化学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 83 ›› Issue (8): 878-886.DOI: 10.6023/A25040134 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
尚建宇a,b, 王超超a,b, 高欣冉a,b, 章寅a,b,*( ), 沙菁㛃a,b,*(
), 沙菁㛃a,b,*( )
)
投稿日期:2025-04-27
发布日期:2025-06-17
通讯作者:
章寅, 沙菁㛃
基金资助:
Jianyu Shanga,b, Chaochao Wanga,b, Xinran Gaoa,b, Yin Zhanga,b,*( ), Jingjie Shaa,b,*(
), Jingjie Shaa,b,*( )
)
Received:2025-04-27
Published:2025-06-17
Contact:
Yin Zhang, Jingjie Sha
Supported by:文章分享
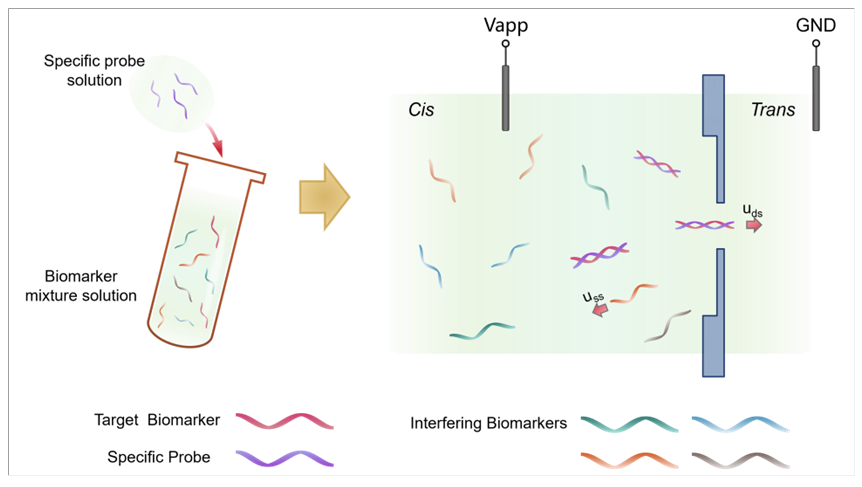
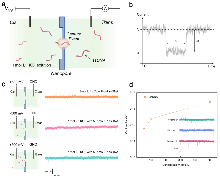
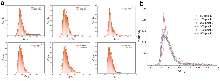
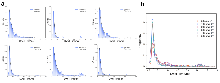
miRNAs的浓度检测在肺癌早期精准诊断中具有重要的应用价值, 然而, 由于miRNAs具有低丰度、短链长等特性, 使得快速、低成本且对浓度变化敏感的miRNA检测平台的开发面临实际挑战性. 本研究以肺癌特异性miRNA-21的替代物(22nt单链DNA)为研究对象, 揭示了固态纳米孔在低浓度检测中存在的捕获率非线性饱和现象. 基于此, 提出了孔口竞争理论模型, 认为生物标志物分子在孔口附近的竞争性引发的空间位阻效应是限制检测灵敏度的关键因素. 为克服这一限制, 本研究采用构象转换策略, 将单链DNA (ssDNA)转化为双链DNA (dsDNA), 从而显著降低了孔口的位阻效应和穿孔能垒. 通过数值模拟, 进一步验证了电泳力、电渗力以及位阻效应对分子易位动力学的影响. 实验结果表明, 双链化策略极大提高了相同条件下的捕获率, 并使捕获率与浓度之间的响应曲线转变为线性关系. 同时, 双链化还改变了生物标志物的易位方向, 为基于固态纳米孔技术的复杂生物样本中低丰度生物标志物的超灵敏检测提供了重要的理论基础.
尚建宇, 王超超, 高欣冉, 章寅, 沙菁㛃. 构象转换策略驱动固态纳米孔实现高灵敏生物标志物的定量检测[J]. 化学学报, 2025, 83(8): 878-886.
Jianyu Shang, Chaochao Wang, Xinran Gao, Yin Zhang, Jingjie Sha. Conformational Conversion Strategy-Driven Solid-State Nanopore Enables Concentration-Sensitive Quantification of Biomarkers[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2025, 83(8): 878-886.








| [1] |
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.002 pmid: 19167326 |
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
doi: 10.1038/nrc1840 pmid: 16557279 |
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2010.194 pmid: 21116241 |
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
doi: 10.1038/cr.2008.282 pmid: 18766170 |
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
|
(马超凡, 徐伟, 刘巍, 徐昌晖, 沙菁㛃, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 857).
|
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
doi: 10.1038/s41588-022-01024-z pmid: 35379992 |
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2023.08.019 pmid: 37666365 |
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
doi: 10.1038/nnano.2009.379 pmid: 20023645 |
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
doi: 10.1038/nnano.2010.213 pmid: 21076404 |
| [38] |
doi: 10.1016/j.plrev.2012.05.010 pmid: 22658507 |
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
pmid: 8127706 |
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
COMSOL Multiphysics® v. 6.2. www.comsol.com. COMSOL AB, Stockholm, Sweden.
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
doi: 10.1021/nn5025829 pmid: 24933128 |
| [53] |
|
| [1] | 李兰英, 陶晴, 闻艳丽, 王乐乐, 郭瑞妍, 刘刚, 左小磊. 多聚腺嘌呤DNA探针及其生物传感应用★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(6): 681-690. |
| [2] | 杨旭, 张泽英, 苏萌, 宋延林. 基于纳米光子技术检测SARS-CoV-2研究进展※[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(1): 80-88. |
| [3] | 易荣楠, 吴燕. 表面增强拉曼光谱技术在microRNA检测中的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(6): 694-704. |
| [4] | 樊蕾, 江群英, 潘敏, 王文晓, 张丽, 刘晓庆. 基于模拟酶-天然酶级联反应的双模式传感平台用于生物标志物的超灵敏检测[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(5): 419-426. |
| [5] | 金鑫, 王晓英. 口腔癌相关唾液肿瘤生物标志物的分析检测研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(4): 340-350. |
| [6] | 沙菁㛃, 徐冰, 陈云飞, 杨颜菁. 固态纳米孔对蛋白质易位的实验研究[J]. 化学学报, 2017, 75(11): 1121-1125. |
| [7] | 胡正利, 杜冀晖, 应佚伦, 彭岳一, 曹婵, 龙亿涛. 纳米孔道单分子检测结直肠癌MicroRNAs[J]. 化学学报, 2017, 75(11): 1087-1090. |
| [8] | 李晓利, 王愈聪, 张学晶, 赵云颉, 刘成辉, 李正平. 双链特异性核酸酶介导的高灵敏度microRNA分析[J]. 化学学报, 2014, 72(3): 395-400. |
| [9] | 王长号, 李英豪, 贾国卿, 卢胜梅, 刘䶮, 李灿. DNA催化水相体系中的二硫缩醛反应[J]. 化学学报, 2013, 71(01): 36-39. |
| [10] | 张良, 于淼, 何川. 老鼠Tet1蛋白能氧化单链脱氧核糖核酸上的5-甲基胞嘧啶到5-羟甲基胞嘧啶和5-羧基胞嘧啶[J]. 化学学报, 2012, 70(20): 2123-2126. |
| [11] | 马蕾, 刘舒, 宋凤瑞, 刘志强, 刘淑莹. 木犀草素-7-O-葡萄糖苷与双链DNA的相互作用研究[J]. 化学学报, 2012, 70(14): 1561-1564. |
| [12] | 张轶, 梁爱惠, 周莲平, 覃惠敏, 欧阳辉祥, 王鹏飞, 蒋治良. 双链DNA裂解-纳米金共振散射光谱探针检测痕量 UO22+ [J]. 化学学报, 2011, 69(18): 2153-2158. |
| [13] | 赵慧辉,王伟. 不稳定性心绞痛血瘀证的血浆蛋白质组学研究[J]. 化学学报, 2009, 67(2): 167-173. |
| [14] | 李凯,朱旭,刘林,王建秀,刘又年. 采用电活性标记物N-(2-乙基-二茂铁)马来酰亚胺检测与表面固定的 一致性双链DNA特异性作用的p53蛋白质[J]. 化学学报, 2008, 66(21): 2379-2383. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||