化学学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 80 ›› Issue (10): 1385-1393.DOI: 10.6023/A22060266 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
投稿日期:2022-06-19
发布日期:2022-08-31
通讯作者:
朱鹏飞, 王传义
基金资助:
Pengfei Zhu( ), Chensi Lou, Yuhan Shi, Chuanyi Wang(
), Chensi Lou, Yuhan Shi, Chuanyi Wang( )
)
Received:2022-06-19
Published:2022-08-31
Contact:
Pengfei Zhu, Chuanyi Wang
Supported by:文章分享
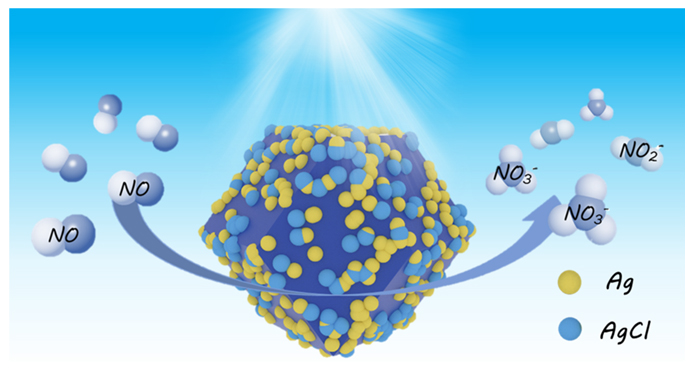
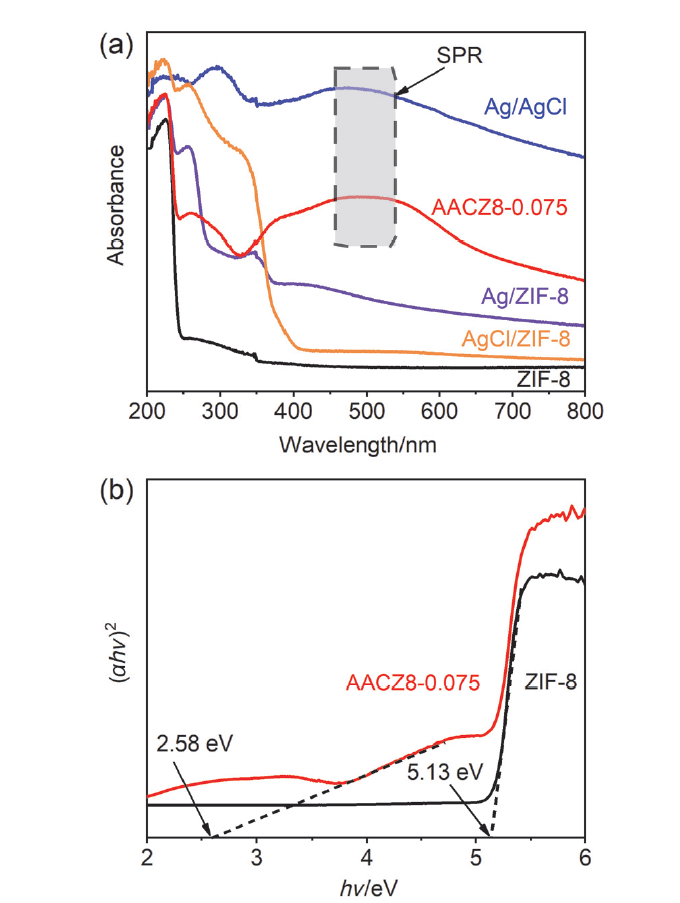
采用室温沉淀法合成菱形十二面体晶体结构ZIF-8(一种Zn金属有机框架材料), 然后通过光还原沉积法将Ag/AgCl纳米颗粒沉积于ZIF-8表面, 得到Ag/AgCl/ZIF-8复合光催化剂, 通过X射线衍射仪(XRD)、扫描电子显微镜(SEM)、透射电子显微镜(TEM)、比表面积测试法(BET)、紫外-可见漫反射吸收光谱(UV-Vis DRS)等一系列表征手段对其晶体结构、形貌、比表面积及吸光性能等进行了表征. 以低浓度NO作为目标去除污染物, 系统研究了Ag/AgCl/ZIF-8复合材料对NO的可见光催化氧化性能, 并对其反应机理进行了深入分析. 结果表明: (1) Ag/AgCl/ZIF-8复合材料中Ag0表面等离子体共振(SPR)效应增强了可见光的吸收; (2) ZIF-8具有大的比表面积, 使其能富集更多的氧分子和NO分子, 促进生成超氧自由基和NO光催化氧化; (3) 复合材料中光生空穴能够转移到AgCl的表面氧化Cl-为Cl0, Cl0具有强氧化性, 一方面促进了NO光催化氧化, 另一方面有效抑制了光生电子-空穴的复合, 提高了催化剂的稳定性.
朱鹏飞, 娄晨思, 史雨翰, 王传义. Ag/AgCl/ZIF-8复合材料的制备及其对NO光催化氧化性能的研究[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(10): 1385-1393.
Pengfei Zhu, Chensi Lou, Yuhan Shi, Chuanyi Wang. Study on Preparation of Ag/AgCl/ZIF-8 Composite and Photocatalytic NO Oxidation Performance[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(10): 1385-1393.
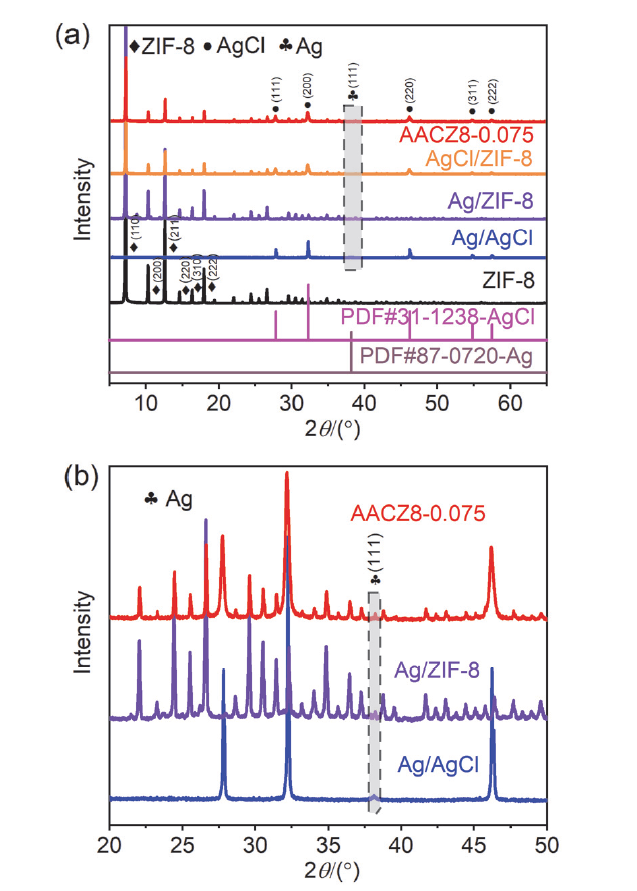


| 样品 | 比表面积/ (m2•g-1) | 孔径/nm | 孔隙体积/ (cm3•g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ZIF-8 | 1270.4993 | 0.3633 | 0.551171 |
| AACZ8-0.075 | 822.8584 | 0.3621 | 0.353376 |
| 样品 | 比表面积/ (m2•g-1) | 孔径/nm | 孔隙体积/ (cm3•g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ZIF-8 | 1270.4993 | 0.3633 | 0.551171 |
| AACZ8-0.075 | 822.8584 | 0.3621 | 0.353376 |
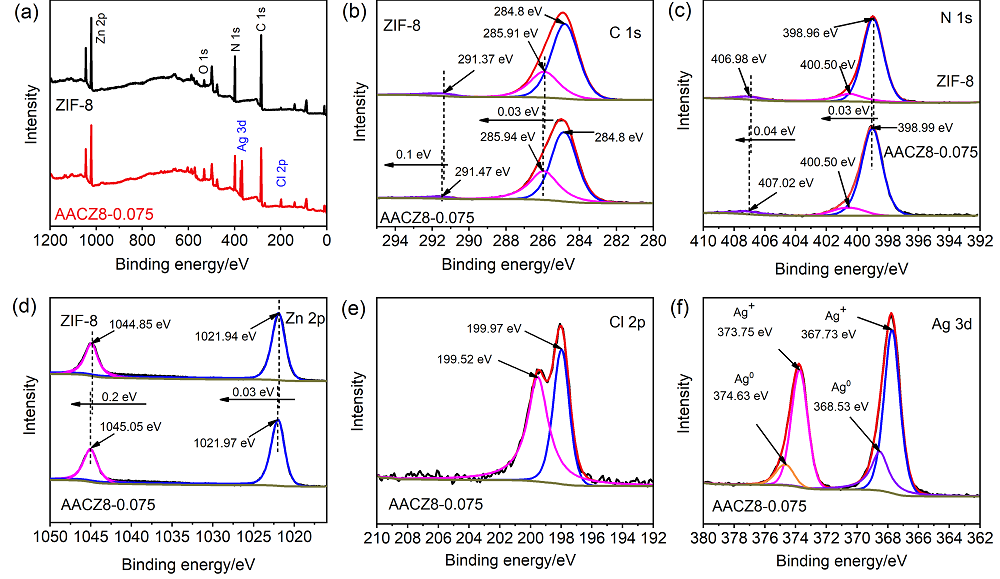



| [1] |
Huang, Y.; Gao, Y. X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y. F.; Cao, J. J.; Ho, W. K.; Lee, S. C. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 354, 54.
doi: S0304-3894(18)30326-1 pmid: 29727790 |
| [2] |
Zhu, P. F.; Yin, X. H.; Gao, X. H.; Dong, G. H.; Xu, J. K.; Wang, C. Y. Chinese J. Catal. 2021, 42, 175.
doi: 10.1016/S1872-2067(20)63592-6 |
| [3] |
Wang, Y. W.; Hu, X. S.; Song, H. R.; Cai, Y.; Li, Z.; Zu, D. Y.; Zhang, P. X.; Chong, D. T.; Gao, N. B.; Shen, Y. M.; Li, C. P. Appl. Catal., B 2021, 299, 120677.
doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2021.120677 |
| [4] |
Li, N.; Shi, M. L.; Xin, Y.; Zhang, W.; Qin, J. N.; Zhang, K.; Lv, H. Q.; Yuan, M. Z.; Wang, C. Y. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107420.
doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2022.107420 |
| [5] |
Zhou, M.; Dong, G. H.; Yu, F. K.; Huang, Y. Appl. Catal., B 2019, 256, 117825.
doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.117825 |
| [6] |
Zhao, S. H.; Fu, M.; Li, Y. X.; Hu, X. L.; Yuan, C. X.; Pan, R. Mol. Catal. 2021, 507, 111570.
|
| [7] |
Li, G. J.; Lian, Z.; Wan, Z. W.; Liu, Z. N.; Qian, J. W.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, S. L.; Zhong, Q. Appl. Catal., B 2022, 317, 121787.
doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2022.121787 |
| [8] |
Qi, K.; Jing, J.; Dong, G. H.; Li, P. N.; Huang, Y. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113405.
doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2022.113405 |
| [9] |
Chen, X. L.; Cai, Y.; Liang, R.; Tao, Y.; Wang, W. C.; Zhao, J. J.; Chen, X. F.; Li, H. X.; Zhang, D. Q. Appl. Catal. B 2020, 267, 118687.
doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.118687 |
| [10] |
Qi, Y.; Zhang, F.-X. Acta Chim. Sinica 2022, 80, 827. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A21120607 |
|
(祁育, 章福祥, 化学学报, 2022, 80, 827.)
doi: 10.6023/A21120607 |
|
| [11] |
Li, W. X.; Huang, J. H.; Fu, X. H.; Xu, J. G.; Yu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y. M. Surf. Interfaces 2021, 27, 101541.
|
| [12] |
Chen, Q.; Kuang, Q.; Xie, Z.-X. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 10. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A20080384 |
|
(陈钱, 匡勤, 谢兆雄, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 10.)
doi: 10.6023/A20080384 |
|
| [13] |
Xu, Y. G.; Xu, H.; Li, H. M.; Xia, J. X.; Liu, C. T.; Liu, L. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 3286.
doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2010.11.193 |
| [14] |
Zhao, W. Y.; Ding, T.; Wang, Y. T.; Wu, M. Q.; Jin, W. F.; Tian, Y.; Li, X. G. Chinese J. Catal. 2019, 40, 1187.
doi: 10.1016/S1872-2067(19)63377-2 |
| [15] |
Chang, N.; Chen, Y. R.; Xie, F.; Liu, Y. P.; Wang, H. T. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2020, 307, 110530.
doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2020.110530 |
| [16] |
Mu, F. H.; Liu, C. X.; Xie, Y.; Zhou, S. J.; Dai, B. L.; Xia, D. H.; Huang, H. B.; Zhao, W.; Sun, C.; Kong, Y. Leung, D. Y. C. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 415, 129010.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.129010 |
| [17] |
Dai, Y. X.; Liu, Y.; Kong, J. J.; Yuan, J. L.; Sun, C.; Xian, Q. M.; Yang, S. G.; He, H. Solid State Sci. 2019, 96, 105946.
doi: 10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2019.105946 |
| [18] |
Fan, G. D.; Chen, Z.; Yan, Z. S.; Du, B. H.; Pang, H. L.; Tang, D. S.; Luo, J.; Lin, J. Y. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 409, 125018.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.125018 |
| [19] |
Liu, J. X.; Li, R.; Wang, Y. F.; Wang, Y. W.; Zhang, X. C.; Fan, C. M. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 693, 543.
doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.09.201 |
| [20] |
Fan, G. D.; Luo, J.; Guo, L.; Lin, R. J.; Zheng, X. M.; Snyder, S. A. Chemosphere 2018, 209, 4452.
|
| [21] |
Izadpanah Ostad, M.; Niknam Shahrak, M.; Galli, F. J. CO2 Util. 2021, 43, 101373.
|
| [22] |
He, Y. M.; Zeng, L.; Feng, Z.; Zhang, Q. L.; Zhao, X. Y.; Ge, S. F.; Hu, X.; Lin, H. J. Adv. Powder Technol. 2020, 31, 439.
doi: 10.1016/j.apt.2019.11.002 |
| [23] |
Ning, R. S.; Pang, H. L.; Yan, Z. S.; Lu, Z. Y.; Wang, Q. K.; Wu, Z. L.; Dai, W. X.; Liu, L. S.; Li, Z. S.; Fan, G. D.; Fu, X. Z. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 435, 129061.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.129061 |
| [24] |
Qiu, Y. L.; Xing, Z. P.; Guo, M. J.; Zhao, T. Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, P.; Li, Z. Z.; Pan, K.; Zhou, W. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 582, 752.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2020.08.079 |
| [25] |
He, W.; Liu, L.; Ma, T. T.; Han, H. M.; Zhu, J. J.; Liu, Y. P.; Fang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Guo, K. Appl. Catal., B 2022, 306, 121107.
doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2022.121107 |
| [26] |
Luo, T.; Hu, X. F.; She, Z. Z.; Wei, J. S.; Feng, X.; Chang, F. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 324, 114772.
doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2020.114772 |
| [27] |
Li, X.; He, W. M.; Li, C. H.; Song, B.; Liu, S. W. Appl. Catal., B 2021, 287, 119934.
doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2021.119934 |
| [28] |
Zhang, C. J.; Jia, M. Y.; Xu, Z. Y.; Xiong, W. P.; Yang, Z. H.; Cao, J.; Peng, H. H.; Xu, H. Y.; Xiang, Y. P.; Jing, Y. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 132652.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.132652 |
| [29] |
Chang, F.; Wang, X. M.; Yang, C.; Li, S. S.; Wang, J. L.; Yang, W. P.; Dong, F.; Hu, X. F.; Liu, D. G.; Kong, Y. Composites Part B-Eng. 2022, 231, 109600.
doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2021.109600 |
| [30] |
Li, W.; Wang, X.; Ma, Q.; Wang, F.; Chu, X. S.; Wang, X. C.; Wang, C. Y. Appl. Catal., B 2021, 284, 119688.
doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.119688 |
| [31] |
Ye, J.; Yang, D. Y.; Dai, J. D.; Li, C. X.; Yan, Y. S.; Wang, Y. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 431, 133972.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.133972 |
| [32] |
Zhang, C.; Qin, D. Y.; Zhou, Y.; Qin, F. Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, W. J.; Yang, Y.; Zeng, G. M. Appl. Catal., B 2022, 303, 120904.
doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2021.120904 |
| [33] |
Hu, X. S.; Wang, Y. W.; Ling, Z.; Song, H. R.; Cai, Y.; Li, Z.; Zu, D. Y.; Li, C. P. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 556, 149817.
doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.149817 |
| [34] |
Zhang, Q.; Huang, Y.; Xu, L. F.; Cao, J. J.; Ho, W. K.; Lee, S. C. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 4165.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.5b11887 |
| [35] |
Sun, N.; Zhu, Y. X.; Li, M. W.; Zhang, J.; Qin, J. N.; Li, Y. X.; Wang, C. Y. Appl. Catal., B 2021, 298, 120565.
doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2021.120565 |
| [36] |
Wang, A. W.; Ni, J. X.; Wang, W.; Wang, X. Y.; Liu, D. M.; Zhu, Q. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 426, 128106.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.128106 |
| [37] |
Xiao, Y.; Wang, X. L.; Yu, H.; Yang, Y.; Dong, X. T. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2021, 149, 109793.
doi: 10.1016/j.jpcs.2020.109793 |
| [38] |
Chang, Q. Q.; Cui, Y. W.; Zhang, H. H.; Chang, F.; Zhu, B. H.; Yu, S. Y. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 12689.
doi: 10.1039/C8RA09985E |
| [39] |
Liu, G. M.; Huang, Y.; Lv, H. Q.; Wang, H.; Zeng, Y. B.; Yuan, M. Z.; Meng, Q. G.; Wang, C. Y. Appl. Catal., B 2021, 284, 119683.
doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.119683 |
| [40] |
Chang, H. Z.; Yi, H.; Ke, Q. Q.; Zhang, J. W. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 10927.
doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c00695 |
| [1] | 孙博, 琚雯雯, 王涛, 孙晓军, 赵婷, 卢晓梅, 陆峰, 范曲立. 高分散共轭聚合物-金属有机框架纳米立方体的制备及抗肿瘤应用[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(7): 757-762. |
| [2] | 陈俊畅, 张明星, 王殳凹. 晶态多孔材料合成方法的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(2): 146-157. |
| [3] | 闫绍兵, 焦龙, 何传新, 江海龙. ZIF-67/石墨烯复合物衍生的氮掺杂碳限域Co纳米颗粒用于高效电催化氧还原[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(8): 1084-1090. |
| [4] | 刘欢, 李京哲, 李平, 张广智, 张广智, 张豪, 邱灵芳, 齐晖, 多树旺. 2D/3D ZnIn2S4/TiO2复合物的原位构筑及其提高的光催化性能[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(10): 1293-1301. |
| [5] | 张晋维, 李平, 张馨凝, 马小杰, 王博. 水稳定性金属有机框架材料的水吸附性质与应用[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(7): 597-612. |
| [6] | 郭振彬, 张媛媛, 冯霄. 金属有机框架分离纯化C4~C6碳氢化合物的研究[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(5): 397-406. |
| [7] | 于越, 张新波. 多孔金属有机框架材料作为锂金属负极保护层助力长寿命锂氧气电池[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(12): 1434-1440. |
| [8] | 刘玉成, 郑啸, 黄培强. 光催化氧化还原体系中硝酮与芳香叔胺的自由基偶联反应[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(9): 850-855. |
| [9] | 李阳雪, 张巍, 刘智, 谢志刚. 用环糊精的金属有机框架材料作为模板制备多孔有机笼[J]. 化学学报, 2015, 73(6): 641-645. |
| [10] | 吴运东, 彭莎, 欧阳跃军, 钱鹏程, 何卫民, 向建南. 金催化分子间氧化炔合成5-(3-吲哚基)-噁唑天然产物[J]. 化学学报, 2012, 70(12): 1367-1370. |
| [11] | 杨迎春, 卢远刚, 叶芝祥, 刘盛余, 余静, 胡蕾. La 掺杂Bi2O3的制备、表征与可见光催化活性[J]. 化学学报, 2012, 70(11): 1250-1256. |
| [12] | 叶青, 闫立娜, 霍飞飞, 王海平, 程水源, 康天放. Cu负载Fe柱撑钠化海泡石: 结构特点及其丙烯选择性催化还原NO性质研究[J]. 化学学报, 2011, 69(13): 1524-1532. |
| [13] | 赵莉,赵毅,韩静,宋立琴. 光催化氧化脱除高浓度氮氧化物的实验研究[J]. 化学学报, 2008, 66(17): 2001-2005. |
| [14] | 闫静, 刘志强, 朱海光, 刘淑莹. 马钱子中两种微量生物碱异构体的电喷雾多级串联质谱分析[J]. 化学学报, 2007, 65(1): 49-52. |
| [15] | 丁红春,柴怡浩,张中海,鲜跃仲,潘振声,金利通. 光催化氧化法测定地表水化学需氧量的研究[J]. 化学学报, 2005, 63(2): 148-152. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||