化学学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 80 ›› Issue (4): 494-502.DOI: 10.6023/A21120594 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
位亚茹, 马晶*( ), 袁婷婷, 姜嘉伟, 段银利*(
), 袁婷婷, 姜嘉伟, 段银利*( ), 薛娟琴
), 薛娟琴
投稿日期:2021-12-29
发布日期:2022-04-28
通讯作者:
马晶, 段银利
基金资助:
Yaru Wei, Jing Ma( ), Tingting Yuan, Jiawei Jiang, Yinli Duan(
), Tingting Yuan, Jiawei Jiang, Yinli Duan( ), Juanqin Xue
), Juanqin Xue
Received:2021-12-29
Published:2022-04-28
Contact:
Jing Ma, Yinli Duan
Supported by:文章分享
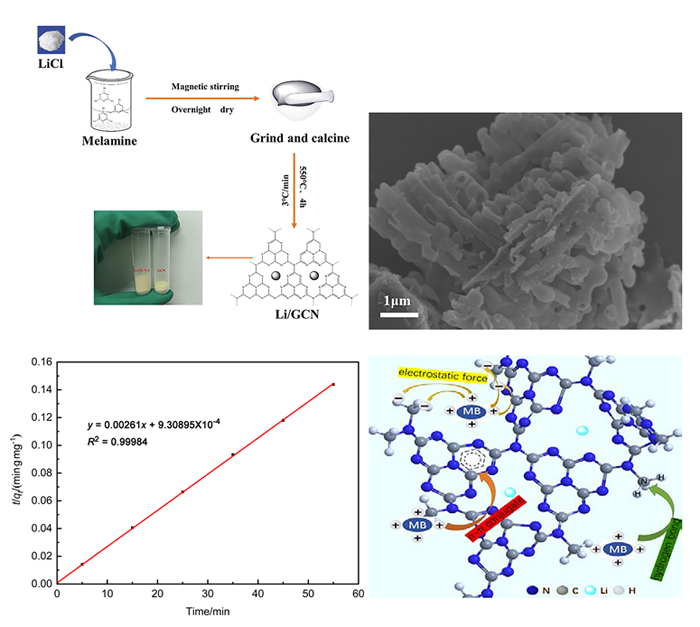
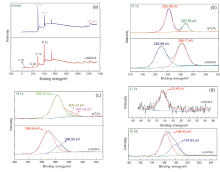
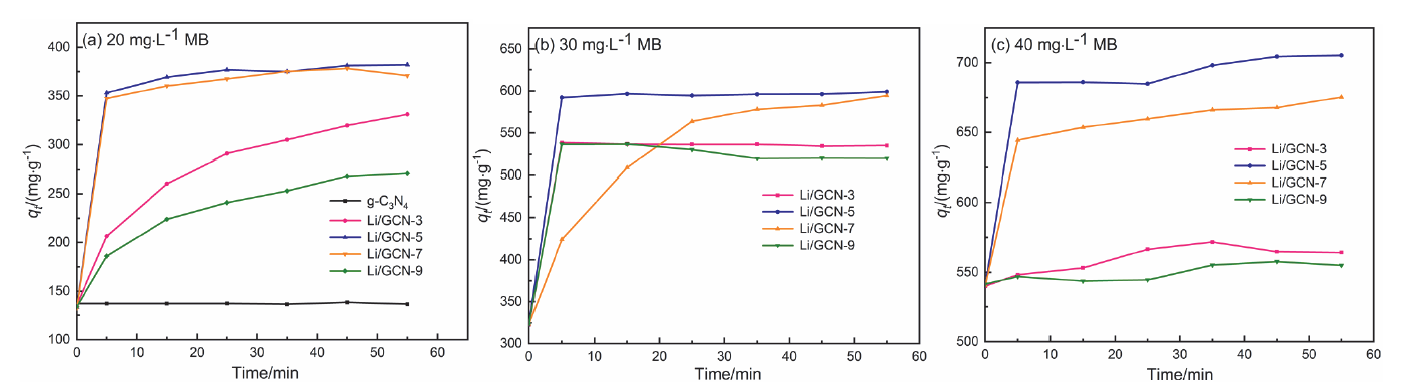
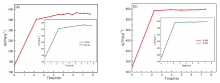
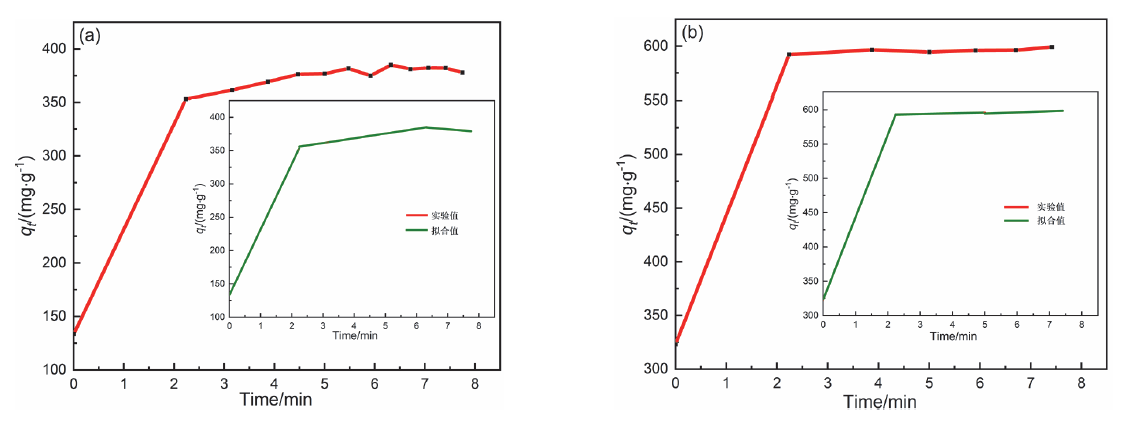
近年来, 有机废水对环境造成的污染已经引起了广泛的关注. 吸附法操作简单, 已经被广泛用于处理染料废水.通过在类石墨相氮化碳(g-C3N4)上用氯化锂(LiCl)插层制备了一系列Li/GCN-x复合材料, 并采用X射线衍射(XRD)、傅里叶变换红外光谱(FT-IR)、N2-吸脱附、场发射扫描电子显微镜(SEM)以及X射线光电子能谱(XPS)等对所得吸附剂的形貌和结构进行了表征. 测试结果表明, g-C3N4具有明显的层状结构, 使得LiCl在层间能够稳定地生长. LiCl的加入使得g-C3N4晶格膨胀, 层间距扩大, 表明LiCl成功插层. 此外, 插层后Li/GCN的比表面积远大于g-C3N4, 扩大的比表面积以及形成的 π 共轭体系使得Li/GCN在吸附方面具有较大的潜力. 通过控制实验条件, 研究了Li/GCN对有机染料亚甲基蓝(MB)的吸附性能. 结果表明, Li/GCN-5吸附剂在pH为6时, 5 min吸附量可达704 mg•g–1. 通过动力学拟合, Li/GCN对MB的吸附过程是由准二级动力学模型占主导地位. 进一步通过Weber-Morris模型探究吸附控制过程, 结果表明MB的吸附由表面扩散和孔内扩散共同作用, 其中表面扩散占主导, 且新增官能团与MB分子间可形成氢键, 并通过π-π键相互作用增强吸附能力. 采用共混热聚合法所制备的Li/GCN吸附剂具有稳定、均一、比表面积大等优点, 且简单快速地实现对MB的吸附, 克服了常用吸附剂动力学缓慢的缺点, 为该材料的工业化应用提供一定的借鉴.
位亚茹, 马晶, 袁婷婷, 姜嘉伟, 段银利, 薛娟琴. 氯化锂插层氮化碳材料的可控制备及吸附性能[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(4): 494-502.
Yaru Wei, Jing Ma, Tingting Yuan, Jiawei Jiang, Yinli Duan, Juanqin Xue. Preparation and Adsorption Properties of Lithium Chloride Intercalation Carbon Nitride[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(4): 494-502.
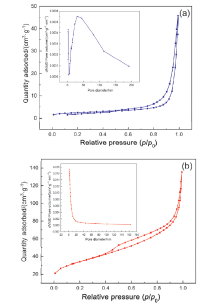
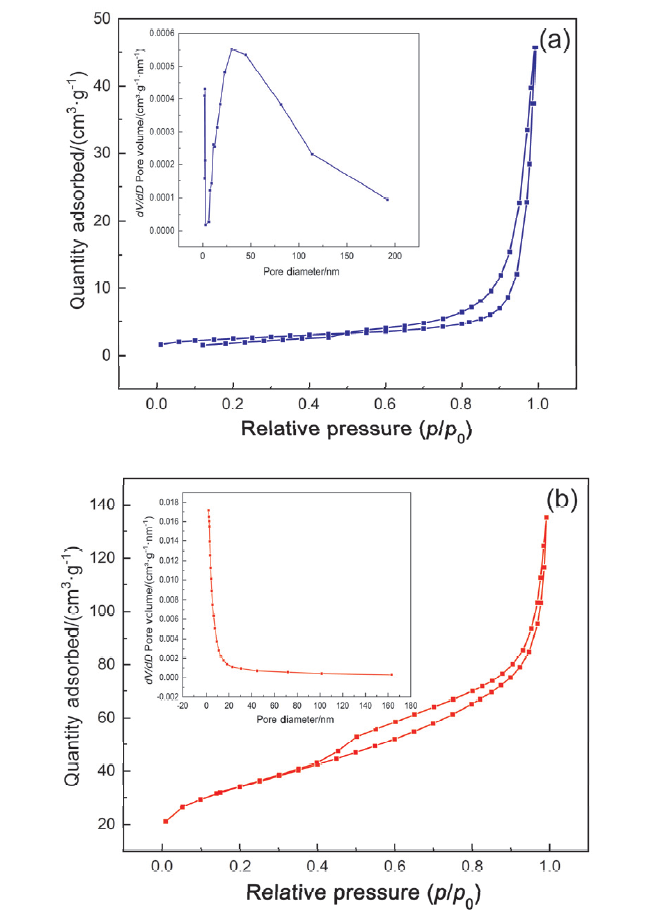
| Sample | Surface area/ (m2•g–1) | Pore volume/ (cm3•g–1) | Pore diameter/ nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| g-C3N4 | 8.30 | 0.07 | 33.52 |
| Li/GCN-5 | 119.3 | 0.21 | 7.02 |
| Sample | Surface area/ (m2•g–1) | Pore volume/ (cm3•g–1) | Pore diameter/ nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| g-C3N4 | 8.30 | 0.07 | 33.52 |
| Li/GCN-5 | 119.3 | 0.21 | 7.02 |

| Adsorbent | Adsorbate | Surface area/(m2•g–1) | qm/(mg•g–1) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li0.5-CN | RhB | 10.1 | — | [ |
| 50-CN | MB | 1.0 | 360 | [ |
| NCG-2 | MB | 432.0 | 348.2 | [ |
| LiCl-CN-4h | Pb(II) | 36.54 | 172.41 | [ |
| g-C3N4 | Pb(II) | 11.0 | 281.79 | [ |
| g-C3N4 | Cd2+ | 52.0 | 94.4 | [ |
| Adsorbent | Adsorbate | Surface area/(m2•g–1) | qm/(mg•g–1) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li0.5-CN | RhB | 10.1 | — | [ |
| 50-CN | MB | 1.0 | 360 | [ |
| NCG-2 | MB | 432.0 | 348.2 | [ |
| LiCl-CN-4h | Pb(II) | 36.54 | 172.41 | [ |
| g-C3N4 | Pb(II) | 11.0 | 281.79 | [ |
| g-C3N4 | Cd2+ | 52.0 | 94.4 | [ |
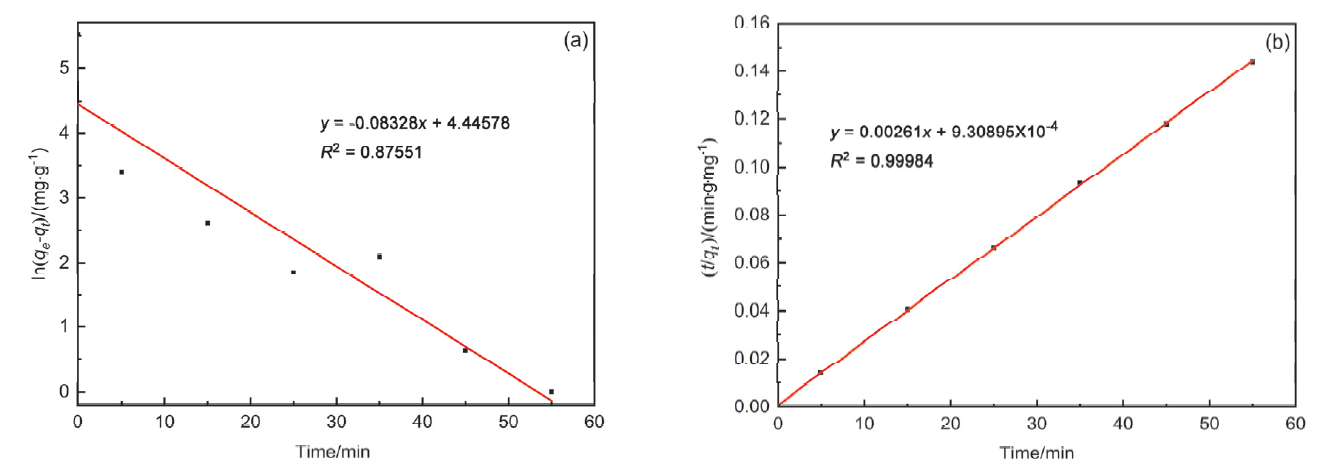
| MB/(mg•L–1) | 准一级动力学 | 准二级动力学 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1/(min–1) | qe/(mg•g–1) | R2 | k2/(g•mg–1•min–1) | qe/(mg•g–1) | R2 | ||
| 20 | 0.08328 | 85.26 | 0.87551 | 0.00732 | 383.14 | 0.99984 | |
| 30 | 0.06911 | 30.28 | 0.56804 | 0.00351 | 598.80 | 0.99999 | |
| 40 | 0.15555 | 169.02 | 0.79305 | 0.00526 | 704.23 | 0.99983 | |
| MB/(mg•L–1) | 准一级动力学 | 准二级动力学 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1/(min–1) | qe/(mg•g–1) | R2 | k2/(g•mg–1•min–1) | qe/(mg•g–1) | R2 | ||
| 20 | 0.08328 | 85.26 | 0.87551 | 0.00732 | 383.14 | 0.99984 | |
| 30 | 0.06911 | 30.28 | 0.56804 | 0.00351 | 598.80 | 0.99999 | |
| 40 | 0.15555 | 169.02 | 0.79305 | 0.00526 | 704.23 | 0.99983 | |
| [1] |
Kumar, Y.; Rani, S.; Shabir, J.; Kumar, L. S. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 13250.
doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c01280 |
| [2] |
Cheng, N.; Tian, J.; Liu, Q.; Ge, C.; Qusti, A. H.; Asiri, A. M.; Al-Youbi, A. O.; Sun, X. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2013, 5, 6815.
doi: 10.1021/am401802r |
| [3] |
Cai, X.; He, J.; Chen, L.; Chen, K.; Li, Y.; Zhang, K.; Jin, Z.; Liu, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Kong, L.; Liu, J. Chemosphere 2017, 171, 192.
doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.12.073 |
| [4] |
Oyewo, O. A.; Adeniyi, A.; Sithole, B. B.; Onyango, M. S. ACS Omega. 2020, 5, 18798.
doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c01924 |
| [5] |
Liu, Q.; Li, Y.; Chen, H.; Lu, J.; Yu, G.; Moslang, M.; Zhou, Y. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 382, 121040.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121040 |
| [6] |
Shen, C.; Chen, C.; Wen, T.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, X.; Xu, A. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2015, 456, 7.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2015.06.004 |
| [7] |
Xiong, Y.; Zhang, C.; Duan, M.; Chen, J.; Fang, S.; Li, J.; Shi, P.; Ren, J.; Wan, H. Langmuir 2021, 37, 7655.
doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.1c00360 pmid: 34129343 |
| [8] |
Li, J.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Luo, H.; Ma, Y.; Xu, X.; Lu, Y.; Lin, J.; Zou, J.; Tang, C. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 8185.
doi: 10.1039/C5TA00601E |
| [9] |
Wang, D.; Shen, H.; Guo, L.; Wang, C.; Fu, F. ACS Omega. 2016, 1, 566.
doi: 10.1021/acsomega.6b00160 |
| [10] |
He, X.; Male, K. B.; Nesterenko, P. N.; Brabazon, D.; Paull, B.; Luong, J. H. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 8796.
doi: 10.1021/am403222u |
| [11] |
Qiu, C.; Xu, Y.; Fan, X.; Xu, D.; Tandiana, R.; Ling, X.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, C.; Yu, L.; Chen, W.; Su, C. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1801403.
doi: 10.1002/advs.201801403 |
| [12] |
Alam, K. M.; Kumar, P.; Kar, P.; Goswami, A.; Thakur, U. K.; Zeng, S.; Vahidzadeh, E.; Cui, K.; Shankar, K. Nanotechnology 2019, 31, 084001.
doi: 10.1088/1361-6528/ab4e2c |
| [13] |
Zhang, Z.; Ge, C.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Q.; Yang, L.; Wang, X.; Hu, Z. Acta Chim. Sinica 2019, 77, 60. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A18080323 |
|
(张志琦, 葛承宣, 陈玉刚, 吴强, 杨立军, 王喜章, 胡征, 化学学报, 2019, 77, 60.)
doi: 10.6023/A18080323 |
|
| [14] |
Chai, B.; Yan, J.; Fan, G.; Song, G.; Wang, C. Chin. J. Catal. 2020, 41, 190. (in Chinese)
|
|
(柴波, 闫俊涛, 范国枝, 宋光森, 王春蕾, 催化学报, 2020, 41, 190.)
|
|
| [15] |
Meng, Q.; Lv, H.; Yuan, M.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Z.; Wang, X. ACS Omega. 2017, 2, 2728.
doi: 10.1021/acsomega.7b00338 |
| [16] |
Tian, W.; Shen, Q.; Li, N.; Zhou, J. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 25568.
doi: 10.1039/C6RA01429A |
| [17] |
Zhou, Y.; Liao, C.; Fan, Y.; Ma, S.; Su, M.; Zhou, Z.; Chan, T.-S.; Lu, Y.-R.; Shih, K. Environ. Sci. Nano 2019, 6, 3324.
doi: 10.1039/C9EN00817A |
| [18] |
Liao, G.; Gong, Y.; Zhang, L.; Gao, H.; Yang, G.-J.; Fang, B. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 2080.
doi: 10.1039/C9EE00717B |
| [19] |
He, L.; Tang, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Xiang, G.; Zhou, X.; Ling, F.; Yao, L.; Jaing, H. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 506. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A20120575 |
|
(何利蓉, 唐笑, 张灵, 李艳虹, 相国涛, 周贤菊, 凌发令, 姚璐, 蒋浩, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 506.)
doi: 10.6023/A20120575 |
|
| [20] |
Song, S.; Lu, C.; Wu, X.; Jiang, S.; Sun, C.; Le, Z. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2018, 227, 145.
doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.01.014 |
| [21] |
Gao, X.; Feng, J.; Su, D.; Ma, Y.; Wang, G.; Ma, H.; Zhang, J. Nano Energy 2019, 59, 598.
doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2019.03.016 |
| [22] |
Gao, H.; Yan, S.; Wang, J.; Huang, Y. A.; Wang, P.; Li, Z.; Zou, Z. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 18077.
doi: 10.1039/c3cp53774a |
| [23] |
Yan, J.; Wu, H.; Chen, H.; Pang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, R.; Li, L.; Liu, S. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2016, 194, 74.
doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.04.048 |
| [24] |
Cui, W.; Li, J.; Cen, W.; Sun, Y.; Lee, S. C.; Dong, F. J. Catal. 2017, 352, 351.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2017.05.017 |
| [25] |
Rajapakse, M.; Karki, B.; Abu, U. O.; Pishgar, S.; Musa, M. R. K.; Riyadh, S. M. S.; Yu, M.; Sumanasekera, G.; Jasinski, J. B. Npj. 2D Mater. Appl. 2021, 5, 1.
doi: 10.1038/s41699-020-00190-0 |
| [26] |
Mashtalir, O.; Naguib, M.; Mochalin, V. N.; Dall'Agnese, Y.; Heon, M.; Barsoum, M. W.; Gogotsi, Y. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1716.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms2664 pmid: 23591883 |
| [27] |
Dong, X.; Cheng, F. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 23642.
doi: 10.1039/C5TA07374J |
| [28] |
Wang, N.; Pang, H.; Yu, S.; Gu, P.; Song, S.; Wang, H.; Wang, X. Acta Chim. Sinica 2019, 77, 143. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A18090404 |
|
(王宁, 庞宏伟, 于淑君, 顾鹏程, 宋爽, 王宏青, 王祥科, 化学学报, 2019, 77, 143.)
doi: 10.6023/A18090404 |
|
| [29] |
Zhu, X.; Liu, B.; Hou, H.; Huang, Z.; Zeinu, K. M.; Huang, L.; Yuan, X.; Guo, D.; Hu, J.; Yang, J. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 248, 46.
doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2017.07.084 |
| [30] |
Cui, W.; Chen, P.; Chen, L.; Li, J.; Zhou, Y.; Dong, F. J. Phys. Energy 2021, 3, 032008.
doi: 10.1088/2515-7655/abda9b |
| [31] |
Zeng, Z.; Quan, X.; Yu, H.; Chen, S.; Choi, W.; Kim, B.; Zhang, S. J. Catal. 2019, 377, 72.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2019.07.018 |
| [32] |
Wang, S.; Zhan, J.; Chen, K.; Ali, A.; Zeng, L.; Zhao, H.; Hu, W.; Zhu, L.; Xu, X. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 8214.
doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c01151 |
| [33] |
Li, J.; Cui, W.; Sun, Y.; Chu, Y.; Cen, W.; Dong, F. J. Mater. Chem. A. 2017, 5, 9358.
doi: 10.1039/C7TA02183F |
| [34] |
Xiong, T.; Cen, W.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, F. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 2462.
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.5b02922 |
| [35] |
Huang, Y.; Su, M.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, D.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Liao, C. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 26492.
doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.07.078 |
| [36] |
Mao, N. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12383.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-48730-z pmid: 31455882 |
| [37] |
Ma, L.; Fan, H.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Tian, H.; Dong, G. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2016, 190, 93.
doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.03.002 |
| [38] |
Xie, Q.; He, W.; Liu, S.; Li, C.; Zhang, J.; Wang, B. Chin. J. Catal. 2020, 41, 153. (in Chinese)
|
|
(谢权, 何婉楣, 刘升卫, 李传浩, 张金锋, 王保强, 催化学报, 2020, 41, 153.)
|
|
| [39] |
Wang, M.; Jin, C.; Li, Z.; You, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, T. J. Colloid. Interf. Sci. 2019, 533, 513.
doi: S0021-9797(18)31036-1 pmid: 30179830 |
| [40] |
Jin, A.; Jia, Y.; Chen, C.; Liu, X.; Jiang, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, F. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 21497.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.7b07243 |
| [41] |
Liu, H.; Chen, D.; Wang, Z.; Jing, H.; Zhang, R. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2017, 203, 300.
doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.10.014 |
| [42] |
Zhu, A.; Qiao, L.; Tan, P.; Pan, J. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2020, 7, 4754.
doi: 10.1039/D0QI01026J |
| [43] |
Liu, W.; Peng, R.; Ye, X.; Guo, J.; Luo, L. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 560, 150013.
doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.150013 |
| [44] |
Zhu, Y. -P.; Li, M.; Liu, Y.-L.; Ren, T.-Z.; Yuan, Z.-Y. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 10963.
doi: 10.1021/jp502677h |
| [45] |
Ma, L.; Fan, H.; Li, M.; Tian, H.; Fang, J.; Dong, G. J. Phys. Chem. A 2015, 3, 22404.
|
| [46] |
Lei, L.; Wang, W.; Wang, C.; Zhang, M.; Zhong, Q.; Fan, H. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 1258.
doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.08.246 |
| [47] |
Fronczak, M.; Demby, K.; Strachowski, P.; Strawski, M.; Bystrzejewski, M. Langmuir 2018, 34, 7272.
doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.8b01041 pmid: 29856628 |
| [48] |
Ren, B.; Miao, J.; Wang, S.; Xu, Y.; Zhai, Z.; Dong, X.; Liu, Z. Adv. Powder Technol. 2021, 32, 1774.
doi: 10.1016/j.apt.2021.03.035 |
| [49] |
Liu, W.; Peng, R.; Luo, L.; Li, C.; Ye, X. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2022, 138.
|
| [50] |
Meng, S.; Wang, M.; Lv, B.; Xue, Q.; Yang, Z. Acta Chim. Sinica 2019, 77, 1184. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A19070268 |
|
(孟双艳, 王明明, 吕柏霖, 薛群基, 杨志旺, 化学学报, 2019, 77, 1184.)
doi: 10.6023/A19070268 |
|
| [51] |
Zhang, G.; Zhang, M.; Ye, X.; Qiu, X.; Lin, S.; Wang, X. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 805.
doi: 10.1002/adma.201303611 |
| [52] |
Hong, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Li, C.; Fan, W.; Yan, X.; Yan, M.; Shi, W. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2016, 180, 663.
doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.06.057 |
| [53] |
Wang, R.; Zou, Y.; Hong, S.; Xu, M.; Ling, L. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 932. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A21030118 |
|
(王瑞兆, 邹云杰, 洪晟, 徐铭楷, 凌岚, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 932.)
doi: 10.6023/A21030118 |
|
| [54] |
Xiong, T.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, Y.; Cen, W.; Huang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, F. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 8066.
doi: 10.1039/c8nr01433g pmid: 29671458 |
| [55] |
Li, D.; Li, B.; Li, C.; Yu, X.; Chan, Y.; Chen, K. Chem. J. Chin. Univ. 2021, 42, 1292. (in Chinese)
|
|
(李冬平, 李彬, 李长恒, 于薛刚, 单妍, 陈克正, 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42, 1292.)
|
|
| [56] |
Islam, M. M.; Tentu, R. D.; Ali, M. A.; Basu, S. ChemistrySelect 2018, 3, 11241.
doi: 10.1002/slct.201802650 |
| [57] |
Geng, A.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.; Bi, H.; Zhu, J. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 2020, 31, 3869.
doi: 10.1007/s10854-020-02932-8 |
| [58] |
Fronczak, M.; Krajewska, M.; Demby, K.; Bystrzejewski, M. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 15756.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.7b03674 |
| [59] |
Ma, C.; Wu, J.; Zhu, L.; Han, X.; Ruan, W.; Song, W.; Wang, X.; Zhao, B. Acta Chim. Sinica 2019, 77, 1024. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A19050191 |
|
(马超, 武佳炜, 朱琳, 韩晓霞, 阮伟东, 宋薇, 王旭, 赵冰, 化学学报, 2019, 77, 1024.)
doi: 10.6023/A19050191 |
|
| [60] |
Feng, M.; You, W.; Wu, Z.; Chen, Q.; Zhan, H. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 12654.
doi: 10.1021/am404011k |
| [61] |
Zhu, W.; Jiang, K.; You, F.; Yao, C.; Wang, K.; Jiang, X. Acta Mater. Compos. Sin. 2021, 38, 1 (in Chinese)
|
|
(朱薇, 江坤, 游峰, 姚楚, 王昆, 江学良, 复合材料学报, 2021, 38, 1.)
|
|
| [62] |
Xu, J.; Li, S.; Wang, F.; Yang, Z.; Liu, H. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2019, 64, 1816.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jced.9b00022 |
| [1] | 王海朋, 蔡文生, 邵学广. 抗冻剂抗冻机制的近红外光谱与分子模拟研究★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(9): 1167-1174. |
| [2] | 王凯晴, 袁硕, 徐王东, 霍丹, 杨秋林, 侯庆喜, 于得海. ZIF-8@B-CNF复合气凝胶的制备及其吸附性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(6): 604-612. |
| [3] | 杨娜, 马建中, 石佳博, 郭旭. 层状复合氢氧化物的有机改性方法及应用研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(2): 207-216. |
| [4] | 解众舒, 薛中鑫, 许子文, 李倩, 王洪宇, 李维实. 石墨相氮化碳的共轭交联修饰及其对可见光催化产氢性能的影响[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(9): 1231-1237. |
| [5] | 李海茹, 张层, 李思殿. 碱土金属Ben (n=1~3)对B12团簇结构的调控研究[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(7): 888-895. |
| [6] | 王瑞兆, 邹云杰, 洪晟, 徐铭楷, 凌岚. Pt0.01Fe0.05-g-C3N4催化剂高效光热催化二氧化碳还原[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(7): 932-940. |
| [7] | 杜英喆, 张恒, 苑世领. Al2O3/PDMS复合材料热传导的分子动力学模拟[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(6): 787-793. |
| [8] | 何利蓉, 唐笑, 张灵, 李艳虹, 相国涛, 周贤菊, 凌发令, 姚璐, 蒋浩. 液相合成彩色氮化碳及其光电化学特性研究[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(4): 506-512. |
| [9] | 徐婕, 魏雨晨, 伍智蔚, 易忠胜. 基于酸度诱导的HSA与BDE154的光谱和计算模拟研究[J]. 化学学报, 2018, 76(5): 408-414. |
| [10] | 郭宇, 姚远, 李慧, 赫兰兰, 朱尊伟, 杨忠志, 宫利东, 刘翠, 赵东霞. 光合释氧机理的ABEEM/MM/MD和BS-DFT理论研究[J]. 化学学报, 2017, 75(9): 903-913. |
| [11] | 康文斌, 夏耘, 王骏, 王炜. 二氧化硫分子通过增强二次成核促进纤维的生长:基于分子动力学的模拟研究[J]. 化学学报, 2016, 74(8): 694-702. |
| [12] | 张川, 张鲁嘉, 张洋, 黄和, 胡燚. 基于分子模拟的离子液体修饰Porcine Pancreas脂肪酶催化性能和稳定性的相关研究[J]. 化学学报, 2016, 74(1): 74-80. |
| [13] | 刘琴, 刘道彬, 何群, 项婷, Adnan Khalil, 宋礼. 基于层状过渡金属氧族化合物原位插层结构的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2015, 73(9): 936-943. |
| [14] | 孙婷, 刘强, 肖继军, 赵峰, 肖鹤鸣. CL-20/HMX共晶及其为基PBX界面作用和力学性能的MD模拟研究[J]. 化学学报, 2014, 72(9): 1036-1042. |
| [15] | 冯石磊, 胡墅, 刘兵, 刘伟. 抗原肽与MHC分子相互作用QM/MM分子动力学模拟研究[J]. 化学学报, 2013, 71(9): 1313-1320. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||