

近红外AIE荧光探针的合成及其对牛磺酸清除活性氧的追踪
收稿日期: 2016-07-14
网络出版日期: 2016-09-06
基金资助
项目受国家重点基础研究发展计划(No.2013CB834702)和国家自然科学基金(Nos.21574044,21474031)资助.
NIR AIE System for Tracking Release of Taurine and ROS Scavenging
Received date: 2016-07-14
Online published: 2016-09-06
Supported by
Project supported by the National Key Basic Research Program of China (Project No. 2013CB834702), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21574044 and 21474031).
王俊 , 武英龙 , 孙立和 , 曾钫 , 吴水珠 . 近红外AIE荧光探针的合成及其对牛磺酸清除活性氧的追踪[J]. 化学学报, 2016 , 74(11) : 910 -916 . DOI: 10.6023/A16070342
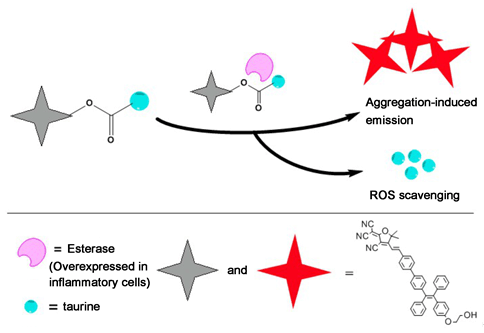
Fluorophores with aggregation-induced emission (AIE) feature are favorable tools for both chemical sensing and bioimaging. Inflammatory cells excessively express hydrolytic enzymes (esterase, protease and phosphatase) and are usually exposed to elevated levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Overexpression of ROS and the insufficient neutralization by antioxidants may give rise to the development of oxidative stress and chronic inflammation. Taurine (2-aminoethanesulfonic acid), as an effective antioxidant, can protect tissues from oxidative stress associated with various inflammatory diseases. Moreover, it has been recently reported that the incorporation of taurine can amazingly boost the cellular uptake for intracellular accumulation. Herein, we designed and synthesized a new near-infrared (NIR) AIE fluorophore DTPE. We anticipate that, the combination of the hydrophilic taurine with the NIR AIE fluorophore through an ester bond could be a remarkable method for extending the applications of AIE-active fluorophores e.g. as a trackable visualized therapeutic system featuring both imaging esterase-activated taurine release and ROS scavenging. Then we obtained the AIE probe system DTPE-Tau by incorporating taurine with the fluorophore through carbamate bond. The hydrophilic taurine moiety endows the system with enhanced water solubility and cellular uptake ability. The system is characterized by several advantages, such as large Stokes shift (225 nm), low cytotoxicity, and good photostability. The ester bond can be hydrolysed by the overexpressed esterase in inflammatory cells, thereby releasing a taurine moiety for ROS scavenging and in the meantime the AIE fluorophore moiety acts as a reporter for tracking esterase-activated taurine release. The enhancement of emission could serve as the reporting signal. The release rate is determined to be 75% for esterase at 0.05 mg/mL, calculated based on the fluorescence-intensity working curve. Also, the probe has been successfully utilized for tracking esterase-activated release of taurine and scavenging intracellular ROS in RAW264.7 cell line, which shows great potential for trackable visualized therapy.
[1] Li, P.; Xiao, H.; Tang, B. Chin. J. Chem. 2012, 30, 1992.
[2] Xia, Z.; Shao, A.; Li, Q.; Zhu, S.; Zhu, W. Acta Chim. Sinica 2016, 74, 351. (夏志清, 邵安东, 李强, 朱世琴, 朱为宏, 化学学报, 2016, 74, 351.)
[3] Fan, J. L.; Xu, Q. L.; Zhu, H.; Peng, X. J. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 34(8), 1623. (樊江莉, 徐群利, 朱浩, 彭孝军, 有机化学, 2014, 34(8), 1623.)
[4] Chen, Y.; Qiu, T.; Zhao, W.; Fan, L. Polym. Chem. 2015, 6, 1576.
[5] Guo, S.; Zheng, F.; Zeng, F.; Wu, S. Z. Chinese J. Polym. Sci. 2016, 34, 830.
[6] Yu, C.; Li, X.; Zeng, F.; Zheng, F.; Wu, S. Z. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 403.
[7] Yu, C.; Wu, Y.; Zeng, F.; Li, X.; Shi, J.; Wu, S. Z. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 4507.
[8] Pan, L.; Luo, W.; Chen, M.; Liu, J.; Xu, L.; Hu, R.; Zhao, Z.; Qin, A.; Tang, B. Z. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 36(6), 1316. (潘凌翔, 罗文文, 陈明, 刘峻恺, 徐露, 胡蓉蓉, 赵祖金, 秦安军, 唐本忠, 有机化学, 2016, 36(6), 1316.)
[9] Chan, J.; Dodani, S. C.; Chang, C. J. Nat. Chem. 2012, 4, 973.
[10] Du, F. K.; Xu, J. S.; Zeng, F.; Wu, S. Z. Acta Chim. Sinica 2016, 74, 241. (杜方凯, 徐江生, 曾钫, 吴水珠, 化学学报, 2016, 74, 241.)
[11] Akdeniz, A.; Mosca, L.; Minami, T.; Anzenbacher Jr., P. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 5770.
[12] Sun, J. B.; Zhang, G. H.; Jia, X. Y.; Xue, P. C.; Jia, J. H.; Lu, R. Acta Chim. Sinica 2016, 74(2), 165. (孙静波, 张恭贺, 贾小宇, 薛鹏冲, 贾俊辉, 卢然, 化学学报, 2016, 74(2), 165.)
[13] Shi, D. T.; Zhou, D.; Zang, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, G. R.; James, T. D.; He, X. P.; Tian, H. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 3653.
[14] Wu, B. Y.; Yan, X. P. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 3903.
[15] Zhang, Z.; Huang, J.; Dong, B.; Yuan, Q.; He, Y.; Wolfbeis, O. S. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 4149.
[16] Hou, X.; Yu, Q.; Zeng, F.; Ye, J.; Wu, S. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 1042.
[17] Ding, J.; Li, H.; Wang, C.; Yang, J.; Xie, Y.; Peng, Q.; Li, Q.; Li, Z. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 11369.
[18] Xu, S. Y.; Sun, X.; Ge, H.; Arrowsmith, R. L.; Fossey, J. S.; Pascu, S. I.; Jiang, Y. B.; James, T. D. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2015, 13, 4143.
[19] Au-Yeung, H. Y.; Chan, J.; Chantarojsiri, T.; Chang, C. J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 15165.
[20] He, X. P.; Tian, H. Small 2016, 12, 144.
[21] Hettiarachchi, S. U.; Prasai, B.; McCarley, R. L. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 7575.
[22] Mei, J.; Leung, N. L.; Kwok, R. T.; Lam, J. W.; Tang, B. Z. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 11718.
[23] Gao, M.; Hu, Q.; Feng, G.; Tang, B. Z.; Liu, B. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 3438.
[24] Tang, X.; Bai, Q.; Peng, Q.; Gao, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Yao, L.; Lu, P.; Yang, B.; Ma, Y. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 7050.
[25] Liu, Z.; Xue, W.; Cai, Z.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, D. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 14487.
[26] Zhang, Y.; Kong, L.; Shi, J.; Tong, B.; Zhi, J.; Feng, X.; Dong, Y. Chin. J. Chem. 2015, 33, 701.
[27] Hu, F.; Zhang, G.; Zhan, C.; Zhang, W.; Yan, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Fu, H.; Zhang, D. Small 2015, 11, 1335.
[28] Yang, J.; Huang, J.; Sun, N.; Peng, Q.; Li, Q.; Ma, D.; Li, Z. Chemistry 2015, 21, 6862.
[29] Gao, Y.; Qu, Y.; Jiang, T.; Zhang, H.; He, N.; Li, B.; Wu, J.; Hua, J. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 6353.
[30] Ma, S.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Wang, L.; Xu, B.; Tian, W. Chin. J. Chem. 2013, 31, 1418.
[31] Ewa, K.; Magdalena, P.; Barbara, L.; Malgorzata, O.; Pawel, M.; Wlodzimierz, M. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2012, 71, 262.
[32] Wu, Y.; Huang, S.; Zeng, F.; Wang, J.; Yu, C.; Huang, J.; Xie, H.; Wu, S. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 12791.
[33] Marcinkiewicz, J.; Kontny, E. Amino Acids 2014, 46, 7.
[34] Hou, J. T.; Li, K.; Yang, J.; Yu, K. K.; Liao, Y. X.; Ran, Y. Z.; Liu, Y. H.; Zhou, X. D.; Yu, X. Q. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 6781.
[35] Long, L.; Wu, Y.; Wang, L.; Gong, A.; Hu, F.; Zhang, C. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 10435.
[36] Reja, S. I.; Bhalla, V.; Sharma, A.; Kaur, G.; Kumar, M. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 11911.
[37] Wu, Y.; Wang, J.; Zeng, F.; Huang, S.; Huang, J.; Xie, H.; Yu, C.; Wu, S. Z. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 1511.
[38] Xiao, H.; Xin, K.; Dou, H.; Yin, G.; Quan, Y.; Wang, R. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 1442.
[39] Zhu, H.; Fan, J.; Wang, J.; Mu, H.; Peng, X. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 12820.
[40] Sun, J. J.; Piao, S.; Cha, Y. N.; Kim, C. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2009, 45, 37.
[41] Zhou, J.; Du, X.; Li, J.; Yamagata, N.; Xu, B. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 10040.
[42] Wang, J.; Wu, Y.; Zeng, F.; Huang, S.; Wu, S. Faraday Discuss. 2016, DOI:10. 1039/C6FD00118A.
[43] Pan, G.; Liu, S.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, J.; Fan, C.; Cui, W. Biomaterials 2015, 53, 202.
[44] Yang, Y.-C.; Lu, H.-H.; Wang, W.-T.; Liau, I. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 8267.
[45] Salonen, T.; Sareila, O. U.; Kankaanranta, H.; Tuominen, R.; Moilanen, E. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 147, 790.
[46] Wang, B.; Yu, P. F.; Song, P.; Sun, X.; Yang, S.; Lou, Z.; Han, K. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 1014.
[47] Karlsson, M.; Kurz, T.; Brunk, U. T.; Nilsson, S. E.; Frennesson, C. I. Biochem. J. 2010, 428, 183.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |