化学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 83 ›› Issue (8): 868-877.DOI: 10.6023/A25040107 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
韦正兵a, 鲍梦凡a, 徐世彪a, 程怡a, 陈诗洁a, 林娜a,*( ), 冒爱琴a,b,*(
), 冒爱琴a,b,*( )
)
投稿日期:2025-04-03
发布日期:2025-06-26
通讯作者:
林娜, 冒爱琴
基金资助:
Zhengbing Weia, Mengfan Baoa, Shibiao Xua, Yi Chenga, Shijie Chena, Na Lina,*( ), Aiqin Maoa,b,*(
), Aiqin Maoa,b,*( )
)
Received:2025-04-03
Published:2025-06-26
Contact:
Na Lin, Aiqin Mao
Supported by:文章分享
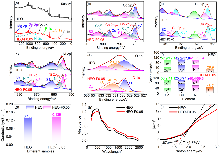
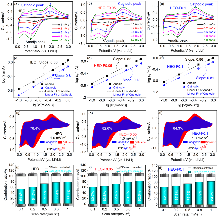
高熵氧化物因其灵活的组分设计和多组元之间的协同效应, 被认为是锂离子电池最具有潜力的负极材料之一. 然而其较低的本征电子/离子电导率严重限制其在锂离子电池存储中的动力学行为, 高熵氧化物负极材料存在倍率性能低、循环稳定性差的现状. 本研究以岩盐型(Co0.2Cu0.2Mg0.2Ni0.2Zn0.2)O为研究基础, 采用溶液燃烧法, 通过高电负性阴离子F-掺杂策略, 调控晶格畸变和氧空位等本征缺陷, 成功制备了具有单一岩盐结构的F-掺杂(Co0.2Cu0.2Mg0.2- Ni0.2Zn0.2)O1-xFx (x=0, 0.05, 0.1)高熵氧化物锂离子电池负极材料. 测试结果表明: (Co0.2Cu0.2Mg0.2Ni0.2Zn0.2)O0.95F0.05负极材料展示了卓越的倍率性能和优异的循环稳定性, 200 mA•g-1下循环150圈后比容量高达389.5 mAh•g-1; 电流密度至1000 mA•g-1循环150圈后比容量仍高达233.4 mAh•g-1, 较未掺杂的样品提升56%, 且容量保持率依然高达93.1%. 其优异的电化学性能归因于: 适量的F-掺杂提升了电极材料的比表面积和表面Cu+含量, 导致晶格畸变降低和氧空位增加, 优化的质构、适度的晶格畸变和氧空位, 不仅提供了更多的电化学反应活性位点和传输通道, 而且还强化了表面赝电容特性, 极大促进了电子和离子的传输动力学.
韦正兵, 鲍梦凡, 徐世彪, 程怡, 陈诗洁, 林娜, 冒爱琴. 氟掺杂诱导岩盐型高熵氧化物本征缺陷调控及其储锂性能优化[J]. 化学学报, 2025, 83(8): 868-877.
Zhengbing Wei, Mengfan Bao, Shibiao Xu, Yi Cheng, Shijie Chen, Na Lin, Aiqin Mao. Fluorine Doping-Induced Intrinsic Defect Modulation in Rock-Salt-Type High-Entropy Oxide for Lithium Storage Performance Optimization[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2025, 83(8): 868-877.


| Sample | a/nm | b/nm | c/nm | V/nm3 | Rwp | Rp |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HEO | 0.42389 | 0.42389 | 0.42389 | 0.07617 | 5.35% | 3.92% |
| HEO-F0.05 | 0.42369 | 0.42369 | 0.42369 | 0.07606 | 3.49% | 2.46% |
| HEO-F0.1 | 0.42351 | 0.42351 | 0.42351 | 0.07596 | 3.67% | 2.62% |
| Sample | a/nm | b/nm | c/nm | V/nm3 | Rwp | Rp |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HEO | 0.42389 | 0.42389 | 0.42389 | 0.07617 | 5.35% | 3.92% |
| HEO-F0.05 | 0.42369 | 0.42369 | 0.42369 | 0.07606 | 3.49% | 2.46% |
| HEO-F0.1 | 0.42351 | 0.42351 | 0.42351 | 0.07596 | 3.67% | 2.62% |


| Sample | SBET/(m2•g-1) | VBJH/(cm3•g-1) | Daver./nm | Dmost/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HEO | 7.564 | 0.022 | 11.474 | 3.278 |
| HEO-F0.05 | 18.810 | 0.016 | 3.399 | 3.092 |
| HEO-F0.1 | 9.200 | 0.018 | 11.740 | 3.290 |
| Sample | SBET/(m2•g-1) | VBJH/(cm3•g-1) | Daver./nm | Dmost/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HEO | 7.564 | 0.022 | 11.474 | 3.278 |
| HEO-F0.05 | 18.810 | 0.016 | 3.399 | 3.092 |
| HEO-F0.1 | 9.200 | 0.018 | 11.740 | 3.290 |








| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
|
(贾洋刚, 陈诗洁, 邵霞, 程捷, 林娜, 方道来, 冒爱琴, 李灿华, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 486.)
doi: 10.6023/A23020046 |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
|
(邵霞, 贾洋刚, 程婕, 方道来, 冒爱琴, 檀杰, 过程工程学报, 2023, 23, 771.)
doi: 10.12034/j.issn.1009-606X.222242 |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
|
(付晨, 王立坤, 邱茹蒙, 王贵, 蔡文豪, 杨静凯, 赵洪力, 材料研究学报, 2019, 33, 277.)
doi: 10.11901/1005.3093.2018.421 |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
|
(鲍梦凡, 陈诗洁, 邵霞, 邓慧娟, 冒爱琴, 檀杰, 化学学报, 2024, 82, 303.)
doi: 10.6023/A23100465 |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
|
(陈见, 尹周澜, 张衡中, 有色金属工程, 2019, 9, 1.)
|
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
|
(陈诗洁, 鲍梦凡, 林娜, 杨海琴, 冒爱琴, 材料研究学报, 2024, 38, 508.)
doi: 10.11901/1005.3093.2023.567 |
| [1] | 徐梦鑫, 杨智健, 孙径, 邹文强, 徐忠宁, 郭国聪. Pd/Pr-CeO2催化剂载体氧空位调控CO酯化制碳酸二甲酯选择性[J]. 化学学报, 2025, 83(7): 655-660. |
| [2] | 张娜娜, 李静. 氧空位增强PdNi/HfO2催化剂在乙二醇电催化氧化中的活性[J]. 化学学报, 2025, 83(7): 709-715. |
| [3] | 孙伟, 辛国祥, 刘飞, 鞠藤, 程宇通, 宋金玲, 包金小, 布林朝克. 三维石墨烯/富含氧空位Fe2O3复合材料的构建实现超级电容器超高能量密度[J]. 化学学报, 2025, 83(3): 256-265. |
| [4] | 张帆帆, 蔡元韬, 陶剑波, 常国菊, 郭欣辰, 郝仕油. Zn, C引入量和煅烧温度对ZnO/C/CeO2光催化还原Cu2+效率的影响[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(8): 871-878. |
| [5] | 王国景, 陈永辉, 张秀芹, 张俊笙, 徐俊敏, 王静. 氧空位控制BiVO4晶面异质结的磁性和光电催化性能[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(4): 409-415. |
| [6] | 税子怡, 于思乐, 陆伟, 许留云, 刘庆叶, 赵炜, 刘益伦. Mn掺杂Co3O4双功能电催化剂在碱性介质下氧还原和析氧反应中的应用[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(10): 1039-1049. |
| [7] | 贾洋刚, 陈诗洁, 邵霞, 程婕, 林娜, 方道来, 冒爱琴, 李灿华. 高性能无钴化钙钛矿型高熵氧化物负极材料的制备及储锂性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(5): 486-495. |
| [8] | 张旭寒, 邓博文, 范海东, 黄文辉, 张彦威. 基于锌锗二元氧化物的光热协同分解CO2研究[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(10): 1120-1126. |
| [9] | 许辰宇, 林伽毅, 潘富强, 邓博文, 王智化, 周俊虎, 陈云, 马京程, 顾志恩, 张彦威. Ni离子替位掺杂TiO2增强光热化学循环还原CO2研究[J]. 化学学报, 2017, 75(7): 699-707. |
| [10] | 王添辉,李越湘,彭绍琴,吕功煊,李树本. 铂修饰的稀土掺杂TiO2的光催化制氢活性[J]. 化学学报, 2005, 63(9): 797-801. |
| [11] | 王智民,李丽,刘静波,张艳熹. Li+-CaxPb1-xTiO3湿敏纳米薄膜的激光拉曼光谱、晶格畸变和激光显微组织——应用“软模理论”解谱[J]. 化学学报, 2005, 63(1): 81-85. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||