化学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 83 ›› Issue (12): 1488-1497.DOI: 10.6023/A25060226 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
石力双a,†, 戴雅男a,†, 伍伟豪a, 李世辉b,*( ), 牟泽怀a,*(
), 牟泽怀a,*( )
)
投稿日期:2025-06-17
发布日期:2025-08-25
基金资助:
Lishuang Shia, Yanan Daia, Weihao Wua, Shihui Lib,*( ), Zehuai Moua,*(
), Zehuai Moua,*( )
)
Received:2025-06-17
Published:2025-08-25
Contact:
* E-mail: shihui-li@ciac.ac.cn;mouzehuai@nbu.edu.cn
About author:Supported by:文章分享
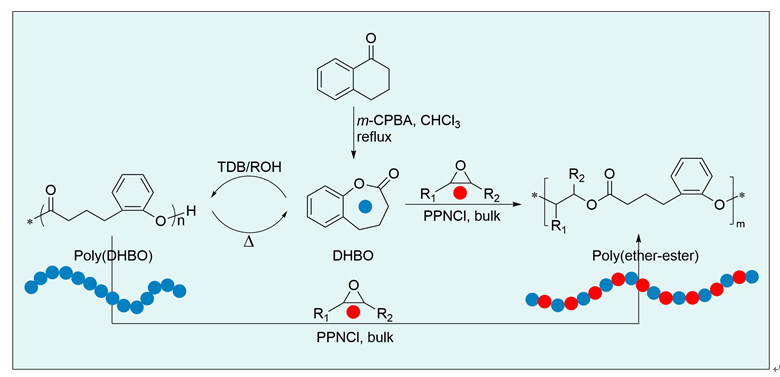
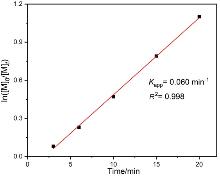
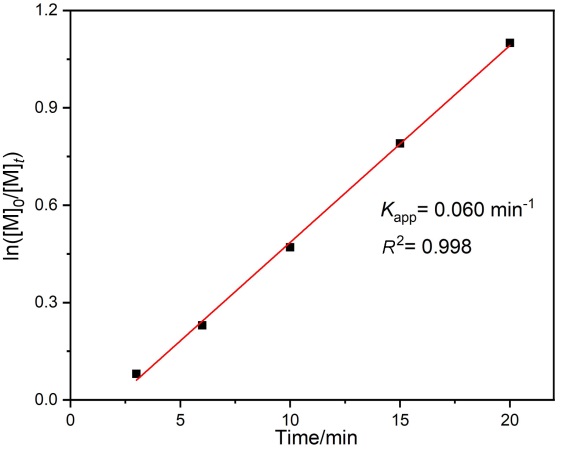
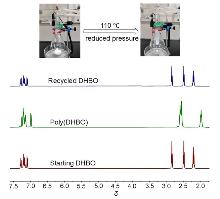
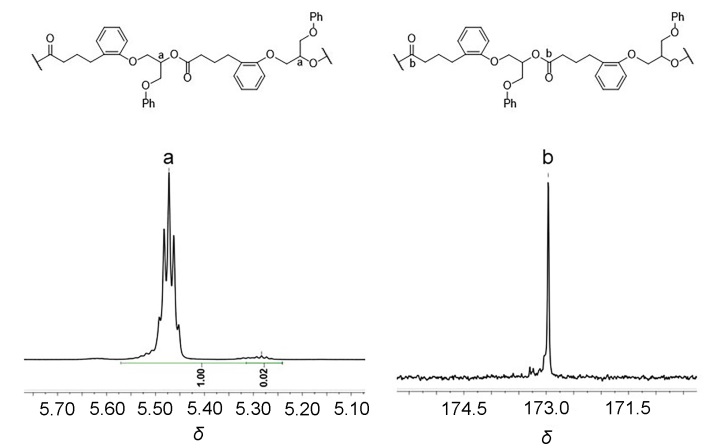
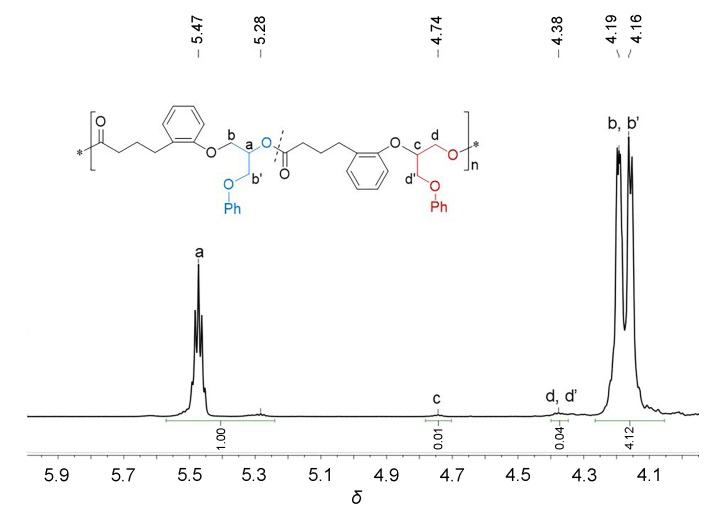
聚酯作为一类重要的高分子材料, 凭借其优异的性能在众多领域得到广泛应用, 并在全球塑料市场中占据约10%的份额, 对塑料经济的发展起到了关键作用. 然而, 废弃塑料所带来的日益严重的环境问题, 促使学术界和工业界将目光聚焦于开发具有闭环化学回收性能的新型聚酯材料. 以市售的α-四氢萘酮作为起始原料, 通过简单的Baeyer- Villiger氧化反应合成了一种芳香族苯并己内酯单体, 即4,5-二氢苯并[b]氧杂䓬-2(3H)-酮(DHBO). 利用1,5,7-三氮杂二环[4,4,0]癸-5-烯(TBD)为催化剂, 深入研究了不同聚合条件下DHBO的开环聚合行为, 制备了一种玻璃化转变温度Tg为4.8 ℃, 热分解温度Td,5%为194 ℃的聚合物Poly(DHBO). 动力学实验表明在甲苯中聚合速率对单体浓度为一级反应. 该聚合物在无催化剂、110 ℃减压条件下能快速热降解为原始单体DHBO, 单体回收率高达97%, 纯度达到99%, 展现出优异的化学回收性能. 此外, 以双(三苯基正膦基)氯化铵(PPNCl)为催化剂, 采用本体熔融聚合方法, 使DHBO与多种环氧化合物[苯基缩水甘油醚(PGE)、烯丙基缩水甘油醚(AGE)、1,2-环氧丁烷(BO)、(R)-BO、(S)-BO、1,2-环氧己烷(HO)及环氧环己烷(CHO)]发生开环共聚反应, 成功制备了一系列聚(醚-酯)材料. 采用核磁共振氢谱(1H NMR)、碳谱(13C NMR)、扩散排序谱(DOSY NMR)以及基质辅助激光解吸飞行时间质谱(MALDI-TOF MS)对代表性共聚合物进行表征, 证实所得聚(醚-酯)为含有醚键和酯基高度交替序列的共聚物. 通过对这些交替共聚物的形成机理进行深入探究, 进一步揭示了其独特的聚合反应机制.
石力双, 戴雅男, 伍伟豪, 李世辉, 牟泽怀. 苯并己内酯的开环聚合及其与环氧化合物共聚合研究[J]. 化学学报, 2025, 83(12): 1488-1497.
Lishuang Shi, Yanan Dai, Weihao Wu, Shihui Li, Zehuai Mou. Ring-opening Polymerization of Benzo-fused Caprolactone and its Copolymerization with Epoxides[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2025, 83(12): 1488-1497.
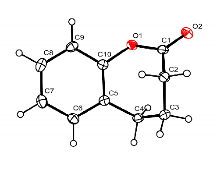
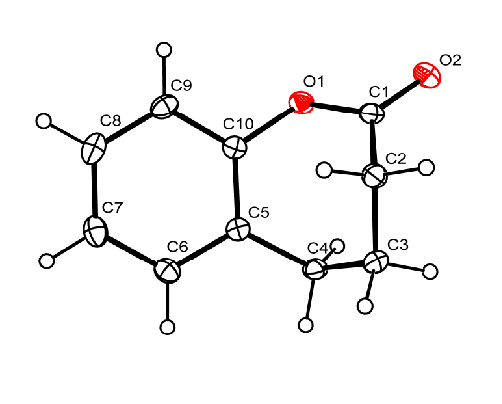
| Entry | [M]0/[Cat.]/[ROH] | Solvent | [M]0/(mol•L-1) | t/h | T/℃ | Conv.b/% | Mn,GPCc/(kg•mol-1) | Ðc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 100/1/1 | toluene | 1 | 5 | r.t. | 73 | 4.79 | 1.88 |
| 2 | 100/1/1 | toluene | 2 | 5 | r.t. | 85 | 7.17 | 1.86 |
| 3 | 100/1/1 | toluene | 4 | 5 | r.t. | 93 | 6.06 | 1.62 |
| 4 | 100/1/1 | THF | 2 | 5 | r.t. | 77 | 6.03 | 1.62 |
| 5 | 100/1/1 | DMF | 2 | 5 | r.t. | 36 | 1.36 | 1.89 |
| 6 | 100/1/1 | DCM | 2 | 5 | r.t. | 48 | 3.00 | 1.24 |
| 7 | 100/1/1 | DCM | 2 | 24 | r.t. | 55 | 8.75 | 2.15 |
| 8 | 100/1/1 | — | — | 10 min | 90 | 90 | 7.49 | 2.09 |
| 9 | 100/1/1 | — | — | 10 min | 110 | 92 | 6.21 | 1.93 |
| 10 | 300/1/1 | — | — | 0.5 | 90 | 84 | 9.00 | 1.89 |
| 11 | 500/1/1 | — | — | 0.5 | 90 | 80 | 10.20 | 2.00 |
| Entry | [M]0/[Cat.]/[ROH] | Solvent | [M]0/(mol•L-1) | t/h | T/℃ | Conv.b/% | Mn,GPCc/(kg•mol-1) | Ðc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 100/1/1 | toluene | 1 | 5 | r.t. | 73 | 4.79 | 1.88 |
| 2 | 100/1/1 | toluene | 2 | 5 | r.t. | 85 | 7.17 | 1.86 |
| 3 | 100/1/1 | toluene | 4 | 5 | r.t. | 93 | 6.06 | 1.62 |
| 4 | 100/1/1 | THF | 2 | 5 | r.t. | 77 | 6.03 | 1.62 |
| 5 | 100/1/1 | DMF | 2 | 5 | r.t. | 36 | 1.36 | 1.89 |
| 6 | 100/1/1 | DCM | 2 | 5 | r.t. | 48 | 3.00 | 1.24 |
| 7 | 100/1/1 | DCM | 2 | 24 | r.t. | 55 | 8.75 | 2.15 |
| 8 | 100/1/1 | — | — | 10 min | 90 | 90 | 7.49 | 2.09 |
| 9 | 100/1/1 | — | — | 10 min | 110 | 92 | 6.21 | 1.93 |
| 10 | 300/1/1 | — | — | 0.5 | 90 | 84 | 9.00 | 1.89 |
| 11 | 500/1/1 | — | — | 0.5 | 90 | 80 | 10.20 | 2.00 |
| Entry | [Epoxide]0/[M]0/[PPNCl]0 | Epoxide | T/℃ | Conv.b/% | Alternatingc/% | Regioselectivityc/% | Mnd/kDa | Ðd |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | —/100/1 | — | 110 | 0 | — | — | ||
| 2 | 20/—/1 | PGE | 110 | 16 | — | — | ||
| 3 | 200/100/1 | PGE | 110 | >99 | 98 | 99 | 14.4 | 1.45 |
| 4 | 200/100/1 | PGE | 90 | 95 | 98 | 98 | 15.0 | 1.47 |
| 5 | 200/100/1 | PGE | 60 | 75 | 96 | 94 | 4.75 | 1.31 |
| 6 | 200/100/1 | AGE | 110 | >99 | 96 | 97 | 16.1 | 1.38 |
| 7 | 200/100/1 | BO | 110 | >99 | 97 | 97 | 13.0 | 1.37 |
| 8e | 200/100/1 | R-BO | 110 | >99 | 98 | 97 | 8.9 | 1.67 |
| 9e | 200/100/1 | S-BO | 110 | >99 | 98 | 97 | 6.6 | 1.62 |
| 10 | 200/100/1 | HO | 110 | >99 | 96 | 98 | 8.8 | 1.34 |
| 11 | 200/100/1 | CHO | 110 | >99 | 95 | — | 11.3 | 1.39 |
| Entry | [Epoxide]0/[M]0/[PPNCl]0 | Epoxide | T/℃ | Conv.b/% | Alternatingc/% | Regioselectivityc/% | Mnd/kDa | Ðd |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | —/100/1 | — | 110 | 0 | — | — | ||
| 2 | 20/—/1 | PGE | 110 | 16 | — | — | ||
| 3 | 200/100/1 | PGE | 110 | >99 | 98 | 99 | 14.4 | 1.45 |
| 4 | 200/100/1 | PGE | 90 | 95 | 98 | 98 | 15.0 | 1.47 |
| 5 | 200/100/1 | PGE | 60 | 75 | 96 | 94 | 4.75 | 1.31 |
| 6 | 200/100/1 | AGE | 110 | >99 | 96 | 97 | 16.1 | 1.38 |
| 7 | 200/100/1 | BO | 110 | >99 | 97 | 97 | 13.0 | 1.37 |
| 8e | 200/100/1 | R-BO | 110 | >99 | 98 | 97 | 8.9 | 1.67 |
| 9e | 200/100/1 | S-BO | 110 | >99 | 98 | 97 | 6.6 | 1.62 |
| 10 | 200/100/1 | HO | 110 | >99 | 96 | 98 | 8.8 | 1.34 |
| 11 | 200/100/1 | CHO | 110 | >99 | 95 | — | 11.3 | 1.39 |
| [1] |
doi: 10.1126/science.aba3656 |
| [2] |
doi: 10.1126/science.abb0354 pmid: 34210876 |
| [3] |
doi: 10.1039/D2PY01613C |
| [4] |
doi: 10.1002/cjoc.v43.3 |
| [5] |
doi: 10.6023/A22050235 |
|
(蔡中正, 刘野, 陶友华, 朱剑波, 化学学报, 2022, 80, 1165.)
doi: 10.6023/A22050235 |
|
| [6] |
doi: 10.1002/cjoc.v42.17 |
| [7] |
doi: 10.1002/cjoc.v41.13 |
| [8] |
doi: 10.1002/cjoc.v42.5 |
| [9] |
doi: 10.1039/D4CS00663A |
| [10] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.3c00848 |
| [11] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.macromol.3c01912 |
| [12] |
|
|
(张红明, 赵君宇, 高凤翔, 刘顺杰, 周庆海, 王献红, 高分子学报, 2022, 53, 1142.)
|
|
| [13] |
doi: 10.1039/D3PY01218B |
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2023.144032 |
| [16] |
doi: 10.1038/s41893-023-01118-4 |
| [17] |
doi: 10.1039/C5PY01606A |
| [18] |
doi: 10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2019.108984 |
| [19] |
doi: 10.1039/D2PY01491B |
| [20] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.macromol.1c00497 |
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
doi: 10.1021/jacs.1c10162 |
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.macromol.2c02172 |
| [25] |
doi: 10.1021/ma070433n |
| [26] |
doi: 10.1002/pola.v45:16 |
| [27] |
doi: 10.1039/c4cc01566e |
| [28] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.macromol.7b02042 |
| [29] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.macromol.6b00840 |
| [30] |
|
|
(宋艳娇, 何江华, 张越涛, 高分子学报, 2022, 53, 1112.)
|
|
| [31] |
doi: 10.1002/pola.v60.24 |
| [32] |
doi: 10.1007/s10118-025-3336-4 |
| [33] |
doi: 10.1039/D1GC04478H |
| [34] |
doi: 10.1021/ol5029157 pmid: 25384601 |
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
doi: 10.1039/D2PY00185C |
| [37] |
doi: 10.1021/acsmacrolett.0c00831 |
| [38] |
doi: 10.1039/D2PY00405D |
| [39] |
doi: 10.1039/C9PY00377K |
| [1] | 黄皓毅, 谢敏, 黄玉婷, 崔嘉豪, 蔡中正, 朱剑波. 螺环-salen配合物催化开环聚合制备立构规整、功能化聚羟基脂肪酸酯★[J]. 化学学报, 2025, 83(8): 810-815. |
| [2] | 王玉娜, 王超, 马海燕. 苯并噁唑取代氨基酚氧基锌氯化物催化外消旋丙交酯开环聚合研究[J]. 化学学报, 2025, 83(1): 25-35. |
| [3] | 王镜焱, 马海燕. 2,6-二亚甲基吡啶桥联双(氨基酚氧基)钠、钾配合物的合成及催化外消旋丙交酯开环聚合研究[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(10): 1058-1068. |
| [4] | 杨贯文, 伍广朋. 模块化双功能有机硼氮和硼磷催化体系的设计及其催化转化★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(11): 1551-1565. |
| [5] | 江金辉, 朱云卿, 杜建忠. 开环聚合诱导自组装的挑战与展望[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(8): 719-724. |
| [6] | 李荣烨, Khiman Mehul, 盛力, 孙静. 两亲性聚氨基酸三嵌段共聚物构筑pH/溶剂可控多级纳米结构[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(11): 1235-1239. |
| [7] | 布美热木·克力木, 马海燕. 非对称β-二亚氨基镁络合物催化丙交酯、己内酯开环聚合/共聚研究[J]. 化学学报, 2018, 76(2): 121-132. |
| [8] | 张弛, 李杰, 罗运军, 葛震. 微波合成3,3'-双叠氮甲基环氧丁烷-3-叠氮甲基-3'-甲基环氧丁烷无规共聚物[J]. 化学学报, 2012, 0(04): 492-498. |
| [9] | 胡承波, 傅亚, 向鸿照, 孙娇霞, 阮长顺, 李香, 向燕, 彭琴, 王远亮. 双(烷氧-亚胺芳氧)基钛(IV)配合物催化D,L-丙交酯开环聚合、动力学及机理[J]. 化学学报, 2011, 69(21): 2574-2582. |
| [10] | 李启蒸, 张国艺, 黄晋, 赵巧玲, 魏柳荷, 何占航, 马志. 结构可控的聚亚甲基/聚乳酸嵌段共聚物的合成及其性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2011, 69(04): 497-502. |
| [11] | 王月强, 唐萍, 杨玉良. A/B/A-b-B/(A-b-B)4四元共混体系相行为的自洽场理论研究[J]. 化学学报, 2011, 69(01): 89-94. |
| [12] | 徐旭,伍国琳,张洁,王亦农,范云鸽,马建标. 具有乙二醇侧链的聚谷氨酸酯的合成、表征及其两亲性[J]. 化学学报, 2008, 66(9): 1102-1106. |
| [13] | 朱荣秀,张冬菊,王若曦,刘成卜. 双官能团硫脲催化丙交酯开环聚合反应的理论研究[J]. 化学学报, 2008, 66(8): 885-889. |
| [14] | 甄红宇,罗潺,朱德喜,叶辉,刘旭. 基于不同辅助配体螯合电磷光聚合物的合成与性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2008, 66(5): 557-562. |
| [15] | 华佳捷,杨建,胡艳飞,韦嘉,李速明. 低毒锌类催化剂制备聚乳酸的研究[J]. 化学学报, 2008, 66(24): 2730-2734. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||