化学学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 82 ›› Issue (6): 677-689.DOI: 10.6023/A24030075 上一篇 下一篇
综述
王丹钰a, 郭子涵a, 郭梦珂a, 易桦a, 黄梦雨a, 段捷a, 张开翔a,b,*( )
)
投稿日期:2024-03-08
发布日期:2024-04-28
作者简介: |
| 王丹钰, 郑州大学药学院2021级药学专业博士研究生. 以第一作者在Nat. Commun., ACS Nano, Small, Adv. Healthcare Mater.及ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces期刊发表研究论文5篇, 累计发表SCI收录论文10篇, 被引180余次, 参与多项国家自然科学基金项目. |
 |
| 张开翔, 郑州大学药学院教授, 博士生导师. 以第一作者或通讯作者在Nat. Commun., Sci. Adv., J. Am. Chem. Soc., Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., Adv. Mater.及Chem. Soc. Rev.等期刊发表研究论文50余篇, 累计发表SCI收录论文100余篇, 被引5000余次, 作为项目负责人承担国家自然科学基金项目4项. |
基金资助:
Danyu Wanga, Zihan Guoa, Mengke Guoa, Hua Yia, Mengyu Huanga, Jie Duana, Kaixiang Zhanga,b,*( )
)
Received:2024-03-08
Published:2024-04-28
Contact:
* E-mail: Supported by:文章分享

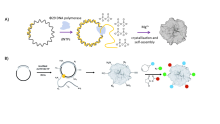
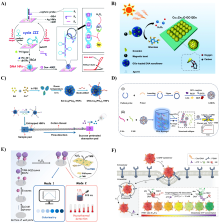
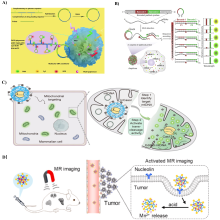
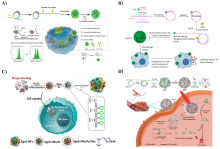
DNA纳米结构因其可编程性、自主设计性和良好的生物相容性, 在生物医学领域显示出巨大的应用潜力. DNA纳米花(DNA nanoflower, DNF)作为一种独特的DNA-有机无机杂化纳米结构, 在近几年内引起了相当多的关注. 其矿化的无机内核不仅有助于维持DNA的稳定性, 还提供了金属离子的辅助矿化功能. 其中DNF凭借其高密度的核酸序列和良好的载荷能力, 可高效装载药物、荧光探针、酶及核酸适配体等功能性分子. 此外, 还可通过控制反应条件调节纳米颗粒的尺寸, 实现在不同生理环境下的高渗透、长滞留效应, 进而应用于生物医学的多个领域. 综述了DNF的合成及其生物医学应用. 首先简要介绍了DNF的合成方法以及合成条件的控制; 其次总结了工程化的DNF在生物检测、生物成像和药物治疗方面的应用; 最后, 讨论了DNF在生物医学应用中的挑战并对其在实际临床的应用进行展望. 未来基于DNF更广泛的生物医学发展有待研究人员们的探索.
王丹钰, 郭子涵, 郭梦珂, 易桦, 黄梦雨, 段捷, 张开翔. DNA纳米花生物医学研究进展概述[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(6): 677-689.
Danyu Wang, Zihan Guo, Mengke Guo, Hua Yi, Mengyu Huang, Jie Duan, Kaixiang Zhang. Overview of Advances in DNA Nanoflower Biomedical Research[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(6): 677-689.




| [1] |
Seeman, N. C. J. Theor. Biol. 1982, 99, 237.
pmid: 6188926 |
| [2] |
Zhu, G.-Z.; Hu, R.; Zhao, Z.-L.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, X.-B.; Tan, W.-H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 16438.
|
| [3] |
Baker, Y. R.; Chen, J.-F.; Brown, J.; El-Sagheer, A. H.; Wiseman, P.; Johnson, E.; Goddard, P.; Brown, T. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 7495.
|
| [4] |
Baker, Y. R.; Yuan, L.; Chen, J.; Belle, R.; Carlisle, R.; El-Sagheer, A. H.; Brown, T. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 9042.
|
| [5] |
Beyer, S.; Nickels, P.; Simmel, F. C. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 719.
|
| [6] |
Wang, Y.-T.; Wang, Z.-Z.; Zhan, Z.-X.; Yan, L-N.; Wang, L.-J.; Xu, H.-Y. Foods 2022, 11, 1852.
|
| [7] |
Lv, J.; Dong, Y.-H.; Gu, Z.; Yang, D.-Y. Chem.-Eur. J. 2020, 26, 14512.
|
| [8] |
Kim, E.; Agarwal, S.; Kim, N.; Hage, F. S.; Leonardo, V.; Gelmi, A.; Stevens, M. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 2888.
|
| [9] |
Lv, Y.-F.; Hu, R.; Zhu, G.-Z.; Zhang, X.-B.; Mei, L.; Liu, Q.-L.; Qiu, L.-P.; Wu, C.-C.; Tan, W.-H. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 1508.
|
| [10] |
Park, K. S.; Batule, B. S.; Chung, M.; Kang, K. S.; Park, T. J.; Kim, M. I.; Park, H. G. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 2231.
doi: 10.1039/c6tb03047e pmid: 32263613 |
| [11] |
Xiang, J.-H.; Feng, K.; Wan, T.; He, S.-Y.; Deng, H.-L.; Li, D.-R. Microchemical Journal 2024, 200, 110289.
|
| [12] |
Zhao, Z.; Fu, J.; Dhakal, S.; Johnson-Buck, A.; Liu, M.; Zhang, T.; Woodbury, N. W.; Liu, Y.; Walter, N. G.; Yan, H. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10619.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms10619 pmid: 26861509 |
| [13] |
Yan, Y.-C.; Li, J.; Li, W.-H.; Wang, Y.; Song, W.-L.; Bi, S. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 22456.
|
| [14] |
Kim, E.; Zwi-Dantsis, L.; Reznikov, N.; Hansel, C. S.; Agarwal, S.; Stevens, M. M. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1701086.
|
| [15] |
Ge, J.; Lei, J.-D.; Zare, R. N. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 428.
|
| [16] |
Liang, Y.; Zhang, J.-G.; Xu, C.-L.; Wang, J.-J.; Han, W.-S.; Yang, J.-L.; Wu, S.-X.; An, J-Y.; Liu, J.-J.; Zhang, Z.-Z.; Shi, J.-J.; Zhang, K.-X. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 15025.
|
| [17] |
Li, C.-Y.; Meng, Y.; Wang, S.-S.; Qian, M.; Wang, J.-X.; Lu, W.-Y.; Huang, R.-Q. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 12096.
|
| [18] |
Li, S.-K.; Chen, A.-Y.; Niu, X.-X.; Liu, Z.-T.; Du, M.; Chai, Y.-Q.; Yuan, R.; Zhuo, Y. Chem. Commum. 2017, 53, 9624.
|
| [19] |
Li, Y.-X.; Wang, W.-Q.; Gong, H.-X.; Xu, J.-H.; Yu, Z.-C.; Wei, Q.-H.; Tang, D.-P. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 6818.
|
| [20] |
Yang, L.-M.; Liu, B.; Li, N.; Tang, B. Acta Chim. Sinica 2017, 75, 1047. (in Chinese)
|
|
(杨立敏, 刘波, 李娜, 唐波, 化学学报, 2017, 75, 1047.)
doi: 10.6023/A17080353 |
|
| [21] |
Wu, T.-T.; Yang, Y.-M.; Cao, Y.; Song, Y.-C.; Xu, L.-P.; Zhang, X.-J.; Wang, S.-T. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 42050.
|
| [22] |
Zeng, R.-J.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.-S.; Tang, D.-P.; Lin, Y. Talanta 2021, 221, 121600.
|
| [23] |
He, H.-Z.; Cheng, L.-J.; He, Y.-H.; Chen, J.-M.; Song, L.; Yang, Y.-Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, Z.-Y.; Hong, G.-L. Sens. Actuators, B 2022, 371, 132532.
|
| [24] |
Edgar, J. R. BMC Biol. 2016, 14, 46.
|
| [25] |
Soung, Y. H.; Ford, S.; Zhang, V.; Chung, J. Cancers 2017, 9, 8.
|
| [26] |
Zhang, X.-Y.; Zhu, X.-Y.; Li, Y.-F.; Hai, X.; Bi, S. Talanta 2023, 258, 124456.
|
| [27] |
Gao, Y.-F.; Yan, Y.-C.; Cao, J.-Y.; Bi, S. J. Instrum. Anal. 2022, 41, 601. (in Chinese)
|
|
(高雨菲, 闫永存, 曹景玉, 毕赛, 分析测试学报, 2022, 41, 601.)
|
|
| [28] |
Tamima, U.; Sarkar, S.; Islam, M. R.; Shil, A.; Kim, K. H.; Reo, Y. J.; Jun, Y. W.; Banna, H.; Lee, S.; Ahn, K. H. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202300580.
|
| [29] |
Tan, K.-Y.; Li, C.-Y.; Li, Y.-F.; Fei, J.; Yang, B.; Fu, Y.-J.; Li, F. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 1749.
|
| [30] |
Kim, N.; Kim, E.; Kim, H.; Thomas, M. R.; Najer, A.; Stevens, M. M. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2007738.
|
| [31] |
Ma, Y.-X.; Chen, Q.-H.; Pan, X.-Y.; Zhang, J. Top. Curr. Chem. 2021, 379, 10.
|
| [32] |
Zhu, H.; Fan, J.; Du, J.; Peng, X. Acc. Chem. Res. 2016, 49, 2115.
|
| [33] |
Hu, R.; Zhang, X.-B.; Zhao, Z.-L.; Zhu, G.-Z.; Chen, T.; Fu, T.; Tan, W.-H. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 5821.
|
| [34] |
Deng, R.-J.; Zhang, K.-X.; Wang, L.-D.; Ren, X.-J.; Sun, Y.-P.; Li, J.-H. Chem 2018, 4, 1373.
|
| [35] |
Li, Y.; Wu, Y.-H.; Xu, R.; Guo, J.-L.; Quan, F.-L.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, D.; Pei, Y.; Gao, H.; Liu, W.; Liu, J.-J.; Zhang, Z.-Z.; Deng, R.-J.; Shi, J.-J.; Zhang, K.-X. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 7722.
|
| [36] |
Dan, Q.; Jiang, X.-P.; Wang, R.; Dai, Z.-F.; Sun, D. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2207090.
|
| [37] |
Zhao, H.-X.; Lv, J.-G.; Li, F.; Zhang, Z.-L.; Zhang, C.-Z.; Gu, Z.; Yang, D.-Y. Biomaterials 2021, 268, 120591.
|
| [38] |
Cesur-Ergün, B.; Demir-Dora, D. J. Gene Med. 2023, 25, e3550.
|
| [39] |
Iglesias-Lopez, C.; Agustí, A.; Obach, M.; Vallano, A. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 921.
doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00921 pmid: 31543814 |
| [40] |
Li, C.; Si, X.; Li, J.-B.; Zhang, Y. Acta Chim. Sinica 2023, 81, 1240. (in Chinese)
|
|
(李琛, 司笑, 李金波, 张艳, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 1240.)
doi: 10.6023/A23040179 |
|
| [41] |
Jin, Y.; Li, Z.-H.; Liu, H.-F.; Chen, S.-Z.; Wang, F.; Wang, L.; Li, N.; Ge, K.; Yang, X.-J.; Liang, X.-J. NPG Asia Mater. 2017, 9, 365.
|
| [42] |
Huang, C.-H.; Lee, K.-C.; Doudna, J. A. Trends in Cancer 2018, 4, 499.
|
| [43] |
Shi, J.-J.; Yang, X.; Li, Y.-N.; Wang, D.-Y.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Z.-Z.; Liu, J.-J.; Zhang, K.-X. Biomaterials 2020, 256, 120221.
|
| [44] |
Krieg, A. M. Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 2006, 5, 471.
|
| [45] |
Krieg, A. M. Oncogene 2008, 27, 161.
doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210911 pmid: 18176597 |
| [46] |
Wang, D.-Y.; Liu, J.-W.; Duan, J.; Ma, Y.-R.; Gao, H.; Zhang, Z.-Z.; Liu, J.-J.; Shi, J.-J.; Zhang, K.-X. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 44183.
|
| [47] |
Zhang, L.-Q.; Zhu, G.-Z.; Mei, L.; Wu, C.-C.; Qiu, L.-P.; Cui, C.; Liu, Y.; Teng, I. T.; Tan, W.-H. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 24069.
|
| [48] |
Wang, J.; Gan, M.-Z. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 16030.
|
| [49] |
Wang, J.; Wang, H.-M.; Wang, H.; He, S.-Z.; Li, R.-M.; Deng, Z.; Liu, X.-Q.; Wang, F. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 5852.
|
| [50] |
Zhang, K.-X.; Liu, J.-J.; Song, Q.-L.; Wang, D.-Y.; Shi, J.-J. Chem. J. Chin. Univ. 2020, 41, 1461. (in Chinese)
|
|
(张开翔, 刘军杰, 宋巧丽, 王丹钰, 史进进, 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41, 1461.)
doi: 10.7503/cjcu20200242 |
|
| [51] |
Zhang, L.-L.; Abdullah, R.; Hu, X.-X.; Bai, H.-R.; Fan, H.-H.; He, L.; Liang, H.; Zou, J.-M.; Liu, Y.-F.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, X.-B.; Tan, W.-H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 4282.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.8b10795 pmid: 30730715 |
| [52] |
Liao, H.-J.; Cao, Y.-C.; Hu, C.; Shen, S.-F.; Zhang, Z.-F.; Li, D.-R.; Du, Y.-H. Mater. Today Bio 2024, 25, 101005.
|
| [53] |
Zhang, K-X.; Liu, J.-J.; Song, Q.-L.; Yang, X.; Wang, D.-Y.; Liu, W.; Shi, J.; Zhang, Z. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 46604.
|
| [54] |
Gu, C.; Liu, X.-L.; Luo, L.; Chen, J.-Q.; Zhou, X.; Chen, G.-H.; Huang, X.; Yu, L.; Chen, Q.; Yang, Y. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202307020.
|
| [55] |
Chen, X.; He, X.-Y.; Gao, R.-X.; Lan, X.-Y.; Zhu, L.-J.; Chen, K.-R.; Hu, Y.-Z.; Huang, K.-L.; Xu, W.-T. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 1036.
|
| [56] |
Ouyang, Q.; Liu, K.; Zhu, Q.; Deng, H.; Le, Y.; Ouyang, W.; Yan, X.; Zhou, W.; Tong, J. Small 2022, 18, e2107534.
|
| [57] |
Imashiro, C.; Takeshita, H.; Morikura, T.; Miyata, S.; Takemura, K.; Komotori, J. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21466.
|
| [58] |
Ghahremani, F. H.; Sazgarnia, A.; Bahreyni-Toosi, M. H.; Rajabi, O.; Aledavood, A. Int. J. Hyperthermia 2011, 27, 625.
|
| [59] |
Shen, S.; Qiu, J.-C.; Huo, D.; Xia, Y.-N. Small 2023, 20, 2305426.
|
| [60] |
Hai, X.; Ji, M.-J.; Yu, K.-X.; Tian, T.; Cui, Z.-M.; Bi, S.; Zhang, X.-J. Mater. Today Nano 2023, 23, 100355.
|
| [61] |
Shi, J-J.; Wang, D.-Y.; Ma, Y.-R.; Liu, J.-W.; Li, Y.-N.; Reza, R.; Zhang, Z.-Z.; Liu, J.-J.; Zhang, K.-X. Small 2021, 17, 2104722.
|
| [1] | 王博, 蔡向东, 肖建喜. 肿瘤特异性多肽探针及其在生物成像中的应用[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(3): 367-376. |
| [2] | 李佳欣, 李蓓, 王纪康, 何蕾, 赵宇飞. 水滑石(LDHs)及其衍生物在生物医药领域的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(3): 238-256. |
| [3] | 贾伊祎, 王文杰, 梁玲, 袁荃. 核酸功能化稀土基纳米材料在生物检测中的应用[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(11): 1177-1184. |
| [4] | 熊麟, 凡勇, 张凡. 稀土纳米晶用于近红外区活体成像和传感研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(12): 1239-1249. |
| [5] | 苏莹莹, 彭天欢, 邢菲菲, 李迪, 樊春海. 纳米等离子体生物传感及成像[J]. 化学学报, 2017, 75(11): 1036-1046. |
| [6] | 纪光, 闫路林, 王慧, 马莲, 徐斌, 田文晶. 高效近红外聚集诱导发光纳米粒子用于生物成像的研究[J]. 化学学报, 2016, 74(11): 917-922. |
| [7] | 刘腾, 程亮, 刘庄. 二维过渡金属硫族化合物在生物医学中的应用[J]. 化学学报, 2015, 73(9): 902-912. |
| [8] | 刘丽赏, 刘洪娜, 李松, 邓燕, 李小龙, 何农跃. 用于生物检测的链霉亲和素修饰γ-Fe2O3@Au复合颗粒的制备与表征[J]. 化学学报, 2010, 68(20): 2041-2046. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||