

介观结构氮掺杂碳纳米笼负载铂-钌合金催化剂的优异甲醇电氧化性能
收稿日期: 2016-04-20
网络出版日期: 2016-06-07
基金资助
项目受国家重大科学研究计划纳米专项(No.2013CB932902)、国家自然科学基金(Nos.21473089,51232003,21373108,51571110,21573107)、苏州市科技计划(ZXG2013025)、常州市科技计划(CE20130032)和江苏高校优势学科建设工程资助.
Alloyed Pt–Ru Nanoparticles Immobilized on Mesostructured Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Nanocages for Efficient Methanol Electrooxidation
Received date: 2016-04-20
Online published: 2016-06-07
Supported by
Project supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program, No. 2013CB932902), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21473089, 51232003, 21373108, 51571110, 21573107), Suzhou Science and Technology Project (ZXG2013025) and Changzhou Technology Support Program (CE20130032). This work was also supported by a Project Funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
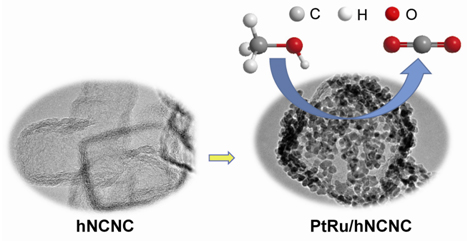
利用氮掺杂碳纳米笼(hNCNC)的高比表面积及掺杂氮原子的锚定作用,方便地将约3 nm的Pt-Ru合金纳米粒子均匀地负载在hNCNC表面,制得了Pt和Ru比例可调的Pt-Ru/hNCNC双金属合金催化剂.这些催化剂展现出优异的甲醇催化氧化活性和稳定性,且具有良好的抗CO中毒能力,显著优于Pt/hNCNC和商业PtRu/C等对照组催化剂.其优异的电化学性能可归因于以下因素的协同作用:(1) Pt-Ru合金的双功能机制增强了催化剂的CO氧化脱附能力从而使活性位重新暴露,(2) hNCNC的氮掺杂及高比表面积有利于获得粒径小且均匀的合金纳米粒子,(3) hNCNC的多尺度分级孔结构有利于甲醇等参与反应物质的传输.
黎聃勤 , 张志琦 , 臧鹏远 , 马延文 , 吴强 , 杨立军 , 陈强 , 王喜章 , 胡征 . 介观结构氮掺杂碳纳米笼负载铂-钌合金催化剂的优异甲醇电氧化性能[J]. 化学学报, 2016 , 74(7) : 587 -592 . DOI: 10.6023/A16040196
Direct methanol fuel cells (DMFC) have attracted extensive attention as ideal candidates for automotive and portable applications owing to the fascinating advantages such as high conversion efficiency, environmental friendliness, safety, wide sources of methanol, and simple cell structure. Electrocatalysts are one of crucial factors limiting the performance of DMFC. Nowadays, precious Pt-based catalyst, in spite of costliness and scarcity, is the most popular catalyst for methanol oxidation reaction (MOR) at anode due to the much better performances than those of the non-Pt catalysts. But there exists some shortcomings such as poor CO-tolerance and durability. Pt alloying with other metals, e.g. Ru, is an effective strategy to improve the catalytic performance. In addition, the support with a large specific surface area (SSA), high conductivity and suitable porous structure, such as sp2 carbon, could lead to high dispersion, high utilization and stability of Pt-based nanoparticles, also favorable for MOR. Recently, by in situ MgO template method, we reported the unique 3D hierarchical carbon-based nanocages featured with ultrahigh SSA, micro-meso-macro-pore coexistence, good conductivity and easy doping, which exhibited excellent electrochemical performances. Herein, taking the advantages of nitrogen-dopant anchoring function and unique mesostructures of hierarchical N-doped carbon nanocages (hNCNC), we report the Pt-Ru electrocatalysts immobilized on hNCNC (Pt-Ru/hNCNC) prepared via modified microwave-assisted ethylene glycol (EG) reduction method. The so-constructed Pt-Ru/hNCNC catalysts with ca. 30 wt% loading and tunable atomic ratio of Pt to Ru have a highly homogeneous dispersion of metal nanoparticles with the average size of ca. 3 nm. The alloying Pt-Ru/hNCNC catalysts demonstrate good CO-tolerance, high MOR activity and durability, superior to those of the counterparts of Pt/hNCNC and commercial PtRu/C. The good electrochemical performance can be ascribed to the synergistic effects of the bifunctional effect due to introduction of Ru, small size and high dispersion of metal nanoparticles induced by the large SSA and nitrogen participation of hNCNC, and multi-scaled hierarchical pore structures beneficial to the mass transportation. These results proposed a potential strategy to develop the high-performance Pt-based MOR catalysts based on the novel mesostructured hNCNC.

[1] Chen, A.; Holt-Hindle, P. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 3767.
[2] Kakati, N.; Maiti, J.; Lee, S. H.; Jee, S. H.; Viswanathan, B.; Yoon, Y. S. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 12397.
[3] Gasteiger, H. A.; Markovic, N.; Ross, P. N.; Cairns, E. J. J. Phys. Chem. 1994, 98, 617.
[4] Liu, Z. L.; Guo, B.; Hong, L.; Lim, T. H. Electrochem. Commun. 2006, 8, 83.
[5] Pereira, L. G. S.; dos Santos, F. R.; Pereira, M. E.; Paganin, V. A.; Ticianelli, E. A. Electrochim. Acta 2006, 51, 4061.
[6] Sun, J.; Ma, H.; Jiang, H.; Dang, L.; Lu, Q.; Gao, F. J. Mater. Chem. 2015, 3, 15882.
[7] Mylswamy, S.; Wang, C. Y.; Liu, R. S.; Lee, J. F.; Tang, M. J.; Lee, J. J.; Weng, B. J. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2005, 412, 444.
[8] Watanabe, M.; Motoo, S. J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem. 1975, 60, 267.
[9] Yue, B.; Ma, Y. W.; Tao, H. S.; Yu, L. S.; Jian, G. Q.; Wang, X. Z.; Wang, X. S.; Lu, Y. N.; Hu, Z. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 1747.
[10] Jiang, S.; Zhu, L.; Ma, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Zhu, J.; Fan, Y.; Zou, Z.; Hu, Z. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 7578.
[11] Feng, H.; Ma, J.; Hu, Z. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 1702.
[12] Joo, S. H.; Kwon, K.; You, D. J.; Pak, C.; Chang, H.; Kim, J. M. Electrochim. Acta 2009, 54, 5746.
[13] Guerrero-Ruiz, A.; Badenes, P.; Rodriguez-Ramos, I. Appl. Catal. A: Gen. 1998, 173, 313.
[14] Kuang, Y.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J. Chem. Eur. J. 2012, 18, 1522.
[15] Che, G.; Lakshmi, B. B.; Fisher, E. R.; Martin, C. R. Nature 1998, 393, 346.
[16] Lin, M. L.; Huang, C. C.; Lo, M. Y.; Mou, C. Y. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 867.
[17] Liu, Z.; Su, F.; Zhang, X.; Tay, S. W. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 3824.
[18] Yu, J. S.; Kang, S.; Yoon, S. B.; Chai, G. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 9382.
[19] Li, F.; Chan, K.-Y.; Yung, H.; Yang, C.; Ting, S. W. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 13570.
[20] Cong, H.-P.; Ren, X.-C.; Yu, S.-H. ChemCatChem 2012, 4, 1555.
[21] Bin, D.; Ren, F.; Wang, H.; Zhang, K.; Yang, B.; Zhai, C.; Zhu, M.; Yang, P.; Du, Y. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 39612.
[22] La-Torre-Riveros, L.; Guzman-Blas, R.; Méndez-Torres, A. E.; Prelas, M.; Tryk, D. A.; Cabrera, C. R. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 1134.
[23] Jiang, S.; Ma, Y.; Jian, G.; Tao, H.; Wang, X.; Fan, Y.; Lu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Chen, Y. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 4953.
[24] Chen, S.; Bi, J.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhang, C.; Ma, Y.; Wu, Q.; Wang, X.; Hu, Z. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 5593.
[25] Xie, K.; Qin, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Tao, H.; Wu, Q.; Yang, L.; Hu, Z. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 347.
[26] Jiang, Y.; Yang, L.; Sun, T.; Zhao, J.; Lyu, Z.; Zhuo, O.; Wang, X.; Wu, Q.; Ma, J.; Hu, Z. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 6707.
[27] Lyu, Z.; Xu, D.; Yang, L.; Che, R.; Feng, R.; Zhao, J.; Li, Y.; Wu, Q.; Wang, X.; Hu, Z. Nano Energy 2015, 12, 657.
[28] Zhao, J.; Lai, H.; Lyu, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Xie, K.; Wang, X.; Wu, Q.; Yang, L.; Jin, Z.; Ma, Y.; Liu, J.; Hu, Z. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 3541.
[29] Lyu, Z.; Feng, R.; Zhao, J.; Fan, H.; Xu, D.; Wu, Q.; Yang, L.; Chen, Q.; Wang, X.; Hu, Z. Acta Chim. Sinica 2015, 73, 1013. (吕之阳, 冯瑞, 赵进, 范豪, 徐丹, 吴强, 杨立军, 陈强, 王喜章, 胡征, 化学学报, 2015, 73, 1013.)
[30] Feng, R.; Wang, L.; Lyu, Z.; Wu, Q.; Yang, L.; Wang, X.; Hu, Z. Acta Chim. Sinica 2014, 72, 653. (冯瑞, 王立伟, 吕之阳, 吴强, 杨立军, 王喜章, 胡征, 化学学报, 2014, 72, 653.)
[31] Prabhuram, J.; Zhao, T. S.; Liang, Z. X.; Chen, R. Electrochim. Acta 2007, 52, 2649.
[32] Roth, C.; Benker, N.; Theissmann, R.; Nichols, R. J.; Schiffrin, D. J. Langmuir 2008, 24, 2191.
[33] Bock, C.; Paquet, C.; Couillard, M.; Botton, G. A.; MacDougall, B. R. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 8028.
[34] Giorgi, L.; Pozio, A.; Bracchini, C.; Giorgi, R.; Turtù, S. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2001, 31, 325.
[35] Wang, Z.-C.; Ma, Z.-M.; Li, H.-L. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 254, 6521.
[36] Liu, S.-H.; Yu, W.-Y.; Chen, C.-H.; Lo, A.-Y.; Hwang, B.-J.; Chien, S.-H.; Liu, S.-B. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 1622.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |