化学学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 80 ›› Issue (8): 1091-1099.DOI: 10.6023/A22010041 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
王怡戈a,b, 李航越a,b, 吕泽伟a,b, 韩敏芳a,b,*( ), 孙凯华c
), 孙凯华c
投稿日期:2022-01-22
发布日期:2022-09-01
通讯作者:
韩敏芳
基金资助:
Yige Wanga,b, Hangyue Lia,b, Zewei Lyua,b, Minfang Hana,b( ), Kaihua Sunc
), Kaihua Sunc
Received:2022-01-22
Published:2022-09-01
Contact:
Minfang Han
Supported by:文章分享
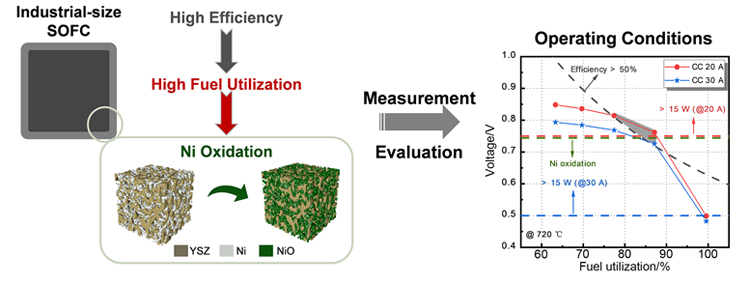
固体氧化物燃料电池(Solid Oxide Fuel Cell, SOFC)是一种清洁高效的能源转化装置, 如何提高SOFC的发电效率, 并保证阳极不发生局部氧化, 是工业界与学术界的焦点问题之一. 建立了工业尺寸SOFC的效率测试与评价方法, 通过对比多组高燃料利用率下的电池效率测试结果, 发现在相同燃料利用率下, 电压会随电流的增大而下降. 因此, 较低的电流有利于达到更高的效率, 较大的电流则有利于输出更高的功率. 此外, 研究了高燃料利用率下放电时电压波动与阳极局部氧化的关联, 通过分析阳极Ni的临界氧化条件, 提出了避免发生阳极局部氧化的电池安全运行条件: 电池的输出电压应高于Ni的临界氧化电动势. 基于所采用的电池和测试参数, 发现在各个电流及温度下, SOFC发电效率大于50%时, 对应的燃料利用率一般在77%~90%这一区间内, 当燃料利用率为87.10%时, 电池具有最大的发电效率. 尽管对于不同材料、结构和制备工艺的SOFC, 其最高效率所对应的工况会有所差异, 但所提出的效率测试及评价方法和阳极安全运行的判断条件具有一定的普适性, 可以根据实际需求中高功率、高效率及长期稳定运行的重要程度, 确定相应的高效及阳极安全运行条件.
王怡戈, 李航越, 吕泽伟, 韩敏芳, 孙凯华. 工业尺寸固体氧化物燃料电池高效及阳极安全运行条件研究[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(8): 1091-1099.
Yige Wang, Hangyue Li, Zewei Lyu, Minfang Han, Kaihua Sun. Study of Operating Conditions for High Efficiency and Anode Safety of Industrial-Size Solid Oxide Fuel Cell[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(8): 1091-1099.
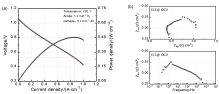

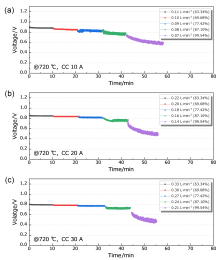


| Current/A | ηele,maxa/% | Ufuelb/% | Fuel flow rate/(L•min–1) | Voltage/V | Power/W |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 53.57 | 87.10 | 0.08 | 0.771 | 7.71 |
| 20 | 52.92 | 87.10 | 0.16 | 0.761 | 15.23 |
| 30 | 50.47 | 87.10 | 0.24 | 0.726 | 21.78 |
| Current/A | ηele,maxa/% | Ufuelb/% | Fuel flow rate/(L•min–1) | Voltage/V | Power/W |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 53.57 | 87.10 | 0.08 | 0.771 | 7.71 |
| 20 | 52.92 | 87.10 | 0.16 | 0.761 | 15.23 |
| 30 | 50.47 | 87.10 | 0.24 | 0.726 | 21.78 |
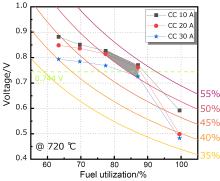

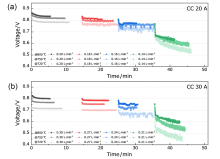

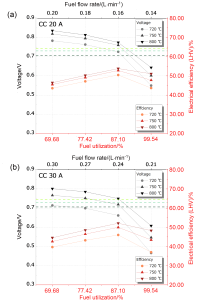

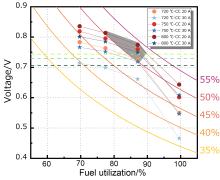

| Fuel utilization/% | ΔV/mVa | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 A | 20 A | 30 A | |
| 63.34 | 7 | 2 | 2 |
| 69.68 | 15 | 3 | 3 |
| 77.42 | 40 | 14 | 8 |
| 87.10 | 57 | 49 | 35 |
| 99.54 | 73 | 85 | 100 |
| Fuel utilization/% | ΔV/mVa | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 A | 20 A | 30 A | |
| 63.34 | 7 | 2 | 2 |
| 69.68 | 15 | 3 | 3 |
| 77.42 | 40 | 14 | 8 |
| 87.10 | 57 | 49 | 35 |
| 99.54 | 73 | 85 | 100 |

| Fuel utilization/% | 20 A | 30 A | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 800 ℃ | 750 ℃ | 720 ℃ | 800 ℃ | 750 ℃ | 720 ℃ | ||
| 69.68 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
| 77.42 | 8 | 15 | 23 | 5 | 5 | 7 | |
| 87.10 | 13 | 41 | 53 | 19 | 33 | 45 | |
| 99.54 | 38 | 61 | 73 | 45 | 62 | 63 | |
| Fuel utilization/% | 20 A | 30 A | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 800 ℃ | 750 ℃ | 720 ℃ | 800 ℃ | 750 ℃ | 720 ℃ | ||
| 69.68 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
| 77.42 | 8 | 15 | 23 | 5 | 5 | 7 | |
| 87.10 | 13 | 41 | 53 | 19 | 33 | 45 | |
| 99.54 | 38 | 61 | 73 | 45 | 62 | 63 | |

| No. | Temperature/℃ | E*a/V | Current/A | Ufuelb/% | Uc/V | Power/W | ηeled/% | Evaluation of this condition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before degradation (1st day) | ||||||||
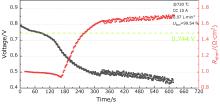
| 1 | 720 | 0.744 | 20 | 77.42 | 0.814 | 16.28 | 50.31 | U>E*, Higher power |
| 2 | 720 | 0.744 | 20 | 87.10 | 0.761 | 15.23 | 52.92 | U>E*, Higher efficiency |
| 3 | 720 | 0.744 | 30 | 87.10 | 0.726 | 21.78 | 50.47 | U<E*, not safe enough |
| After degradation (7th day) | ||||||||
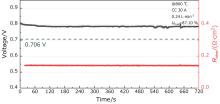
| 4 | 750 | 0.730 | 20 | 87.10 | 0.760 | 15.20 | 52.83 | U>E*, Better for stability |
| 5 | 800 | 0.706 | 20 | 77.42 | 0.813 | 16.27 | 50.26 | U>E*, Higher power |
| 6 | 800 | 0.706 | 20 | 87.10 | 0.774 | 15.48 | 53.81 | U>E*, Higher efficiency |
| 7 | 800 | 0.706 | 30 | 87.10 | 0.750 | 22.49 | 52.10 | U>E*, Higher power & efficiency |
| No. | Temperature/℃ | E*a/V | Current/A | Ufuelb/% | Uc/V | Power/W | ηeled/% | Evaluation of this condition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before degradation (1st day) | ||||||||
| 1 | 720 | 0.744 | 20 | 77.42 | 0.814 | 16.28 | 50.31 | U>E*, Higher power |
| 2 | 720 | 0.744 | 20 | 87.10 | 0.761 | 15.23 | 52.92 | U>E*, Higher efficiency |
| 3 | 720 | 0.744 | 30 | 87.10 | 0.726 | 21.78 | 50.47 | U<E*, not safe enough |
| After degradation (7th day) | ||||||||
| 4 | 750 | 0.730 | 20 | 87.10 | 0.760 | 15.20 | 52.83 | U>E*, Better for stability |
| 5 | 800 | 0.706 | 20 | 77.42 | 0.813 | 16.27 | 50.26 | U>E*, Higher power |
| 6 | 800 | 0.706 | 20 | 87.10 | 0.774 | 15.48 | 53.81 | U>E*, Higher efficiency |
| 7 | 800 | 0.706 | 30 | 87.10 | 0.750 | 22.49 | 52.10 | U>E*, Higher power & efficiency |
| Fuel utilization/% | Fuel flow rate of dry H2/(L•min–1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 A | 20 A | 30 A | |
| 63.34 | 0.11 | 0.22 | 0.33 |
| 69.68 | 0.10 | 0.20 | 0.30 |
| 77.42 | 0.09 | 0.18 | 0.27 |
| 87.10 | 0.08 | 0.16 | 0.24 |
| 99.54 | 0.07 | 0.14 | 0.21 |
| Fuel utilization/% | Fuel flow rate of dry H2/(L•min–1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 A | 20 A | 30 A | |
| 63.34 | 0.11 | 0.22 | 0.33 |
| 69.68 | 0.10 | 0.20 | 0.30 |
| 77.42 | 0.09 | 0.18 | 0.27 |
| 87.10 | 0.08 | 0.16 | 0.24 |
| 99.54 | 0.07 | 0.14 | 0.21 |
| [1] |
Nakao, T.; Inoue, S.; Uenoyama, S.; Takuwa, Y.; Suzuki, M. ECS Trans. 2019, 91, 43.
doi: 10.1149/09101.0043ecst |
| [2] |
Suzuki, M.; Inoue, S.; Shigehisa, T. ECS Trans. 2021, 103, 25.
doi: 10.1149/10301.0025ecst |
| [3] |
Ballard, A.; Domanski, T.; Rees, L.; Nobbs, C.; Lawrence, N.; Heffer, K.; Harman, J.; Evans, C.; Barnard, P.; Mukerjee, S.; Selby, M. ECS Trans. 2019, 91, 117.
doi: 10.1149/09101.0117ecst |
| [4] |
Sumi, H.; Nakabayashi, S.; Kawada, T.; Uchiyama, Y.; Uchiyama, N.; Ichihara, K. ECS Trans. 2019, 91, 149.
doi: 10.1149/09101.0149ecst |
| [5] |
Vora, S. D.; Jesionowski, G.; Williams, M. C. ECS Trans. 2019, 91, 27.
doi: 10.1149/09101.0027ecst |
| [6] |
Santhanam, S.; Ullmer, D.; Wuillemin, Z.; Varkaraki, E.; Beetschen, C.; Antonetti, Y.; Ansar, A. ECS Trans. 2019, 91, 159.
doi: 10.1149/09101.0159ecst |
| [7] |
Hara, D. ECS Trans. 2019, 91, 3.
doi: 10.1149/09101.0003ecst |
| [8] |
Horita, T. ECS Trans. 2021, 103, 1023.
doi: 10.1149/10301.1023ecst |
| [9] |
Mai, A.; Grolig, J. G.; Dold, M.; Vandercruysse, F.; Denzler, R.; Schindler, B.; Schuler, A. ECS Trans. 2019, 91, 63.
doi: 10.1149/09101.0063ecst |
| [10] |
Noponen, M.; Torri, P.; Göös, J.; Puranen, J.; Kaar, H.; Pylypko, S.; Roostar, M.; Õunpuu, E. ECS Trans. 2019, 91, 91.
doi: 10.1149/09101.0091ecst |
| [11] |
Vora, S.; Williams, M.; Jesionowski, G. ECS Trans. 2021, 103, 3.
doi: 10.1149/10301.0003ecst |
| [12] |
Fu, C.; Yan, D.; Jia, L.; Pu, J.; Chi, B.; Li, J. J. Ceram. 2020, 41, 869.
|
| [13] |
Futamura, S.; Tachikawa, Y.; Matsuda, J.; Lyth, S. M.; Shiratori, Y.; Taniguchi, S.; Sasaki, K. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2017, 164, F3055.
doi: 10.1149/2.0071710jes |
| [14] |
Min, G.; Park, Y. J.; Hong, J. Energy Convers. Manage. 2020, 209, 112614.
doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2020.112614 |
| [15] |
Li, H.; Cui, T.; Han, M. ECS Trans. 2021, 103, 831.
doi: 10.1149/10301.0831ecst |
| [16] |
Fang, Q.; Blum, L.; Peters, R.; Peksen, M.; Batfalsky, P.; Stolten, D. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 1128.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2014.11.094 |
| [17] |
Nehter, P. J. Power Sources 2007, 164, 252.
doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2006.08.037 |
| [18] |
Klotz, D.; Weber, A.; Ivers-Tiffée, E. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 227, 110.
doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2016.12.148 |
| [19] |
Brus, G.; Miyoshi, K.; Iwai, H.; Saito, M.; Yoshida, H. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 6927.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2015.03.143 |
| [20] |
Kawasaki, T.; Matsuda, J.; Tachikawa, Y.; Lyth, S. M.; Shiratori, Y.; Taniguchi, S.; Sasaki, K. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 9386.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.02.136 |
| [21] |
Feng, Y.; Ding, X.; Ma, Z.; Li, Y.; Zeng, F.; Zhou, J.; Wang, S. J. Ceram. 2021, 42, 360.
|
| [22] |
Wang, Y.; Shi, W.; Li, H.; Han, M.; Sun, Z. ECS Trans. 2019, 91, 707.
doi: 10.1149/09101.0707ecst |
| [23] |
Heo, Y. H.; Lee, J. W.; Lee, S. B.; Lim, T. H.; Park, S. J.; Song, R. H.; Park, C. O.; Shin, D. R. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 797.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2010.10.038 |
| [24] |
Lyu, Z.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, Z.; Sun, Z.; Sun, K.; Zhang, S.; Han, M. J. Power Sources 2021, 510, 230432.
doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2021.230432 |
| [25] |
Yang, B., Chen, Z., Qin, Z. Urban Gas 2019, 4.
|
| [26] |
Lyu, Z.; Meng, H.; Zhu, J.; Han, M.; Sun, Z.; Xue, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, F. Appl. Energy 2020, 270, 115220.
doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2020.115220 |
| [27] |
Peters, R.; Deja, R.; Blum, L.; Pennanen, J.; Kiviaho, J.; Hakala, T. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 6809.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2013.03.110 |
| [28] |
Calise, F.; Dentice d’Accadia, M.; Palombo, A.; Vanoli, L. Energy 2006, 31, 3278.
doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2006.03.006 |
| [29] |
Nakamura, K.; Ide, T.; Kawabata, Y.; Nakajima, T.; Dohkoh, T.; Tsuji, M.; Akabane, S.; Hatae, T. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 114516.
doi: 10.1149/1945-7111/aba791 |
| [30] |
Ramos, T.; Søgaard, M.; Mogensen, M. B. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2014, 161, F434.
doi: 10.1149/2.045404jes |
| [31] |
Lang, M.; Bohn, C.; Henke, M.; Schiller, G.; Willich, C.; Hauler, F. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2017, 164, F1460.
doi: 10.1149/2.1541713jes |
| [32] |
Brus, G.; Iwai, H.; Sciazko, A.; Saito, M.; Yoshida, H.; Szmyd, J. S. J. Power Sources 2015, 288, 199.
doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2015.04.092 |
| [33] |
Sugihara, S.; Iwai, H. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 25227.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.06.033 |
| [34] |
Blum, L.; Fang, Q.; Groß-Barsnick, S. M.; de Haart, L. G. J. (Bert.; Malzbender, J.; Menzler, N. H.; Quadakkers, W. J. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 8955.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.01.074 |
| [35] |
Lyu, Z.; Han, M.; Sun, Z.; Sun, K. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 763. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A21020065 |
|
(吕泽伟, 韩敏芳, 孙再洪, 孙凯华, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 763.)
doi: 10.6023/A21020065 |
|
| [36] |
Wang, Y.; Lyu, Z.; Han, M.; Sun, Z.; Sun, K. ECS Trans. 2021, 103, 1261.
doi: 10.1149/10301.1261ecst |
| [37] |
Cui, T.; Li, H.; Lyu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Han, M.; Sun, Z.; Sun, K. Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin. 2022, 38, 2011009. (in Chinese)
|
|
(崔同慧, 李航越, 吕泽伟, 王怡戈, 韩敏芳, 孙再洪, 孙凯华, 物理化学学报, 2022, 38, 2011009.)
|
| [1] | 吕泽伟, 韩敏芳, 孙再洪, 孙凯华. 固体氧化物燃料电池运行初期电化学性能演变机制[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(6): 763-770. |
| [2] | 胡瑜辉, 武文林, 于立扬, 骆开均, 徐小鹏, 李瑛, 彭强. 基于吡咯并吡咯二酮核心的苝二酰亚胺类受体分子的合成及光伏性能[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(11): 1246-1254. |
| [3] | 陈薪羽, 解俊杰, 王炜, 袁慧慧, 许頔, 张焘, 何云龙, 沈沪江. 钙钛矿材料组分调控策略及其光电器件性能研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(1): 9-23. |
| [4] | 郭旭东, 牛广达, 王立铎. 高效率钙钛矿型太阳能电池的化学稳定性及其研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2015, 73(3): 211-218. |
| [5] | 周德凤, 郭微, 朱建新, 郝险峰, 葛志敏, 叶俊峰, 孟健. Pr掺杂对Ce5.2Sm0.8MoO15-δ晶界及电性能的影响[J]. 化学学报, 2007, 65(14): 1313-1317. |
| [6] | 徐加焕,黄喜强,吕喆,张耀辉,葛晓东,苏文辉. Pr1-xSrxAlO3-δ的合成及其作为固体氧化物燃料电池阴极的性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2006, 64(5): 449-452. |
| [7] | 刘荣梅,马桂林,周丽,陈蓉. (ZrO2)0.86(Sm2O3)0.14纳米粉体的水热法合成及其烧结体的电性能[J]. 化学学报, 2005, 63(6): 491-496. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||