化学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 83 ›› Issue (12): 1480-1487.DOI: 10.6023/A25080288 上一篇 下一篇
所属专题: “中国青年化学家”合辑
研究论文
投稿日期:2025-08-25
发布日期:2025-10-10
作者简介:★ “中国青年化学家”专辑.
基金资助:
Hu Xuea, Shan Xua, Fuzhou Wanga,*( ), Changle Chenb,*(
), Changle Chenb,*( )
)
Received:2025-08-25
Published:2025-10-10
Contact:
* E-mail: wangfuzhou@ahu.edu.cn;changle@ustc.edu.cn
About author:★For the VSI "Rising Stars in Chemistry".
Supported by:文章分享

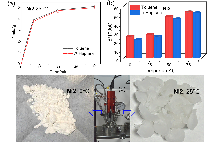
聚乙烯蜡具备乙烯低聚物所特有的物理特性, 可用作润滑剂、稳定剂及粘合剂, 广泛应用于塑料、橡胶、油墨和化妆品等多个领域, 其制备技术已从传统的热裂解工艺升级为催化乙烯聚合技术. 此研究合成了三种具有不同位阻效应吡啶亚胺镍催化剂Ni1~Ni3, 亚胺一侧包含具有大位阻特性的2,4,6-三(双(4-氟苯基)甲基)苯基取代基, 并探究了其在乙烯链行走聚合过程中的催化性能. 研究结果表明, 催化剂结构和聚合条件的变化直接影响乙烯的催化活性, 以及所制备聚乙烯蜡的分子量和支化度. 所有催化剂均成功合成了以甲基和长支链为主窄分散度的支化聚乙烯蜡. 通过调节聚合温度(0~75 ℃), 能够有效调控聚乙烯蜡的支化结构(15~61/1000C). 在较低温度条件下, 可获得主要含有甲基支链的粉末状聚乙烯固体. 该系列催化剂在工业常用溶剂正庚烷中, 表现出与甲苯几乎一致的卓越性能. 苯基取代的Ni2在正庚烷中的催化活性高达4.55×106 g•mol-1•h-1, 而在甲苯中则为4.72×106 g•mol-1•h-1. 该技术通过链行走聚合直接合成出支化可控的聚乙烯蜡材料, 其催化剂制备过程简洁且成本低廉, 具备高效催化性能, 对溶剂具有良好的耐受性, 有望为工业化聚乙烯蜡的高值化生产开辟新的思路和途径.
薛虎, 徐姗, 王福周, 陈昶乐. 大位阻亚胺吡啶镍催化乙烯链行走聚合制备支化聚乙烯蜡★[J]. 化学学报, 2025, 83(12): 1480-1487.
Hu Xue, Shan Xu, Fuzhou Wang, Changle Chen. Synthesis of Branched Polyethylene Wax using Bulky Iminopyridyl Nickel-Catalyzed Ethylene Chain-Walking Polymerization★[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2025, 83(12): 1480-1487.
| Entry | Cat. | T/℃ | Yieldb/g | Act.b | Mnc | PDIc | Bd | Tme/℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ni1 | 0 | 0.67 | 0.80 | 4600 | 1.93 | 26 | 121.1 |
| 2 | Ni1 | 25 | 2.15 | 2.58 | 9800 | 1.98 | 45 | 111.7 |
| 3 | Ni1 | 50 | 1.26 | 1.51 | 6100 | 2.17 | 50 | 92.1 |
| 4 | Ni1 | 75 | 0.88 | 1.06 | 3200 | 2.30 | 61 | — |
| 5 | Ni2 | 0 | 1.36 | 1.63 | 5600 | 2.46 | 25 | 121.6 |
| 6 | Ni2 | 25 | 3.93 | 4.72 | 22900 | 2.07 | 27 | 112.6 |
| 7 | Ni2 | 50 | 2.18 | 2.62 | 11300 | 2.12 | 48 | 94.6 |
| 8 | Ni2 | 75 | 1.07 | 1.28 | 4500 | 2.42 | 53 | — |
| 9 | Ni3 | 0 | 0.92 | 1.10 | 6100 | 1.85 | 17 | 123.3 |
| 10 | Ni3 | 25 | 3.01 | 3.61 | 52100 | 2.33 | 26 | 119.2 |
| 11 | Ni3 | 50 | 1.87 | 2.24 | 13900 | 2.45 | 39 | 99.7 |
| 12 | Ni3 | 75 | 0.99 | 1.19 | 5100 | 2.61 | 51 | — |
| Entry | Cat. | T/℃ | Yieldb/g | Act.b | Mnc | PDIc | Bd | Tme/℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ni1 | 0 | 0.67 | 0.80 | 4600 | 1.93 | 26 | 121.1 |
| 2 | Ni1 | 25 | 2.15 | 2.58 | 9800 | 1.98 | 45 | 111.7 |
| 3 | Ni1 | 50 | 1.26 | 1.51 | 6100 | 2.17 | 50 | 92.1 |
| 4 | Ni1 | 75 | 0.88 | 1.06 | 3200 | 2.30 | 61 | — |
| 5 | Ni2 | 0 | 1.36 | 1.63 | 5600 | 2.46 | 25 | 121.6 |
| 6 | Ni2 | 25 | 3.93 | 4.72 | 22900 | 2.07 | 27 | 112.6 |
| 7 | Ni2 | 50 | 2.18 | 2.62 | 11300 | 2.12 | 48 | 94.6 |
| 8 | Ni2 | 75 | 1.07 | 1.28 | 4500 | 2.42 | 53 | — |
| 9 | Ni3 | 0 | 0.92 | 1.10 | 6100 | 1.85 | 17 | 123.3 |
| 10 | Ni3 | 25 | 3.01 | 3.61 | 52100 | 2.33 | 26 | 119.2 |
| 11 | Ni3 | 50 | 1.87 | 2.24 | 13900 | 2.45 | 39 | 99.7 |
| 12 | Ni3 | 75 | 0.99 | 1.19 | 5100 | 2.61 | 51 | — |
| Entry | Cat. | T/℃ | Yieldb/g | Act.b | Mnc | PDIc | Bd | Tme/℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ni1 | 0 | 0.55 | 0.66 | 4300 | 1.96 | 26 | 121.8 |
| 2 | Ni1 | 25 | 2.01 | 2.41 | 8700 | 2.05 | 33 | 112.9 |
| 3 | Ni1 | 50 | 1.13 | 1.36 | 5300 | 2.13 | 48 | 88.4 |
| 4 | Ni1 | 75 | 0.76 | 0.91 | 3100 | 2.32 | 60 | — |
| 5 | Ni2 | 0 | 1.14 | 1.37 | 5200 | 2.01 | 21 | 122.0 |
| 6 | Ni2 | 25 | 3.79 | 4.55 | 21000 | 2.11 | 26 | 114.7 |
| 7 | Ni2 | 50 | 2.03 | 2.44 | 9800 | 2.30 | 45 | 94.1 |
| 8 | Ni2 | 75 | 0.95 | 1.14 | 3700 | 2.49 | 52 | — |
| 9 | Ni3 | 0 | 0.82 | 0.98 | 5800 | 1.91 | 15 | 123.5 |
| 10 | Ni3 | 25 | 2.81 | 3.37 | 43700 | 2.03 | 21 | 120.1 |
| 11 | Ni3 | 50 | 1.70 | 2.04 | 12100 | 2.38 | 35 | 113.0 |
| 12 | Ni3 | 75 | 0.86 | 1.03 | 4700 | 2.56 | 50 | — |
| Entry | Cat. | T/℃ | Yieldb/g | Act.b | Mnc | PDIc | Bd | Tme/℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ni1 | 0 | 0.55 | 0.66 | 4300 | 1.96 | 26 | 121.8 |
| 2 | Ni1 | 25 | 2.01 | 2.41 | 8700 | 2.05 | 33 | 112.9 |
| 3 | Ni1 | 50 | 1.13 | 1.36 | 5300 | 2.13 | 48 | 88.4 |
| 4 | Ni1 | 75 | 0.76 | 0.91 | 3100 | 2.32 | 60 | — |
| 5 | Ni2 | 0 | 1.14 | 1.37 | 5200 | 2.01 | 21 | 122.0 |
| 6 | Ni2 | 25 | 3.79 | 4.55 | 21000 | 2.11 | 26 | 114.7 |
| 7 | Ni2 | 50 | 2.03 | 2.44 | 9800 | 2.30 | 45 | 94.1 |
| 8 | Ni2 | 75 | 0.95 | 1.14 | 3700 | 2.49 | 52 | — |
| 9 | Ni3 | 0 | 0.82 | 0.98 | 5800 | 1.91 | 15 | 123.5 |
| 10 | Ni3 | 25 | 2.81 | 3.37 | 43700 | 2.03 | 21 | 120.1 |
| 11 | Ni3 | 50 | 1.70 | 2.04 | 12100 | 2.38 | 35 | 113.0 |
| 12 | Ni3 | 75 | 0.86 | 1.03 | 4700 | 2.56 | 50 | — |

| [27] |
doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b08975 pmid: 29261306 |
| [28] |
doi: 10.1039/c2dt31771k |
| [29] |
doi: 10.1007/s10118-022-2847-5 |
| [30] |
doi: 10.1002/pola.v55.20 |
| [31] |
doi: 10.1021/ja411945n pmid: 24450458 |
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
doi: 10.1002/anie.v55.42 |
| [34] |
doi: 10.1002/anie.v54.34 |
| [35] |
doi: 10.3390/polym9010010 |
| [36] |
doi: 10.1002/anie.v56.38 |
| [37] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.macromol.7b01087 |
| [38] |
doi: 10.1002/anie.v55.25 |
| [39] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.macromol.8b00467 |
| [40] |
doi: 10.1016/j.polymer.2017.08.050 |
| [41] |
doi: 10.1016/j.molcata.2014.11.004 |
| [42] |
doi: 10.1021/om400704h |
| [1] |
doi: 10.1360/TB-2021-1187 |
|
(陈敏, 陈昶乐, 科学通报, 2022, 67, 1881.)
|
|
| [2] |
doi: 10.6023/A23010004 |
|
(汪阳, 阎敬灵, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 275.)
doi: 10.6023/A23010004 |
|
| [3] |
doi: 10.6023/A23040162 |
|
(王子豪, 陈敏, 陈昶乐, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 559.)
doi: 10.6023/A23040162 |
|
| [4] |
|
|
(庄严俊, 中国科学:化学, 2025, 55, 1917.)
|
|
| [5] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00310 pmid: 26375718 |
| [6] |
doi: 10.1007/s10973-016-5706-1 |
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
doi: 10.1021/acsaem.1c02052 |
| [43] |
doi: 10.1039/D5PY00083A |
| [44] |
doi: 10.1016/S0022-328X(00)00291-6 |
| [45] |
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.4c02708 |
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
doi: 10.1039/c8dt02824a pmid: 30358779 |
| [48] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.organomet.8b00669 |
| [49] |
doi: 10.1007/s10118-014-1436-7 |
| [50] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jorganchem.2004.12.035 |
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
doi: 10.1039/c2dt30989k |
| [53] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.organomet.6b00165 |
| [54] |
doi: 10.1039/C6CC00457A |
| [55] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.organomet.7b00698 |
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
|
(曲琳, 李肖夫, 李汝贤, 刘金伟, 广东化工, 2025, 52, 77.)
|
|
| [12] |
|
|
(吴杰, 李阳培, 付延明, 李有桂, 化工矿物与加工, 2024, 53, 1.)
|
|
| [13] |
|
|
(徐珂, 石油化工, 2025, 54, 954.)
|
|
| [14] |
doi: 10.3390/ma13010018 |
| [15] |
doi: 10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2007.08.022 |
| [16] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.macromol.9b02647 |
| [17] |
doi: 10.6023/A21080377 |
|
(李勇, 王晓艳, 唐勇, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 1320.)
doi: 10.6023/A21080377 |
|
| [58] |
doi: 10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2019.05.015 |
| [59] |
doi: 10.1021/cr068437y |
| [18] |
doi: 10.6023/A22020066 |
|
(王玉银, 胡小强, 穆红亮, 夏艳, 迟悦, 简忠保, 化学学报, 2022, 80, 741.)
doi: 10.6023/A22020066 |
|
| [19] |
doi: 10.1021/ma062214s |
| [20] |
doi: 10.1002/aoc.v21:8 |
| [21] |
doi: 10.1126/science.abi8183 |
| [22] |
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.4c02385 |
| [23] |
doi: 10.1021/ja00128a054 |
| [24] |
doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2021.213802 |
| [25] |
doi: 10.1002/anie.201814634 pmid: 30719812 |
| [26] |
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.6b03394 |
| [1] | 王子豪, 陈敏, 陈昶乐. 不对称α-二亚胺镍催化制备聚烯烃弹性体★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(6): 559-564. |
| [2] | 王新科, Sit Met-Met, 孙杰, 唐勇, 谢作伟. 边臂修饰的水杨醛亚胺第四族金属配合物的合成、结构及其乙烯聚合行为研究[J]. 化学学报, 2012, 70(18): 1909-1916. |
| [3] | 袁建超, 刘玉凤, 梅铜简, 王学虎. 高活性a-二亚胺基Ni(II)配合物的合成、表征及其催化乙烯聚合研究[J]. 化学学报, 2011, 69(07): 798-802. |
| [4] | 何静,段雪,R.F. Howe. Cr/MCM-41催化剂的结构特征及其纳米尺寸孔内聚乙烯的形成[J]. 化学学报, 1999, 57(2): 125-131. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||