 洪涛, 周张锋, 庄伯涛. 非线性光学极化率密度泛函理论计算的基组效应[J]. 化学学报, 2004, 62(6): 578-582. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||