化学学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 82 ›› Issue (4): 449-457.DOI: 10.6023/A23120541 上一篇 下一篇
综述
谷琪, 刘夏夏, 周鑫宇, 李江, 林秀婧*( ), 马延文*(
), 马延文*( )
)
投稿日期:2023-12-25
发布日期:2024-03-21
作者简介: |
谷琪, 就读于南京邮电大学材料科学与工程学院, 2021级电子信息专业硕士生. 主要研究方向为聚离子液体基固态电解质的制备及其在锂金属电池中的应用. |
 |
刘夏夏, 就读于南京邮电大学材料科学与工程学院, 2022级电子信息专业硕士生. 主要研究方向为聚离子液体基固态电解质的制备及其在锂金属电池中的应用. |
 |
周鑫宇, 就读于南京邮电大学材料科学与工程学院, 2022级电子信息专业硕士生. 主要研究方向为聚离子液体基固态电解质的制备及其在锂硫电池中的应用. |
 |
李江, 就读于南京邮电大学材料科学与工程学院, 2022级电子信息专业硕士生. 主要研究方向为硅负极粘结剂的制备及其在锂电池中的应用. |
 |
林秀婧, 2015年博士毕业于复旦大学物理化学专业, 现任南京邮电大学材料科学与工程学院副教授. 主要研究方向为聚离子液体基高分子聚合物的设计合成及应用. |
 |
马延文, 2007年博士毕业于南京大学物理化学专业, 现任苏州工业职业技术学院院长、南京邮电大学材料科学与工程学院纳米材料研究所所长, 入选江苏省“333工程”第三层次培养对象、江苏省六大人才高峰(A类)、“青蓝工程”学术带头人. 长期致力于柔性能源电子器件、锂/钠离子电池和碱金属电池的研究和产业化应用. |
基金资助:
Qi Gu, Xiaxia Liu, Xinyu Zhou, Jiang Li, Xiujing Lin*( ), Yanwen Ma*(
), Yanwen Ma*( )
)
Received:2023-12-25
Published:2024-03-21
Contact:
* E-mail: Supported by:文章分享
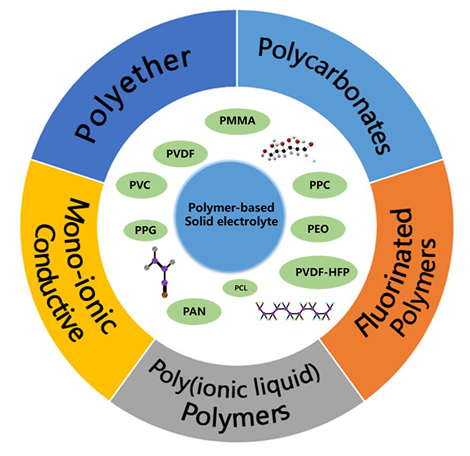
聚合物固态电解质因其质轻安全、结构可设计以及优异的机械性能, 成为高能量密度、高安全性全固态电池的潜在材料, 逐渐成为研究的重点. 但因其结晶度高、室温离子电导率低等缺陷也限制其进一步商业化. 本综述梳理了近年来比较优越的聚合物固态电解质种类, 包括聚醚类聚合物、聚碳酸酯类聚合物、氟化聚合物、聚离子液体聚合物、单离子传导聚合物, 围绕如何提升离子电导率, 重点回顾了针对不同基质的结构设计和合成工艺方面的创新. 最后阐述了聚合物固态电解质目前面临的基础研究和应用问题, 以期为新型聚合物固态电解质的设计与制备提供新思路.
谷琪, 刘夏夏, 周鑫宇, 李江, 林秀婧, 马延文. 用于锂金属电池的聚合物固态电解质的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(4): 449-457.
Qi Gu, Xiaxia Liu, Xinyu Zhou, Jiang Li, Xiujing Lin, Yanwen Ma. Recent Progress on Polymer Solid Electrolytes for Lithium Metal Batteries[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(4): 449-457.

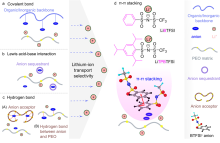

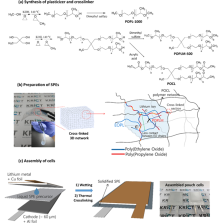



| [1] |
Kong, Y.-M.; Wang, Z.-Q. Jilin Water Res. 2018, 437, 57. (in Chinese)
|
|
(孔玉明, 王志清, 吉林水利, 2018, 437, 57.)
|
|
| [2] |
Li, H.-J. China Plant Eng. 2023, 2, 189. (in Chinese)
|
|
(李海杰, 中国设备工程, 2023, 2, 189.)
|
|
| [3] |
Chen, L.-W.; Gao, R.-Z. Transp. Energy Conser. Envir. Protect. 2021, 17, 14. (in Chinese)
|
|
(陈力维, 高润泽, 交通节能与环保, 2021, 17, 14.)
|
|
| [4] |
Fan, X.; Zhong, C.; Liu, J.; Ding, J.; Deng, Y.; Han, X.; Zhang, L.; Hu, W.; Wilkinson, D. P.; Zhang, J. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 17155.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.2c00196 |
| [5] |
Lu, G.-L. Mod. Chem. Res. 2021, 20, 159. (in Chinese)
|
|
(卢国龙, 当代化工研究, 2021, 20, 159.)
|
|
| [6] |
Hu, M.; Wang, H.; Chen, Q. New Energy Vehicles 2020, 9, 8. (in Chinese)
|
|
(胡敏, 王恒, 陈琪, 新能源汽车, 2020, 9, 8.)
|
|
| [7] |
Ren, Y.-Y. Sci. Technol. Rev. 2017, 35, 26. (in Chinese)
|
|
(任耀宇, 科技导报, 2017, 35, 26.)
doi: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2017.08.003 |
|
| [8] |
Du, X.-J.; Peng, H.-L.; Yu, H.-J.; Zhang, H.-B.; Wang, Y. Sci. Technol. Vis. 2019, 18, 91. (in Chinese)
|
|
(杜宪军, 彭慧丽, 于恒杰, 张会斌, 王瑛, 科技视界, 2019, 18, 91.)
|
|
| [9] |
Mao, J.-R.; Jia, Q.-F.; Zhao, X.; Chen, B.-S.; Zhao, T.-B. Polym. Bull. 2022, 9, 8. (in Chinese)
|
|
(毛家容, 贾其凡, 赵芯, 陈宝书, 赵天宝, 高分子通报, 2022, 9, 8.)
|
|
| [10] |
Chen, L.; Chi, S.-S.; Dong, Y.; Li, D.; Zhang, B.-C.; Fan, L.-Z. J. Chin. Silic. Soc. 2018, 46, 21. (in Chinese)
|
|
(陈龙, 池上森, 董源, 李丹, 张博晨, 范丽珍, 硅酸盐学报, 2018, 46, 21.)
|
|
| [11] |
Wei, T.; Lu, J.-H.; Wang, M.-T.; Sun, C.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, S.-J; Zhou, Y.-Y.; Chen, D.-F.; Lan, Y.-Q. Chinese J. Chem. 2023, 41, 1861.
doi: 10.1002/cjoc.v41.15 |
| [12] |
Baskoro, F.; Wong, H. Q.; Yen, H. J. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2019, 2, 3937.
doi: 10.1021/acsaem.9b00295 |
| [13] |
Wang, A.-L.; Ji, W.-X.; Chen, J.; Wang, X.-P.; Zhang, T.-Y.; Zhang, L.-Y. Polym. Bull. 2019, 9, 1. (in Chinese)
|
|
(王蔼廉, 计文希, 陈婧, 王晓鹏, 张韬毅, 张辽云, 高分子通报, 2019, 9, 1.)
|
|
| [14] |
Zhou, W.-D.; Huang, Q.; Xie, X.-X.; Chen, K.-J.; Li, W.; Qiu, J.-S. Energy Storage Sci. Technol. 2022, 11, 1788. (in Chinese)
|
|
(周伟东, 黄秋, 谢晓新, 陈科君, 李薇, 邱介山, 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11, 1788.)
doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2022.0168 |
|
| [15] |
Xi, L.; Zhang, D.-C.; Liu, J. Mater. China 2021, 40, 607. (in Chinese)
|
|
(习磊, 张德超, 刘军, 中国材料进展, 2021, 40, 607.)
|
|
| [16] |
Chen, L.; Huang, Y.; Ma, J.; Ling, H.; Kang, F.; He, Y. Energ Fuel. 2020, 34, 13456.
doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.0c02915 |
| [17] |
Liu, L.; Zhang, D.; Xu, X.; Liu, Z.; Liu, J. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2021, 37, 210.
doi: 10.1007/s40242-021-0007-z |
| [18] |
Zhang, D. F.; Liu, M.; Ma, J. B.; Yang, K.; Chen, Z.; Li, K. K.; Zhang, C.; Wei, Y. P.; Zhou, M.; Wang, P.; He, Y. B.; Lv, W.; He, Y. B. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6966.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-34717-4 |
| [19] |
Fenton, D. M. J. Org. Chem. 1973, 38, 3192.
doi: 10.1021/jo00958a026 |
| [20] |
Berthier, L.; Richard, M.; Henri, D.; Emmanuel, B.; Philippe, J.; Alain, M. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 2193.
doi: 10.1021/jf980920p |
| [21] |
Fan, X.-H.; Deng, D.-R.; Wu, Q.-H. J. Jimei Univ., Nat. Sci. 2022, 57, 447. (in Chinese)
|
|
(樊晓红, 邓丁榕, 吴启辉, 集美大学学报, 2022, 57, 447.)
|
|
| [22] |
Chen, J.-M.; Xiong, J.-W.; Ji, S.-M.; Huo, Y.-P.; Zhao, J.-W.; Liang, L. Prog. Chem. 2021, 32, 481. (in Chinese)
|
|
(陈嘉苗, 熊靖雯, 籍少敏, 霍延平, 赵经纬, 梁亮, 化学进展, 2021, 32, 481.)
|
|
| [23] |
Choo, Y.; Halat, D. M.; Villaluenga, I.; Timachova, K.; Balsara, N. P. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2020, 103, 101220.
doi: 10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2020.101220 |
| [24] |
Shi, P. R.; Ma, J. B.; Liu, M.; Guo, S. K.; Huang, Y. F.; Wang, S. W.; Zhang, L. H.; Chen, L. K.; Yang, K.; Liu, X. T.; Li, Y. H.; An, X. F.; Zhang, D. F.; Cheng, X.; Li, Q. D.; Lv, W.; Zhong, G. M.; He, Y. B.; Kang, F. Y. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2023, 18, 602.
doi: 10.1038/s41565-023-01341-2 |
| [25] |
Xu, H.; Ye, W.; Wang, Q.; Han, B.; Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Deng, Y. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 9826.
doi: 10.1039/D1TA00745A |
| [26] |
Yuan, Y.; Chen, L. K.; Li, Y. H.; An, X. F.; Lv, J. S.; Guo, K.; Cheng, X.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, M.; He, Y. B.; Kang, F. Y. Energy Materials and Devices 2023, 1, 9370004.
doi: 10.26599/EMD.2023.9370004 |
| [27] |
Hu, Y.; Xie, X.; Li, W.; Huang, Q.; Huang, H.; Hao, S.; Fan, L.; Zhou, W. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 1253.
doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.2c05879 |
| [28] |
Fu, F.-Y.; Xing, G.-E.; Wang, X.-H.; Gao, Z.-H.; Niu, L.-L. Chem. Bull. 2022, 85, 211. (in Chinese)
|
|
(付凤艳, 邢广恩, 王晓红, 高志华, 牛丽丽, 化学通报, 2022, 85, 211.)
|
|
| [29] |
Yin, K.; Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Yang, L.; Tachibana, K.; Hirano, S. J. Mater. Chem. A. 2015, 3, 170.
doi: 10.1039/C4TA05106H |
| [30] |
Tian, S.-W.; Zhou, L.-X.; Zhang, B.-Q.; Zhang, J.-J.; Du, X.-P.; Zhang, H.; Hu, S.-J.; Yuan, Z.-X.; Han, P.-X.; Li, S.-L.; Zhao, W.; Zhou, X.-H.; Cui, G.-L. Acta Chim. Sinica 2022, 80, 56. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A21090440 |
|
(田宋炜, 周丽雪, 张秉乾, 张建军, 杜晓璠, 张浩, 胡思伽, 苑志祥, 韩鹏献, 李素丽, 赵伟, 周新红, 崔光磊, 化学学报, 2022, 80, 56.)
|
|
| [31] |
Song, Z. Y.; Chen, F. F.; Martinez-Ibañez, M.; Feng, W. F.; Forsyth, M.; Zhou, Z. B.; Armand, M.; Zhang, H. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4884.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-40609-y |
| [32] |
Barbosa, J. C.; Goncalves, R.; Costa, C. M.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 14457.
doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c01926 pmid: 35572743 |
| [33] |
Kang, S.-S.; Fan, S.-C.; Liu, Y.; Wei, Y.-C.; Li, Y.; Fang, J.-G.; Meng, C.-Z. Acta Chim. Sinica 2019, 77, 64. (in Chinese)
|
|
(康树森, 范少聪, 刘岩, 魏彦存, 李营, 房金刚, 孟垂舟, 化学学报, 2019, 77, 64.)
|
|
| [34] |
Qu, X.-X.; Guo, Y.; Liu, X.-K. Chinese J. Chem. 2022, 40, 2559.
doi: 10.1002/cjoc.v40.21 |
| [35] |
Choi, W.; Kang, Y.; Kim, I. J.; Seong, B. G.; Yu, W. R.; Kim, D. W. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 35664.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.1c07734 |
| [36] |
Sun, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Shi, L.; Wu, H.; Bu, H.; Ding, S. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 11069.
doi: 10.1039/C9TA00634F |
| [37] |
Sun, C.; Yusuf, A.; Li, S.; Qi, X.; Ma, Y.; Wang, D. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 414, 524.
|
| [38] |
Cabañero, M. A.; Boaretto, N.; Naylor, A. J.; Alcaide, F.; Salian, G. D.; Palombarini, F.; Ayerbe, E.; Borras, M.; Casas-Cabanas, M. Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 12, 33.
|
| [39] |
Chen, L.; Fu, J.; Lu, Q.; Shi, L.; Li, M.; Dong, L.; Xu, Y.; Jia, R. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 378, 1667.
|
| [40] |
Chen, R.; Li, Q.; Yu, X.; Chen, L.; Li, H. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 6820.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.9b00268 |
| [41] |
Yi, J.; Zhou, H. ChemSusChem 2016, 9, 2391.
doi: 10.1002/cssc.v9.17 |
| [42] |
Chai, J.; Liu, Z.; Ma, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; Cui, G.; Chen, L. Adv. Sci. (Weinh) 2017, 4, 1600377.
|
| [43] |
Xue, B. J.; Quesnel, F.; Wang, C.; Liu, W. Electrochim. Acta 2009, 44, 269.
doi: 10.1016/S0013-4686(98)00118-2 |
| [44] |
Zheng, Z.-N.; Gao, X.; Luo, Y.-W.; Huang, J. J. Chem. Ind. Eng. 2022, 71, 421. (in Chinese)
|
|
(郑哲楠, 高翔, 罗英武, 黄杰, 化工学报, 2022, 71, 421.)
|
|
| [45] |
Goodenough, J. B. Annu. Rev. Mat. Res. 2003, 33, 91.
doi: 10.1146/matsci.2003.33.issue-1 |
| [46] |
Shu, Z. X.; McMillan, R. S.; Murray, J. J. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1993, 140, 922.
doi: 10.1149/1.2056228 |
| [47] |
Zhao, Y.; Bai, Y.; Li, W.; An, M.; Bai, Y.; Chen, G. Chem. Mater. 2020, 32, 6811.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.9b04521 |
| [48] |
Yang, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, Q.; Qu, H.; Dong, T.; Zhang, M.; Tang, B.; Zhang, J.; Cui, G. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 17109.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.9b01239 |
| [49] |
Huang, S.; Cui, Z.; Qiao, L.; Xu, G.; Zhang, J.; Tang, K.; Liu, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, B.; Cui, G. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 299, 820.
doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2019.01.039 |
| [50] |
Sha, Y.; Yu, T.; Dong, T.; Wu, X.; Tao, H.; Zhang, H. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2021, 4, 14755.
doi: 10.1021/acsaem.1c03443 |
| [51] |
Pan, Q.; Jiang, S.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Du, Y.; Zhao, N.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 636, 119601.
doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2021.119601 |
| [52] |
Yuan, J. M.; Mecerreyes, D. P.; Antonietti, M. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2013, 38, 1009.
doi: 10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2013.04.002 |
| [53] |
Yu, B.; Zhou, F.; Wang, C.; Liu, W. Eur. Polym. J. 2007, 43, 2699.
doi: 10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2007.03.027 |
| [54] |
Guo, C.; Cao, Y.; Li, J.; Li, H.; Kumar, S.; Oleksandr, S.; Chen, F. Appl. Energ. 2022, 323, 119571.
doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2022.119571 |
| [55] |
Lin, X. J.; Xu, S. Y.; Tong, Y. Q.; Liu, X. S.; Liu, Z. Y.; Li, P.; Liu, R. Q.; Feng, X. M.; Shi, L.; Ma, Y. W. Mater. Horiz. 2023, 10, 859.
doi: 10.1039/D2MH01289H |
| [56] |
Ye, Y.; Elabd, Y. Polymer 2011, 52, 1309.
doi: 10.1016/j.polymer.2011.01.031 |
| [57] |
Meng, N.; Ye, Y. N.; Yang, Z. X.; Li, H.; Lian, F. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2305072.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.v33.43 |
| [58] |
Zhang, Y.-F.; Wang, J.-Y.; Li, X.-J.; Zhao, S.-Y.; He, Y.; Huo, S.-K.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Tan, C. J. Electrochem. 2021, 27, 413. (in Chinese)
|
|
(张运丰, 王佳颖, 李晓洁, 赵诗宇, 何阳, 霍士康, 王雅莹, 谭畅, 电化学, 2021, 27, 413.)
doi: 10.13208/j.electrochem.200915 |
|
| [59] |
Renaud, B.; Sébastien, M.; Rachid, M.; Abdelmaula, A.; Livie, L.; Jean, P. B.; Trang, N. T.; Denis, B.; Didier, G.; Didier, D.; Denoyel, R.; Armand, M. Nat. Mater. 2013, 9, 1.
doi: 10.1038/nmat2602 |
| [60] |
Qiao, L.; Rodriguez, P. S.; MartinezIbanez, M.; Santiago, A.; Aldalur, I.; Lobato, E.; SanchezDiez, E.; Zhang, Y.; Manzano, H.; Zhu, H.; Forsyth, M.; Armand, M.; Carrasco, J.; Zhang, H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 9806.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.2c02260 |
| [61] |
Zhang, Y.-F.; Dong, J.-M.; Tan, C.; Huo, S.-K.; Wang, J.-Y.; He, Y.; Wang, Y.-Y. J. Electrochem. 2021, 27, 108. (in Chinese)
|
|
(张运丰, 董佳明, 谭畅, 霍士康, 王佳颖, 何阳, 王雅莹, 电化学, 2021, 27, 108.)
doi: 10.13208/j.electrochem.200409 |
|
| [62] |
Zhou, H.-L.; Ma, X.-Y.; Wang, Y.-F.; Guan, X.; Wang, B. Acta Chim. Sinica 2012, 70, 783. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A1108281 |
|
(周华龙, 马晓燕, 王毅霏, 管兴, 王波, 化学学报, 2012, 70, 783.)
doi: 10.6023/A1108281 |
|
| [63] |
Xie, J. B.; Xu, H. L.; Wang, Q. R.; Ke, R. H.; Han, B.; Chang, J.; Wang, J.; Deng, Y. H. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2022, 169, 562.
|
| [64] |
Liu, X.; Ding, G.; Zhou, X.; Li, S.; He, W.; Chai, J.; Pang, C.; Liu, Z.; Cui, G. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 11124.
doi: 10.1039/C7TA02423A |
| [65] |
Chen, Z.-P.; Huang, S.-X.; Zhu, H.-B.; Feng, Y.-F. Insul. Mater. 2018, 51, 1. (in Chinese)
|
|
(陈志平, 黄孙息, 朱恒斌, 冯羽风, 绝缘材料, 2018, 51, 1.)
|
|
| [66] |
Wang, L.; Xu, S.; Wang, Z.; Yang, E.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, S.; Jian, X.; Hu, F. eScience 2023, 3, 100090.
doi: 10.1016/j.esci.2022.100090 |
| [67] |
Yang, Q.; Deng, N.-P.; Cheng, B.-W.; Kang, W.-M. Prog. Chem. 2022, 33, 2270. (in Chinese)
|
|
(杨琪, 邓南平, 程博闻, 康卫民, 化学进展, 2022, 33, 2270.)
|
|
| [68] |
Whba, R.; Su'ait, M. S.; TianKhoon, L.; Ibrahim, S.; Mohamed, N. S.; Ahmad, A. React. Funct. Polym. 2021, 164, 104938.
doi: 10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2021.104938 |
| [69] |
Tseng, Y.-C.; Hsiang, S.-H.; Lee, T.-Y.; Teng, H.; Jan, J.-S.; Kyu, T. ACS Appl. Energ. Mater. 2021, 4, 14309.
doi: 10.1021/acsaem.1c03011 |
| [70] |
Zheng, T.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Lin, S.; Zhou, J. Chin. J. Power Sources 2021, 5, 569. (in Chinese)
|
|
(郑涛, 刘婧, 李杨, 林桑, 周江, 电源技术, 2021, 5, 569.)
|
|
| [71] |
Vijayakumar, V.; Anothumakkool, B.; Kurungot, S.; Winter, M.; Nair, J. R. Energy Environ. Sci. 2021, 14, 2708.
doi: 10.1039/D0EE03527K |
| [72] |
Niu, C.; Zhang, M.; Chen, G.; Cao, B.; Shi, J.; Du, J.; Chen, Y. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 283, 349.
doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2018.06.169 |
| [73] |
Yan, Y. Y.; Ju, J. W.; Dong, S. M.; Wang, Y. T.; Huang, L.; Cui, L. F.; Jiang, F.; Wang, Q. L.; Zhang, Y. F.; Cui, G. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2003887.
doi: 10.1002/advs.v8.9 |
| [74] |
Tian, J.-X.; Guo, H.-J.; Wan, J.; Liu, G.-X.; Yan, H.-J.; Wen, R.; Wan, L. J. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 1179. (in Chinese)
|
|
(田建鑫, 郭慧娟, 万静, 刘桂贤, 严会娟, 文锐, 万立骏, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 1179.)
|
|
| [75] |
Yang, K.; Zhao, L.; An, X. F.; Chen, L. K.; Ma, J. B.; Mi, J. S.; He, Y. B. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202302586.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v62.24 |
| [1] | 苑志祥, 张浩, 胡思伽, 张波涛, 张建军, 崔光磊. 离子聚合原位固态化构建高安全锂电池固态聚合物电解质的研究进展★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(8): 1064-1080. |
| [2] | 崔国庆, 胡溢玚, 娄颖洁, 周明霞, 李宇明, 王雅君, 姜桂元, 徐春明. CO2加氢制醇类催化剂的设计制备及性能研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(8): 1081-1100. |
| [3] | 张雅岚, 苑志祥, 张浩, 张建军, 崔光磊. 高镍三元高比能固态锂离子电池的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(12): 1724-1738. |
| [4] | 常婉莹, 谭莹瑛, 吴静怡, 刘英杰, 蔡金海, 赖春艳. 三维结构Li6.28La3Zr2Al0.24O12增强聚氧化乙烯基固态电解质的性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(12): 1708-1715. |
| [5] | 张冠华, 杨子涵, 马越. 混合工艺对氧化物/硫化物复合固态电解质电化学性能的影响[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(10): 1387-1393. |
| [6] | 梁世硕, 康树森, 杨东, 胡建华. 锂金属负极界面修饰及其在硫化物全固态电池中的应用[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(9): 1264-1268. |
| [7] | 宋云霞, 梁飞, 田皓天, 吴燕, 罗敏. 基于分子工程的方法设计首例具有Sr2Be2B2O7 (SBBO)结构的深紫外氟碳酸盐双折射晶体AMgLi2(CO3)2F (A=K, Rb)※[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(2): 105-109. |
| [8] | 李泽洋, 杨宇森, 卫敏. 二氧化碳还原电催化剂的结构设计及性能研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(2): 199-213. |
| [9] | 田宋炜, 周丽雪, 张秉乾, 张建军, 杜晓璠, 张浩, 胡思伽, 苑志祥, 韩鹏献, 李素丽, 赵伟, 周新红, 崔光磊. 聚环氧乙烷聚合物电解质基高电压固态锂金属电池的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(10): 1410-1423. |
| [10] | 庄容, 许潇洒, 曲昌镇, 徐顺奇, 于涛, 王洪强, 徐飞. 多孔聚合物在锂金属负极保护中的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(4): 378-387. |
| [11] | 王静, 王锦. 气凝胶维度结构设计与功能化应用的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(4): 430-442. |
| [12] | 常智, 乔羽, 杨慧军, 邓瀚, 朱星宇, 何平, 周豪慎. 金属有机框架(MOFs)材料在锂离子电池及锂金属电池电解液中的应用[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(2): 139-145. |
| [13] | 康树森, 杨程响, 杨泽林, 吴宁宁, 赵姗, 陈晓涛, 刘富亮, 石斌. 旋涂法制备PEO-PAN-PMMA三组分共混凝胶聚合物电解质[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(12): 1441-1447. |
| [14] | 林祖金, 曹荣. 多孔氢键有机框架(HOFs):现状与挑战[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(12): 1309-1335. |
| [15] | 康树森, 范少聪, 刘岩, 魏彦存, 李营, 房金刚, 孟垂舟. 铝离子聚合物固态电解质[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(7): 647-652. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||