化学学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 80 ›› Issue (3): 259-264.DOI: 10.6023/A21120585 上一篇 下一篇
所属专题: 中国科学院青年创新促进会合辑
研究论文
赵锦旭a,b, 张铭枢a, 陈文发a, 姜小明a, 刘彬文a,*( ), 郭国聪a,*(
), 郭国聪a,*( )
)
投稿日期:2021-12-27
发布日期:2022-01-12
通讯作者:
刘彬文, 郭国聪
作者简介:基金资助:
Jinxu Zhaoa,b, Mingshu Zhanga, Wenfa Chena, Xiaoming Jianga, Binwen Liua( ), Guocong Guoa(
), Guocong Guoa( )
)
Received:2021-12-27
Published:2022-01-12
Contact:
Binwen Liu, Guocong Guo
About author:Supported by:文章分享

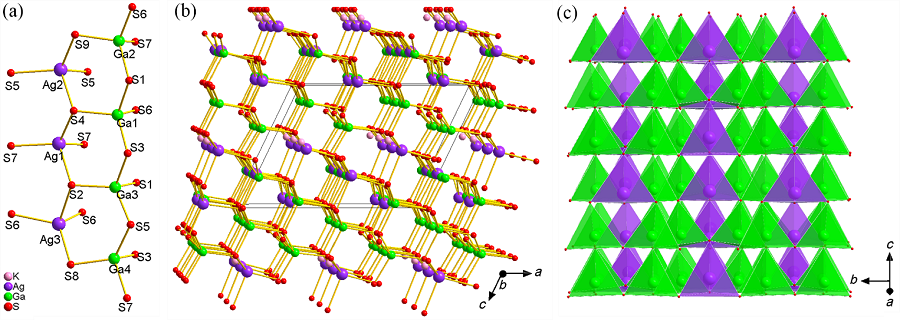
兼具大的非线性光学(NLO)效应和高的激光损伤阈值(LIDT)是中远红外NLO材料领域最具挑战性的问题之一. 这里, 将碱金属离子K+引入到以黄铜矿AgGaS2为基底的材料中, 获得硫属化合物KAg3Ga8S14. 它的晶体结构采用与黄铜矿相类似的三维蜂窝状开放框架, 其中畸变四面体GaS4和AgS4以高度定向的方式排列, 产生中等的倍频效应 (0.4×AgGaS2 @1910 nm). 值得注意的是, 通过拓宽带隙(2.95 eV), 该化合物拥有高的激光损伤阈值(4.6×AgGaS2 @1064 nm). 此外, 通过理论计算表明四面体GaS4和AgS4决定硫属化合物KAg3Ga8S14的NLO光学性质.
赵锦旭, 张铭枢, 陈文发, 姜小明, 刘彬文, 郭国聪. KAg3Ga8S14: 一种高激光损伤阈值的中远红外非线性光学材料※[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(3): 259-264.
Jinxu Zhao, Mingshu Zhang, Wenfa Chen, Xiaoming Jiang, Binwen Liu, Guocong Guo. KAg3Ga8S14: An Mid- and Far-infrared Nonlinear Optical Material Exhibiting High Laser-induced Damage Threshold※[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(3): 259-264.
| Empirical formula | KAg3Ga8S14 |
|---|---|
| Fw | 1369.31 |
| Temperature/K | 293(2) |
| Space group | Cm |
| a/nm | 1.23185(6) |
| b/nm | 1.11823(4) |
| c/nm | 0.92501(4) |
| α/(°) | 90 |
| β/(°) | 115.661(4) |
| γ/(°) | 90 |
| Volume/nm3 | 1.14852(9) |
| Z | 2 |
| Dcalc/(g•cm-3) | 3.960 |
| μ/mm-1 | 13.161 |
| GOF on F2 | 1.062 |
| R1a [I≥2σ (I)] | 0.0172 |
| wR2b [I≥2σ (I)] | 0.0350 |
| R1a [all data] | 0.0176 |
| wR2b [all data] | 0.0351 |
| Flack | 0.032(10) |
| (Δρmax/Δρmin)/(e•nm-3) | 820/–500 |
| Empirical formula | KAg3Ga8S14 |
|---|---|
| Fw | 1369.31 |
| Temperature/K | 293(2) |
| Space group | Cm |
| a/nm | 1.23185(6) |
| b/nm | 1.11823(4) |
| c/nm | 0.92501(4) |
| α/(°) | 90 |
| β/(°) | 115.661(4) |
| γ/(°) | 90 |
| Volume/nm3 | 1.14852(9) |
| Z | 2 |
| Dcalc/(g•cm-3) | 3.960 |
| μ/mm-1 | 13.161 |
| GOF on F2 | 1.062 |
| R1a [I≥2σ (I)] | 0.0172 |
| wR2b [I≥2σ (I)] | 0.0350 |
| R1a [all data] | 0.0176 |
| wR2b [all data] | 0.0351 |
| Flack | 0.032(10) |
| (Δρmax/Δρmin)/(e•nm-3) | 820/–500 |
| Bond | Distance/nm | Bond | Distance/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| K1—S5 | 0.3496(4) | Ga1—S1 | 0.2319(1) |
| K1—S5 | 0.3496(4) | Ga1—S3 | 0.2308(2) |
| K1—S6 | 0.3436(2) | Ga1—S4 | 0.2251(9) |
| K1—S6 | 0.3436(2) | Ga1—S6 | 0.2235(9) |
| K1—S7 | 0.3445(2) | Ga2—S1 | 0.2348(4) |
| K1—S7 | 0.3445(2) | Ga2—S6 | 0.2256(2) |
| K1—S8 | 0.3297(3) | Ga2—S7 | 0.2259(2) |
| K1—S9 | 0.3312(3) | Ga2—S9 | 0.2266(2) |
| Ag1—S2 | 0.2591(2) | Ga3—S1 | 0.2318(2) |
| Ag1—S4 | 0.2534(2) | Ga3—S2 | 0.2250(4) |
| Ag1—S7 | 0.2490(5) | Ga3—S3 | 0.2322(2) |
| Ag1—S7 | 0.2490(5) | Ga3—S5 | 0.2250(1) |
| Ag2—S4 | 0.2616(2) | Ga4—S3 | 0.2370(2) |
| Ag2—S5 | 0.2573(8) | Ga4—S5 | 0.2259(2) |
| Ag2—S5 | 0.2573(8) | Ga4—S7 | 0.2262(2) |
| Ag2—S9 | 0.2564(5) | Ga4—S8 | 0.2271(1) |
| Ag3—S2 | 0.2602(2) | ||
| Ag3—S6 | 0.2518(6) | ||
| Ag3—S6 | 0.2518(6) | ||
| Ag3—S8 | 0.2492(2) |
| Bond | Distance/nm | Bond | Distance/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| K1—S5 | 0.3496(4) | Ga1—S1 | 0.2319(1) |
| K1—S5 | 0.3496(4) | Ga1—S3 | 0.2308(2) |
| K1—S6 | 0.3436(2) | Ga1—S4 | 0.2251(9) |
| K1—S6 | 0.3436(2) | Ga1—S6 | 0.2235(9) |
| K1—S7 | 0.3445(2) | Ga2—S1 | 0.2348(4) |
| K1—S7 | 0.3445(2) | Ga2—S6 | 0.2256(2) |
| K1—S8 | 0.3297(3) | Ga2—S7 | 0.2259(2) |
| K1—S9 | 0.3312(3) | Ga2—S9 | 0.2266(2) |
| Ag1—S2 | 0.2591(2) | Ga3—S1 | 0.2318(2) |
| Ag1—S4 | 0.2534(2) | Ga3—S2 | 0.2250(4) |
| Ag1—S7 | 0.2490(5) | Ga3—S3 | 0.2322(2) |
| Ag1—S7 | 0.2490(5) | Ga3—S5 | 0.2250(1) |
| Ag2—S4 | 0.2616(2) | Ga4—S3 | 0.2370(2) |
| Ag2—S5 | 0.2573(8) | Ga4—S5 | 0.2259(2) |
| Ag2—S5 | 0.2573(8) | Ga4—S7 | 0.2262(2) |
| Ag2—S9 | 0.2564(5) | Ga4—S8 | 0.2271(1) |
| Ag3—S2 | 0.2602(2) | ||
| Ag3—S6 | 0.2518(6) | ||
| Ag3—S6 | 0.2518(6) | ||
| Ag3—S8 | 0.2492(2) |
| Bond | Angle/(°) | Bond | Angle/(°) |
|---|---|---|---|
| S6—K1—S6 | 70.64(7) | S4—Ga1—S1 | 104.51(6) |
| S6—K1—S7 | 101.95(8) | S4—Ga1—S3 | 110.72(6) |
| S6—K1—S7 | 61.16(4) | S6—Ga1—S1 | 111.14(6) |
| S7—K1—S5 | 61.36(3) | S6—Ga1—S3 | 116.20(6) |
| S7—K1—S5 | 133.90(7) | S6—Ga1—S4 | 107.34(6) |
| S7—K1—S5 | 133.89(7) | S6—Ga2—S1 | 108.19(6) |
| S7—K1—S7 | 73.19(6) | S6—Ga2—S7 | 115.76(6) |
| S8—K1—S5 | 88.42(4) | S6—Ga2—S9 | 104.80(7) |
| S8—K1—S6 | 124.55(6) | S7—Ga2—S1 | 110.09(6) |
| S8—K1—S7 | 63.44(5) | S7—Ga2—S9 | 104.53(6) |
| S8—K1—S9 | 168.34(10) | S9—Ga2—S1 | 113.49(7) |
| S9—K1—S5 | 89.48(4) | S1—Ga3—S3 | 109.81(6) |
| S9—K1—S6 | 64.10(5) | S2—Ga3—S1 | 108.62(6) |
| S9—K1—S7 | 124.94(7) | S2—Ga3—S3 | 109.34(7) |
| S4—Ag1—S2 | 96.10(7) | S5—Ga3—S1 | 106.19(6) |
| S7—Ag1—S2 | 107.33(5) | S5—Ga3—S2 | 116.45(7) |
| S7—Ag1—S7 | 111.08(7) | S5—Ga3—S3 | 106.28(6) |
| S5—Ag2—S4 | 106.49(5) | S5—Ga4—S3 | 103.62(6) |
| S5—Ag2—S5 | 113.54(7) | S5—Ga4—S7 | 112.28(6) |
| S9—Ag2—S4 | 97.06(7) | S5—Ga4—S8 | 123.47(6) |
| S9—Ag2—S5 | 115.49(4) | S7—Ga4—S3 | 105.67(6) |
| S6—Ag3—S2 | 101.87(5) | S7—Ga4—S8 | 103.00(6) |
| S6—Ag3—S2 | 101.88(5) | S8—Ga4—S3 | 107.60(6) |
| S6—Ag3—S6 | 104.13(8) | ||
| Bond | Angle/(°) | Bond | Angle/(°) |
|---|---|---|---|
| S6—K1—S6 | 70.64(7) | S4—Ga1—S1 | 104.51(6) |
| S6—K1—S7 | 101.95(8) | S4—Ga1—S3 | 110.72(6) |
| S6—K1—S7 | 61.16(4) | S6—Ga1—S1 | 111.14(6) |
| S7—K1—S5 | 61.36(3) | S6—Ga1—S3 | 116.20(6) |
| S7—K1—S5 | 133.90(7) | S6—Ga1—S4 | 107.34(6) |
| S7—K1—S5 | 133.89(7) | S6—Ga2—S1 | 108.19(6) |
| S7—K1—S7 | 73.19(6) | S6—Ga2—S7 | 115.76(6) |
| S8—K1—S5 | 88.42(4) | S6—Ga2—S9 | 104.80(7) |
| S8—K1—S6 | 124.55(6) | S7—Ga2—S1 | 110.09(6) |
| S8—K1—S7 | 63.44(5) | S7—Ga2—S9 | 104.53(6) |
| S8—K1—S9 | 168.34(10) | S9—Ga2—S1 | 113.49(7) |
| S9—K1—S5 | 89.48(4) | S1—Ga3—S3 | 109.81(6) |
| S9—K1—S6 | 64.10(5) | S2—Ga3—S1 | 108.62(6) |
| S9—K1—S7 | 124.94(7) | S2—Ga3—S3 | 109.34(7) |
| S4—Ag1—S2 | 96.10(7) | S5—Ga3—S1 | 106.19(6) |
| S7—Ag1—S2 | 107.33(5) | S5—Ga3—S2 | 116.45(7) |
| S7—Ag1—S7 | 111.08(7) | S5—Ga3—S3 | 106.28(6) |
| S5—Ag2—S4 | 106.49(5) | S5—Ga4—S3 | 103.62(6) |
| S5—Ag2—S5 | 113.54(7) | S5—Ga4—S7 | 112.28(6) |
| S9—Ag2—S4 | 97.06(7) | S5—Ga4—S8 | 123.47(6) |
| S9—Ag2—S5 | 115.49(4) | S7—Ga4—S3 | 105.67(6) |
| S6—Ag3—S2 | 101.87(5) | S7—Ga4—S8 | 103.00(6) |
| S6—Ag3—S2 | 101.88(5) | S8—Ga4—S3 | 107.60(6) |
| S6—Ag3—S6 | 104.13(8) | ||

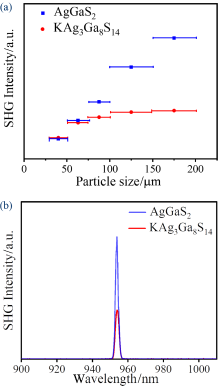

| 样品 | 能量/ mJ | 光斑面积/ mm2 | 脉冲宽度/ns | LIDT/ (MW•cm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AGS | 3.2 | 4.1 | 10 | 2.4 |
| KAg3Ga8S14 | 14.6 | 4.1 | 10 | 11.1 |
| 样品 | 能量/ mJ | 光斑面积/ mm2 | 脉冲宽度/ns | LIDT/ (MW•cm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AGS | 3.2 | 4.1 | 10 | 2.4 |
| KAg3Ga8S14 | 14.6 | 4.1 | 10 | 11.1 |
| [1] |
Dong, C. M.; Wang, S. P.; Tao, X. T. J. Synth. Cryst. 2006, 35, 5. (in Chinese)
|
|
(董春明, 王善朋, 陶绪堂, 人工晶体学报, 2006, 35, 5.)
|
|
| [2] |
Zhai, Y.; Xu, W.; Meng, X.; Hou, H. Acta Chim. Sinica 2020, 78, 256. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A19120427 |
|
(翟亚丽, 许文娟, 孟祥茹, 侯红卫, 化学学报, 2020, 78, 256.)
doi: 10.6023/A19120427 |
|
| [3] |
Jin, F.; Ma, M. Y.; Lv, J. J.; Guo, X. J.; Zha, Q. J.; Sun, L.; Zhang, L.; Liao, R. B. Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2019, 38, 1099.
|
| [4] |
Jia, N.; Wang, S. P.; Tao, X. T. Acta Phys. Sin. 2018, 67, 12. (in Chinese)
|
|
(贾宁, 王善朋, 陶绪堂, 物理学报, 2018, 67, 12.)
|
|
| [5] |
Sun, Y. L.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Jiang, X. X.; Sun, J. Sci. Technol. Chem. Ind. 2011, 19, 4. (in Chinese)
|
|
(孙玉玲, 王新, 刘杰, 蒋新星, 孙瑾, 化工科技, 2011, 19, 4.)
|
|
| [6] |
Zhou, W.; Zhang, Q.; Yao, W. D.; Xue, H.; Guo, S. P. Inorg. Chem. 2021, 60, 12536.
doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.1c01793 |
| [7] |
Chen, J. D.; Lin, C. S.; Ye, N. J. Synth. Cryst. 2020, 49, 7. (in Chinese)
|
|
(陈金东, 林晨升, 叶宁, 人工晶体学报, 2020, 49, 7.)
|
|
| [8] |
Li, S. F.; Zeng, H. Y.; Jiang, X. M.; Liu, B. W.; Guo, G. C. J. Chin. Rare Earth Soc. 2016, 34, 8. (in Chinese)
|
|
(李淑芳, 曾卉一, 姜小明, 刘彬文, 郭国聪, 中国稀土学报, 2016, 34, 8.)
|
|
| [9] |
Chen, C.; Wu, B.; Jiang, A.; You, G. 1985, 28, 235.
|
| [10] |
Chen, C.; Wu, Y.; Jiang, A.; Wu, B.; You, G.; Li, R.; Lin, S. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 1989, 6, 616.
doi: 10.1364/JOSAB.6.000616 |
| [11] |
Xu, Q. T.; Guo, S. P. Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2020, 39, 1564.
|
| [12] |
Zhang, G.; Qin, J.; Liu, T.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; Chen, C. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 95, 10.
|
| [13] |
Fan, Y. X.; Eckardt, R. C.; Byer, R. L.; Route, R. K.; Feigelson, R. S. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1984, 45, 313.
doi: 10.1063/1.95275 |
| [14] |
Eckardt, R. C.; Fan, Y. X.; Byer, R. L.; Marquardt, C. L.; Storm, M. E.; Esterowitz, L. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1986, 49, 608.
doi: 10.1063/1.97055 |
| [15] |
Vodopyanov, K. L.; Ganikhanov, F.; Maffetone, J. P.; Zwieback, I.; Ruderman, W. Opt. Lett. 2000, 25, 841.
pmid: 18064202 |
| [16] |
Zhuang, L.; Yao, J. Y.; Wu, Y. C. Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2020, 39, 1559.
|
| [17] |
Chen, C. T. Sci. China 1977, 75. (in Chinese)
|
|
(陈创天, 中国科学, 1977, 75.)
|
|
| [18] |
Li, M. Y.; Ma, Z.; Li, B.; Wu, X. T.; Lin, H.; Zhu, Q. L. Chem. Mater. 2020, 32, 4331.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.0c01258 |
| [19] |
Han, S. S.; Yao, W. D.; Yu, S. X.; Sun, Y.; Gong, A.; Guo, S. P. Inorg. Chem. 2021, 60, 3375.
doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.0c03780 |
| [20] |
Zhang, J. H.; Clark, D. J.; Brant, J. A.; Rosmus, K. A.; Grima, P.; Lekse, J. W.; Jang, J. I.; Aitken, J. A. Chem. Mater. 2020, 32, 8947.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.0c02929 |
| [21] |
Chen, J.; Hu, C. L.; Kong, F.; Mao, J. G. Acc. Chem. Res. 2021, 54, 2775.
doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.1c00188 |
| [22] |
Wu, K.; Yang, Y.; Gao, L. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2020, 418, 213380.
doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2020.213380 |
| [23] |
Nian, L.; Huang, J.; Wu, K.; Su, Z.; Yang, Z.; Pan, S. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 29378.
doi: 10.1039/C7RA05022D |
| [24] |
Li, Y. Y.; Wang, W. J.; Wang, H.; Lin, H.; Wu, L. M. Cryst. Growth Des. 2019, 19, 4172.
doi: 10.1021/acs.cgd.9b00358 |
| [25] |
Chu, Y.; Wu, K.; Su, X.; Han, J.; Yang, Z.; Pan, S. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 57, 11310.
doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.8b01788 pmid: 30141919 |
| [26] |
Lin, H.; Wei, W. B.; Chen, H.; Wu, X. T.; Zhu, Q. L. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2020, 406, 213150.
doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2019.213150 |
| [27] |
Liu, B. W.; Jiang, X. M.; Zeng, H. Y.; Guo, G. C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 10641.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.0c04738 |
| [28] |
Li, R. A.; Zhou, Z.; Lian, Y. K.; Jia, F.; Jiang, X.; Tang, M. C.; Wu, L. M.; Sun, J.; Chen, L. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 11861.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v59.29 |
| [29] |
Chen, W. F.; Liu, B. W.; Pei, S. M.; Yan, Q. N.; Jiang, X. M.; Guo, G. C. Chem. Mater. 2021, 33, 3729.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.1c00794 |
| [30] |
Huang, X.; Yang, S.-H.; Liu, W.; Guo, S. P. Inorg. Chem. 2021, 10, 16932.
|
| [31] |
Yang, Y.; Wu, K.; Zhang, B.; Wu, X.; Lee, M. H. Chem. Mater. 2020, 32, 1281.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.9b04842 |
| [32] |
Zhang, J. J.; Zhang, Z. H.; Tao, X. T. J. Shandong Univ., Nat. Sci. 2011, 46, 22. (in Chinese)
|
|
(张俊杰, 张中晗, 陶绪堂, 山东大学学报: 理学版, 2011, 46, 22.)
|
|
| [33] |
Zhou, M.; Kang, L.; Yao, J.; Lin, Z.; Wu, Y.; Chen, C. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 55, 3724.
doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.6b00517 |
| [34] |
Li, J. N.; Yao, W. D.; Li, X. H.; Liu, W.; Xue, H. G.; Guo, S. P. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 1109.
doi: 10.1039/D0CC07396B |
| [35] |
Li, J. N.; Li, X. H.; Yao, W. D.; Liu, W.; Guo, S. P. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 5175.
doi: 10.1039/D1CC01275D |
| [36] |
Li, Z.; Yang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Xing, W.; Luo, X.; Lin, Z.; Yao, J.; Wu, Y. Chem. Mater. 2019, 31, 1110.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.8b04981 |
| [37] |
Chen, H.; Liu, P. F.; Li, B. X.; Lin, H.; Wu, L. M.; Wu, X. T. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 429.
doi: 10.1039/C7DT04178K |
| [38] |
Li, Z.; Zhang, S.; Yin, W.; Kang, K.; Guo, Y.; Xing, W.; Lin, Z.; Yao, J.; Wu, Y. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 7516.
doi: 10.1039/C9TC01587F |
| [39] |
Rigaku Oxford Diffraction, CrysAlisPro Software System, version v40.67a, Rigaku Corporation, Oxford, UK, 2019.
|
| [40] |
Sheldrick, G. M. SHELXTL, Crystallographic Software Package, Version 5.1, Bruker-Axs Madison, WI, 1998.
|
| [41] |
Spek, A. L.; Platon, A. Multipurpose Crystallographic Tool, Utrecht University, Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2005.
|
| [42] |
Kortüm, G. Reflectance Spectroscopy, Springer, New York, 1969, pp. 1-336.
|
| [43] |
Chen, M. M.; Zhou, S. H.; Wei, W.; Wu, X. T.; Lin, H.; Zhu, Q. L. Inorg. Chem. 2021, 60, 10038.
doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.1c01359 |
| [44] |
Chu, Y.; Wang, P.; Zeng, H.; Cheng, S.; Su, X.; Yang, Z.; Li, J.; Pan, S. Chem. Mater. 2021, 33, 6514.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.1c01982 |
| [45] |
Lin, H.; Zhou, L. J.; Chen, L. Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 3406.
doi: 10.1021/cm301550a |
| [46] |
Zhang, M. J.; Jiang, X. M.; Zhou, L. J.; Guo, G. C. J. Mater. Chem. C 2013, 1, 4754.
doi: 10.1039/c3tc30808a |
| [47] |
Kurtz, S. K.; Perry, T. T. J. Appl. Phys. 1968, 39, 3798.
doi: 10.1063/1.1656857 |
| [48] |
Kang, L.; Zhou, M.; Yao, J.; Lin, Z.; Wu, Y.; Chen, C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 13049.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.5b07920 pmid: 26397313 |
| [49] |
Payne, M. C.; Arias, T. A.; Joannopoulos, J. D. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1992, 64, 1045.
doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.64.1045 |
| [50] |
Clark, S. J.; Segallii, M. D.; Pickardii, C. J.; Hasnipiii, P. J.; Probertiv, M. Z. Kristallogr. - New Cryst. Struct. 2005, 220, 5.
|
| [1] | 刘洋, 高丰琴, 马占营, 张引莉, 李午戊, 侯磊, 张小娟, 王尧宇. 一例钴基金属有机框架化合物活化过氧单硫酸盐高效降解水中亚甲基蓝研究[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(2): 152-159. |
| [2] | 郝良朦, 朱伟钢. 有机共晶非线性光学材料及应用研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(2): 191-206. |
| [3] | 柴贤丹, 陈文发, 闫秋楠, 刘彬文, 姜小明, 郭国聪. Rb2MGe3S8 (M=Zn, Cd): [MGe3S8]2–单元构型变换导致化合物从中心到非心的转变※[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(5): 633-639. |
| [4] | 吕天天, 马文, 詹冬笋, 邹燕敏, 李继龙, 冯美玲, 黄小荥. 两例新的镧系金属-有机框架化合物高效去除Cs+离子研究※[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(5): 640-646. |
| [5] | 方婧, 赵文娟, 张明浩, 方千荣. 一种新型酰胺功能化的共价有机框架用于选择性染料吸附[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(2): 186-191. |
| [6] | 付静茹, 贲腾. 一种新型的共价有机骨架膜的制备与气体分离性能[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(8): 805-814. |
| [7] | 陈光辉, 何燕萍, 张磊, 张健. 系列Ti4L6-笼基配合物的合成与结构研究[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(12): 1411-1417. |
| [8] | 王志涛, 李辉, 颜士臣, 方千荣. 一种沿骨架进行质子传导的二维共价有机框架的合成[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(1): 63-68. |
| [9] | 李攀, 刘建, 孙惟袆, 陶占良, 陈军. 铜钱状二硫化钒的制备及储钠性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2018, 76(4): 286-291. |
| [10] | 何学侠, 刘富才, 曾庆圣, 刘政 . 二维材料双电层场晶体管的研究[J]. 化学学报, 2015, 73(9): 924-935. |
| [11] | 徐伟高, 赵琰媛, 申超, 张俊, 熊启华. 二维单层硒化钼和硒化钨晶体的声子辅助上转换荧光光谱[J]. 化学学报, 2015, 73(9): 959-964. |
| [12] | 何燕萍, 谭衍曦, 张健. 基于尺寸识别和离子交换实现有机染料分离的一例阴离子型MOF[J]. 化学学报, 2014, 72(12): 1228-1232. |
| [13] | 倪春燕, 陈阳, 李端秀, 任志刚, 李红喜, 孙真荣, 郎建平. 卤离子导向合成配位聚合物[Hg2X4(ppt)]n (X=I和Br; ppt=1-(4-吡啶基)-吡啶铵-4-硫醇盐)及不同的一维链状结构和三阶非线性光学响应[J]. 化学学报, 2013, 71(06): 906-912. |
| [14] | 韩聪, 徐喆, 刁春华, 陈鑫, 刘靖, 郭敏杰, 樊志. 2-呋喃甲硫醇修饰环糊精形成互锁式螺旋柱状超分子的自组装行为[J]. 化学学报, 2013, 71(03): 439-442. |
| [15] | 段显英, 郭利兵, 王建莉. 具有优良传导性能杂多酸复合物{[Co(H2O)8][H(H2O)3](HINO)4(PW12O40)}n的合成, 结构和性质研究[J]. 化学学报, 2013, 71(01): 107-113. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||