化学学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 80 ›› Issue (5): 679-689.DOI: 10.6023/A21120610 上一篇 下一篇
所属专题: 中国科学院青年创新促进会合辑
综述
投稿日期:2021-12-31
发布日期:2022-05-31
通讯作者:
孙佳姝
作者简介: |
刘超, 国家纳米科学中心研究员. 2010年6月于河北工业大学获得工学学士学位, 2016年1月于中国科学院大学获得理学博士学位, 2016年加入国家纳米科学中心. 主要研究方向为微流控分离分析与肿瘤液体活检. |
 |
田飞, 国家纳米科学中心特别研究助理. 于2011年6月获得河北工业大学工学学士学位, 于2019年6月获得河北工业大学工学博士学位. 主要研究方向为基于微流控技术的循环肿瘤靶标分离分析与病原体检测. |
 |
邓瑾琦, 国家纳米科学中心任特别研究助理. 于2016年6月在武汉大学化学与分子科学学院取得理学学士学位, 于2021年6月在中国科学院大学中丹学院取得理学博士学位, 专业为纳米科学与技术. 研究方向为基于微流控技术的生化分析. |
 |
孙佳姝, 国家纳米科学中心研究员, 国家杰出青年科学基金 (2020年)和国家优秀青年科学基金获得者(2016年). 主要研究方向为微流控分离分析技术与纳米生物医学研究. 提出了微流控热泳测量的新理念, 实现循环肿瘤标志物的高灵敏定量检测. 已发表SCI收录论文90余篇, 引用5,600余次, 并多次被Nature子刊等作为研究亮点报道. 有10余项微流控相关发明专利授权. |
基金资助:
Chao Liua, Fei Tiana, Jinqi Denga, Jiashu Suna,b( )
)
Received:2021-12-31
Published:2022-05-31
Contact:
Jiashu Sun
About author:Supported by:文章分享
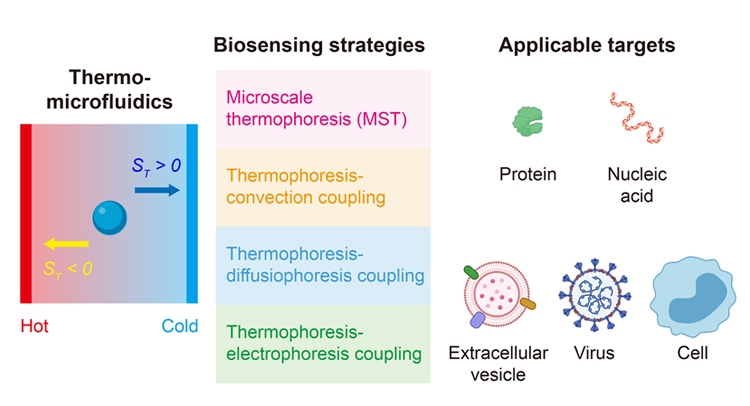
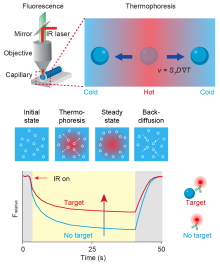
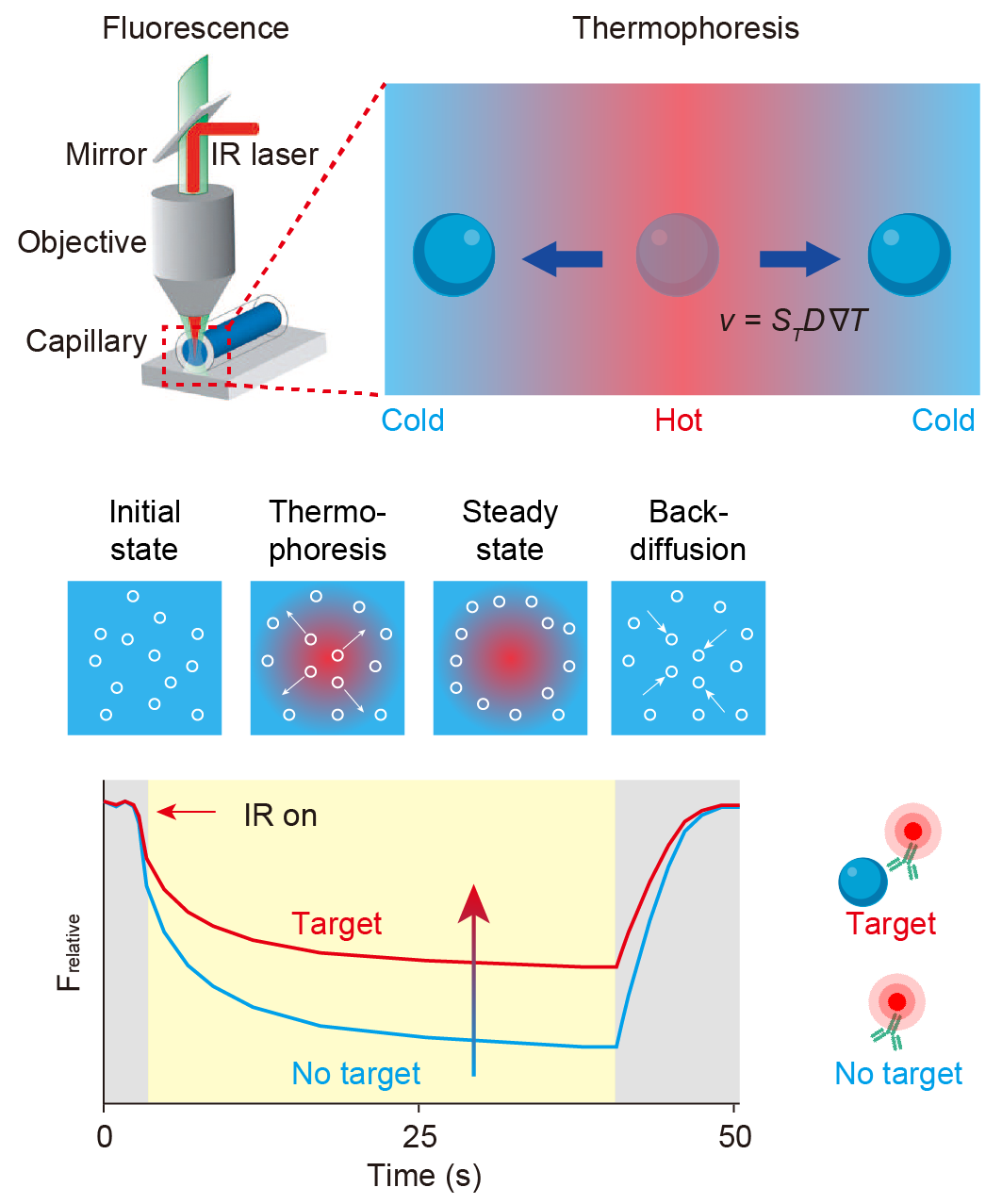
复杂生命体系中关键分子及微纳生物粒子的高灵敏、高特异检测, 对理解多层次多尺度生物学过程、阐明疾病发生发展机制和探索新型生物标志物等具有重要意义. 微流控生物传感器整合了微流控技术和生物传感技术的诸多优势, 在微量生物样本精准测量方面取得了显著进展. 近年来, 微流控热泳生物传感技术(Thermomicrofluidic biosensing)利用物质在局域温度梯度场中的热泳定向迁移现象, 并结合均相生物传感及信号放大新策略, 实现了复杂样本中生物分子及微纳生物粒子的快速、高灵敏、原位检测. 重点阐述了以热泳为核心的微流控传感技术, 包括微量热泳、热泳-对流耦合、热泳-扩散泳耦合以及热泳-电泳耦合等方法, 总结了不同传感方法的原理、特点及其在生物分子(蛋白、核酸等)与微纳生物粒子(细胞外囊泡、病毒、细胞等)检测中的应用, 并探讨了微流控热泳技术在生物医学检测领域中面临的挑战与未来发展方向.
刘超, 田飞, 邓瑾琦, 孙佳姝. 基于微流控热泳的生物传感技术※[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(5): 679-689.
Chao Liu, Fei Tian, Jinqi Deng, Jiashu Sun. Thermomicrofluidic Biosensing Systems※[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(5): 679-689.
| 加热方式 | 激光波长/nm | 功率密度/(mW•μm–2) | 温度梯度/(K•μm–1) | 检测温度/℃ | 应用 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 水体加热 | 1480 | — | ≈0.1 | <35 | 生物分子、EV蛋白检测 | [ |
| 水体加热 | 1480 | ≈0.01 | 0.3~1 | 28~42 | EV蛋白/核酸、病毒抗原检测 | [ |
| Cr基底加热 | 1064 | — | ≈0.1 | 33 | DNA检测 | [ |
| Cr基底加热 | 808 | ≈0.01 | ≈1.8 | ≈30 | 淀粉样纤维生长动力学研究 | [ |
| Au基底加热 | 532 | <0.1 | ≈0.6 | 25 | 原位SERS | [ |
| Au基底加热 | 532 | ≈0.02 | 5~30 | 33 | 单颗粒操控与暗场光学表征 | [ |
| Au基底加热 | 532 | 0.06 | 3.5~8.5 | 27 | 单细胞操控 | [ |
| 加热方式 | 激光波长/nm | 功率密度/(mW•μm–2) | 温度梯度/(K•μm–1) | 检测温度/℃ | 应用 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 水体加热 | 1480 | — | ≈0.1 | <35 | 生物分子、EV蛋白检测 | [ |
| 水体加热 | 1480 | ≈0.01 | 0.3~1 | 28~42 | EV蛋白/核酸、病毒抗原检测 | [ |
| Cr基底加热 | 1064 | — | ≈0.1 | 33 | DNA检测 | [ |
| Cr基底加热 | 808 | ≈0.01 | ≈1.8 | ≈30 | 淀粉样纤维生长动力学研究 | [ |
| Au基底加热 | 532 | <0.1 | ≈0.6 | 25 | 原位SERS | [ |
| Au基底加热 | 532 | ≈0.02 | 5~30 | 33 | 单颗粒操控与暗场光学表征 | [ |
| Au基底加热 | 532 | 0.06 | 3.5~8.5 | 27 | 单细胞操控 | [ |
| 颗粒分子 | 尺寸 | 溶液环境 | Soret系数/K–1 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 聚苯乙烯颗粒 (羧基修饰) | 200 nm | 1 mmol•L–1 Tris | 0.7 | [ |
| 聚苯乙烯颗粒 (羧基修饰) | 92 nm | 水 | 0.23 | [ |
| 聚苯乙烯颗粒 | 100 nm | 10 mmol•L–1 Tris | 0.35 | [ |
| 聚苯乙烯颗粒 | 100 nm | 10 mmol•L–1 Tris+PEG 6K (w=5%) | –1.5 | [ |
| SDS胶束 | 5 nm | 10 mmol•L–1 NaCl | 0.024 (25 ℃) | [ |
| CTAC胶束 | — | 水 | ≈0.1 | [ |
| HepG2 EVs | ≈100 nm | PBS | 0.03 | [ |
| Aβ40 fibril | ≈2 μm | 6 mmol•L–1 NaCl (pH=8.4) | ≈2.6 | [ |
| 溶菌酶 | 14 kDa | 100 mmol•L–1 NaCl (pH=4.65) | 0.0013 (27 ℃) | [ |
| DNA (SYBR Green I 标记) | 5.6 kbp | 10 mmol•L–1 Tris (pH=7.8) | 0.14 (24 ℃) | [ |
| λ-DNA (SYBR Green I 标记) | 48.5 kbp | 10 mmol•L–1 Tris (pH=7.8) | 0.4 | [ |
| PEG | 6 kDa | 10 mmol•L–1 Tris | 0.046 | [ |
| 颗粒分子 | 尺寸 | 溶液环境 | Soret系数/K–1 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 聚苯乙烯颗粒 (羧基修饰) | 200 nm | 1 mmol•L–1 Tris | 0.7 | [ |
| 聚苯乙烯颗粒 (羧基修饰) | 92 nm | 水 | 0.23 | [ |
| 聚苯乙烯颗粒 | 100 nm | 10 mmol•L–1 Tris | 0.35 | [ |
| 聚苯乙烯颗粒 | 100 nm | 10 mmol•L–1 Tris+PEG 6K (w=5%) | –1.5 | [ |
| SDS胶束 | 5 nm | 10 mmol•L–1 NaCl | 0.024 (25 ℃) | [ |
| CTAC胶束 | — | 水 | ≈0.1 | [ |
| HepG2 EVs | ≈100 nm | PBS | 0.03 | [ |
| Aβ40 fibril | ≈2 μm | 6 mmol•L–1 NaCl (pH=8.4) | ≈2.6 | [ |
| 溶菌酶 | 14 kDa | 100 mmol•L–1 NaCl (pH=4.65) | 0.0013 (27 ℃) | [ |
| DNA (SYBR Green I 标记) | 5.6 kbp | 10 mmol•L–1 Tris (pH=7.8) | 0.14 (24 ℃) | [ |
| λ-DNA (SYBR Green I 标记) | 48.5 kbp | 10 mmol•L–1 Tris (pH=7.8) | 0.4 | [ |
| PEG | 6 kDa | 10 mmol•L–1 Tris | 0.046 | [ |

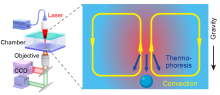
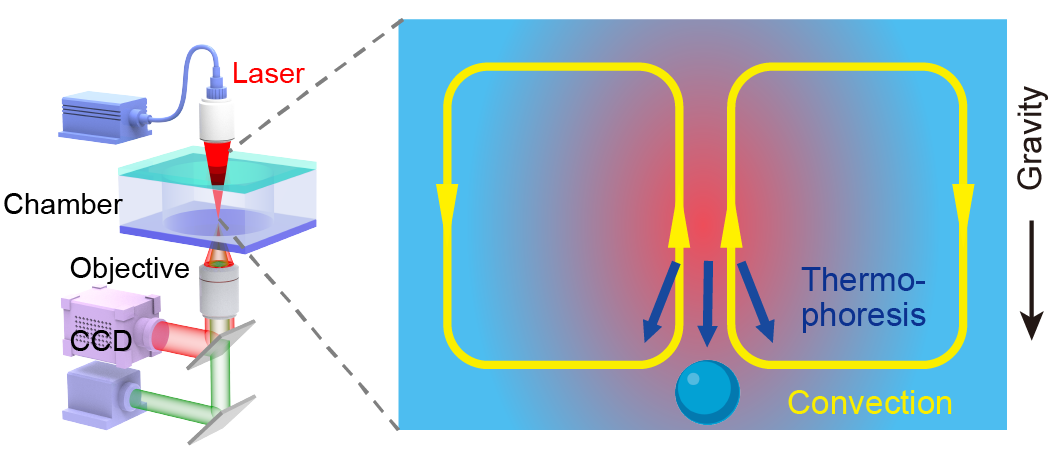


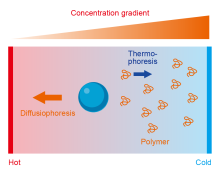
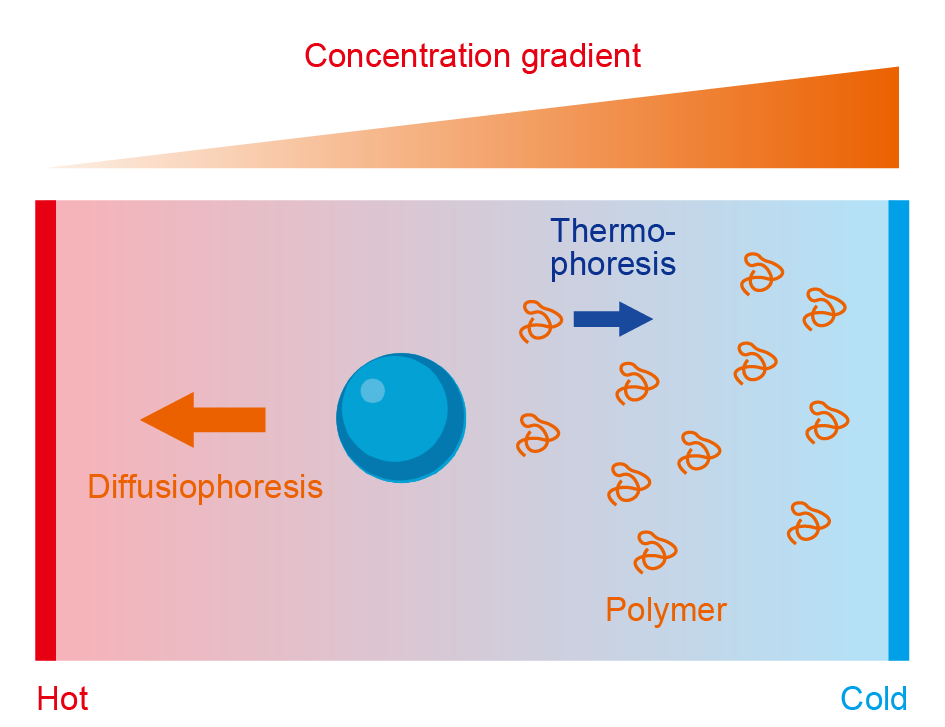

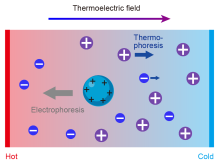
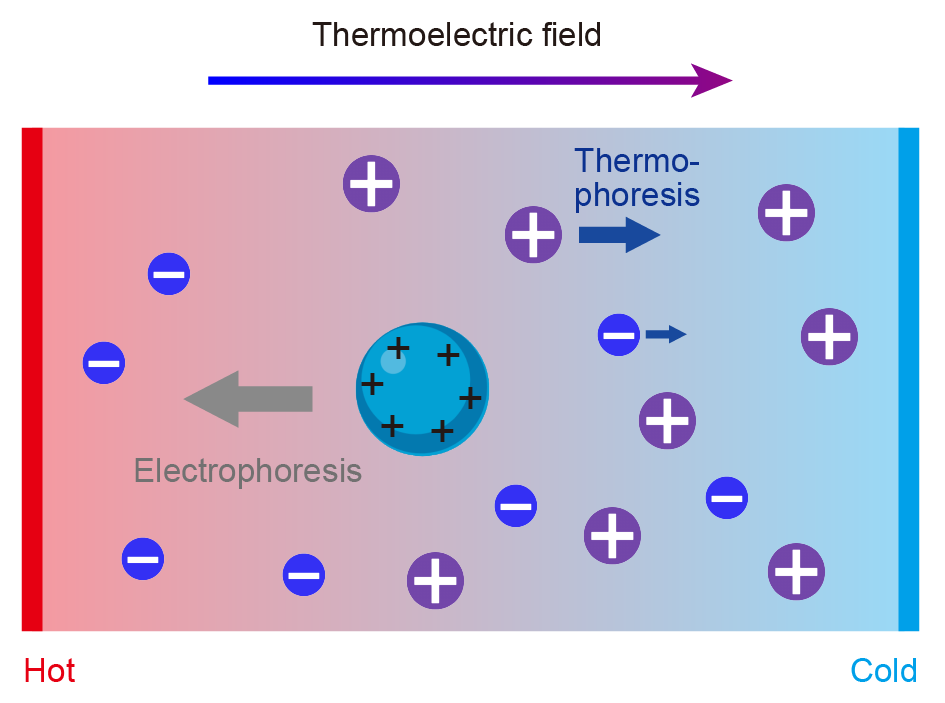

| 传感原理 | 优势 | 局限性 | 适用靶标与应用场景 | 主要设计因素 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 微量热泳技术 | 应用靶标范围广 | 灵敏度较低、 方法单一 | 蛋白、核酸、生物小分子、 EV测量 | 探针类型、基团修饰、 缓冲液性质 | [ |
| 热泳-对流耦合 | 灵敏度高、无需复杂前处理 | 依赖靶标自身 热泳性质 | EV蛋白/核酸检测 | 靶标与探针尺寸差别、 芯片高度、导热性质 | [ |
| 热泳-扩散泳耦合 | 不依赖靶标自身热泳性质、 检测速度快 | 汇聚范围小、 灵敏度较低 | 病毒颗粒、DNA检测 | 靶标与探针尺寸差别、 PEG浓度、分子量 | [ |
| 热泳-电泳耦合 | 单颗粒操控、 空间分辨率高 | 芯片成本高、 激光光路设计复杂 | 单细胞、单纳米颗粒操控 | 颗粒自身电学性质、 电解质种类 | [ |
| 传感原理 | 优势 | 局限性 | 适用靶标与应用场景 | 主要设计因素 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 微量热泳技术 | 应用靶标范围广 | 灵敏度较低、 方法单一 | 蛋白、核酸、生物小分子、 EV测量 | 探针类型、基团修饰、 缓冲液性质 | [ |
| 热泳-对流耦合 | 灵敏度高、无需复杂前处理 | 依赖靶标自身 热泳性质 | EV蛋白/核酸检测 | 靶标与探针尺寸差别、 芯片高度、导热性质 | [ |
| 热泳-扩散泳耦合 | 不依赖靶标自身热泳性质、 检测速度快 | 汇聚范围小、 灵敏度较低 | 病毒颗粒、DNA检测 | 靶标与探针尺寸差别、 PEG浓度、分子量 | [ |
| 热泳-电泳耦合 | 单颗粒操控、 空间分辨率高 | 芯片成本高、 激光光路设计复杂 | 单细胞、单纳米颗粒操控 | 颗粒自身电学性质、 电解质种类 | [ |
| [1] |
Wan, J. C. M.; Massie, C.; Garcia-Corbacho, J.; Mouliere, F.; Brenton, J. D.; Caldas, C.; Pacey, S.; Baird, R.; Rosenfeld, N. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 223.
doi: 10.1038/nrc.2017.7 |
| [2] |
Borrebaeck, C. A. K. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 199.
doi: 10.1038/nrc.2016.153 pmid: 28154374 |
| [3] |
Tian, F.; Liu, C.; Lin, L.; Chen, Q.; Sun, J. TrAC, Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 117, 128.
doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2019.05.013 |
| [4] |
Kalluri, R.; LeBleu, V. S. Science 2020, 367, eaau6977.
|
| [5] |
Kevadiya, B. D.; Machhi, J.; Herskovitz, J.; Oleynikov, M. D.; Blomberg, W. R.; Bajwa, N.; Soni, D.; Das, S.; Hasan, M.; Patel, M.; Senan, A. M.; Gorantla, S.; McMillan, J.; Edagwa, B.; Eisenberg, R.; Gurumurthy, C. B.; Reid, S. P. M.; Punyadeera, C.; Chang, L.; Gendelman, H. E. Nat. Mater. 2021, 20, 593.
doi: 10.1038/s41563-020-00906-z pmid: 33589798 |
| [6] |
Möller, A.; Lobb, R. J. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 697.
doi: 10.1038/s41568-020-00299-w |
| [7] |
Lim, C. Z. J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, H.; Stephenson, M. C.; Ho, N. R. Y.; Chen, Y.; Chung, J.; Reilhac, A.; Loh, T. P.; Chen, C. L. H.; Shao, H. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1144.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09030-2 |
| [8] |
Tsokos, G. C. Nat. Immunol. 2020, 21, 605.
doi: 10.1038/s41590-020-0677-6 |
| [9] |
Ma, Q.-L.; Feng, N.; Ju, H.-X. Acta Chim. Sinica 2020, 78, 1213. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A20060259 |
|
(马秋琳, 冯楠, 鞠熀先, 化学学报, 2020, 78, 1213.)
doi: 10.6023/A20060259 |
|
| [10] |
Li, Y.-Y.; Peng, Y.; Lu, H.-J. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 705. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A21020048 |
|
(李月悦, 彭叶, 陆豪杰, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 705.)
doi: 10.6023/A21020048 |
|
| [11] |
Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xie, X.-L.; Zhang, J.; Tang, B. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 36. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A20080383 |
|
(李勇, 王栩, 解希雷, 张建, 唐波, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 36.)
doi: 10.6023/A20080383 |
|
| [12] |
Wu, L.; Qu, X. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 2963.
doi: 10.1039/C4CS00370E |
| [13] |
Kwong, G. A.; Ghosh, S.; Gamboa, L.; Patriotis, C.; Srivastava, S.; Bhatia, S. N. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2021, 21, 655.
doi: 10.1038/s41568-021-00389-3 |
| [14] |
Lu, J.-M.; Wang, H.-F.; Pan, J.-Z.; Fang, Q. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 809. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A21030086 |
|
(卢佳敏, 王慧峰, 潘建章, 方群, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 809.)
doi: 10.6023/A21030086 |
|
| [15] |
Su, Y.-Y.; Peng, T.-H.; Xing, F.-F.; Li, D.; Fan, C.-H. Acta Chim. Sinica 2017, 75, 1036. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A17060289 |
|
(苏莹莹, 彭天欢, 邢菲菲, 李迪, 樊春海, 化学学报, 2017, 75, 1036.)
doi: 10.6023/A17060289 |
|
| [16] |
Lin, L.; Hill, E. H.; Peng, X.; Zheng, Y. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 1465.
doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.8b00102 |
| [17] |
Niether, D.; Wiegand, S. J. Phys.-Condes. Matter 2019, 31, 503003.
|
| [18] |
Chen, J.; Loo, J. F.-C.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Kong, S.-K.; Ho, H.-P. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2020, 8, 1900829.
|
| [19] |
Tian, F.; Han, Z.; Deng, J.; Liu, C.; Sun, J. View 2021, 2, 20200148.
|
| [20] |
Gooding, J. J.; Gaus, K. Angew. Chem., nt. Ed. 2016, 55, 11354.
|
| [21] |
Wienken, C. J.; Baaske, P.; Rothbauer, U.; Braun, D.; Duhr, S. Nat. Commun. 2010, 1, 100.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms1093 |
| [22] |
Baaske, P.; Wienken, C. J.; Reineck, P.; Duhr, S.; Braun, D. Angew. Chem.,Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 2238.
doi: 10.1002/anie.200903998 |
| [23] |
Asmari, M.; Ratih, R.; Alhazmi, H. A.; El Deeb, S. Methods 2018, 146, 107.
doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2018.02.003 |
| [24] |
Braun, D.; Libchaber, A. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 89, 188103.
|
| [25] |
Duhr, S.; Braun, D. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2006, 103, 19678.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0603873103 |
| [26] |
Würger, A. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 101, 108302.
|
| [27] |
Jerabek-Willemsen, M.; Wienken, C. J.; Braun, D.; Baaske, P.; Duhr, S. Assay Drug Dev. Technol. 2011, 9, 342.
doi: 10.1089/adt.2011.0380 |
| [28] |
Duhr, S.; Braun, D. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 96, 168301.
|
| [29] |
Putnam, S. A.; Cahill, D. G.; Wong, G. C. L. Langmuir 2007, 23, 9221.
pmid: 17655335 |
| [30] |
Iacopini, S.; Piazza, R. Europhys. Lett. 2003, 63, 247.
doi: 10.1209/epl/i2003-00520-y |
| [31] |
Duhr, S.; Arduini, S.; Braun, D. Eur. Phys. J. E: Soft Matter Biol. Phys. 2004, 15, 277.
doi: 10.1140/epje/i2004-10073-5 pmid: 15592768 |
| [32] |
Piazza, R.; Guarino, A. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 88, 208302.
|
| [33] |
Seidel, S. A. I.; Wienken, C. J.; Geissler, S.; Jerabek-Willemsen, M.; Duhr, S.; Reiter, A.; Trauner, D.; Braun, D.; Baaske, P. Angew. Chem., nt. Ed. 2012, 51, 10656.
|
| [34] |
Shang, X.; Marchioni, F.; Evelyn, C. R.; Sipes, N.; Zhou, X.; Seibel, W.; Wortman, M.; Zheng, Y. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2013, 110, 3155.
|
| [35] |
Möller, F. M.; Kieß, M.; Braun, D. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 5363.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b01756 |
| [36] |
Liu, T.; Zhang, H.; Sun, L.; Zhao, D.; Liu, P.; Yan, M.; Zaidi, N.; Izadmehr, S.; Gupta, A.; Abu-Amer, W.; Luo, M.; Yang, J.; Ou, X.; Wang, Y.; Bai, X.; Wang, Y.; New, M. I.; Zaidi, M.; Yuen, T.; Liu, C. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2017, 114, 7683.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1621486114 |
| [37] |
Lee, G.-Y.; Min, P.; Kang, M.-J.; Langer, K.; Jose, J.; Pyun, J.-C. Sens. Actuator, B 2018, 258, 1131.
doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2017.12.019 |
| [38] |
Lee, G.-Y.; Bong, J.-H.; Jung, J.; Kang, M.-J.; Jose, J.; Pyun, J.-C. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 156, 112110.
doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2020.112110 |
| [39] |
Franz, P.; Gassl, V.; Topf, A.; Eckelmann, L.; Iorga, B.; Tsiavaliaris, G. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 169, 112616.
doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2020.112616 |
| [40] |
Stein, J. A. C.; Ianeselli, A.; Braun, D. Angew. Chem., nt. Ed. 2021, 60, 13988.
|
| [41] |
Xu, R.; Rai, A.; Chen, M.; Suwakulsiri, W.; Greening, D. W.; Simpson, R. J. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 617.
doi: 10.1038/s41571-018-0036-9 |
| [42] |
Huang, M.; Yang, J.; Wang, T.; Song, J.; Xia, J.; Wu, L.; Wang, W.; Wu, Q.; Zhu, Z.; Song, Y.; Yang, C. Angew. Chem., nt. Ed. 2020, 59, 4800.
|
| [43] |
Braun, M.; Bregulla, A. P.; Günther, K.; Mertig, M.; Cichos, F. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 5499.
doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b01999 |
| [44] |
Fränzl, M.; Thalheim, T.; Adler, J.; Huster, D.; Posseckardt, J.; Mertig, M.; Cichos, F. Nat. Methods 2019, 16, 611.
doi: 10.1038/s41592-019-0451-6 |
| [45] |
Braun, M.; Cichos, F. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 11200.
doi: 10.1021/nn404980k |
| [46] |
Duhr, S.; Braun, D. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 86, 131921.
doi: 10.1063/1.1888036 |
| [47] |
Baaske, P.; Weinert, F. M.; Duhr, S.; Lemke, K. H.; Russell, M. J.; Braun, D. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2007, 104, 9346.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0609592104 |
| [48] |
Mast, C. B.; Schink, S.; Gerland, U.; Braun, D. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2013, 110, 8030.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1303222110 |
| [49] |
Kreysing, M.; Keil, L.; Lanzmich, S.; Braun, D. Nat. Chem. 2015, 7, 203.
doi: 10.1038/nchem.2155 pmid: 25698328 |
| [50] |
Mast, C. B.; Braun, D. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 104, 188102.
doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.104.188102 |
| [51] |
Liu, C.; Zhao, J.; Tian, F.; Cai, L.; Zhang, W.; Feng, Q.; Chang, J.; Wan, F.; Yang, Y.; Dai, B.; Cong, Y.; Ding, B.; Sun, J.; Tan, W. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 3, 183.
doi: 10.1038/s41551-018-0343-6 |
| [52] |
Zhang, L.; Wan, S.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fu, T.; Liu, Q.; Cao, Z.; Qiu, L.; Tan, W. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 2532.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b10646 |
| [53] |
Tian, F.; Zhang, S.; Liu, C.; Han, Z.; Liu, Y.; Deng, J.; Li, Y.; Wu, X.; Cai, L.; Qin, L.; Chen, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Cong, Y.; Ding, B.; Jiang, Z.; Sun, J. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2536.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-22913-7 pmid: 33953198 |
| [54] |
Li, Y.; Deng, J.; Han, Z.; Liu, C.; Tian, F.; Xu, R.; Han, D.; Zhang, S.; Sun, J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 1290.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.0c12016 |
| [55] |
O’Brien, K.; Breyne, K.; Ughetto, S.; Laurent, L. C.; Breakefield, X. O. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 585.
doi: 10.1038/s41580-020-0251-y |
| [56] |
Zhao, J.; Liu, C.; Li, Y.; Ma, Y.; Deng, J.; Li, L.; Sun, J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 4996.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b13960 |
| [57] |
Han, Z.; Wan, F.; Deng, J.; Zhao, J.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Ding, B.; Liu, C.; Dai, B.; Sun, J. Nano Today 2021, 38, 101203.
doi: 10.1016/j.nantod.2021.101203 |
| [58] |
Abécassis, B.; Cottin-Bizonne, C.; Ybert, C.; Ajdari, A.; Bocquet, L. Nat. Mater. 2008, 7, 785.
doi: 10.1038/nmat2254 pmid: 18711384 |
| [59] |
Rasmussen, M. K.; Pedersen, J. N.; Marie, R. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2337.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-15889-3 pmid: 32393750 |
| [60] |
Jiang, H.-R.; Wada, H.; Yoshinaga, N.; Sano, M. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 102, 208301.
doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.102.208301 |
| [61] |
Maeda, Y. T.; Buguin, A.; Libchaber, A. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 107, 038301.
doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.107.038301 |
| [62] |
Maeda, Y. T.; Tlusty, T.; Libchaber, A. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2012, 109, 17972.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1215764109 |
| [63] |
Deng, J.; Tian, F.; Liu, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Fu, T.; Sun, J.; Tan, W. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 7261.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.1c02929 |
| [64] |
Yu, L.-H.; Chen, Y.-F. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 2845.
doi: 10.1021/ac504296e |
| [65] |
Dietzel, M.; Hardt, S. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 116, 225901.
doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.116.225901 |
| [66] |
Li, J.; Zheng, Y. Acc Mater. Res. 2021, 2, 352.
doi: 10.1021/accountsmr.1c00033 |
| [67] |
Lin, L.; Zhang, J.; Peng, X.; Wu, Z.; Coughlan, A. C. H.; Mao, Z.; Bevan, M. A.; Zheng, Y. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1700458.
|
| [68] |
Lin, L.; Peng, X.; Mao, Z.; Wei, X.; Xie, C.; Zheng, Y. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 3061.
doi: 10.1039/C7LC00432J |
| [69] |
Lin, L.; Peng, X.; Wang, M.; Scarabelli, L.; Mao, Z.; Liz-Marzán, L. M.; Becker, M. F.; Zheng, Y. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 9659.
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.6b05486 |
| [70] |
Lin, L.; Wang, M.; Peng, X.; Lissek, E. N.; Mao, Z.; Scarabelli, L.; Adkins, E.; Coskun, S.; Unalan, H. E.; Korgel, B. A.; Liz-Marzán, L. M.; Florin, E.-L.; Zheng, Y. Nat. Photonics 2018, 12, 195.
doi: 10.1038/s41566-018-0134-3 |
| [71] |
Lin, L.; Peng, X.; Wei, X.; Mao, Z.; Xie, C.; Zheng, Y. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 3147.
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.7b00207 |
| [72] |
Hill, E. H.; Li, J.; Lin, L.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, Y. Langmuir 2018, 34, 13252.
doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.8b01979 |
| [1] | 李兰英, 陶晴, 闻艳丽, 王乐乐, 郭瑞妍, 刘刚, 左小磊. 多聚腺嘌呤DNA探针及其生物传感应用★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(6): 681-690. |
| [2] | 朱子煜, 梁阿新, 浩天瑞霖, 唐珊珊, 刘淼, 解炳腾, 罗爱芹. 生物传感器在新冠病毒检测中的应用[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(3): 253-263. |
| [3] | 浩天瑞霖, 朱子煜, 蔡艳慧, 王微, 王祯, 梁阿新, 罗爱芹. 基于共价有机框架的电化学生物传感器在生物样品检测中的应用[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(11): 1524-1535. |
| [4] | 师瑶, 夏乾峰, 何政清, 鞠熀先. 登革热病毒检测的生物传感技术[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(1): 69-79. |
| [5] | 卢佳敏, 王慧峰, 潘建章, 方群. 微流控技术在微/纳米材料合成中的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(7): 809-819. |
| [6] | 廖妮, 钟霞, 梁文斌, 袁若, 卓颖. ECL金属-有机框架(MOF)生物传感平台用于肿瘤细胞分泌H2O2的测定[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(10): 1257-1264. |
| [7] | 樊蕾, 江群英, 潘敏, 王文晓, 张丽, 刘晓庆. 基于模拟酶-天然酶级联反应的双模式传感平台用于生物标志物的超灵敏检测[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(5): 419-426. |
| [8] | 金鑫, 王晓英. 口腔癌相关唾液肿瘤生物标志物的分析检测研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(4): 340-350. |
| [9] | 刘娇, 孙海龙, 印璐, 袁亚仙, 徐敏敏, 姚建林. 微流控芯片结合表面增强拉曼光谱实时监测α-苯乙醇的微量合成反应[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(3): 257-262. |
| [10] | 熊麟, 凡勇, 张凡. 稀土纳米晶用于近红外区活体成像和传感研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(12): 1239-1249. |
| [11] | 胡正利, 杜冀晖, 应佚伦, 彭岳一, 曹婵, 龙亿涛. 纳米孔道单分子检测结直肠癌MicroRNAs[J]. 化学学报, 2017, 75(11): 1087-1090. |
| [12] | 刘兴奋, 王亚腾, 黄艳琴, 冯晓苗, 范曲立, 黄维. 基于水溶性共轭聚合物分子刷的高灵敏凝血酶生物传感器[J]. 化学学报, 2016, 74(8): 664-668. |
| [13] | 崔向红, 陈怀银, 杨涛. 纳米尺寸二硫化钼的制备与应用研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2016, 74(5): 392-400. |
| [14] | 张佳佳, 代佩卿, 李超, 李南忘, 程圭芳, 何品刚, 方禹之. 基于磁纳米颗粒的二段对称分裂式G-四分体DNA酶生物传感器用于Hg2+的快速检测[J]. 化学学报, 2014, 72(9): 1029-1035. |
| [15] | 郝锐, 邓霄, 杨毅彪, 陈德勇. ZnO纳米线/棒阵列的水热法制备及应用研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2014, 72(12): 1199-1208. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||