化学学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 80 ›› Issue (8): 1071-1083.DOI: 10.6023/A22040141 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
投稿日期:2022-04-01
发布日期:2022-09-01
通讯作者:
钱鹰
基金资助:
Badi Liu, Chengjun Wang, Ying Qian( )
)
Received:2022-04-01
Published:2022-09-01
Contact:
Ying Qian
Supported by:文章分享

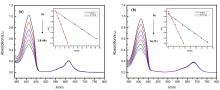
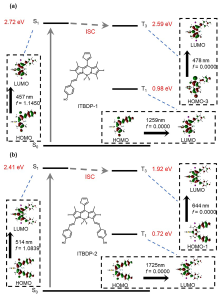
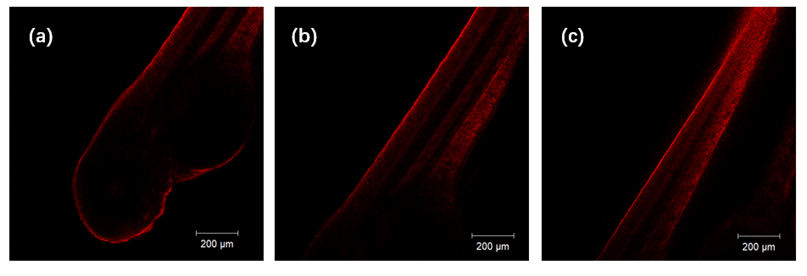
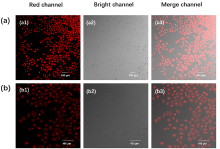
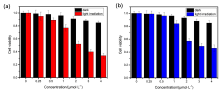
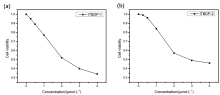
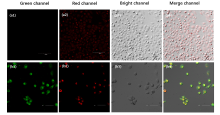
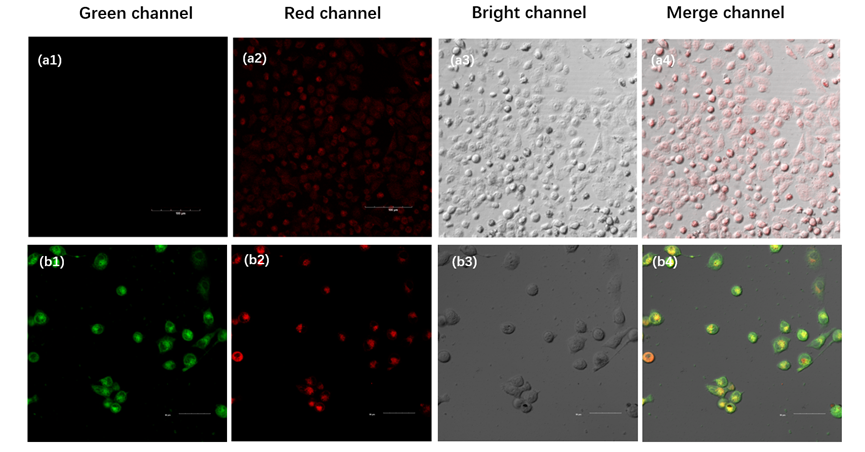
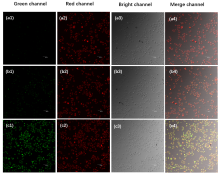
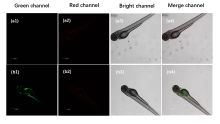
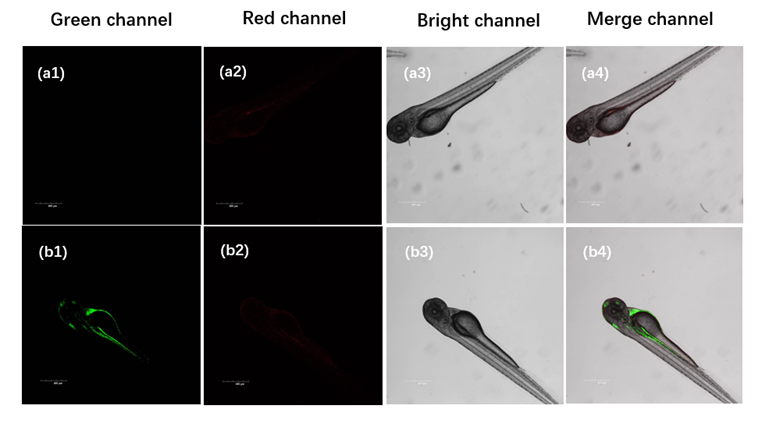
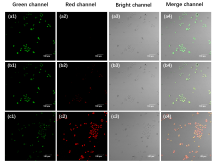
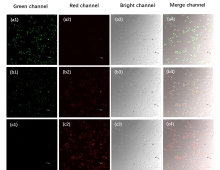
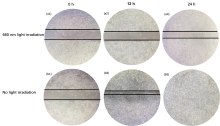
设计并合成了两种新型噻吩基氟硼二吡咯(Thienyl-BODIPY)近红外光敏染料ITBDP-1和ITBDP-2. 两种光敏染料的吸收和发射波长均达到近红外区, ITBDP-1的吸收与发射峰分别是617 nm和650 nm; ITBDP-2的吸收与发射峰分别是687 nm和731 nm. 两种光敏剂均具有较高的单线态氧产率, ITBDP-1与ITBDP-2的单线态氧产率(ΦΔ)分别为51%和24%. 通过密度泛函理论(DFT)计算研究了光敏染料激发态下的能量变化, 理论计算表明, ITBDP-1和ITBDP-2在激发至单重态后可通过系间窜越(ISC)到达三重态, 从而提高单线态氧产率. ITBDP-1和ITBDP-2在A549细胞内具有良好的的荧光成像效果, 并且在900 nm激光激发下, ITBDP-1能够在斑马鱼体内显示出清晰的双光子荧光成像. 单线态氧成像实验证明了光敏染料在光激发下可以在肿瘤细胞和斑马鱼中产生单线态氧. 通过噻唑蓝(MTT)比色法测定了两种光敏染料的光毒性和暗毒性, ITBDP-1和ITBDP-2的最大半抑制浓度(IC50)分别为2.22 μmol•L-1和2.86 μmol•L-1, 并且无光照条件下细胞的存活率在80%以上, 证明了两种光敏染料均具有较高的光毒性和良好的生物相容性. ITBDP-1和ITBDP-2可以在近红外光激发下实现荧光成像指导的光动力学治疗, 并且可以实现生物体内的双光子荧光成像, 这一结果也为噻吩基氟硼二吡咯光敏染料在长波激发下的双光子光动力学治疗应用打下了基础.
刘巴蒂, 王承俊, 钱鹰. 噻吩基氟硼二吡咯近红外光敏染料的合成、双光子荧光成像及光动力治疗研究[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(8): 1071-1083.
Badi Liu, Chengjun Wang, Ying Qian. Synthesis, Two-photon Fluorescence Imaging and Photodynamic Therapy of Near Infrared Thienyl-BODIPY Photosensitizer[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(8): 1071-1083.

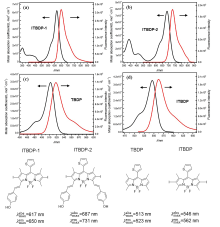


| Compound | $\lambda _{\max }^{\text{abs}}$/ nm | $\varepsilon _{\max }^{\text{abs}}$/(104 L•mol-1•cm-1) | $\lambda _{\max }^{em}$/nm | ΦΔ | IC50/ (μmol•L-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ITBDP-1 | 617 | 0.62 | 650 | 0.51 | 2.22 |
| ITBDP-2 | 687 | 7.60 | 731 | 0.24 | 2.86 |
| TBDP | 513 | 3.50 | 523 | — | — |
| ITBDP | 546 | 3.90 | 562 | 0.63 | — |
| Compound | $\lambda _{\max }^{\text{abs}}$/ nm | $\varepsilon _{\max }^{\text{abs}}$/(104 L•mol-1•cm-1) | $\lambda _{\max }^{em}$/nm | ΦΔ | IC50/ (μmol•L-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ITBDP-1 | 617 | 0.62 | 650 | 0.51 | 2.22 |
| ITBDP-2 | 687 | 7.60 | 731 | 0.24 | 2.86 |
| TBDP | 513 | 3.50 | 523 | — | — |
| ITBDP | 546 | 3.90 | 562 | 0.63 | — |









| [1] |
Pham, T. C.; Nguyen, V.; Choi, Y.; Lee, S.; Yoon, J. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 13454.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.1c00381 |
| [2] |
Celli, J. P.; Spring, B. Q.; Rizvi, I.; Evans, C. L.; Samkoe, K. S.; Verma, S.; Pogue, B. W.; Hasan, T. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 2795.
doi: 10.1021/cr900300p |
| [3] |
Chinna Ayya Swamy, P.; Sivaraman, G.; Priyanka, R. N.; Raja, S. O.; Ponnuvel, K.; Shanmugpriya, J.; Gulyani, A. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2020, 411, 213233.
doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2020.213233 |
| [4] |
Xu, F.; Li, H.; Yao, Q.; Ge, H.; Fan, J.; Sun, W.; Wang, J.; Peng, X. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 10586.
doi: 10.1039/C9SC03355F |
| [5] |
Zheng, J.; Liu, Y.; Song, F.; Jiao, L.; Wu, Y.; Peng, X. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 5819.
doi: 10.1039/D0CC02019B |
| [6] |
Dong, Y.; Kumar, P.; Maity, P.; Kurganskii, I.; Li, S.; Elmali, A.; Zhao, J.; Escudero, D.; Wu, H.; Karatay, A.; Mohammed, O. F.; Fedin, M. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2021, 23, 8641.
doi: 10.1039/d1cp00948f pmid: 33876025 |
| [7] |
Hu, W.; Zhang, X.; Liu, M. J. Phys. Chem. C 2021, 125, 5233.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.1c00001 |
| [8] |
Turksoy, A.; Yildiz, D.; Akkaya, E. U. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 379, 47.
doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2017.09.029 |
| [9] |
Liu, M.; Wang, C.; Qian, Y. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 18082.
doi: 10.1039/D1NJ03628A |
| [10] |
Wang, C.; Qian, Y. Biomaterials 2020, 8, 830.
|
| [11] |
Lee, J. M.; Kang, S.; Hwang, T. G.; Kim, H. M.; Lee, W. S.; Kim, D.; Kim, J. P. Dyes Pigm. 2021, 187, 109051.
doi: 10.1016/j.dyepig.2020.109051 |
| [12] |
Wang, L.; Qian, Y. Dyes Pigm. 2021, 195, 109711.
doi: 10.1016/j.dyepig.2021.109711 |
| [13] |
Tian, R.; Sun, W.; Li, M.; Long, S.; Li, M.; Fan, J.; Guo, L.; Peng, X. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 10106.
doi: 10.1039/C9SC04034J |
| [14] |
Xiang, W.-H.; Zhang, L.; Zhi, X.; Qian, Y. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 41, 3578 (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202104040 |
|
(项雯晖, 张磊, 支旭, 钱鹰, 有机化学, 2021, 41, 3578.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202104040 |
|
| [15] |
Zhi, X.; Xiang, W.; Qian, Y. J. Lumin. 2021, 240, 118424.
doi: 10.1016/j.jlumin.2021.118424 |
| [16] |
Dong, Y.; Dick, B.; Zhao, J. Org. Lett. 2020, 22, 5535.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.0c01903 pmid: 32643941 |
| [17] |
Dong, Y.; Taddei, M.; Doria, S.; Bussotti, L.; Zhao, J.; Mazzone, G.; Di Donato, M. J. Phys. Chem. B 2021, 125, 4779.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.1c00053 |
| [18] |
Nguyen, V.; Yan, Y.; Zhao, J.; Yoon, J. Acc. Chem. Res. 2022, 54, 207.
doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.0c00606 |
| [19] |
Qi, S.; Kwon, N.; Yim, Y.; Nguyen, V.; Yoon, J. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 6479.
doi: 10.1039/D0SC01171A |
| [20] |
Lin, G.; Hu, M.; Zhang, R.; Zhu, Y.; Gu, K.; Bai, J.; Li, J.; Dong, X.; Zhao, W. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 18143.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c01643 |
| [21] |
Bassan, E.; Gualandi, A.; Cozzi, P. G.; Ceroni, P. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 6607.
doi: 10.1039/d1sc00732g pmid: 34040736 |
| [22] |
Dartar, S.; Ucuncu, M.; Karakus, E.; Hou, Y.; Zhao, J.; Emrullahoglu, M. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 639.
doi: 10.1039/D0CC07269A |
| [23] |
Wen, H.; Wu, Q.; Li, C.; Sun, T.; Xie, Z. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 1500.
doi: 10.1021/acsanm.1c04143 |
| [24] |
Yuan, P.; Ruan, Z.; Yan, L. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 1043.
doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.9b01662 pmid: 33464862 |
| [25] |
Jiang, G.; Li, M.; Wen, Y.; Zeng, W.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, C.; Yuan, H.; Liu, C.; Liu, C. ACS Sensors 2019, 4, 434.
doi: 10.1021/acssensors.8b01423 |
| [26] |
Guo, Z.; Park, S.; Yoon, J.; Shin, I. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 16.
doi: 10.1039/C3CS60271K |
| [27] |
Pandith, A.; Siddappa, R. G.; Seo, Y. J. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C 2019, 40, 81.
doi: 10.1016/j.jphotochemrev.2019.08.001 |
| [28] |
Chin, J.; Kim, H. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 354, 169.
doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2017.07.009 |
| [29] |
Yuan, L.; Lin, W.; Zheng, K.; He, L.; Huang, W. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 622.
doi: 10.1039/c2cs35313j pmid: 23093107 |
| [30] |
Bai, J.; Zhang, L.; Qian, Y. Spectrochim. Acta A 2021, 252, 119512.
doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2021.119512 |
| [31] |
Ren, A.; Feng, J.; Guo, J.; Zhang, S.; Cheng, H. Acta Chim. Sinica 2001, 59, 2126 (in Chinese)
|
|
(任爱民, 封继康, 郭景富, 张锁秦, 程红, 化学学报, 2001, 59, 2126.)
|
|
| [32] |
Ji, L. Ph.D. Dissertation, Shandong University, Jinan, 2011. (in Chinese)
|
|
(纪雷, 博士论文, 山东大学, 济南, 2011.)
|
|
| [33] |
Xia, G.-M. Ph.D. Dissertation, Shandong University, Jinan, 2003. (in Chinese)
|
|
(夏光明, 博士论文, 山东大学, 济南, 2003.)
|
|
| [34] |
Xia, G.-M.; Fang, Q.; Xu, X.-G.; Xu, G.-B.; Liu, Z.-Q. Acta Chim. Sinica 2003, 61, 976 (in Chinese)
|
|
(夏光明, 方奇, 许心光, 许贵宝, 刘志强, 化学学报, 2003, 61, 976.)
|
|
| [35] |
Wang, F. M.S. Thesis, Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Nanjing, 2020. (in Chinese)
|
|
王飞, 硕士论文, 南京邮电大学, 南京, 2020.)
|
|
| [36] |
Redmond, R. W.; Gamlin, J. N. Photochem. Photobiol. 1999, 70, 391.
pmid: 10546544 |
| [37] |
Wu, Z.; Liu, M.; Liu, Z.; Tian, Y. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 7532.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.0c00771 |
| [38] |
Fang, H.; Zhang, H.; Li, L.; Ni, Y.; Shi, R.; Li, Z.; Yang, X.; Ma, B.; Zhang, C.; Wu, Q.; Yu, C.; Yang, N.; Yao, S. Q.; Huang, W. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 7536.
doi: 10.1002/anie.202000059 |
| [39] |
Wu, L.; Ishigaki, Y.; Hu, Y.; Sugimoto, K.; Zeng, W.; Harimoto, T.; Sun, Y.; He, J.; Suzuki, T.; Jiang, X.; Chen, H.; Ye, D. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-13993-7 |
| [40] |
Fan, N.; Li, P.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, C.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z.; Tang, B. ACS Sensors 2021, 7, 71.
doi: 10.1021/acssensors.1c01630 |
| [41] |
Liu, H.-W.; Zhu, L.-M.; Lou, X.-F.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, X.-B. Acta Chim. Sinica 2020, 78, 1240 (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A20070323 |
|
(刘红文, 朱隆民, 娄霄峰, 袁林, 张晓兵, 化学学报, 2020, 78, 1240.)
doi: 10.6023/A20070323 |
| No related articles found! |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||