化学学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 79 ›› Issue (8): 1037-1041.DOI: 10.6023/A21050212 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
投稿日期:2021-05-13
发布日期:2021-07-04
通讯作者:
臧双全
基金资助:
Hao-Nan Qin, Zhao-Yang Wang, Shuang-Quan Zang( )
)
Received:2021-05-13
Published:2021-07-04
Contact:
Shuang-Quan Zang
Supported by:文章分享

铜基纳米材料在发光和(生物)化学传感领域展现出广阔的应用前景. 铜纳米团簇作为一种新型的纳米材料, 由于其具有原子级精确的结构而引起了研究人员的广泛关注, 但是合成稳定并且具有优异性能的铜簇仍然具有挑战性. 本工作通过引入还原剂(NaBH4)成功地制备出一种新型的巯基咪唑配体保护的一价铜纳米团簇[Cu13(SR)12]NO3 (Cu13 NC, 其中RSH=2-巯基苯并咪唑), 并通过单晶X射线衍射分析和电喷雾电离质谱(ESI-MS)对其结构和组成进行了表征. Cu13 NC的金属骨架可以看成是三个三角双锥共享一个或两个顶点构成, 并通过简单的桥联模式被12个巯基配体保护. 固态Cu13 NC具有良好的稳定性及亮红色的发光(λem=627 nm). 同时, 结构的两端有两个裸露的铜原子, 这使其在电化学检测H2O2的实验中表现出良好的电化学活性. 本工作为更好地研究纳米铜簇的结构和其光、电性能之间的联系提供了机会.
秦浩男, 王朝阳, 臧双全. 原子级结构精确Cu13团簇的光致发光和电化学传感研究[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(8): 1037-1041.
Hao-Nan Qin, Zhao-Yang Wang, Shuang-Quan Zang. Photoluminescence and Electrochemical Sensing of Atomically Precise Cu13 Cluster[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(8): 1037-1041.
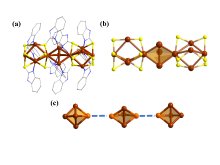

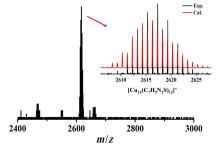

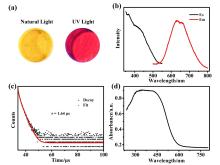

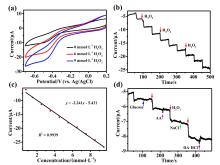

| [1] |
Jin, R.; Zeng, C.; Zhou, M.; Chen, Y. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 10346.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00703 |
| [2] |
Wan, X. K.; Cheng, X. L.; Tang, Q.; Han, Y. Z.; Hu, G.; Jiang, D. E.; Wang, Q. M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 9451.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b04622 |
| [3] |
Shen, Y. L.; Jin, J. L.; Duan, G. X.; Xie, Y. P.; Lu, X. Acta Chim. Sinica 2020, 78, 1255. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A20070317 |
|
( 沈扬林, 金俊玲, 段光雄, 谢云鹏, 卢兴, 化学学报, 2020, 78, 1255.)
doi: 10.6023/A20070317 |
|
| [4] |
Su, Y. M.; Wang, Z.; Schein, S.; Tung, C. H.; Sun, D. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3316.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-17198-1 |
| [5] |
Edwards, A. J.; Dhayal, R. S.; Liao, P. K.; Liao, J. H.; Chiang, M. H.; Piltz, R. O.; Kahlal, S.; Saillard, J. Y.; Liu, C. W. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 7214.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v53.28 |
| [6] |
Deng, G.; Malola, S.; Yan, J.; Han, Y.; Yuan, P.; Zhao, C.; Yuan, X.; Lin, S.; Tang, Z.; Teo, B. K.; Hakkinen, H.; Zheng, N. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 3421.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201800327 |
| [7] |
Zhu, M.; Qian, H.; Meng, X.; Jin, S.; Wu, Z.; Jin, R. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 3963.
doi: 10.1021/nl202288j |
| [8] |
Han, Z.; Dong, X. Y.; Luo, P.; Li, S.; Wang, Z. Y.; Zang, S. Q.; Mak, T. C.W. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6,eaay0107.
|
| [9] |
Song, Y.; Weng, S.; Li, H.; Yu, H.; Zhu, M. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 58, 7136.
doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.9b00547 |
| [10] |
He, W. M.; Zhou, Z.; Han, Z.; Li, S.; Zhou, Z.; Ma, L. F.; Zang, S. Q. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 8505.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v60.15 |
| [11] |
Kang, X.; Zhu, M. Z. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 2422.
doi: 10.1039/c8cs00800k pmid: 30838373 |
| [12] |
Liu, H.; Hong, G.; Luo, Z.; Chen, J.; Chang, J.; Gong, M.; He, H.; Yang, J.; Yuan, X.; Li, L.; Mu, X.; Wang, J.; Mi, W.; Luo, J.; Xie, J.; Zhang, X. D. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31,e1901015.
|
| [13] |
Tang, Q.; Lee, Y.; Li, D. Y.; Choi, W.; Liu, C. W.; Lee, D.; Jiang, D. E. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 9728.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b05591 |
| [14] |
Chen, Y.; Liu, C.; Tang, Q.; Zeng, C.; Higaki, T.; Das, A.; Jiang, D. E.; Rosi, N. L.; Jin, R. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 1482.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.5b12094 |
| [15] |
Wu, Z. Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin. 2017, 33, 1930. (in Chinese)
|
|
( 伍志鲲, 物理化学学报, 2017, 33, 1930.)
|
|
| [16] |
Zhang, Y.; Wu, M.; Wu, M.; Guo, L.; Cao, L.; Wu, H.; Zhang, X. Acta Chim. Sinica 2018, 76, 709. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A18060225 |
|
( 张燕燕, 武明豪, 武明杰, 国林沛, 曹琳, 吴虹仪, 张雪宁, 化学学报, 2018, 76, 709.)
doi: 10.6023/A18060225 |
|
| [17] |
Yan, J.; Su, H.; Yang, H.; Malola, S.; Lin, S.; Hakkinen, H.; Zheng, N. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 11880.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.5b07186 |
| [18] |
Liao, L.; Wang, C.; Zhuang, S.; Yan, N.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Deng, H.; Wu, Z. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 731.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v59.2 |
| [19] |
Jin, F. M.; Dong, H. W.; Zhao, Y.; Zhuang, S. L.; Liao, L. W.; Yan, N.; Gu, W. M.; Zha, J.; Yuan, J. Y.; Li, J.; Deng, H. T.; Gan, Z. B.; Yang, J. L.; Wu, Z. K. Acta Chim. Sinica 2020, 78, 407.
doi: 10.6023/A20040134 |
| [20] |
Wang, Z. Y.; Wang, M. Q.; Li, Y. L.; Luo, P.; Jia, T. T.; Huang, R. W.; Zang, S. Q.; Mak, T. C.W. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 1069.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b11338 |
| [21] |
Dai, L.; Qin, Q.; Wang, P.; Zhao, X.; Hu, C.; Liu, P.; Qin, R.; Chen, M.; Ou, D.; Xu, C.; Mo, S.; Wu, B.; Fu, G.; Zhang, P.; Zheng, N. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1701069.
doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1701069 |
| [22] |
Gawande, M. B.; Goswami, A.; Felpin, F. X.; Asefa, T.; Huang, X.; Silva, R.; Zou, X.; Zboril, R.; Varma, R. S. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 3722.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00482 pmid: 26935812 |
| [23] |
Guo, Y.; Cao, F.; Lei, X.; Mang, L.; Cheng, S.; Song, J. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 4852.
doi: 10.1039/C6NR00145A |
| [24] |
Iyengar, P.; Huang, J.; De Gregorio, G. L.; Gadiyar, C.; Buonsanti, R. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 8796.
doi: 10.1039/C9CC02522G |
| [25] |
Kas, R.; Kortlever, R.; Milbrat, A.; Koper, M. T.; Mul, G.; Baltrusaitis, J. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 12194.
doi: 10.1039/C4CP01520G |
| [26] |
Lan, Y.; Xie, Y.; Chen, J.; Hu, Z.; Cui, D. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 8068.
doi: 10.1039/C9CC02891A |
| [27] |
Alayon, E. M.C.; Nachtegaal, M.; Bodi, A.; van Bokhoven, J. A. ACS Catal. 2013, 4, 16.
doi: 10.1021/cs400713c |
| [28] |
Yang, L.; Kinoshita, S.; Yamada, T.; Kanda, S.; Kitagawa, H.; Tokunaga, M.; Ishimoto, T.; Ogura, T.; Nagumo, R.; Miyamoto, A.; Koyama, M. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 5348.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v49:31 |
| [29] |
Gao, X.; Lu, Y.; Liu, M.; He, S.; Chen, W. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 4050.
doi: 10.1039/C5TC00246J |
| [30] |
Jia, X.; Li, J.; Han, L.; Ren, J.; Yang, X.; Wang, E. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 3311.
doi: 10.1021/nn3002455 |
| [31] |
Jia, X.; Yang, X.; Li, J.; Li, D.; Wang, E. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 237.
doi: 10.1039/C3CC47771A |
| [32] |
Yang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Shi, Y.; Long, C.; Zhang, B.; Yan, S.; Chang, L.; Tang, Z. Acta Chim. Sinica 2020, 78, 980. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A20050165 |
|
( 杨忠杰, 张小飞, 施亚男, 隆昶, 张彬灏, 闫书豪, 常琳, 唐智勇, 化学学报, 2020, 78, 980.)
doi: 10.6023/A20050165 |
|
| [33] |
Cook, A. W.; Jones, Z. R.; Wu, G.; Scott, S. L.; Hayton, T. W. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 394.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b10960 |
| [34] |
Han, B. L.; Liu, Z.; Feng, L.; Wang, Z.; Gupta, R. K.; Aikens, C. M.; Tung, C. H.; Sun, D. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 5834.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.0c01053 |
| [35] |
Nguyen, D.; Jones, Z. R.; Leto, D. F.; Wu, G.; Scott, S. L.; Hayton, T. W. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 8385.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.6b03879 |
| [36] |
Xie, Y. -P.; Wen, J. -B.; Pan, C. -W.; Duan, G. -X.; Li, L. -Y.; Lu, X. Cryst. Growth Des. 2019, 19, 5791.
doi: 10.1021/acs.cgd.9b00803 |
| [37] |
Yuan, P.; Chen, R.; Zhang, X.; Chen, F.; Yan, J.; Sun, C.; Ou, D.; Peng, J.; Lin, S.; Tang, Z.; Teo, B. K.; Zheng, L. S.; Zheng, N. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 835.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v58.3 |
| [38] |
Zhang, M. M.; Dong, X. Y.; Wang, Z. Y.; Li, H. Y.; Li, S. J.; Zhao, X.; Zang, S. Q. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 10052.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v59.25 |
| [39] |
Anzlovar, A.; Orel, Z. C.; Zigon, M. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2007, 27, 987.
doi: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2006.04.131 |
| [40] |
Wei, W.; Lu, Y.; Chen, W.; Chen, S. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 2060.
doi: 10.1021/ja109303z |
| [41] |
Kawasaki, H.; Kosaka, Y.; Myoujin, Y.; Narushima, T.; Yonezawa, T.; Arakawa, R. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 7740.
doi: 10.1039/c1cc12346g |
| [42] |
Lu, Y.; Wei, W.; Chen, W. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2012, 57, 41.
doi: 10.1007/s11434-011-4896-y |
| [43] |
Khatun, E.; Bodiuzzaman, M.; Sugi, K. S.; Chakraborty, P.; Paramasivam, G.; Dar, W. A.; Ahuja, T.; Antharjanam, S.; Pradeep, T. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 5753.
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.9b01189 pmid: 31017759 |
| [44] |
Han, H.; Yao, Y.; Bhargava, A.; Wei, Z.; Tang, Z.; Suntivitch, J.; Voznyy, O.; Robinson, R. D. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 14495.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.0c04764 |
| [45] |
Liu, M.; Liu, R.; Chen, W. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 45, 206.
doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2013.02.010 |
| [46] |
Xu, F.; Deng, M.; Li, G.; Chen, S.; Wang, L. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 88, 59.
doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2012.10.070 |
| [1] | 陈慧敏, 王龙, 张盼, 白西林, 周国君. 高效率Tb3+单掺绿色荧光粉的光致/应力发光研究[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(7): 771-776. |
| [2] | 张少秦, 李美清, 周中军, 曲泽星. 多共振热激活延迟荧光过程的理论研究[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(2): 124-130. |
| [3] | 梁华润, 马浩轩, 段新荣, 于洁, 王灏珉, 李硕, 朱梦嘉, 陈爱兵, 郑晖, 张莹莹. 柔性电化学传感器及其在无创医学检测中的应用★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(10): 1402-1419. |
| [4] | 王文涛, 赵高崇, 杨柳, 周意诚, 丁黎明. 基于磁响应光子晶体与量子点的多重变色防伪研究[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(12): 1576-1582. |
| [5] | 许道兰, 杨颖, 范文涛, 何宗兵, 邹家丰, 冯磊, 李漫波, 伍志鲲. 单个、自生的RP-Au-PR结构增强金属纳米团簇的光致发光量子产率19倍[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(1): 1-6. |
| [6] | 孙延慧, 齐有啸, 申优, 井翠洁, 陈笑笑, 王新星. 基于RGO-Au-ZIF-8复合材料的电化学传感器制备及其在铅离子和铜离子同时检测中的应用[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(2): 147-154. |
| [7] | 王琴, 聂舟, 胡宇芳, 姚守拙. 基于铜-巯基配位聚合物电化学催化的新型乙酰胆碱酯酶电化学传感器[J]. 化学学报, 2017, 75(11): 1109-1114. |
| [8] | 于小雯, 盛凯旋, 陈骥, 李春, 石高全. 基于石墨烯修饰电极的电化学生物传感[J]. 化学学报, 2014, 72(3): 319-332. |
| [9] | 范存华, 杨逸群, 赵伟, 肖宇, 罗静, 刘晓亚. 双亲聚合物分子印迹自组装胶束电化学传感器研究[J]. 化学学报, 2013, 71(06): 934-940. |
| [10] | 谭学才, 王琳, 李鹏飞, 龚琦, 刘力, 赵丹丹, 雷福厚, 黄在银. 以马来松香丙烯酸乙二醇酯为交联剂的茶碱分子印迹膜电化学传感器的研究[J]. 化学学报, 2012, 70(9): 1088-1094. |
| [11] | 李建平, 李玉平, 魏小平. 基于三聚氰胺膜电催化与酶催化放大的分子印迹电化学传感器测定绿麦隆[J]. 化学学报, 2012, 70(17): 1853-1857. |
| [12] | 杜燕荣, 焦桓, 何地平. 水热法合成AgGd0.9Eu0.1(WO4)2及其发光性能[J]. 化学学报, 2011, 69(21): 2550-2554. |
| [13] | 谢劲松, 吴庆生. 一锅甘氨酸/水热法合成具有发光性能的NdOHCO3纳米盘及三维纳米结构[J]. 化学学报, 2011, 69(16): 1865-1873. |
| [14] | 杨嘉伟, 方正, 潘义, 刘仁红, 王佳黎, 但德忠. 甲醛电化学传感器多孔气体扩散电极不同催化层结构与响应性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2011, 69(01): 65-70. |
| [15] | 张朝晖, 胡宇芳, 张华斌, 曹娇, 姚守拙. 新型多壁碳纳米管/白藜芦醇印迹溶胶-凝胶层层组装电化学传感器研究[J]. 化学学报, 2010, 68(05): 431-436. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||