化学学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 80 ›› Issue (4): 563-569.DOI: 10.6023/A21120602 上一篇 下一篇
所属专题: 中国科学院青年创新促进会合辑
综述
赵佳雨a,b, 宋万通a,c,*( ), 汤朝晖a,b,c, 陈学思a,b,c
), 汤朝晖a,b,c, 陈学思a,b,c
投稿日期:2021-12-30
发布日期:2022-04-28
通讯作者:
宋万通
作者简介: |
赵佳雨, 2017年至今博士就读于中国科学院长春应用化学研究所, 高分子化学与物理专业, 主要从事于高分子免疫刺激材料应用于抗肿瘤疫苗设计的研究. |
 |
宋万通, 中国科学院长春应用化学研究所研究员. 2008年本科毕业于南京大学, 2013年于中国科学院长春应用化学研究所取得博士学位(导师陈学思院士), 2016~2018年赴美国北卡罗来纳大学教堂山分校药学院进行博士后研究(导师Leaf Huang教授). 主要从事高分子疫苗载体与肿瘤免疫治疗方向的研究工作. 先后以第一/通讯作者在Nat. Nanotechnol., Nat. Commun., Adv. Mater., ACS Nano, Nano Lett., Biomaterials等杂志发表研究及综述论文60余篇. |
 |
汤朝晖, 中国科学院长春应用化学研究所研究员, 博士生导师. 曾在英国帝国理工学院和美国纽约州立大学石溪分校做博士后. 主要从事高分子载体抗肿瘤纳米药物研究. 在Adv. Mater., Adv. Sci., Prog. Polym. Sci., Chem. Sci., Biomaterials, J. Control. Release等知名期刊发表学术论文100余篇. |
 |
陈学思, 中国科学院院士, 中国科学院长春应用化学研究所研究员、博士生导师, 中国科学院生态环境高分子材料重点实验室学委会副主任. 主要从事生物降解医用高分子材料、组织工程和药物缓释、聚乳酸和聚-己内酯产业化等方向的研究与开发工作, 发表SCI学术论文700余篇, 授权专利260余项. |
基金资助:
Jiayu Zhaoa,b, Wantong Songa,c( ), Zhaohui Tanga,b,c, Xuesi Chena,b,c
), Zhaohui Tanga,b,c, Xuesi Chena,b,c
Received:2021-12-30
Published:2022-04-28
Contact:
Wantong Song
About author:Supported by:文章分享
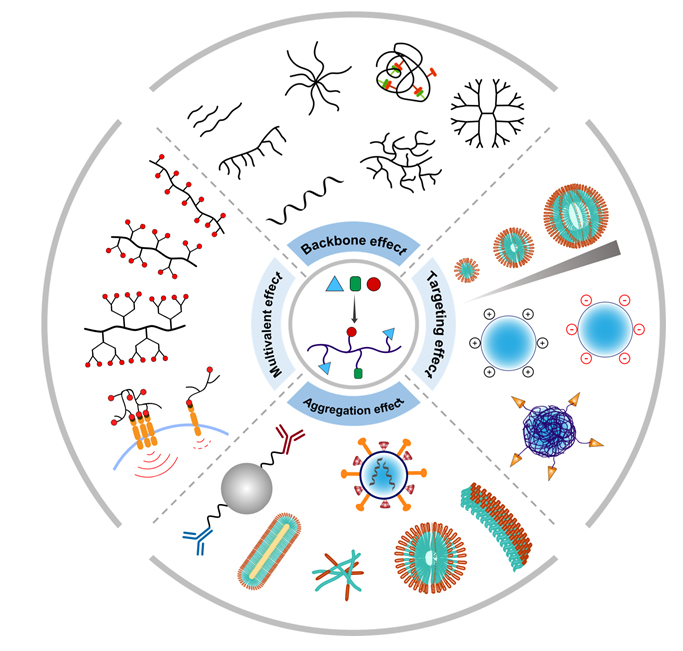
药物种类按照分子量来划分可以分为小分子药物(自然提取或化学合成的)和大分子药物(生物制剂). 尽管目前小分子药物仍然是市场的主流, 但其研发增速趋缓, 而大分子药物在药物研发中的地位日渐突显, 并被预期在未来药物市场中占据越来越高的份额. 除了生物制剂大分子药物, 将小分子药物与天然或合成大分子结合制备得到的化学合成大分子药物, 近年来受到药物研究者们越来越多的关注. 由于大分子具有丰富的骨架结构及空间构架, 其所特有的骨架效应、多价效应, 以及通过分子组装而产生的聚集效应和靶向效应等, 能够为药物化学的设计带来更多新的可能. 有鉴于此, 本综述将简略介绍药物化学设计中的大分子效应, 重点讨论合成大分子的骨架效应、多价效应、聚集效应和靶向效应等为药物化学设计所带来的新性能. 通过对药物化学中大分子效应所带来的优势、问题和重要研究进展的探讨, 以期能够推动化学合成大分子药物的发展, 为药物化学设计提供新的思路.
赵佳雨, 宋万通, 汤朝晖, 陈学思. 药物化学中的大分子效应※[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(4): 563-569.
Jiayu Zhao, Wantong Song, Zhaohui Tang, Xuesi Chen. Macromolecular Effects in Medicinal Chemistry※[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(4): 563-569.

| [1] |
Wong, H. N. C. Innovation (N Y) 2021, 2, 100086.
|
| [2] |
Kwon, Y.; Kang, S.; Choi, Y. S.; Kim, I. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17304.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-96812-8 |
| [3] |
Dong, S.; Ma, S.; Liu, Z. L.; Ma, L.-L.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, Z. H.; Deng, M. X.; Song, W. T. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2021, 39, 865.
doi: 10.1007/s10118-021-2547-6 |
| [4] |
Ma, Y.; Yang, H. M.; Chen, Z. H.; Li, Y. N.; Li, J. F.; Sun, X. L.; Wang, X. Y.; Tang, Y. Polym. Chem. 2021, 12, 6606.
doi: 10.1039/D1PY01273H |
| [5] |
Lin, M. H.; Hung, C. F.; Hsu, C. Y.; Lin, Z. C.; Fang, J. Y. Future Med. Chem. 2019, 11, 2131.
doi: 10.4155/fmc-2018-0388 |
| [6] |
Zhou, K.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, L.; Xu, W. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2020, 114, 111006.
doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2020.111006 |
| [7] |
Yang, C.; Xue, Z.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, L.; Guo, J.; Lin, W. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2018, 84, 254.
doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2017.12.003 |
| [8] |
Debele, T. A.; Yu, L. Y.; Yang, C. S.; Shen, Y. A.; Lo, C. L. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 3725.
doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.8b00856 |
| [9] |
Si, X.; Song, W.; Yang, S.; Ma, L.; Yang, C.; Tang, Z. Macromol. Biosci. 2020, 20, e2000243.
|
| [10] |
Ma, S.; Song, W.; Xu, Y.; Si, X.; Lv, S.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, Z.; Chen, X. Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 2514.
doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.9b05265 |
| [11] |
Chen, D.; Zhang, G.; Li, Q.; Guan, M.; Wang, X.; Zou, T.; Zhang, Y.; Shu, C.; Hong, H.; Wan, L. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 7373.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b12025 |
| [12] |
Zhang, L.; Chen, Q.; Wang, J. Acta Chim. Sinica 2020, 78, 642. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A20040116 |
|
(张留伟, 陈麒先, 王静云, 化学学报, 2020, 78, 642.)
doi: 10.6023/A20040116 |
|
| [13] |
Ma, S.; Song, W.; Xu, Y.; Si, X.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, Z.; Chen, X. CCS Chemistry 2020, 2, 390.
doi: 10.31635/ccschem.020.202000140 |
| [14] |
Zhang, J.; Wu, L.; Meng, F.; Wang, Z.; Deng, C.; Liu, H.; Zhong, Z. Langmuir 2012, 28, 2056.
doi: 10.1021/la203843m |
| [15] |
Chen, W.; Zhong, P.; Meng, F.; Cheng, R.; Deng, C.; Feijen, J.; Zhong, Z. J. Control. Release 2013, 169, 171.
doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2013.01.001 |
| [16] |
Ma, S.; Song, W.; Xu, Y.; Si, X.; Zhang, D.; Lv, S.; Yang, C.; Ma, L.; Tang, Z.; Chen, X. Biomaterials 2020, 232, 119676.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2019.119676 |
| [17] |
Si, X.; Ma, S.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Shen, N.; Yu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Song, W.; Tang, Z.; Chen, X. J. Control. Release 2020, 320, 83.
doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.01.021 |
| [18] |
Cheng, R.; Meng, F.; Deng, C.; Klok, H. A.; Zhong, Z. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 3647.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.01.084 pmid: 23415642 |
| [19] |
Tu, L.; Liao, Z.; Luo, Z.; Wu, Y. L.; Herrmann, A.; Huo, S. Exploration 2021, 1, 20210023.
doi: 10.1002/EXP.20210023 |
| [20] |
Zhao, J.; Ma, S.; Xu, Y.; Si, X.; Yao, H.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, H.; Tang, Z.; Song, W.; Chen, X. Biomaterials 2021, 268, 120542.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2020.120542 |
| [21] |
Tang, J. C.; Huang, K. L.; Yu, J. G.; Liu, S. Q. Acta Chim. Sinica 2008, 66, 541. (in Chinese)
|
|
(唐金春, 黄可龙, 于金刚, 刘素琴, 化学学报, 2008, 66, 541.)
|
|
| [22] |
Dahlman, J. E.; Kauffman, K. J.; Xing, Y.; Shaw, T. E.; Mir, F. F.; Dlott, C. C.; Langer, R.; Anderson, D. G.; Wang, E. T. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2017, 114, 2060.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1620874114 pmid: 28167778 |
| [23] |
Choi, K. Y.; Chung, H.; Min, K. H.; Yoon, H. Y.; Kim, K.; Park, J. H.; Kwon, I. C.; Jeong, S. Y. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 106.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2009.09.030 |
| [24] |
Dai, Q.; Wilhelm, S.; Ding, D.; Syed, A. M.; Sindhwani, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y. Y.; MacMillan, P.; Chan, W. C. W. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 8423.
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.8b03900 |
| [25] |
Kunjachan, S.; Pola, R.; Gremse, F.; Theek, B.; Ehling, J.; Moeckel, D.; Hermanns-Sachweh, B.; Pechar, M.; Ulbrich, K.; Hennink, W. E.; Storm, G.; Lederle, W.; Kiessling, F.; Lammers, T. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 972.
doi: 10.1021/nl404391r pmid: 24422585 |
| [26] |
Bandyopadhyay, A.; Fine, R. L.; Demento, S.; Bockenstedt, L. K.; Fahmy, T. M. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 3094.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.12.054 pmid: 21262534 |
| [27] |
Yuan, H.; Jiang, W.; von Roemeling, C. A.; Qie, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wharen, R. E.; Yun, K.; Bu, G.; Knutson, K. L.; Kim, B. Y. S. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2017, 12, 763.
doi: 10.1038/nnano.2017.69 |
| [28] |
Song, W. T.; Tang, Z. H.; Zhang, D. W.; Li, M. Q.; Gu, J. K.; Chen, X. S. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 728.
doi: 10.1039/C5SC01698C |
| [29] |
Wang, J.; Hao, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, T.; Guan, X.; Wang, K. Polym. Bull. 2011, 1, 9. (in Chinese)
|
|
(王君莲, 郝红, 王扬, 赵涛, 管晓玉, 王凯, 高分子通报, 2011, 1, 9.)
|
|
| [30] |
Kalafati, L.; Kourtzelis, I.; Schulte-Schrepping, J.; Li, X.; Hatzioannou, A.; Grinenko, T.; Hagag, E.; Sinha, A.; Has, C.; Dietz, S.; de Jesus Domingues, A. M.; Nati, M.; Sormendi, S.; Neuwirth, A.; Chatzigeorgiou, A.; Ziogas, A.; Lesche, M.; Dahl, A.; Henry, I.; Subramanian, P.; Wielockx, B.; Murray, P.; Mirtschink, P.; Chung, K. J.; Schultze, J. L.; Netea, M. G.; Hajishengallis, G.; Verginis, P.; Mitroulis, I.; Chavakis, T. Cell 2020, 183, 771.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.09.058 pmid: 33125892 |
| [31] |
Carroll, E. C.; Jin, L.; Mori, A.; Munoz-Wolf, N.; Oleszycka, E.; Moran, H. B. T.; Mansouri, S.; McEntee, C. P.; Lambe, E.; Agger, E. M.; Andersen, P.; Cunningham, C.; Hertzog, P.; Fitzgerald, K. A.; Bowie, A. G.; Lavelle, E. C. Immunity 2016, 44, 597.
doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2016.02.004 |
| [32] |
Chen, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, S.; Chen, Y.; Lan, J.; Liu, L. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 77, 389.
doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2009.01.009 |
| [33] |
Luo, M.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Cai, H.; Lu, Z.; Li, Y.; Du, M.; Huang, G.; Wang, C.; Chen, X.; Porembka, M. R.; Lea, J.; Frankel, A. E.; Fu, Y. X.; Chen, Z. J.; Gao, J. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2017, 12, 648.
doi: 10.1038/nnano.2017.52 |
| [34] |
Li, S.; Luo, M.; Wang, Z.; Feng, Q.; Wilhelm, J.; Wang, X.; Li, W.; Wang, J.; Cholka, A.; Fu, Y. X.; Sumer, B. D.; Yu, H.; Gao, J. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 5, 455.
doi: 10.1038/s41551-020-00675-9 |
| [35] |
Manna, S.; Howitz, W. J.; Oldenhuis, N. J.; Eldredge, A. C.; Shen, J.; Nihesh, F. N.; Lodoen, M. B.; Guan, Z.; Esser-Kahn, A. P. ACS Cent. Sci. 2018, 4, 982.
doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.8b00218 |
| [36] |
Fan, Z.; Jan, S.; Hickey, J. C.; Davies, D. H.; Felgner, J.; Felgner, P. L.; Guan, Z. Biomacromolecules 2021, 22, 5074.
doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.1c01052 |
| [37] |
Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Tang, Z. Acta Chim. Sinica 2022, 80, 291. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A21120544 |
|
(李嫣然, 王子贵, 汤朝晖, 化学学报, 2022, 80, 291.)
doi: 10.6023/A21120544 |
|
| [38] |
Langer, C. J.; Facp, M.; Byrne, K. J. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2008, 3, 623.
doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e3181753b4b pmid: 18520802 |
| [39] |
Schluep, T.; Hwang, J.; Cheng, J.; Heidel, J. D.; Bartlett, D. W.; Hollister, B.; Davis, M. E. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 1606.
pmid: 16533788 |
| [40] |
Numbenjapon, T.; Wang, J.; Colcher, D.; Schluep, T.; Davis, M. E.; Duringer, J.; Kretzner, L.; Yen, Y.; Forman, S. J.; Raubitschek, A. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 4365.
doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-2619 pmid: 19549776 |
| [41] |
Koizumi, F.; Kitagawa, M.; Negishi, T.; Onda, T.; Matsumoto, S.; Hamaguchi, T.; Matsumura, Y. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 10048.
doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-1605 |
| [42] |
Alami, N.; Banerjee, K.; Juste, S.; Page, V.; Brossard, M.; Hayashi, T.; Igarashi, E.; Leyland-Jones, B. AACR 2006, 1, 133.
|
| [43] |
Zhang, Y.; Ma, S.; Liu, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Si, X.; Li, H.; Huang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Tang, Z.; Song, W.; Chen, X. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, e2007293.
|
| [44] |
Lynn, G. M.; Laga, R.; Darrah, P. A.; Ishizuka, A. S.; Balaci, A. J.; Dulcey, A. E.; Pechar, M.; Pola, R.; Gerner, M. Y.; Yamamoto, A.; Buechler, C. R.; Quinn, K. M.; Smelkinson, M. G.; Vanek, O.; Cawood, R.; Hills, T.; Vasalatiy, O.; Kastenmuller, K.; Francica, J. R.; Stutts, L.; Tom, J. K.; Ryu, K. A.; Esser-Kahn, A. P.; Etrych, T.; Fisher, K. D.; Seymour, L. W.; Seder, R. A. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 1201.
doi: 10.1038/nbt.3371 |
| [45] |
Lynn, G. M.; Sedlik, C.; Baharom, F.; Zhu, Y.; Ramirez-Valdez, R. A.; Coble, V. L.; Tobin, K.; Nichols, S. R.; Itzkowitz, Y.; Zaidi, N.; Gammon, J. M.; Blobel, N. J.; Denizeau, J.; de la Rochere, P.; Francica, B. J.; Decker, B.; Maciejewski, M.; Cheung, J.; Yamane, H.; Smelkinson, M. G.; Francica, J. R.; Laga, R.; Bernstock, J. D.; Seymour, L. W.; Drake, C. G.; Jewell, C. M.; Lantz, O.; Piaggio, E.; Ishizuka, A. S.; Seder, R. A. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 320.
doi: 10.1038/s41587-019-0390-x |
| [46] |
Zhao, J.; Xu, Y.; Ma, S.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Qu, H.; Yao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, G.; Huang, L.; Song, W.; Tang, Z.; Chen, X. Adv. Mater. 2022, e2109254.
|
| [47] |
Shen, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wan, P.; An, L.; Zhang, P.; Xiao, C.; Chen, X. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, e2001108.
|
| [48] |
Xiong, M.; Han, Z.; Song, Z.; Yu, J.; Ying, H.; Yin, L.; Cheng, J. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 10826.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201706071 |
| [49] |
Hasirci, V. N.; Holt, P. F. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Hlth. 1977, 38, 177.
doi: 10.1007/BF00378355 |
| [50] |
Paluck, S. J.; Nguyen, T. H.; Maynard, H. D. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 3417.
doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.6b01147 |
| [51] |
Pouyan, P.; Nie, C.; Bhatia, S.; Wedepohl, S.; Achazi, K.; Osterrieder, N.; Haag, R. Biomacromolecules 2021, 22, 1545.
doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.0c01789 pmid: 33706509 |
| [52] |
Vance, D.; Shah, M.; Joshi, A.; Kane, R. S. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2008, 101, 429.
doi: 10.1002/bit.22056 |
| [53] |
Joshi, A.; Vance, D.; Rai, P.; Thiyagarajan, A.; Kane, R. S. Chemistry 2008, 14, 7738.
|
| [54] |
Lee, Y. C.; Lee, R. T. Acc. Chem. Res. 2002, 28, 321.
doi: 10.1021/ar00056a001 |
| [55] |
Toone, J. J. L. a. E. J. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 555.
doi: 10.1021/cr000418f |
| [56] |
Hudak, J. E.; Canham, S. M.; Bertozzi, C. R. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2014, 10, 69.
doi: 10.1038/nchembio.1388 |
| [57] |
Hong, S.; Yu, C.; Rodrigues, E.; Shi, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, P.; Chapla, D. G.; Gao, T.; Zhuang, R.; Moremen, K. W.; Paulson, J. C.; Macauley, M. S.; Wu, P. ACS Cent. Sci. 2021, 7, 1338.
doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.1c00064 |
| [58] |
Delaveris, C. S.; Chiu, S. H.; Riley, N. M.; Bertozzi, C. R. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2021, 118, e2012408118.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.2012408118 |
| [59] |
Delaveris, C. S.; Wilk, A. J.; Riley, N. M.; Stark, J. C.; Yang, S. S.; Rogers, A. J.; Ranganath, T.; Nadeau, K. C.; Stanford, C.-B.; Blish, C. A.; Bertozzi, C. R. ACS Cent. Sci. 2021, 7, 650.
doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.0c01669 |
| [60] |
Su, L.; Zhang, W.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Liu, G.; Chen, G.; Jiang, M. Small 2015, 11, 4191.
doi: 10.1002/smll.201403838 |
| [61] |
Wu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Yang, G.; Kochovski, Z.; Chen, G.; Jiang, M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 14684.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b07768 |
| [62] |
Papp, I.; Sieben, C.; Sisson, A. L.; Kostka, J.; Bottcher, C.; Ludwig, K.; Herrmann, A.; Haag, R. ChemBioChem 2011, 12, 887.
doi: 10.1002/cbic.201000776 |
| [63] |
Nie, C.; Parshad, B.; Bhatia, S.; Cheng, C.; Stadtmuller, M.; Oehrl, A.; Kerkhoff, Y.; Wolff, T.; Haag, R. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 15532.
doi: 10.1002/anie.202004832 |
| [64] |
Rodriguez-Perez, L.; Ramos-Soriano, J.; Perez-Sanchez, A.; Illescas, B. M.; Munoz, A.; Luczkowiak, J.; Lasala, F.; Rojo, J.; Delgado, R.; Martin, N. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 9891.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.8b03847 |
| [65] |
Ramos-Soriano, J.; Reina, J. J.; Illescas, B. M.; de la Cruz, N.; Rodriguez-Perez, L.; Lasala, F.; Rojo, J.; Delgado, R.; Martin, N. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 15403.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b08003 pmid: 31469952 |
| [66] |
Illescas, B. M.; Rojo, J.; Delgado, R.; Martin, N. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 6018.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b01683 pmid: 28394600 |
| [67] |
Cai, H.; Sun, Z. Y.; Chen, M. S.; Zhao, Y. F.; Kunz, H.; Li, Y. M. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 1699.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201308875 |
| [68] |
Cuesta, A. M.; Sainz-Pastor, N.; Bonet, J.; Oliva, B.; Alvarez-Vallina, L. Trends Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 355.
doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2010.03.007 pmid: 20447706 |
| [69] |
Johnson, R. N.; Kopecˇkova´, P.; Kopecˇek, J. Bioconjugate Chem. 2009, 20, 129.
doi: 10.1021/bc800351m |
| [70] |
Zhang, N.; Khawli, L. A.; Hu, P.; Epstein, A. L. Clin Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 5971.
pmid: 16115941 |
| [71] |
Xie, J.; Wang, J.; Chen, H.; Shen, W.; Sinko, P. J.; Dong, H.; Zhao, R.; Lu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Jia, L. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9445.
doi: 10.1038/srep09445 |
| [72] |
Martin, J. T.; Douaisi, M.; Arsiwala, A.; Arha, M.; Kane, R. S. Int. J. Nanomedicine 2018, 13, 5249.
doi: 10.2147/IJN.S174673 |
| [73] |
Vorobyeva, M.; Vorobjev, P.; Venyaminova, A. Molecules 2016, 21, 1613.
doi: 10.3390/molecules21121613 |
| [74] |
Hong, Y.; Lamab, J. W. Y.; Tang, B. Z. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 5361.
doi: 10.1039/c1cs15113d |
| [75] |
Liu, S.; Cai, X.; Wu, J.; Cong, Q.; Chen, X.; Li, T.; Du, F.; Ren, J.; Wu, Y. T.; Grishin, N. V.; Chen, Z. J. Science 2015, 347, aaa2630.
|
| [76] |
Li, L. L.; Qiao, Z. Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, H. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, e1804971.
|
| [77] |
Yang, P. P.; Luo, Q.; Qi, G. B.; Gao, Y. J.; Li, B. N.; Zhang, J. P.; Wang, L.; Wang, H. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1605869.
doi: 10.1002/adma.201605869 |
| [78] |
Cheng, D. B.; Wang, D.; Gao, Y. J.; Wang, L.; Qiao, Z. Y.; Wang, H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 4406.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.8b13512 |
| [79] |
Zhang, X. H.; Cheng, D. B.; Ji, L.; An, H. W.; Wang, D.; Yang, Z. X.; Chen, H.; Qiao, Z. Y.; Wang, H. Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 1286.
doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.9b04752 |
| [80] |
Zhang, L.; Jing, D.; Jiang, N.; Rojalin, T.; Baehr, C. M.; Zhang, D.; Xiao, W.; Wu, Y.; Cong, Z.; Li, J. J.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Lam, K. S. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2020, 15, 145.
doi: 10.1038/s41565-019-0626-4 pmid: 31988501 |
| [81] |
Jiang, C. T.; Chen, K. G.; Liu, A.; Huang, H.; Fan, Y. N.; Zhao, D. K.; Ye, Q. N.; Zhang, H. B.; Xu, C. F.; Shen, S.; Xiong, M. H.; Du, J. Z.; Yang, X. Z.; Wang, J. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1359.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21497-6 |
| [82] |
Mi, Y.; Smith, C. C.; Yang, F.; Qi, Y.; Roche, K. C.; Serody, J. S.; Vincent, B. G.; Wang, A. Z. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, e1706098.
|
| [83] |
Veneziano, R.; Moyer, T. J.; Stone, M. B.; Wamhoff, E. C.; Read, B. J.; Mukherjee, S.; Shepherd, T. R.; Das, J.; Schief, W. R.; Irvine, D. J.; Bathe, M. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2020, 15, 716.
doi: 10.1038/s41565-020-0719-0 pmid: 32601450 |
| [84] |
Vargason, A. M.; Anselmo, A. C.; Mitragotri, S. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 5, 951.
doi: 10.1038/s41551-021-00698-w pmid: 33795852 |
| [85] |
Das, R. P.; Gandhi, V. V.; Singh, B. G.; Kunwar, A. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 3034.
doi: 10.2174/1381612825666190830155319 |
| [86] |
Groves, E.; Dart, A. E.; Covarelli, V.; Caron, E. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2008, 65, 1957.
doi: 10.1007/s00018-008-7578-4 pmid: 18322649 |
| [87] |
Vonarbourg, A.; Passirani, C.; Saulnier, P.; Benoit, J. P. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 4356.
pmid: 16650890 |
| [88] |
Uster, P. S.; Working, P. K.; Vaage, J. Int. J. Pharm. 1998, 162, 77.
doi: 10.1016/S0378-5173(97)00415-8 |
| [89] |
Gradishar, W. J.; Tjulandin, S.; Davidson, N.; Shaw, H.; Desai, N.; Bhar, P.; Hawkins, M.; O'Shaughnessy, J. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 7794.
pmid: 16172456 |
| [90] |
Bugno, J.; Poellmann, M. J.; Sokolowski, K.; Hsu, H. J.; Kim, D. H.; Hong, S. Nanomedicine 2019, 21, 102059.
|
| [91] |
Cabral, H.; Matsumoto, Y.; Mizuno, K.; Chen, Q.; Murakami, M.; Kimura, M.; Terada, Y.; Kano, M. R.; Miyazono, K.; Uesaka, M.; Nishiyama, N.; Kataoka, K. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 815.
doi: 10.1038/nnano.2011.166 pmid: 22020122 |
| [92] |
Ji, J.; Ma, F.; Zhang, H.; Liu, F.; He, J.; Li, W.; Xie, T.; Zhong, D.; Zhang, T.; Tian, M.; Zhang, H.; Santos, H. A.; Zhou, M. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1801738.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.201801738 |
| [93] |
Wang, H.; Wang, S.; Su, H.; Chen, K. J.; Armijo, A. L.; Lin, W. Y.; Wang, Y.; Sun, J.; Kamei, K.; Czernin, J.; Radu, C. G.; Tseng, H. R. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 4344.
doi: 10.1002/anie.200900063 pmid: 19425037 |
| [94] |
Miller, J. B.; Zhang, S.; Kos, P.; Xiong, H.; Zhou, K.; Perelman, S. S.; Zhu, H.; Siegwart, D. J. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 1059.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201610209 pmid: 27981708 |
| [95] |
Kranz, L. M.; Diken, M.; Haas, H.; Kreiter, S.; Loquai, C.; Reuter, K. C.; Meng, M.; Fritz, D.; Vascotto, F.; Hefesha, H.; Grunwitz, C.; Vormehr, M.; Husemann, Y.; Selmi, A.; Kuhn, A. N.; Buck, J.; Derhovanessian, E.; Rae, R.; Attig, S.; Diekmann, J.; Jabulowsky, R. A.; Heesch, S.; Hassel, J.; Langguth, P.; Grabbe, S.; Huber, C.; Tureci, O.; Sahin, U. Nature 2016, 534, 396.
doi: 10.1038/nature18300 |
| [96] |
Cheng, Q.; Wei, T.; Farbiak, L.; Johnson, L. T.; Dilliard, S. A.; Siegwart, D. J. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2020, 15, 313.
doi: 10.1038/s41565-020-0669-6 |
| [97] |
Zhou, Q.; Shao, S.; Wang, J.; Xu, C.; Xiang, J.; Piao, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Yu, Q.; Tang, J.; Liu, X.; Gan, Z.; Mo, R.; Gu, Z.; Shen, Y. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2019, 14, 799.
doi: 10.1038/s41565-019-0485-z |
| [98] |
Wang, G.; Wu, B.; Li, Q.; Chen, S.; Jin, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Shen, Y.; Huang, P. Small 2020, 16, e2004172.
|
| [99] |
Wang, Y.; Shen, N.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, Z.; Chen, X. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, e2002094.
|
| [100] |
Xia, X.; Yang, X.; Huang, W.; Xia, X.; Yan, D. Nanomicro Lett. 2021, 14, 33.
|
| [101] |
Sakamoto, K. M.; Kim, K. B.; Kumagai, A.; Mercurio, F.; Crews, C. M.; Deshaies, R. J. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2001, 98, 8554.
pmid: 11438690 |
| [1] | 程翼宇,陈慰浙,刘平. 一种预测药物活性的神经元计算新方法[J]. 化学学报, 2001, 59(7): 1145-1149. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||