化学学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 80 ›› Issue (11): 1536-1554.DOI: 10.6023/A22080345 上一篇 下一篇
综述
杨思明a, 刘爱荣a,*( ), 刘静a, 刘钊丽a, 张伟贤a,b
), 刘静a, 刘钊丽a, 张伟贤a,b
投稿日期:2022-08-05
发布日期:2022-10-08
通讯作者:
刘爱荣
作者简介: |
杨思明, 同济大学环境科学与工程学院2020级硕士研究生, 研究方向为硫化纳米零价铁界面化学及应用. |
 |
刘爱荣, 同济大学环境科学与工程学院副教授、博士生导师, 研究方向为铁环境化学、地下水防控材料与技术、水环境化学理论与技术. 主持国家自然科学基金项目三项, 作为子课题负责人参与国家重点研发计划项目, 已发表本领域SCI论文三十余篇. |
 |
刘静, 同济大学环境科学与工程学院博士后, 研究方向为纳米零价铁环境化学研究, 发表本领域SCI论文10余篇, 参与多项国家级科研项目, 从事铁环境化学研究10余年. |
 |
刘钊丽, 同济大学环境科学与工程学院2021级博士研究生, 研究方向为电解质修饰的硫化纳米零价铁的界面化学和除砷机制. |
 |
张伟贤, 教授、博士生导师, 国家高层次特聘专家, 2011年5月起任污染控制与资源化研究国家重点实验室主任. 1984年毕业于同济大学, 1996年获美国约翰·霍普金斯大学(The Johns Hopkins University)环境工程博士学位, 曾任美国里海大学(Lehigh University)教授. 2000年获美国国家科学基金会(NSF)青年教授奖(CAREER AWARD). 主持过国家自然科学基金海外及港澳学者合作研究基金及多项国家自然科学基金项目. 长期致力于环境中重金属及持久性有机污染物的基础与应用研究, 是环境纳米技术的先驱之一, 纳米零价铁技术的创始研究者. 在纳米零价铁合成、表征、污染物反应机理、应用于地下水修复及废水处理方面发表了系列经典论文. |
基金资助:
Siming Yanga, Airong Liua( ), Jing Liua, Zhaoli Liua, Weixian Zhanga,b
), Jing Liua, Zhaoli Liua, Weixian Zhanga,b
Received:2022-08-05
Published:2022-10-08
Contact:
Airong Liu
Supported by:文章分享

纳米零价铁(nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron, nZVI)是水环境修复领域研究最广泛的材料之一, 但易团聚和氧化、电子选择性差等缺点制约了其实际应用. 对nZVI表面进行硫化制备成硫化纳米零价铁(Sulfidated nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron, S-nZVI), 能够提高纳米颗粒的分散性能、增强稳定性, 提高电子选择性, 已成为目前研究热点. 本综述以“合成方法—理化性质—应用性能”为主线展开论述, 首先总结了不同的硫化方法对S-nZVI理化性质的影响, 重点阐释通过调控合成条件(硫化顺序、硫化剂种类、硫铁比等)以调节S-nZVI的微观结构和界面元素化学形态(实际S/Fe、硫分布、FeSx形态等), 从而改变其宏观性质(亲疏水、析氢、导电性等), 最终实现对有机污染物与金属污染物的定向去除. 此外, 详细综述了S-nZVI用于去除卤代有机物、硝基苯有机物和重金属等污染物方面的研究进展, 并对未来的研究方向进行了展望.
杨思明, 刘爱荣, 刘静, 刘钊丽, 张伟贤. 硫化纳米零价铁研究进展: 合成、性质及环境应用[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(11): 1536-1554.
Siming Yang, Airong Liu, Jing Liu, Zhaoli Liu, Weixian Zhang. Advance of Sulfidated Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron: Synthesis, Properties and Environmental Application[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(11): 1536-1554.
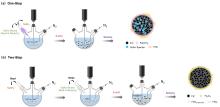

| 合成方法 | 硫化剂 | 反应方程式 | 序号 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na2S | S2-+H2O→HS-+OH- | (1) | [ | |
| Fe2++2HS-→FeS+H2S | (2) | |||
| 一步合成法 | Na2S2O4 | 2S2O42-+H2O→2HSO3-+S2O32- | (3) | [ |
| S2O32-→SO3-+S0 | (4) | |||
| S2O42-+S2O32-+2H2O+H+→H2S+3HSO3- | (5) | |||
| H2S→H++S2- | (6) | |||
| Fe2++S2-→FeS | (7) | |||
| S2O42-+6OH-→5SO3-+S2-+3H2O | (8) | [ | ||
| 两步合成法 | Na2S | Fe0+2H2O→Fe(OH)2+H2 | (9) | [ |
| Fe(OH)2→Fe2++2OH- | (10) | |||
| Fe2++S2-→FeS | (11) | |||
| S2-+H2O→HS-+OH- | (12) | |||
| Fe2++2S2-→FeS+H2S | (13) | |||
| 2FeS+2H+→FeS2+Fe2++H2 | (14) | |||
| Na2S2O3 | S2O32-→S0+SO32- | (15) | [ | |
| Fe0+S0→FeS | (16) |
| 合成方法 | 硫化剂 | 反应方程式 | 序号 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na2S | S2-+H2O→HS-+OH- | (1) | [ | |
| Fe2++2HS-→FeS+H2S | (2) | |||
| 一步合成法 | Na2S2O4 | 2S2O42-+H2O→2HSO3-+S2O32- | (3) | [ |
| S2O32-→SO3-+S0 | (4) | |||
| S2O42-+S2O32-+2H2O+H+→H2S+3HSO3- | (5) | |||
| H2S→H++S2- | (6) | |||
| Fe2++S2-→FeS | (7) | |||
| S2O42-+6OH-→5SO3-+S2-+3H2O | (8) | [ | ||
| 两步合成法 | Na2S | Fe0+2H2O→Fe(OH)2+H2 | (9) | [ |
| Fe(OH)2→Fe2++2OH- | (10) | |||
| Fe2++S2-→FeS | (11) | |||
| S2-+H2O→HS-+OH- | (12) | |||
| Fe2++2S2-→FeS+H2S | (13) | |||
| 2FeS+2H+→FeS2+Fe2++H2 | (14) | |||
| Na2S2O3 | S2O32-→S0+SO32- | (15) | [ | |
| Fe0+S0→FeS | (16) |
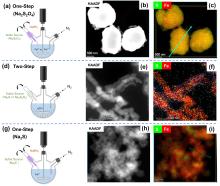

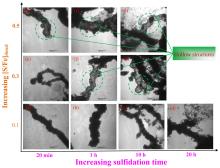

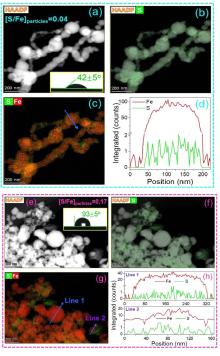



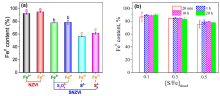
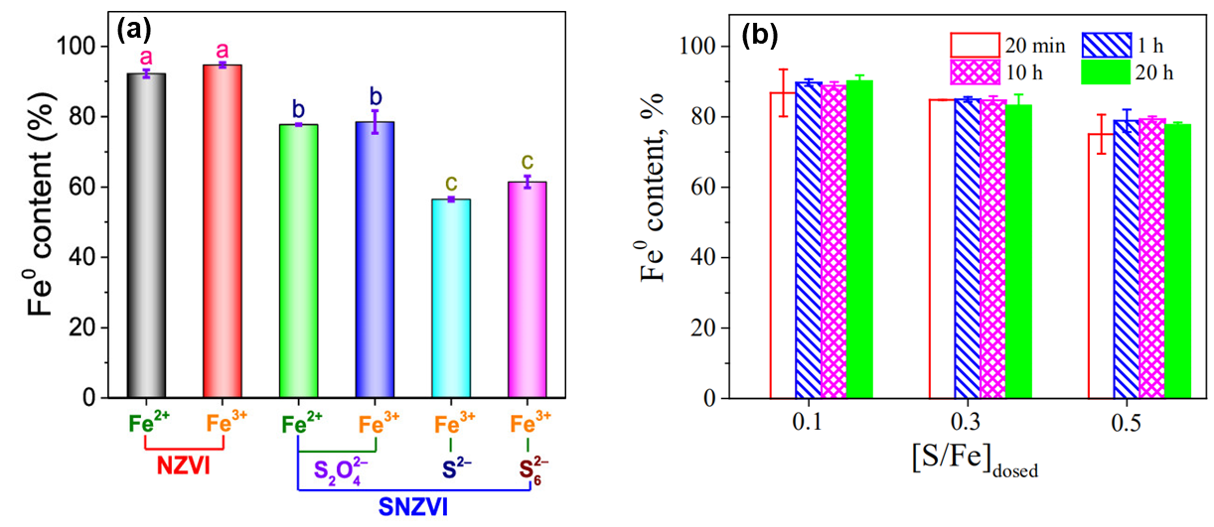
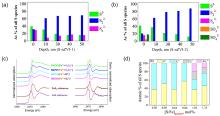

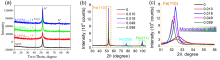

| 合成方法 | 形貌与稳定性 | 硫分布 | 实际S/Fe | Fe0含量 | 界面FeSx形态 | 晶相结构 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 一步硫化 | (1)粒径100~300 nm; (2)部分采用Na2S2O4作硫化剂时粒径约为1 μm, 显著高于Na2S作硫化剂; (3)核壳结构扭曲变形, 稳定性显著提升, 颗粒团聚现象减少. | (1) Na2S2O4作硫化剂时颗粒间大体均匀分布; (2) Na2S作硫化剂时颗粒间分布存在差异, 均匀度明显下降. | (1)较高, 约为实际投加量的37%. | (1) Na2S2O4作硫化剂时约为78%; (2) Na2S作硫化剂时约为50%. | (1)界面存在S2-与S22-, 内核存在Sn2-; (2) Na2S2O4作硫化剂时界面以FeS2为主; (3) Na2S作硫化剂时界面以FeS为主. | (1) S改变Fe0的BCC晶体结构, 形成Fe-S类合金; (2) Na2S2O4作硫化剂时晶格常数高于Na2S作硫化剂. |
| 两步硫化 | (1)粒径20~150 nm; (2)具有明显的核壳结构, 颗粒间呈链状排列, 存在团聚现象; (3)硫化剂投加量增加、硫化时间延长时外层FeSx厚度增加, 并形成明显的中空结构. | (1)主要集中在颗粒外壳层, 内部区域含量相对较低; (2)硫化剂投加量较高时颗粒间分布存在差异, 均匀度明显下降. | (1)较低, 约为投加量的0.2%~10%; (2)与硫化剂投加量和硫化时间的乘积呈线性关系:[S/Fe]particle=k×[S/Fe]dose×tsulfidation | (1) Na2S作硫化剂时约为85.4%; (2)硫化剂投加量增加时显著降低. | (1)界面存在S2-、S22-、 SO32-与SO42-; (2)硫化不改变内核结构, 内核不存在Sn2-; (3)硫化剂投加量较低、硫化时间较短时界面处FeS与FeS2含量接近; (4)硫化剂投加量增加、硫化时间延长时以FeS为主, FeS2逐渐减少, 出现Sn2-与SO42-. | — |
| 合成方法 | 形貌与稳定性 | 硫分布 | 实际S/Fe | Fe0含量 | 界面FeSx形态 | 晶相结构 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 一步硫化 | (1)粒径100~300 nm; (2)部分采用Na2S2O4作硫化剂时粒径约为1 μm, 显著高于Na2S作硫化剂; (3)核壳结构扭曲变形, 稳定性显著提升, 颗粒团聚现象减少. | (1) Na2S2O4作硫化剂时颗粒间大体均匀分布; (2) Na2S作硫化剂时颗粒间分布存在差异, 均匀度明显下降. | (1)较高, 约为实际投加量的37%. | (1) Na2S2O4作硫化剂时约为78%; (2) Na2S作硫化剂时约为50%. | (1)界面存在S2-与S22-, 内核存在Sn2-; (2) Na2S2O4作硫化剂时界面以FeS2为主; (3) Na2S作硫化剂时界面以FeS为主. | (1) S改变Fe0的BCC晶体结构, 形成Fe-S类合金; (2) Na2S2O4作硫化剂时晶格常数高于Na2S作硫化剂. |
| 两步硫化 | (1)粒径20~150 nm; (2)具有明显的核壳结构, 颗粒间呈链状排列, 存在团聚现象; (3)硫化剂投加量增加、硫化时间延长时外层FeSx厚度增加, 并形成明显的中空结构. | (1)主要集中在颗粒外壳层, 内部区域含量相对较低; (2)硫化剂投加量较高时颗粒间分布存在差异, 均匀度明显下降. | (1)较低, 约为投加量的0.2%~10%; (2)与硫化剂投加量和硫化时间的乘积呈线性关系:[S/Fe]particle=k×[S/Fe]dose×tsulfidation | (1) Na2S作硫化剂时约为85.4%; (2)硫化剂投加量增加时显著降低. | (1)界面存在S2-、S22-、 SO32-与SO42-; (2)硫化不改变内核结构, 内核不存在Sn2-; (3)硫化剂投加量较低、硫化时间较短时界面处FeS与FeS2含量接近; (4)硫化剂投加量增加、硫化时间延长时以FeS为主, FeS2逐渐减少, 出现Sn2-与SO42-. | — |
| 铁氧化物 | 能隙/eV | 铁硫化物 | 能隙/eV |
|---|---|---|---|
| FeO | 2.40 | FeS | 0.10 |
| Fe2O3 | 2.20 | FeS2 | 0.95 |
| Fe3O4 | 0.10 | Fe3S4 | 0.00 |
| FeOOH | 2.60 |
| 铁氧化物 | 能隙/eV | 铁硫化物 | 能隙/eV |
|---|---|---|---|
| FeO | 2.40 | FeS | 0.10 |
| Fe2O3 | 2.20 | FeS2 | 0.95 |
| Fe3O4 | 0.10 | Fe3S4 | 0.00 |
| FeOOH | 2.60 |

| 污染物 | 硫化方法 | 硫化剂 | 最佳S/Fe(物质的量比) | 速率提升比 | 去除机理 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 三氯乙烯 | 一步法 | Na2S2O4 | 0.14 | 14 | 提高电导率和疏水性, 抑制析氢 | [ |
| 三氯乙烯 | 一步法 | Na2S2O4 | 0.10 | 11.8 | 增强电子转移效率 | [ |
| 三氯乙烯 | 一步法 | Na2S | 0.4 | 106 | 提高电导率和疏水性 | [ |
| 三氯乙烯 | 两步法 | Na2S | 0.045 | 37.8 | 提高电导率和疏水性 | [ |
| 三氯乙烯 | 两步法 | Na2S | 0.087 | 12 | 提高电导率和疏水性 | [ |
| 四氯乙烯 | 两步法 | NaHS | 0.011 | — | 提高电导率 | [ |
| 四氯乙烯 | 两步法 | Na2S2O3 | 0.05 | 1.4 | 提高电导率 提高活性 | [ |
| 二氯乙烷 | 两步法 | Na2S2O4 | 0.25 | — | — | [ |
| 四氯化碳 | 两步法 | Na2S2O3 | 0.025 | 1 | 促进电子转移 | [ |
| 四氯化碳 | 一步法 | Na2S2O4 | 0.14 | 1.8 | — | [ |
| 二氯乙烯 | 一步法 | Na2S2O4 | 0.10 | 0.26 | 促进界面电荷重排 | [ |
| 氟苯尼考 | 一步法 | Na2S2O4 | 0.14 | 48 | 提高电导率和疏水性 | [ |
| 氟苯尼考 | 一步法 | Na2S2O4 | 0.14 | 8 | 提高疏水性 | [ |
| 氟苯尼考 | 两步法 | Na2S2O4 | 0.07 | 9.3 | 提高疏水性 | [ |
| 氟苯尼考 | 两步法 | Na2S | 0.07 | 11.3 | 提高疏水性 | [ |
| 氯霉素 | 一步法 | Na2S2O4 | 0.14 | 0.033 | 提高疏水性 | [ |
| 氯霉素 | 两步法 | Na2S | 0.14 | — | 提高疏水性 | [ |
| 四溴双酚A | 一步法 | Na2S2O4 | — | 1.65 | 提高电导率、疏水性和比表面积 | [ |
| 四溴双酚A | 两步法 | Na2S | 0.3 | 1.5 | 抑制析氢 | [ |
| 双氯芬酸 | 一步法 | Na2S2O4 | 0.3 | 3.5 | 提高电子传递效率 | [ |
| 双氯芬酸 | 一步法 | Na2S2O4 | 0.3 | 3.5 | 提高电导率 | [ |
| 苯甲酸 | 一步法 | Na2S2O4 | 0.08 | — | 加快铁溶解 | [ |
| 六溴环十二烷 | 一步法 | Na2S2O4 | 0.2 | 1.35 | — | [ |
| 十溴二苯乙烷 | 一步法 | Na2S2O4 | 0.2 | 7.1 | 提高电导率, 抑制析氢 | [ |
| 硝基苯 | 一步法 | Na2S2O4 | 0.3 | 7.4 | 提高电导率 | [ |
| 对硝基酚 | 两步法 | Na2S | 0.14 | 1.46 | 提高疏水性 | [ |
| 对硝基酚 | 两步法 | Na2S | 0.1 | 16 | 促进芬顿反应的发生 | [ |
| 污染物 | 硫化方法 | 硫化剂 | 最佳S/Fe(物质的量比) | 速率提升比 | 去除机理 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 三氯乙烯 | 一步法 | Na2S2O4 | 0.14 | 14 | 提高电导率和疏水性, 抑制析氢 | [ |
| 三氯乙烯 | 一步法 | Na2S2O4 | 0.10 | 11.8 | 增强电子转移效率 | [ |
| 三氯乙烯 | 一步法 | Na2S | 0.4 | 106 | 提高电导率和疏水性 | [ |
| 三氯乙烯 | 两步法 | Na2S | 0.045 | 37.8 | 提高电导率和疏水性 | [ |
| 三氯乙烯 | 两步法 | Na2S | 0.087 | 12 | 提高电导率和疏水性 | [ |
| 四氯乙烯 | 两步法 | NaHS | 0.011 | — | 提高电导率 | [ |
| 四氯乙烯 | 两步法 | Na2S2O3 | 0.05 | 1.4 | 提高电导率 提高活性 | [ |
| 二氯乙烷 | 两步法 | Na2S2O4 | 0.25 | — | — | [ |
| 四氯化碳 | 两步法 | Na2S2O3 | 0.025 | 1 | 促进电子转移 | [ |
| 四氯化碳 | 一步法 | Na2S2O4 | 0.14 | 1.8 | — | [ |
| 二氯乙烯 | 一步法 | Na2S2O4 | 0.10 | 0.26 | 促进界面电荷重排 | [ |
| 氟苯尼考 | 一步法 | Na2S2O4 | 0.14 | 48 | 提高电导率和疏水性 | [ |
| 氟苯尼考 | 一步法 | Na2S2O4 | 0.14 | 8 | 提高疏水性 | [ |
| 氟苯尼考 | 两步法 | Na2S2O4 | 0.07 | 9.3 | 提高疏水性 | [ |
| 氟苯尼考 | 两步法 | Na2S | 0.07 | 11.3 | 提高疏水性 | [ |
| 氯霉素 | 一步法 | Na2S2O4 | 0.14 | 0.033 | 提高疏水性 | [ |
| 氯霉素 | 两步法 | Na2S | 0.14 | — | 提高疏水性 | [ |
| 四溴双酚A | 一步法 | Na2S2O4 | — | 1.65 | 提高电导率、疏水性和比表面积 | [ |
| 四溴双酚A | 两步法 | Na2S | 0.3 | 1.5 | 抑制析氢 | [ |
| 双氯芬酸 | 一步法 | Na2S2O4 | 0.3 | 3.5 | 提高电子传递效率 | [ |
| 双氯芬酸 | 一步法 | Na2S2O4 | 0.3 | 3.5 | 提高电导率 | [ |
| 苯甲酸 | 一步法 | Na2S2O4 | 0.08 | — | 加快铁溶解 | [ |
| 六溴环十二烷 | 一步法 | Na2S2O4 | 0.2 | 1.35 | — | [ |
| 十溴二苯乙烷 | 一步法 | Na2S2O4 | 0.2 | 7.1 | 提高电导率, 抑制析氢 | [ |
| 硝基苯 | 一步法 | Na2S2O4 | 0.3 | 7.4 | 提高电导率 | [ |
| 对硝基酚 | 两步法 | Na2S | 0.14 | 1.46 | 提高疏水性 | [ |
| 对硝基酚 | 两步法 | Na2S | 0.1 | 16 | 促进芬顿反应的发生 | [ |
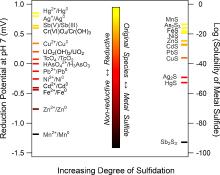
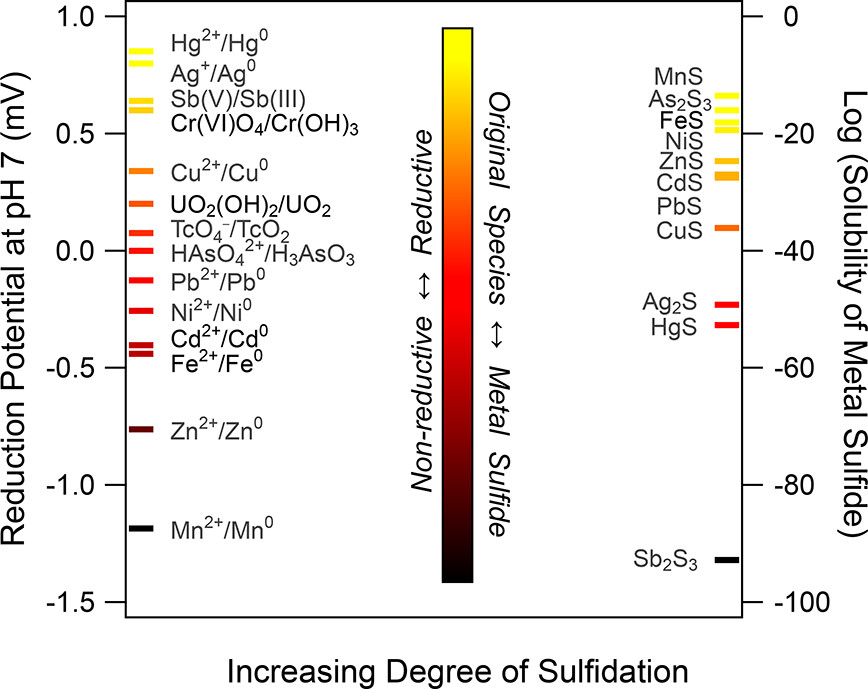
| 污染物 | 硫化方法 | 硫化剂 | 最佳S/Fe | 有氧/缺氧 | 产物 | 去除机理 | 硫化作用 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tc(VII) | 两步法 | Na2S | 0.056~0.2 | 缺氧 | TcO2; TcS2 | 吸附、还原 | 提高结合力 | [ |
| Cd(II) | 一步法 | Na2S2O4 | 0.28 | 缺氧 | CdS; Fe(1-x)CdxS | 吸附、共沉淀 | — | [ |
| Cd(II) | 一步法 | Na2S2O4 | 0.28 | 缺氧 | — | 吸附、共沉淀 | — | [ |
| Cr(VI) | 一步法 | Na2S2O4 | 0.50 | 缺氧 | (CrxFe1-x)(OH)3 | 吸附、还原、共沉淀 | 增大表面积, 提高电子转移效率 | [ |
| Cr(VI) | 一步法 | Na2S2O4 | 0.21 | 缺氧 | (CrxFe1-x)(OH)3; FeCr2S4 | 吸附、还原、共沉淀 | 增大表面积, 抑制团聚 | [ |
| U(VI) | 一步法 | Na2S2O4 | 0.14 | 缺氧 | — | 吸附、还原 | — | [ |
| U(VI) | 一步法 | Na2S2O4 | 0.14 | 缺氧 | — | 吸附、还原 | — | [ |
| Ni(II) | 一步法 | Na2S2O4 | 0.10 | 缺氧 | — | 吸附 | — | [ |
| Cu(II) | 一步法 | Na2S2O4 | 0.10 | 缺氧 | — | 还原 | — | [ |
| As(III) | 一步法 | Na2S2O4 | 0.21 | 缺氧 | — | 吸附、共沉淀 | — | [ |
| As(III) | 一步法 | Na2S2O4 | 0.10 | 缺氧 | As2S3 | 吸附、氧化、共沉淀 | 降低表面钝化, 形成As2S3沉淀 | [ |
| Sb(III) | 两步法 | Na2S | 0.10 | 缺氧 | Sb(V); Fe-Sb-S | 吸附、氧化、共沉淀 | 加快芬顿反应进行, 促进自由基产生, 提高电子转移效率 | [ |
| Sb(III) | 两步法 | Na2S | 0.084 | 有氧 | Sb(V) | 吸附、氧化 | 提高电子转移效率 | [ |
| 污染物 | 硫化方法 | 硫化剂 | 最佳S/Fe | 有氧/缺氧 | 产物 | 去除机理 | 硫化作用 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tc(VII) | 两步法 | Na2S | 0.056~0.2 | 缺氧 | TcO2; TcS2 | 吸附、还原 | 提高结合力 | [ |
| Cd(II) | 一步法 | Na2S2O4 | 0.28 | 缺氧 | CdS; Fe(1-x)CdxS | 吸附、共沉淀 | — | [ |
| Cd(II) | 一步法 | Na2S2O4 | 0.28 | 缺氧 | — | 吸附、共沉淀 | — | [ |
| Cr(VI) | 一步法 | Na2S2O4 | 0.50 | 缺氧 | (CrxFe1-x)(OH)3 | 吸附、还原、共沉淀 | 增大表面积, 提高电子转移效率 | [ |
| Cr(VI) | 一步法 | Na2S2O4 | 0.21 | 缺氧 | (CrxFe1-x)(OH)3; FeCr2S4 | 吸附、还原、共沉淀 | 增大表面积, 抑制团聚 | [ |
| U(VI) | 一步法 | Na2S2O4 | 0.14 | 缺氧 | — | 吸附、还原 | — | [ |
| U(VI) | 一步法 | Na2S2O4 | 0.14 | 缺氧 | — | 吸附、还原 | — | [ |
| Ni(II) | 一步法 | Na2S2O4 | 0.10 | 缺氧 | — | 吸附 | — | [ |
| Cu(II) | 一步法 | Na2S2O4 | 0.10 | 缺氧 | — | 还原 | — | [ |
| As(III) | 一步法 | Na2S2O4 | 0.21 | 缺氧 | — | 吸附、共沉淀 | — | [ |
| As(III) | 一步法 | Na2S2O4 | 0.10 | 缺氧 | As2S3 | 吸附、氧化、共沉淀 | 降低表面钝化, 形成As2S3沉淀 | [ |
| Sb(III) | 两步法 | Na2S | 0.10 | 缺氧 | Sb(V); Fe-Sb-S | 吸附、氧化、共沉淀 | 加快芬顿反应进行, 促进自由基产生, 提高电子转移效率 | [ |
| Sb(III) | 两步法 | Na2S | 0.084 | 有氧 | Sb(V) | 吸附、氧化 | 提高电子转移效率 | [ |
| 金属 | Ksp (OH-) | Ksp (S2-) | 金属 | Ksp (OH-) | Ksp (S2-) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni | 1.6×10-16 | 3×10-21 | Hg | — | 6.44×10-53 |
| Co | 2.5×10-16 | 5×10-22 | Ag | 2.0×10-8 | 6.3×10-50 |
| Zn | 4.5×10-17 | 2.5×10-22 | Cu | 5.66×10-20 | 1.27×10-36 |
| Cd | 2.0×10-14 | 1.0×10-28 | Pb | 1.43×10-20 | 9.0×10-29 |
| 金属 | Ksp (OH-) | Ksp (S2-) | 金属 | Ksp (OH-) | Ksp (S2-) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni | 1.6×10-16 | 3×10-21 | Hg | — | 6.44×10-53 |
| Co | 2.5×10-16 | 5×10-22 | Ag | 2.0×10-8 | 6.3×10-50 |
| Zn | 4.5×10-17 | 2.5×10-22 | Cu | 5.66×10-20 | 1.27×10-36 |
| Cd | 2.0×10-14 | 1.0×10-28 | Pb | 1.43×10-20 | 9.0×10-29 |
| [1] |
Podgorski, J.; Berg, M. Science 2020, 368, 845.
doi: 10.1126/science.aba1510 pmid: 32439786 |
| [2] |
Turner, S. W. D.; Rice, J. S.; Nelson, K. D.; Vernon, C. R.; McManamay, R.; Dickson, K.; Marston, L. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 7254.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-27509-9 pmid: 34903744 |
| [3] |
Yang, H.; Flower, R. J.; Thompson, J. R. Science 2013, 339, 141.
|
| [4] |
Zuo, W.; Yu, Y.; Huang, H. Water Res. 2021, 195, 116984.
|
| [5] |
Zhu, J.; Wei, S.; Gu, H.; Rapole, S. B.; Wang, Q.; Luo, Z.; Haldolaarachchige, N.; Young, D. P.; Guo, Z. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 977.
doi: 10.1021/es2014133 |
| [6] |
Esmaielzadeh Kandjani, A.; Sabri, Y. M.; Mohammad-Taheri, M.; Bansal, V.; Bhargava, S. K. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 1578.
doi: 10.1021/es503527e pmid: 25407243 |
| [7] |
Chen, M.; Chen, Z.; Wu, P.; Chen, J. P. Water Res. 2021, 201, 117312.
|
| [8] |
Liu, J.; Gu, T. H.; Wang, W.; Liu, A. R.; Zhang, W. X. Acta Chim. Sinica 2019, 77, 121. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A18100412 |
|
(刘静, 顾天航, 王伟, 刘爱荣, 张伟贤, 化学学报, 2019, 77, 121.)
doi: 10.6023/A18100412 |
|
| [9] |
Liu, A.; Fu, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, W. ACS ES&T Water 2022, https://doi.org/10.1021/acsestwater.2c00080
|
| [10] |
Zhang, L. Z.; Zhang, W. X. Acta Chim. Sinica 2017, 75, 519. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A1706E001 |
|
(张礼知, 张伟贤, 化学学报, 2017, 75, 519.)
doi: 10.6023/A1706E001 |
|
| [11] |
Kao, L. C.; Ha, Y.; Chang, W. J.; Feng, X. F.; Ye, Y. F.; Chen, J. L.; Pao, C. W.; Yang, F. P.; Zhu, C.; Yang, W. L.; Guo, J. H.; Liou, S. Y. H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 16538.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.1c06159 |
| [12] |
Ling, L.; Huang, X. Y.; Zhang, W. X. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, e1705703.
|
| [13] |
Tesh, S. J.; Scott, T. B. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 6056.
doi: 10.1002/adma.201401376 |
| [14] |
Liu, X.; Cao, Z.; Yuan, Z. L.; Zhang, J.; Guo, X. P.; Yang, Y.; He, F.; Zhao, Y. P.; Xu, J. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 508.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.10.060 |
| [15] |
Li, J. X.; Qin, H. J.; Zhang, X. Y.; Guan, X. H. Acta Chim. Sinica 2017, 75, 544. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A17010007 |
|
(李锦祥, 秦荷杰, 张雪莹, 关小红, 化学学报, 2017, 75, 544.)
doi: 10.6023/A17010007 |
|
| [16] |
Liu, J.; Liu, A.; Li, J.; Liu, S.; Zhang, W. X. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 346, 131201.
|
| [17] |
He, F.; Zhao, D. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 3314.
doi: 10.1021/es048743y |
| [18] |
Phenrat, T.; Saleh, N.; Sirk, K.; Tilton, R. D.; Lowry, G. V. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 284.
doi: 10.1021/es061349a |
| [19] |
Xu, W. Q.; Li, Z. J.; Shi, S. S.; Qi, J. L.; Cai, S. C.; Yu, Y.; O'Carroll, D. M.; He, F. Appl. Catal. B 2020, 262, 118303.
|
| [20] |
Shi, L. N.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Z. L. Water Res. 2011, 45, 886.
doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2010.09.025 |
| [21] |
Greenlee, L. F.; Torrey, J. D.; Amaro, R. L.; Shaw, J. M. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 12913.
doi: 10.1021/es303037k pmid: 23130994 |
| [22] |
Bae, S.; Collins, R. N.; Waite, T. D.; Hanna, K. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 12010.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.8b01734 |
| [23] |
Xie, Y.; Cwiertny, D. M. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 8649.
doi: 10.1021/es102451t |
| [24] |
He, F.; Li, Z.; Shi, S.; Xu, W.; Sheng, H.; Gu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Xi, B. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 8627.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.8b01735 |
| [25] |
Liu, Y.; Lowry, G. V. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 6085.
doi: 10.1021/es060685o |
| [26] |
Su, Y.; Adeleye, A. S.; Keller, A. A.; Huang, Y.; Dai, C.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y. Water Res. 2015, 74, 47.
doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2015.02.004 |
| [27] |
Cao, Z.; Liu, X.; Xu, J.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Xu, X.; Lowry, G. V. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 11269.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.7b02480 |
| [28] |
Qin, H.; Guan, X.; Bandstra, J. Z.; Johnson, R. L.; Tratnyek, P. G. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 13887.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.8b04436 |
| [29] |
Xu, J.; Wang, Y.; Weng, C.; Bai, W.; Jiao, Y.; Kaegi, R.; Lowry, G. V. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 5936.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.9b00511 |
| [30] |
Fan, D.; O'Brien Johnson, G.; Tratnyek, P. G.; Johnson, R. L. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 9558.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.6b02170 |
| [31] |
Nunez Garcia, A.; Boparai, H. K.; de Boer, C. V.; Chowdhury, A. I. A.; Kocur, C. M. D.; Austrins, L. M.; Herrera, J.; O'Carroll, D. M. Water Res. 2020, 170, 115319.
|
| [32] |
Han, Y.; Yan, W. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 12992.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.6b03997 |
| [33] |
Su, Y.; Jassby, D.; Song, S.; Zhou, X.; Zhao, H.; Filip, J.; Petala, E.; Zhang, Y. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 6466.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.8b00231 |
| [34] |
Feitz, A. US 7674526, 2004, [Chem. Abstr. 2004, 142, 26219 ]
|
| [35] |
Kim, E. J.; Kim, J. H.; Azad, A. M.; Chang, Y. S. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 1457.
doi: 10.1021/am200016v |
| [36] |
Xu, J.; Cao, Z.; Zhou, H.; Lou, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xu, X.; Lowry, G. V. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 13344.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.9b04210 |
| [37] |
Xu, J.; Avellan, A.; Li, H.; Liu, X.; Noel, V.; Lou, Z.; Wang, Y.; Kaegi, R.; Henkelman, G.; Lowry, G. V. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, e1906910.
|
| [38] |
Garcia, A. N.; Zhang, Y.; Ghoshal, S.; He, F.; O'Carroll, D. M. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 8464.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.1c01251 |
| [39] |
Hassan, S. M. Chemosphere 2000, 40, 1357.
pmid: 10789975 |
| [40] |
de Carvalho, L. M.; Schwedt, G. Anal. Chim. Acta 2001, 436, 293.
doi: 10.1016/S0003-2670(01)00921-7 |
| [41] |
Bhattacharjee, S.; Ghoshal, S. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 11078.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.8b02399 pmid: 30188121 |
| [42] |
Xiao, S.; Jin, Z.; Dong, H.; Xiao, J.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Li, R.; Chen, J.; Tian, R.; Xie, Q. Water Res. 2022, 212, 118097.
|
| [43] |
Rajajayavel, S. R.; Ghoshal, S. Water Res. 2015, 78, 144.
doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2015.04.009 pmid: 25935369 |
| [44] |
Nunez Garcia, A.; Boparai, H. K.; O'Carroll, D. M. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 5243.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.6b00734 pmid: 27128632 |
| [45] |
Nzengung, V. A.; Castillo, R. M.; Gates, W. P.; Mills, G. L. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 2244.
pmid: 11414025 |
| [46] |
Fan, D.; Anitori, R. P.; Tebo, B. M.; Tratnyek, P. G.; Lezama Pacheco, J. S.; Kukkadapu, R. K.; Engelhard, M. H.; Bowden, M. E.; Kovarik, L.; Arey, B. W. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 5302.
doi: 10.1021/es304829z |
| [47] |
Tang, J.; Tang, L.; Feng, H.; Zeng, G.; Dong, H.; Zhang, C.; Huang, B.; Deng, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 320, 581.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.07.042 |
| [48] |
Xu, C.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Y.; Shao, Q.; Zhou, W.; Fan, D.; Bandstra, J. Z.; Shi, Z.; Tratnyek, P. G. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 11879.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.6b03184 |
| [49] |
Fan, D.; Lan, Y.; Tratnyek, P. G.; Johnson, R. L.; Filip, J.; O'Carroll, D. M.; Nunez Garcia, A.; Agrawal, A. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 13070.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.7b04177 |
| [50] |
Wu, D. L.; Peng, S. H.; Yan, K. L.; Shao, B. B.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, Y. L. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 3039.
doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b02787 |
| [51] |
Xu, J.; Avellan, A.; Li, H.; Clark, E. A.; Henkelman, G.; Kaegi, R.; Lowry, G. V. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 13294.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.0c03879 |
| [52] |
Xu, R. H.; Fu, Y.; Xu, Y. B.; Zheng, X.; Huang, Y. X.; Meng, F. G. Chemosphere 2022, 296, 133996.
|
| [53] |
Mangayayam, M. C.; Perez, J. P. H.; Dideriksen, K.; Freeman, H. M.; Bovet, N.; Benning, L. G.; Tobler, D. J. Environ. Sci. Nano 2019, 6, 3422.
doi: 10.1039/C9EN00876D |
| [54] |
Yin, Y.; Rioux, R. M.; Erdonmez, C. K.; Hughes, S.; Somorjai, G. A.; Alivisatos, A. P. Science 2004, 304, 711.
doi: 10.1126/science.1096566 |
| [55] |
Su, Y. M.; Jassby, D.; Zhang, Y. L.; Keller, A. A.; Adeleye, A. S. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 396, 122691.
|
| [56] |
Cao, Z.; Li, H.; Lowry, G. V.; Shi, X.; Pan, X.; Xu, X.; Henkelman, G.; Xu, J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 2628.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.0c07319 |
| [57] |
Xu, J.; Li, H.; Lowry, G. V. Acc. Chem. Res. 2021, 2, 420.
|
| [58] |
Mangayayam, M. C.; Alonso-de-Linaje, V.; Dideriksen, K.; Tobler, D. J. Chemosphere 2020, 249, 126137.
|
| [59] |
Cao, Z.; Xu, J.; Li, H.; Ma, T. Y.; Lou, L. P.; Henkelman, G.; Xu, X. H. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 400, 125900.
|
| [60] |
Hammer, B.; Norskov, J. K. Nature 1995, 376, 238.
doi: 10.1038/376238a0 |
| [61] |
Wu, J.; Zhao, J.; Hou, J.; Zeng, R. J.; Xing, B. S. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 8105.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.8b06834 |
| [62] |
Mangayayam, M.; Dideriksen, K.; Ceccato, M.; Tobler, D. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 4389.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.8b06480 pmid: 30859830 |
| [63] |
Duan, J.; Zhao, D. Y. Abstr. Pap. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 257, 1617.
|
| [64] |
Wei, X. P.; Yin, H.; Peng, H.; Guo, Z. Y.; Lu, G. N.; Dang, Z. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 395, 125085.
|
| [65] |
Xu, Y.; Schoonen, M. A. A. Am. Mineral. 2000, 85, 543.
doi: 10.2138/am-2000-0416 |
| [66] |
Bhattacharjee, S.; Ghoshal, S. Environ. Sci. Nano 2018, 5, 782.
doi: 10.1039/C7EN01205E |
| [67] |
Gong, L.; Lv, N.; Qi, J. L.; Qiu, X. J.; Gu, Y. W.; He, F. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 396, 122620.
|
| [68] |
Gong, L.; Qi, J. L.; Lv, N.; Qiu, X. J.; Gu, Y. W.; Zhao, J. W.; He, F. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123844.
|
| [69] |
Wang, B.; Dong, H. R.; Li, L.; Wang, Y. Y.; Ning, Q.; Tang, L.; Zeng, G. M. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 381, 122773.
|
| [70] |
Kim, E. J.; Kim, J. H.; Chang, Y. S.; Turcio-Ortega, D.; Tratnyek, P. G. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 4002.
doi: 10.1021/es405622d |
| [71] |
Zou, H. W.; Hu, E. D.; Yang, S. Y.; Gong, L.; He, F. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 419.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.09.003 |
| [72] |
Gu, Y.; Wang, B.; He, F.; Bradley, M. J.; Tratnyek, P. G. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 12653.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.7b03604 |
| [73] |
Islam, S.; Han, Y. L.; Yan, W. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2020, 22, 759.
doi: 10.1039/C9EM00593E |
| [74] |
Jin, X.; Chen, H.; Yang, Q.; Hu, Y. A.; Yang, Z. L. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2018, 35, 560.
doi: 10.1089/ees.2016.0580 |
| [75] |
Vogel, M.; Georgi, A.; Kopinke, F. D.; Mackenzie, K. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 665, 235.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.136 |
| [76] |
Li, T.; Farrell, J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 173.
doi: 10.1021/es9907358 |
| [77] |
Elsner, M.; Hofstetter, T. B. Aquatic Redox Chemistry 2011, 1071, 407.
|
| [78] |
Song, H.; Carraway, E. R. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 6237.
doi: 10.1021/es048262e |
| [79] |
Song, H.; Carraway, E. R. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2006, 23, 272.
doi: 10.1089/ees.2006.23.272 |
| [80] |
Patel, M.; Kumar, R.; Kishor, K.; Mlsna, T.; Pittman, C. U.; Mohan, D. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 3510.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00299 |
| [81] |
Colomban, C.; Kudrik, E. V.; Afanasiev, P.; Sorokin, A. B. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 11321.
doi: 10.1021/ja505437h pmid: 25031156 |
| [82] |
Cui, B. Q.; Jia, S. C.; Tokunaga, E.; Shibata, N. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4393.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-06830-w |
| [83] |
Ahrens, T.; Kohlmann, J.; Ahrens, M.; Braun, T. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 931.
doi: 10.1021/cr500257c |
| [84] |
Brumovsky, M.; Filip, J.; Malina, O.; Oborna, J.; Sracek, O.; Reichenauer, T. G.; Andryskova, P.; Zboril, R. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 35424.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.0c08626 |
| [85] |
Cao, Z.; Li, H.; Xu, X. H.; Xu, J. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 394, 124876.
|
| [86] |
Li, D.; Mao, Z.; Zhong, Y.; Huang, W. L.; Wu, Y. D.; Peng, P. A. Water Res. 2016, 103, 1.
doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2016.07.003 |
| [87] |
Song, S. K.; Su, M. M.; Adeleye, A. S.; Zhang, Y. L.; Zhou, X. F. Appl. Catal. B 2017, 201, 211.
doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.07.055 |
| [88] |
Rayaroth, M. P.; Lee, C.-S.; Aravind, U. K.; Aravindakumar, C. T.; Chang, Y.-S. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 315, 426.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.01.031 |
| [89] |
Li, D.; Zhu, X.; Zhong, Y.; Huang, W.; Peng, P. a. Water Res. 2017, 121, 140.
doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2017.05.019 |
| [90] |
Wei, X.; Yin, H.; Peng, H.; Chen, R.; Lu, G.; Dang, Z. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 253, 161.
doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.07.007 |
| [91] |
Zhang, D.; Li, Y.; Sun, A.; Tong, S.; Jiang, X.; Mu, Y.; Li, J.; Han, W.; Sun, X.; Wang, L.; Shen, J. Chemosphere 2020, 247, 125832.
|
| [92] |
Tian, X. K.; Wang, X.; Nie, Y. L.; Yang, C.; Dionysiou, D. D. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 2403.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.0c07475 |
| [93] |
Su, Y. M.; Rao, U.; Khor, C. M.; Jensen, M. G.; Teesch, L. M.; Wong, B. M.; Cwiertny, D. M.; Jassby, D. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 33913.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.9b10449 |
| [94] |
Rao, U.; Su, Y. M.; Khor, C. M.; Jung, B.; Ma, S. C.; Cwiertny, D. M.; Wong, B. M.; Jassby, D. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 10668.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.0c02773 |
| [95] |
Wu, G.; Kong, W.; Gao, Y.; Kong, Y.; Dai, Z.; Dan, H.; Shang, Y.; Wang, S.; Yin, F.; Yue, Q.; Gao, B. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131876.
|
| [96] |
Qin, H. J.; Guan, X. H.; Tratnyek, P. G. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 9744.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.9b02419 |
| [97] |
Zhang, Y. L.; Yan, J.; Dai, C. M.; Li, Y. T.; Zhu, Y.; Zhou, X. F. J. Nanopart. Res. 2015, 17, 455.
doi: 10.1007/s11051-015-3256-2 |
| [98] |
Li, X. Q.; Zhang, W. X. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 6939.
doi: 10.1021/jp0702189 |
| [99] |
Li, S. L.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y. Y.; Zhang, W. X. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 254, 115.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2014.05.111 |
| [100] |
Gu, T. H.; Shi, J. M.; Hua, Y. L.; Liu, J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, W. X. Acta Chim. Sinica 2017, 75, 991. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A17070345 |
|
(顾天航, 石君明, 滑熠龙, 刘静, 王伟, 张伟贤, 化学学报, 2017, 75, 991.)
doi: 10.6023/A17070345 |
|
| [101] |
Liu, A. R.; Dai, Y. W.; Xia, Z. Y.; Liu, J. Acta Sci. Circumst. 2022, 42, 92. (in Chinese)
|
|
(刘爱荣, 戴雨薇, 夏泽阳, 刘静, 环境科学学报, 2022, 42, 92.)
|
|
| [102] |
Liu, A. R.; Wang, W.; Liu, J.; Fu, R. B.; Zhang, W. X. Sci. Bull. 2018, 63, 1641.
doi: 10.1016/j.scib.2018.12.002 |
| [103] |
Huang, Q.; Gu, T. H.; Liu, A. R.; Liu, J.; Zhang, W. X. Environ. Sci. Nano 2021, 8, 2650.
doi: 10.1039/D1EN00458A |
| [104] |
Xia, X. F.; Hua, Y. L.; Huang, X. Y.; Ling, L.; Zhang, W. X. Acta Chim. Sinica 2017, 75, 594. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A17030099 |
|
(夏雪芬, 滑熠龙, 黄潇月, 凌岚, 张伟贤, 化学学报, 2017, 75, 594.)
doi: 10.6023/A17030099 |
|
| [105] |
Li, M. R.; Tang, C. L.; Zhang, W. X.; Ling, L. Prog. Chem. 2022, 34, 846. (in Chinese)
|
|
(李美蓉, 唐晨柳, 张伟贤, 凌岚, 化学进展, 2022, 34, 846.)
|
|
| [106] |
Wolthers, M.; Charlet, L.; Van der Weijden, C. H.; Van der Linde, P. R.; Rickard, D. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2005, 69, 3483.
doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2005.03.003 |
| [107] |
Farquhar, M. L.; Charnock, J. M.; Livens, F. R.; Vaughan, D. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 1757.
pmid: 11993874 |
| [108] |
Coles, C. A.; Rao, S. R.; Yong, R. N. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 996.
doi: 10.1021/es990773r |
| [109] |
Du, J.; Bao, J.; Lu, C.; Werner, D. Water Res. 2016, 102, 73.
doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2016.06.009 |
| [110] |
Su, Y. M.; Adeleye, A. S.; Huang, Y. X.; Zhou, X. F.; Keller, A. A.; Zhang, Y. L. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24358.
doi: 10.1038/srep24358 |
| [111] |
Lv, D.; Zhou, J. S.; Cao, Z.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y. L.; Li, Y. Z.; Yang, K. L.; Lou, Z. M.; Lou, L. P.; Xu, X. H. Chemosphere 2019, 224, 306.
doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.02.109 |
| [112] |
Gong, Y. Y.; Gai, L. S.; Tang, J. C.; Fu, J.; Wang, Q. L.; Zeng, E. Y. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 595, 743.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.03.282 |
| [113] |
Pang, H. W.; Diao, Z. F.; Wang, X. X.; Ma, Y.; Yu, S. J.; Zhu, H. T.; Chen, Z. S.; Hu, B. W.; Chen, J. R.; Wang, X. K. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 366, 368.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.02.098 |
| [114] |
Bai, Z. A.; Chen, R. X.; Pang, H. W.; Wang, X. X.; Song, G.; Yu, S. J. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 1265. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A21060263 |
|
(白子昂, 陈瑞兴, 庞宏伟, 王祥学, 宋刚, 于淑君, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 1265.)
doi: 10.6023/A21060263 |
|
| [115] |
Xu, W. J.; Hu, X. Y.; Lou, Y. L.; Jiang, X. D.; Shi, K. K.; Tong, Y. N.; Xu, X. H.; Shen, C. F.; Hu, B. L.; Lou, L. P. Environ. Res. 2020, 187, 109662.
|
| [116] |
Singh, P.; Pal, P.; Mondal, P.; Saravanan, G.; Nagababu, P.; Majumdar, S.; Labhsetwar, N.; Bhowmick, S. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 412, 128667.
|
| [117] |
Liu, S.; Feng, H.; Tang, L.; Dong, H.; Wang, J.; Yu, J.; Feng, C.; Liu, Y.; Luo, T.; Ni, T. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 736, 139629.
|
| [118] |
Huang, S. S.; Xu, C. H.; Shao, Q. Q.; Wang, Y. H.; Zhang, B. L.; Gao, B. Y.; Zhou, W. Z.; Tratnyek, P. G. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 338, 539.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.01.033 |
| [119] |
Liang, L.; Li, X. Q. Acta Sci. Circumst. 2019, 39, 1166. (in Chinese)
|
|
(梁莉, 李筱琴, 环境科学学报, 2019, 39, 1166.)
|
|
| [120] |
Liang, L.; Li, X.; Guo, Y.; Lin, Z.; Su, X.; Liu, B. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 404, 124057.
|
| [121] |
Gallegos, T. J.; Han, Y. S.; Hayes, K. F. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 9338.
pmid: 19174913 |
| [122] |
Ling, L.; Zhang, W. X. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 2288.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.6b04315 pmid: 28081365 |
| [123] |
Hou, K.; Pi, Z.; Chen, F.; He, L.; Yao, F.; Chen, S.; Li, X.; Dong, H.; Yang, Q. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 435, 128970.
|
| [124] |
Zhou, Z.; Huang, J.; Xu, Z.; Ali, M.; Shan, A.; Fu, R.; Lyu, S. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 273, 118990.
|
| [125] |
Stevenson, L. M.; Adeleye, A. S.; Su, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Keller, A. A.; Nisbet, R. M. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 10558.
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.7b05970 pmid: 28985677 |
| [126] |
Adeleye, A. S.; Stevenson, L. M.; Su, Y. M.; Nisbet, R. M.; Zhang, Y. L.; Keller, A. A. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 5597.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.5b06251 |
| [1] | 杨铃悦, 李赟婷, 舒超. 亚磺酸内酯研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(2): 171-189. |
| [2] | 黄广龙, 薛小松. “陈试剂”作为三氟甲基源机理的理论研究[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(2): 132-137. |
| [3] | 万义, 何江华, 张越涛. Lewis酸碱对催化极性烯烃单体精准聚合的研究进展★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(9): 1215-1230. |
| [4] | 付信朴, 王秀玲, 王伟伟, 司锐, 贾春江. 团簇Au/CeO2的制备及其催化CO氧化反应构效关系的研究★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(8): 874-883. |
| [5] | 甘绍艳, 钟晟昱, 王力廷, 史雷. 有机高价溴试剂的合成及其应用研究[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(8): 1030-1042. |
| [6] | 崔国庆, 胡溢玚, 娄颖洁, 周明霞, 李宇明, 王雅君, 姜桂元, 徐春明. CO2加氢制醇类催化剂的设计制备及性能研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(8): 1081-1100. |
| [7] | 洪梅, 高金强, 李彤, 杨世和. 原位刻蚀调控多级孔分子筛策略及其应用进展★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(8): 937-948. |
| [8] | 张艳东, 朱守非. 环丙烷骨架膦配体的研究展望★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(7): 777-783. |
| [9] | 郑文山, 高冠斌, 邓浩, 孙涛垒. Ag2Se@Ag2S核壳量子点的室温合成及其近红外荧光性能优化[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(7): 763-770. |
| [10] | 坎比努尔•努尔买买提, 王超, 罗时玮, 阿布都热西提•阿布力克木. 电化学条件下α,α,α-三卤(氯, 溴)甲基酮类化合物的选择性脱卤反应研究[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(6): 582-587. |
| [11] | 刘坜, 郑刚, 范国强, 杜洪光, 谭嘉靖. 4-酰基/氨基羰基/烷氧羰基取代汉斯酯参与的有机反应研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(6): 657-668. |
| [12] | 王俊, 许晓梅, 周姣龙, 赵雅男, 孙秀丽, 唐勇, 何素芳, 杨红梅. 新型无硫无磷醚-酯化合物的合成及其作为无灰摩擦改进剂的性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(5): 461-468. |
| [13] | 齐学平, 王飞, 张健. 后合成法构筑钛基金属有机框架及其应用[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(5): 548-558. |
| [14] | 魏颖, 周平, 陈鑫, 包秋景, 解令海. 有机纳米环/格的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(3): 289-308. |
| [15] | 陈俊畅, 张明星, 王殳凹. 晶态多孔材料合成方法的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(2): 146-157. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||