化学学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 82 ›› Issue (8): 856-864.DOI: 10.6023/A24040125 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
李梦丽a,b, 张婕a,b, 刘丽珍a,b, 徐首红a,b,*( ), 刘洪来a,b
), 刘洪来a,b
投稿日期:2024-04-10
发布日期:2024-06-24
基金资助:
Mengli Lia,b, Jie Zhanga,b, Lizhen Liua,b, Shouhong Xua,b,*( ), Honglai Liua,b
), Honglai Liua,b
Received:2024-04-10
Published:2024-06-24
Contact:
* E-mail: Supported by:文章分享
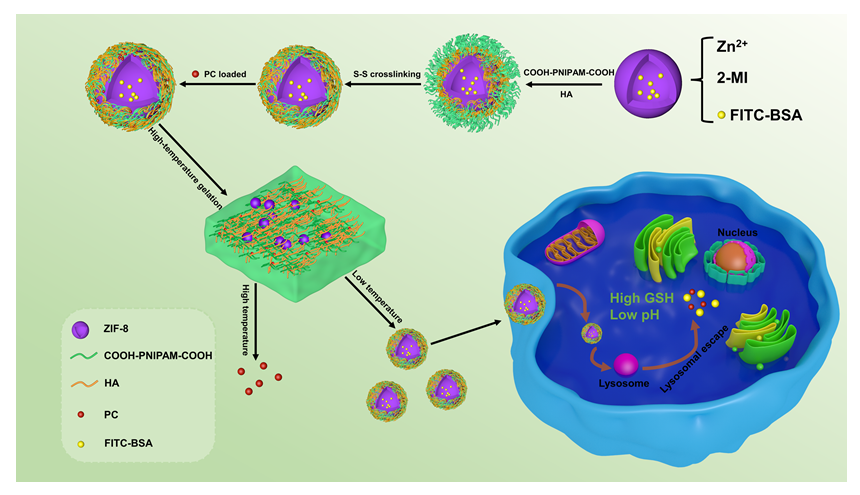
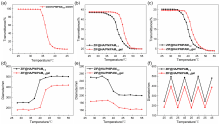
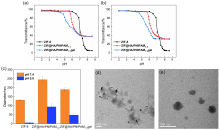
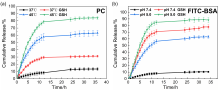
生物大分子药物疗效优、特异性强, 但细胞转染困难且容易失活, 本工作开发了一种多功能微凝胶载体ZIF@HA/PNIPAM1:kgel, 用于多药分区共载及细胞内、外的独立释放. 该微凝胶表现出多重刺激响应能力, 其核ZIF-8遇酸溶解, 凝胶层高温收缩且可被谷胱甘肽(GSH)还原解离. 小分子药物原花青素(PC)和大分子牛血清蛋白(FITC-BSA)作为药物模型可以分别包载于凝胶层和ZIF-8中. 体外释药实验证明微凝胶在正常生理环境下能有效防止药物泄漏; 在模拟肿瘤细胞外、内部微环境时, PC和FITC-BSA最高可分别达到74%和88%的释放量. 本工作构建的载药系统将有助于生物大分子的胞内安全、有效递送及解决多药耐药问题, 研究思路将对于大病化疗、受损组织修复等所需大分子胞内递送的研究提供有意义的科学指导.
李梦丽, 张婕, 刘丽珍, 徐首红, 刘洪来. 用于生物大分子药物胞内递送的多重刺激响应型微凝胶载体[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(8): 856-864.
Mengli Li, Jie Zhang, Lizhen Liu, Shouhong Xu, Honglai Liu. Multi-Responsive Microgel Carrier for Intracellular Delivery of Biomacromolecular Drugs[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(8): 856-864.
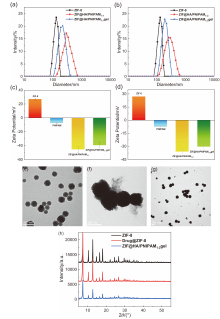

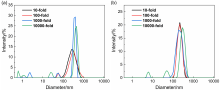
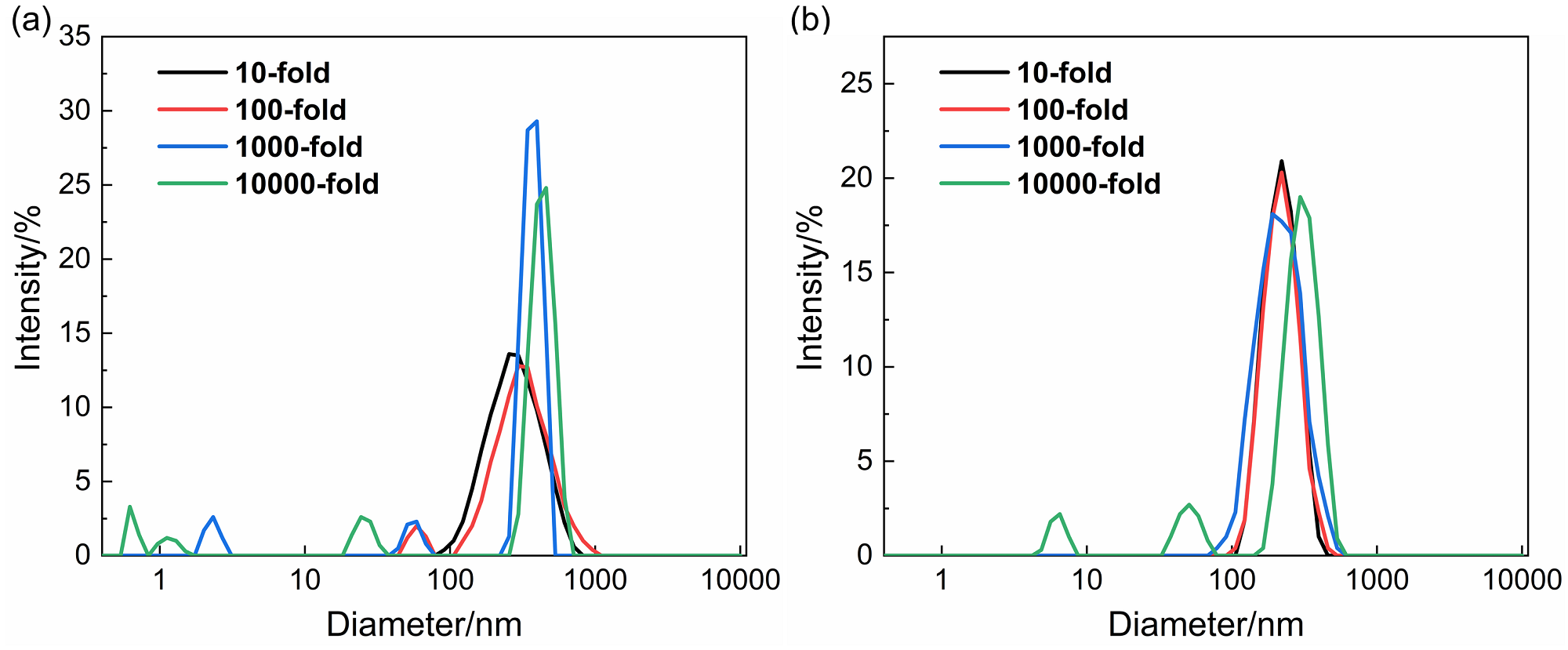

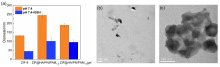


| drug@microgel | DLC/% | DLE/% |
|---|---|---|
| PC@ZIF@HA/PNIPAM1:2gel | 15.22 | 52.34 |
| BSA@ZIF@HA/PNIPAM1:2gel | 1.11 | 79.45 |
| drug@microgel | DLC/% | DLE/% |
|---|---|---|
| PC@ZIF@HA/PNIPAM1:2gel | 15.22 | 52.34 |
| BSA@ZIF@HA/PNIPAM1:2gel | 1.11 | 79.45 |



| [1] |
Shanmuganathan, R.; Edison, T. N. J. I.; LewisOscar, F.; Kumar, P.; Shanmugam, S.; Pugazhendhi, A. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 130, 727.
doi: S0141-8130(18)37203-9 pmid: 30771392 |
| [2] |
Liao, Y.; Wang, D. M.; Gu, Z. J. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 1438 (in Chinese).
doi: 10.6023/A21070319 |
|
(廖友, 王冬梅, 谷战军, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 1438.)
doi: 10.6023/A21070319 |
|
| [3] |
Wang, T.; Zhao, L.; Wang, K. W.; Bai, Y. F.; Feng, F. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 600 (in Chinese).
doi: 10.6023/A20120578 |
|
(王涛, 赵璐, 王科伟, 白云峰, 冯锋, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 600.)
doi: 10.6023/A20120578 |
|
| [4] |
Zhang, C.; Yang, K.; Yang, G. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 258, 129070.
|
| [5] |
Mishra, V.; Tripathi, V.; Yadav, P.; Singh, M. P. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 234, 123617.
|
| [6] |
Wang, Y. Z.; Liu, Y. H.; Xu, S. H.; Liu, H. L. Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin. 2019, 35, 876 (in Chinese).
|
|
(王义洲, 刘晔宏, 徐首红, 刘洪来, 物理化学学报, 2019, 35, 876.)
|
|
| [7] |
Hashemzadeh, A.; Amerizadeh, F.; Asgharzadeh, F.; Drummen, G. P. C.; Hassanian, S. M.; Landarani, M.; Avan, A.; Sabouri, Z.; Darroudi, M.; Khazaei, M. J. Cluster Sci. 2022, 33, 2345.
|
| [8] |
Song, Y.; Han, S.; Liu, S.; Sun, R.; Zhao, L.; Yan, C. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 25339.
|
| [9] |
Lawson, H. D.; Walton, S. P.; Chan, C. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 7004.
|
| [10] |
Tian, Y.; Gao, Z.; Li, M.; Hu, M.; Hao, J.; Cui, J. Chem. Mater. 2023, 35, 5593.
|
| [11] |
Duan, W.; Hang, L.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Q.; Tang, X.; Jiang, W.; Wu, Y.; Lv, W.; Wang, Y. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 39039.
|
| [12] |
Long, Y.; Feng, Y.; He, Y.; Luo, B.; Liu, M. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 5813.
|
| [13] |
Parsaei, M.; Akhbari, K. Inorg. Chem. 2022, 61, 14528.
|
| [14] |
Jung, S.; Chang, S.; Kim, N.-E.; Choi, S.-O.; Song, Y.-J.; Yuan, Y.; Kim, J. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 13671.
|
| [15] |
Ho, P. H.; Salles, F.; Di Renzo, F.; Trens, P. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2020, 500, 119229.
|
| [16] |
Dave, R.; Randhawa, G.; Kim, D.; Simpson, M.; Hoare, T. Mol. Pharmaceutics 2022, 19, 1704.
|
| [17] |
Ayar, Z.; Shafieian, M.; Mahmoodi, N.; Sabzevari, O.; Hassannejad, Z. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, e51167.
|
| [18] |
Caputo, T. M.; Aliberti, A.; Cusano, A. M.; Ruvo, M.; Cutolo, A.; Cusano, A. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, e50147.
|
| [19] |
Jawahar, N.; Meyyanathan, S. Int. J. Hlth. Allied Sc. 2012, 1, 217.
|
| [20] |
Schroeder, R.; Richtering, W.; Potemkin, I. I.; Pich, A. Macromolecules 2018, 51, 6707.
|
| [21] |
Li, C.; Si, X.; Li, J. B.; Zhang, Y. Acta Chim. Sinica 2023, 81, 1240 (in Chinese).
|
|
(李琛, 司笑, 李金波, 张艳, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 1240.)
doi: 10.6023/A23040179 |
|
| [22] |
Pu, X.; Li, Z. J.; Shi, J. Q.; Zhu, Y. Q.; Du, J. Z. Acta Chim. Sinica 2023, 81, 1438 (in Chinese).
|
|
(溥旭, 李泽娟, 石隽秋, 朱云卿, 杜建忠, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 1438.)
doi: 10.6023/A23050246 |
|
| [23] |
Gaur, M.; Maurya, S.; Akhtar, M. S.; Yadav, A. B. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 18751.
|
| [24] |
Lv, M.; Sun, M.; Wu, M.; Zhang, F.; Yin, H.; Sun, Y.; Liu, R.; Fan, Z.; Du, J. Nano Lett. 2022, 22, 9621.
|
| [25] |
He, W.; Xing, X.; Wang, X.; Wu, D.; Wu, W.; Guo, J.; Mitragotri, S. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1910566.
|
| [26] |
Zhang, Y.; Sun, T.; Jiang, C. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2018, 8, 34.
|
| [27] |
Engelbrecht, A. M.; Mattheyse, M.; Ellis, B.; Loos, B.; Thomas, M.; Smith, R.; Peters, S.; Smith, C.; Myburgh, K. Cancer Lett. 2007, 258, 144.
doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2007.08.020 pmid: 17923279 |
| [28] |
Zhang, B.; Kang, M.; Xie, Q.; Xu, B.; Sun, C.; Chen, K.; Wu, Y. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 537.
|
| [29] |
Lacombe, A.; Wu, V. C. H.; White, J.; Tadepalli, S.; Andre, E. E. Food Microbiol. 2012, 30, 124.
doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2011.10.006 pmid: 22265292 |
| [30] |
Vera de Rosso, V.; Hillebrand, S.; Cuevas Montilla, E.; Bobbio, F. O.; Winterhalter, P.; Mercadante, A. Z. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2008, 21, 291.
|
| [31] |
Martí, M. P.; Pantaleón, A.; Rózek, A.; Soler, A.; Valls, J.; Macià, A.; Romero, M.-P.; Motilva, M. J. Sep. Sci. 2010, 33, 2841.
|
| [32] |
Lei, B.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, M.; Xu, S.; Liu, H. Colloid Surface A 2022, 648, 129269.
|
| [1] | 王筑城, 刘磊, 朱梦媛, 孙悦, 赵晴, 丁玉寅, 陆继鑫, 王存国, 李奇, 贺爱华, 叶付臣. 1,5-二氨基蒽醌(AAQ)复合材料用作锂离子电池新型正极材料的性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(6): 589-595. |
| [2] | 王丹, 封波, 张晓昕, 刘亚楠, 裴燕, 乔明华, 宗保宁. 基于热解ZIF-8的氮掺杂碳电化学氧还原合成过氧化氢催化剂[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(6): 772-780. |
| [3] | 朱鹏飞, 娄晨思, 史雨翰, 王传义. Ag/AgCl/ZIF-8复合材料的制备及其对NO光催化氧化性能的研究[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(10): 1385-1393. |
| [4] | 孙延慧, 齐有啸, 申优, 井翠洁, 陈笑笑, 王新星. 基于RGO-Au-ZIF-8复合材料的电化学传感器制备及其在铅离子和铜离子同时检测中的应用[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(2): 147-154. |
| [5] | 李相晔, 练成, 支东彦, 徐首红, 刘洪来. SiO2-HA/PNIPAm核壳温敏微凝胶的合成及其溶胀性能[J]. 化学学报, 2014, 72(6): 689-696. |
| [6] | 李妍, 杨盛, 何桂丽, 焦永华, 付昱, 孙挺. 聚乳酸自支持膜的叠加及其作为药物控释阻隔层的研究[J]. 化学学报, 2014, 72(10): 1110-1114. |
| [7] | 陈栋栋, 王林, 孙俊奇. 表面活性剂胶束实现疏水分子在聚合物微凝胶层层组装膜中的高效负载[J]. 化学学报, 2012, 70(17): 1779-1784. |
| [8] | 张文建, 范溦, 李敏, 洪春雁, 潘才元. 多重响应性超支化星形聚合物的合成与组装以及控制释放研究[J]. 化学学报, 2012, 70(16): 1690-1696. |
| [9] | 吕美丽, 李国梁, 李超, 陈慧强, 张颖. 温敏性P(St-NIPAM)/PNIPAM-Ag复合微凝胶制备及性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2011, 69(20): 2385-2392. |
| [10] | 杨占娴, 宫永宽. 高包封率异烟肼类脂质体的制备与性质研究[J]. 化学学报, 2011, 69(05): 508-514. |
| [11] | 胡炜, 张颖. 温度和pH双重敏感荧光复合微凝胶制备和表征[J]. 化学学报, 2010, 68(18): 1855-1863. |
| [12] | 宁向莉, 张颖, 吴华涛. 多层核-壳结构P(AM-co-MAA)/W/UF复合微球制备研究[J]. 化学学报, 2010, 68(01): 19-26. |
| [13] | 刘聪颖,胡建华,杨东,杨武利. 多重响应性介孔二氧化硅纳米微球的制备及载药研究[J]. 化学学报, 2009, 67(8): 843-849. |
| [14] | 张世平,朱霞霞,宫永宽. 末端带有磷酰胆碱基团的聚丁二酸丁二醇酯的合成、表征和性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2009, 67(16): 1903-1909. |
| [15] | 孙桂香,张明祖,许杨,陆一鸣,倪沛红. pH响应性阳离子型微凝胶的制备及性质研究[J]. 化学学报, 2009, 67(14): 1685-1690. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||